Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Frequency Modulation: 2.1 Objective 2.2 Hardware Required 2.3 Preparation (Pre-Lab)
Frequency Modulation: 2.1 Objective 2.2 Hardware Required 2.3 Preparation (Pre-Lab)
Uploaded by
godnegiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Frequency Modulation: 2.1 Objective 2.2 Hardware Required 2.3 Preparation (Pre-Lab)
Frequency Modulation: 2.1 Objective 2.2 Hardware Required 2.3 Preparation (Pre-Lab)
Uploaded by
godnegiCopyright:
Available Formats
FREQUENCY MODULATION
2.1 OBJECTIVE
In this lab, you will learn how to perform the Frequency modulation using IC 566 and to
calculate the modulation index for various modulating voltages.
2.2 HARDWARE REQUIRED
AFO, IC NE566, Resistors, Capacitor, CRO, Bread board and connecting wires, RPS
2.3 PREPARATION (PRE-LAB)
Do the complete revision of Frequency modulation and its modulation index and also about
IC 566 working principles.
2.4 THEORY
Frequency modulation is a process of changing the frequency of a carrier wave in
accordance with the slowly varying base band signal. The main advantage of this modulation is
that
it can provide better discrimination against noise.
Fig. 2.1 Frequency Modulation
Fig 2.2 Frequency Modulation Model Graph
2.4.1 Frequency Modulation using IC 566
A VCO is a circuit that provides an oscillating signal whose frequency can be adjusted over
a control by Dc voltage. VCO can generate both square and triangular
Wave signal whose frequency is set by an external capacitor and resistor and then varied by an
applied DC voltage. IC 566 contains a current source to charge and discharge an external
capacitor
C1 at a rate set by an external resistor. R1 and a modulating DC output voltage.
The Schmitt trigger circuit present in the IC is used to switch the current source between
charge and discharge capacitor and triangular voltage developed across the capacitor and the
square
wave from the Schmitt trigger are provide as the output of the buffer amplifier.
The R2 and R3 combination is a voltage divider, the voltage VC must be in the range 3/4
VCC < VC < VCC. The modulating voltage must be less than 3/4VCC the frequency fc
can be
Fig. 2.1 Frequency Modulation
Fig 2.2 Frequency Modulation Model Graph
calculated using the formula
fo = 2 (VCC-Vc) R1 C1 VCC
For a fixed value of VC and a constant C1 the frequency can be varied at 10:1 similarly for a
constant R! C1 product value the frequency modulation can be done at 10:1 ratio.
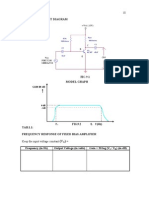
2.4.2 Circuit diagram
Fig. 2.1 Frequency Modulation
Fig 2.2 Frequency Modulation Model Graph
Fig. 2.1 Frequency Modulation
Fig 2.2 Frequency Modulation Model Graph
2.4.3 Test procedure
1. The circuit connection is made as shown in the circuit diagram.
2. The modulating signal FM is given from an AFO (1KHZ)
3. For various values of modulating voltage Vm the values of Fmax and Fmin are noted
4. The values of the modulation index are calculated.
2.5 LAB RESULT
Thus the FM circuit using IC566 was performed and the modulation index was found.
Fig. 2.1 Frequency Modulation
Fig 2.2 Frequency Modulation Model Graph
You might also like
- Lab - 2 Frequency Modulation: 2.1 ObjectiveDocument4 pagesLab - 2 Frequency Modulation: 2.1 ObjectiveJoshua DuffyNo ratings yet
- Lab - 1 Amplitude Modulation and Demodulation: 1.1 ObjectiveDocument13 pagesLab - 1 Amplitude Modulation and Demodulation: 1.1 Objectivetendua_13No ratings yet
- Sound Activated Switch: EE-389 Electronic Design Lab-II Project Report, EE Dept, IIT Bombay, Submitted On 02-12-2005Document12 pagesSound Activated Switch: EE-389 Electronic Design Lab-II Project Report, EE Dept, IIT Bombay, Submitted On 02-12-2005Skfgi EceNo ratings yet
- Sdic II NotesDocument28 pagesSdic II NotesPAVETHRA R SNo ratings yet
- tr138 07Document26 pagestr138 07Shailja VatsNo ratings yet
- Lab. Exercise PL1 CC/CC Converters: Electrònica de Potència Grau en Enginyeria Electrònica Industrial I AutomàticaDocument8 pagesLab. Exercise PL1 CC/CC Converters: Electrònica de Potència Grau en Enginyeria Electrònica Industrial I AutomàticageovannyNo ratings yet
- Ecgr3156 Experiment 8 Amplitude Modulation and DemodulationDocument7 pagesEcgr3156 Experiment 8 Amplitude Modulation and Demodulationelsadiqm7No ratings yet
- Ec 4112: Analog Communication Laboratory List of Experiments: Compulsory ExperimentsDocument68 pagesEc 4112: Analog Communication Laboratory List of Experiments: Compulsory ExperimentsArchit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Frequency Modulator: 1 TheoryDocument7 pagesExperiment 3 Frequency Modulator: 1 TheoryreganoctNo ratings yet
- Exp 12 Single Phase Inverter Part IIDocument7 pagesExp 12 Single Phase Inverter Part IIusmpowerlabNo ratings yet
- S4 EC1 LabDocument87 pagesS4 EC1 LabM N GeethasreeNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of The Inverter SystemDocument10 pagesWorking Principle of The Inverter Systemolawale gbadeboNo ratings yet
- VCO ReportDocument9 pagesVCO ReportGokul SaiNo ratings yet
- FM Mod 2Document5 pagesFM Mod 2Aruna GiriNo ratings yet
- FM ModulationDocument12 pagesFM ModulationPhyo Pyae Pyae ZawNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design For 5kw PFC ConverterDocument4 pagesAnalysis and Design For 5kw PFC Converterranjith120198No ratings yet
- Engineering University of Engineering and Technology Peshawar (Abbottabad Campus) Lab ReportDocument9 pagesEngineering University of Engineering and Technology Peshawar (Abbottabad Campus) Lab ReportTime PresentsNo ratings yet
- FSKDocument10 pagesFSKJyotirmoy Deka100% (1)
- Practicas Digiac 1750 1Document18 pagesPracticas Digiac 1750 1Saga Adolfo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Power Supply For Electro-Optics Applications: IJRRAS 3Document5 pagesHigh Voltage Power Supply For Electro-Optics Applications: IJRRAS 3mishithNo ratings yet
- DiDocument5 pagesDiByron DamaniaNo ratings yet
- DC-to-DC Power Converter by Rodney Yeu and Sudip Kundu ECE 345 Section H TA: Jon Wheeler 4/26/02 Project #34Document22 pagesDC-to-DC Power Converter by Rodney Yeu and Sudip Kundu ECE 345 Section H TA: Jon Wheeler 4/26/02 Project #34Harkishen SinghNo ratings yet
- Current-Controlled Sawtooth Generator: Active and Passive Electronic Components September 2004Document6 pagesCurrent-Controlled Sawtooth Generator: Active and Passive Electronic Components September 2004AquariusNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument50 pagesLab ManualGayathriRajiNo ratings yet
- Lab 8 Report Electronics 1Document13 pagesLab 8 Report Electronics 1Dawn J. OwensNo ratings yet
