0% found this document useful (0 votes)
617 views52 pagesKernel and Nullspace Concepts
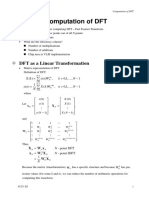
This document discusses the kernel, or nullspace, of a linear transformation. It begins by defining the kernel as the set of all vectors that are transformed to the zero vector. Examples are then provided to illustrate the kernel for various linear transformations. The key points made are:
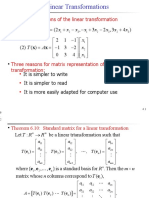
1) The kernel of a linear transformation is a subspace of the domain.
2) The kernel of a linear transformation T is equivalent to the nullspace of the matrix A representing T.
3) Finding the basis of the kernel involves solving the homogeneous system of equations to find the free variables.
Uploaded by
Pilar ZárateCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
617 views52 pagesKernel and Nullspace Concepts
This document discusses the kernel, or nullspace, of a linear transformation. It begins by defining the kernel as the set of all vectors that are transformed to the zero vector. Examples are then provided to illustrate the kernel for various linear transformations. The key points made are:
1) The kernel of a linear transformation is a subspace of the domain.
2) The kernel of a linear transformation T is equivalent to the nullspace of the matrix A representing T.
3) Finding the basis of the kernel involves solving the homogeneous system of equations to find the free variables.
Uploaded by
Pilar ZárateCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd