Professional Documents
Culture Documents
International University (IU) - VNU HCMC: ID Name
Uploaded by
Thu UyênOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
International University (IU) - VNU HCMC: ID Name
Uploaded by
Thu UyênCopyright:
Available Formats
International University (IU) - VNU HCMC
ASSIGNMENT 5
Group 10
ID Name
IELSIU19233 Nguyễn Vũ Hoàng Như
IEIEIU19080 Lê Thanh Cường
IELSIU19051 Trần Thị Bích Ngọc
IELSIU19244 Lê Việt Phương
IELSIU20285 Nguyễn Ngọc Đức
IELSIU20013 Trương Minh Đức
IELSIU20456 Huỳnh Thị Thu Uyên
Question 7.2
Composite load
1 <-> 2 0
1 <-> 3 125
1 <-> 4 100
1 <-> 5 0
1 <-> 6 0
2 <-> 3 45
2 <-> 4 105
2 <-> 5 0
2 <-> 6 0
3 <-> 4 30
3 <-> 5 235
3 <-> 6 240
Course: Production Management
International University (IU) - VNU HCMC
4 <-> 5 85
4 <-> 6 80
5 <-> 6 160
Composite load (descending order)
3 <-> 6 240
3 <-> 5 235
5 <-> 6 160
1 <-> 3 125
2 <-> 4 105
1 <-> 4 100
4 <-> 5 85
4 <-> 6 80
2 <-> 3 45
3 <-> 4 30
1 <-> 2 0
1 <-> 5 0
1 <-> 6 0
2 <-> 5 0
2 <-> 6 0
Current layout (assuming because the layout in the book has fault)
3 1 4
6 2 5
Nonadjacent load = 30 + 235 + 80 + 160 = 505
Layout minimizing nonadjacent movement
2 3 5
1 4 6
Nonadjacent load = 0 + 0 + 0 + 0 = 0
Question 7.5
Let: 1: Management
Course: Production Management
International University (IU) - VNU HCMC
2: Rent collection
3: Sales
4: Grounds
5: Maintenance
Computing total distance between each link is equal sum of distance
Composite Movements
1 <->2 50+20=70
1 <->3 35+40=75
1 <->4 25+20=45
1 <->5 20+20=40
2 <->5 35+10=45
3 <-> 5 10+0=10
4 <->5 40+50=90
Arranging in decreasing order:
Composite Movements
4 <->5 40+50=90
1 <->3 35+40=75
1 <->2 50+20=70
1 <->4 25+20=45
2 <->5 35+10=45
1 <->5 20+20=40
3 <-> 5 10+0=10
Course: Production Management
International University (IU) - VNU HCMC
Option 1 Option 2 Option 3
5 4 2 1 3 4 5
2 1 3 5 4 3 1 2
Question 7.7
In order to evaluate the current layout, we need to calculate the composite, or back-and-forth,
movements between departments. The results below list composite movements and rank
them from highest to lowest.
Composite Movements Composite Movements
1 <-> 6 140 2 <->4 50
3 <-> 6 90 2 <->5 50
3 <-> 5 80 3 <->4 30
2 <-> 6 80 1 <->4 25
5 <->6 80 4 <->5 20
2 <->3 70 1 <->3 10
4 <->6 60 1 <->5 10
1 <->2 50
Next, we evaluate the “goodness” of the layout by scoring it in terms of nonadjacent loads.
Nonadjacent Loads
1 <->3 10
1 <->4 25
3 <-> 5 80
4 <->5 20
Total 135
Course: Production Management
International University (IU) - VNU HCMC
The adjacent moves are marked with a solid line and the nonadjacent moves are shown
with a curved dashed line to highlight the fact that material is moved farther than we would
like, that is, across more than one square.
Thus, the score for this layout is 135 nonadjacent loads.
b) To improve the layout, we can switch department
4 and 5 Nonadjacent Loads
3 <->4 30
4 <->5 20
1 <->3 10
1 <->5 10
Total 70
The score for
this layout in this case is 70 nonadjacent loads.