- FM Modulators: Experiment 7Document17 pagesFM Modulators: Experiment 7banduat83No ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of A Buck-Boost Converters Using IC555Document22 pagesAnalysis and Design of A Buck-Boost Converters Using IC555Eng SamharNo ratings yet
- A Voltage-Mode PWM Buck Regulator With End-Point PredictionDocument5 pagesA Voltage-Mode PWM Buck Regulator With End-Point PredictionWen DwenNo ratings yet
- Analog CommunicationDocument48 pagesAnalog CommunicationBrzata Ptica100% (1)
- Ultra-Low Power Phase-Locked LoopDocument4 pagesUltra-Low Power Phase-Locked Loophawking1122No ratings yet
- 8 ModulationDocument8 pages8 ModulationAhmadAkhbariNo ratings yet
- Am ModulationDocument9 pagesAm ModulationBrzata PticaNo ratings yet
- DC LabDocument11 pagesDC LabdinuNo ratings yet
- DC DC ConvertersDocument4 pagesDC DC Convertersmurthy237No ratings yet
- Power Supply (SPS PCB) Theory of OperationDocument5 pagesPower Supply (SPS PCB) Theory of OperationSv KoNo ratings yet
- SFC On Gas Power PlantDocument9 pagesSFC On Gas Power PlantFauzan PhoneNo ratings yet
- Exp 11 Single Phase Inverter Part IDocument7 pagesExp 11 Single Phase Inverter Part Iusmpowerlab0% (1)
- 1.amplitude Modulation and DemodulationDocument6 pages1.amplitude Modulation and DemodulationKondapalli Abdul Lathief0% (1)
- Experiment Number 2 Frequency Modulation & DemodulationDocument4 pagesExperiment Number 2 Frequency Modulation & DemodulationKarthik Vk100% (1)
- Uc3842 Provides Low-Cost Current-Mode Control: Application NoteDocument16 pagesUc3842 Provides Low-Cost Current-Mode Control: Application NoteLeonardo Ortiz100% (1)
- FSK Demodulator With PLLDocument5 pagesFSK Demodulator With PLLHema100% (1)
- FM Modulation and Demodulation Using PLL: Experiment No 7 Group A-2 19/02/2019Document8 pagesFM Modulation and Demodulation Using PLL: Experiment No 7 Group A-2 19/02/2019Mohamed Bilal50% (2)
- FM Using PLL CompressDocument8 pagesFM Using PLL CompressKARKAR NORANo ratings yet
- 3ECE-AC Lab ManualDocument62 pages3ECE-AC Lab ManualShannon DunnNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Industry:-: Chapter - 1Document35 pagesIntroduction To The Industry:-: Chapter - 1Pratik VasagadekarNo ratings yet
- Ec1355 Esd EceDocument31 pagesEc1355 Esd EceSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- EC - I Lab AmnualDocument44 pagesEC - I Lab AmnualMurali DharanNo ratings yet
- Amplitude Modulation and DemodulationDocument22 pagesAmplitude Modulation and DemodulationSivagnanam NamasivayamurthyNo ratings yet
- Manual MahaDocument81 pagesManual MaharameshdurairajNo ratings yet
- 3ece Ac Lab Manual 2 11Document109 pages3ece Ac Lab Manual 2 11Malladi Sreedevi RajithaNo ratings yet
- Nota Kuliah 4 (Measurement and Instumentation)Document13 pagesNota Kuliah 4 (Measurement and Instumentation)Azizah Mat YusofNo ratings yet
- Lab Report2aDocument18 pagesLab Report2aafshan ishaqNo ratings yet
- Wireless Energy Transmitter With Tariff SystemDocument61 pagesWireless Energy Transmitter With Tariff SystemBattu ChandrahasNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Current Controlled OscillatorDocument4 pagesCurrent Controlled OscillatorajaynkotiNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Case Study For Process Masters EquipmentDocument12 pagesCase Study For Process Masters EquipmentRohit MoreNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper of Facemeta V2Document14 pagesWhitepaper of Facemeta V2r_sartoratoNo ratings yet
- Logic Pro X Course Description-V10!2!0412Document4 pagesLogic Pro X Course Description-V10!2!0412Cristian Montoya Motta0% (1)
- Statement of Purpose For Ms in Mechanical EngineeringDocument2 pagesStatement of Purpose For Ms in Mechanical EngineeringREVANTH KUMAR100% (1)
- Qualification of Safety-Related Cables and Field Splices For Nuclear Power PlantsDocument45 pagesQualification of Safety-Related Cables and Field Splices For Nuclear Power Plantszeeshan_iraniNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Xgboost, Lightgbm and Catboost Using A Home Credit DatasetDocument5 pagesComparison Between Xgboost, Lightgbm and Catboost Using A Home Credit DatasetEduardo Miguel Vásquez SoriaNo ratings yet
- Cisco IP PABXDocument2 pagesCisco IP PABXamilasriNo ratings yet
- 1D Motion Using An Incline Plane For CapstoneDocument6 pages1D Motion Using An Incline Plane For CapstoneWuffen1No ratings yet
- UMTS UL&DL Capacity Improvement Solution - V1R2.0Document66 pagesUMTS UL&DL Capacity Improvement Solution - V1R2.0riamaNo ratings yet
- RS Calibration Isotech-3610DDocument23 pagesRS Calibration Isotech-3610DMe MeNo ratings yet
- Self Driving Car (PowerPoint)Document29 pagesSelf Driving Car (PowerPoint)immi19890% (1)
- Hands-On Networking Fundamentals 2nd Edition Michael Palmer Test Bank 1Document36 pagesHands-On Networking Fundamentals 2nd Edition Michael Palmer Test Bank 1whitneywarrenjqidpnboxz100% (32)
- SWPZ 009 QDocument194 pagesSWPZ 009 QjrnelsonNo ratings yet
- Smart HomesDocument123 pagesSmart Homesmritsoudis100% (1)
- TT Electrician 2017 Pages 129 39Document12 pagesTT Electrician 2017 Pages 129 39Ghodke ParmeshwarNo ratings yet
- User ManualDocument115 pagesUser ManualRick TaylorNo ratings yet
- O-RAN WG7 DSC 0-v03 00Document29 pagesO-RAN WG7 DSC 0-v03 00曹梓艺No ratings yet
- Autodesk Presentation by Daniel Green - USABC Roadshow Jakarta 2019Document33 pagesAutodesk Presentation by Daniel Green - USABC Roadshow Jakarta 2019Fahmi Savero DevtrinaNo ratings yet
- Method Statement Form TemplateDocument2 pagesMethod Statement Form TemplateUbaidullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Gea - Cooling TowersDocument25 pagesGea - Cooling TowersFREDIELABRADOR100% (1)
- ASCO Valve Installation InstructionsDocument4 pagesASCO Valve Installation Instructionsmohamed abouraya100% (1)
- SOB Studio ProfileDocument7 pagesSOB Studio ProfilePrastian Raharjo PutroNo ratings yet
- An 8-Bit in Resistive Memory Computing Core With Regulated Passive Neuron and Bitline Weight MappingDocument13 pagesAn 8-Bit in Resistive Memory Computing Core With Regulated Passive Neuron and Bitline Weight MappingFair KalNo ratings yet
- IIT ISM DhanbadDocument2 pagesIIT ISM Dhanbadniel doriftoNo ratings yet
- 3D Holographic Projection TechnologyDocument18 pages3D Holographic Projection TechnologyShravya 459No ratings yet
- Movie DatabaseDocument3 pagesMovie DatabaseChandrakanth D KulkarniNo ratings yet
- VU All Subjects Solution File (Last Updated 06-08-2019 08.45PM)Document13 pagesVU All Subjects Solution File (Last Updated 06-08-2019 08.45PM)Muhammad Asif0% (1)
- Concept Paper Cell Phone Development in PakistanDocument20 pagesConcept Paper Cell Phone Development in PakistanAisha KhanNo ratings yet
- E-Government and E-Governance: Can Its Improve Indonesian Public Service Deliveries?Document13 pagesE-Government and E-Governance: Can Its Improve Indonesian Public Service Deliveries?samiahescanoNo ratings yet
- ORAN-WG2 AIML v01 00 PDFDocument34 pagesORAN-WG2 AIML v01 00 PDFelectrico servicesNo ratings yet