Question 7.11
Designing the revised layout:
Question 7.12
Facility Layout: It is a significant component of an association. It is required both for compelling
business activities and to meet the prerequisites and necessities of an Individual. At the end of
the day, office format Is the arrangement of physical offices in a characterized manner. An
ineffectively planned format can prompt the conclusion of business.
Fixed position layout: This sort of cycle is regularly utilized in associations. Under this cycle the
machine of hardware is fixed that is it is put at one spot and other crude material, assets and
administrations are conveyed to that place for the additional progressing cycle. The creation of
enormous and substantial hardware like structures, planes, ships trains are viewed as in fixed
position design.
Or then again at the end of the day, we may likewise call it as tasks where an elevated level of
arranging and control is done when contrasted with different sorts of formats.
Course: Production Management
International University (IU) - VNU HCMC
Question 7.15
We got the table below:
Destination X Y Quantity
D1 1000 1250 7000
D2 1500 2700 9000
D3 2000 700 11500
D4 32 25 4300
We have to calculate the center gravity D (Xc,Yc)
Xc =
( X 1 xQ1)+( X 2 xQ 2)+( X 3 xQ3)+( X 4 xQ 4) (1000 x 7000)+(1500 x 9000)+( 2000 x 11500)+(32 x 4300)
=
Q1+Q 2+Q 3+Q 4 7000+ 9000+11500+ 43000
= 1372,25
Course: Production Management
International University (IU) - VNU HCMC
Yc =
(Y 1 xQ 1)+(Y 2 xQ 2)+(Y 3 xQ3)+(Y 4 xQ 4) (1250 x 7000)+(2700 x 9000)+(700 x 11500)+(25 x 4300)
=
Q 1+ Q2+Q 3+Q 4 7000+ 9000+11500+43000
= 1295,83333
=> We got the center of the gravity D (Xc,Yc) in excel
Question 7.16
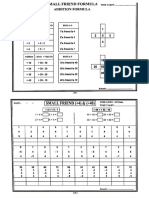
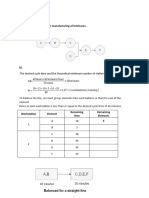
a) Precedence diagram for manufacturing of briefcases.
b)
The desired cycle time and the theoretical minimum number of stations are calculated by
40 hours∗60 minutes /hour
Cd= =48 minutes
50 cases
Course: Production Management
International University (IU) - VNU HCMC
30+15+10+5+10+10
N= =1.67 ≈ 2 workstations( roundup)
48
To balance the line, we must group elements into workstations so that the sum of the
element
times at each workstation is less than or equal to the desired cycle time of 48 minutes.
Remaining Remaining
Workstation Element
time Elements
A 18 B, C,D,E,F
1
B 3 C,D,E,F
C 38 D,E,F
D 33 E,F
2
E 23 F
F 13 none
c)
The flow time is :
Flow time = 45 +35 = 80 minutes
The cycle time necessary to assemble 50 cases in a 40-hour week is
Cycle time = max { 45,35 }=45 minutes
The assembly line has an efficiency of
30+15+10+5+10+10
E= =0.83=83.3 %
2∗48
Course: Production Management
International University (IU) - VNU HCMC
d) Producing 80 cases per week.
The desired cycle time and the theoretical minimum number of stations are calculated by
40 hours∗60 minutes /hour
Cd= =30 minutes
80 cases
30+15+10+5+10+10
N= =2.67 ≈3 workstations (round up)
30
Remaining Remaining
Workstation Element
time Elements
1 A 0 B,C,D,E,F
B 15 C,D,E,F
2 C 5 D,E,F
D 0 E,F
E 20 F
3
F 10 none
Question 7.20
The desired cycle time and the theoretical minimum number of stations are calculated by
40 hours∗60 minutes /hour
Cd= =19.2 minutes
125 cases
8+5+6+ 10+ 2+4 +5+7+2+9+ 3
N= =3.17 ≈ 4 workstations(round up)
19.2
Course: Production Management
International University (IU) - VNU HCMC
Workstation Element Remaining time Remaining Elements
Course: Production Management
International University (IU) - VNU HCMC
A 11,2 B,C,D,E,F,G,H,I,J,K
1 B 6,2 C,D,E,F,G,H,I,J,K
C 0,2 D,E,F,G,H,I,J,K
D 9,2 E,F,G,H,I,J,K
2 E 7,2 F,G,H,I,J,K
F 3,2 G,H,I,J,K
G 14,2 H,I,J,K
3 H 7,2 I,J,K
I 5,2 J,K
J 10,2 K
4
K. 7,2 none
The assembly line has an efficiency of
8+5+6+ 10+ 2+4 +5+7+2+9+ 3
E= =0.79=79 %
4∗19.2
Question 7.21
Course: Production Management
International University (IU) - VNU HCMC
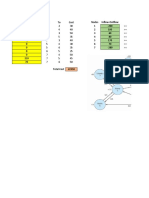
We got Table below presenting the location cordinations
We calculate the x and y coordinates using the following formula
The value of x and y coordinates are as follows:
Course: Production Management
International University (IU) - VNU HCMC
The best site for Somerset’s distribution center
x = 1599.813
y = 1766.822
Question 1
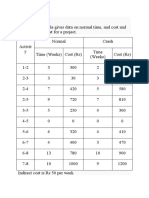
a) Available time = 40*60 minutes = 2400 minutes
Required production = 120 units
So, the cycle time
= Available time / Required production
= 2400/120 = 20 minutes
Theoretical minimum number of workers
= Sum of the task times / Cycle time
= (8+4+7+3+7+11+2+8)/20 = 2.5 i.e., 3
Balance the line using the longest processing time first heuristic as follows:
Idle time
Station (based on
Available Assigned Remaining Idle
Worker Eligibles Was fit cycle improved
time time time time
time cycle
time)
I 20 A A 8 12
12 B, C, D C 7 5
5 B, D B 4 1
1 D, E - 0 1 1 19 0
II 20 D, E E 7 13
13 D, F F 11 2
2 D - 0 2 2 18 1
III 20 D D 3 17
17 G G 2 15
15 H H 8 7 7 13 6
Totals 50 10 7
Three workers will be needed and the assignment is as follows:
Course: Production Management
International University (IU) - VNU HCMC
+ Worker-I: {A, C, B}
+ Worker-II: {E, F}
+ Worker-III: {D, G, H}
Efficiency = Sum of the task times / (Number of workers x Improved cycle time)
= 50/(3*19) = 87.7%
b)
Available time = 40*60 minutes = 2400 minutes
Required production = 100 units
So, the cycle time = Available time / Required production = 2400/100 = 24 minutes
Available Remaining Station cycle
Worker Eligibles Was fit Assigned time Idle time
time time time
I 24 A A 8 16
16 B, C, D C 7 9
9 B, D B 4 5
5 D, E D 3 2
2 E, G G 2 0
0 E, H - 0 0 0 24
II 24 E, H H 8 16
16 E E 7 9
9 F - 0 9 9 15
III 24 F F 11 13
13 - - 0 13 13
Totals 50 22
Still, three workers will be needed and the assignment is as follows:
+ Worker-I: {A, C, B, D, G}
+ Worker-II: {H, E}
+ Worker-III: {F}
Efficiency = Sum of the task times / (Number of workers x Cycle time) = 50/(3*24) = 69.4%
Course: Production Management
International University (IU) - VNU HCMC
Question 2
a)
b)
The flow time is the time required to produce an item completely if only one unit is being
produced at a time.
Flow time = 30 + 15 + 10 + 5 + 10 + 10 = 80 minutes
Cycle time = Weekly production time available/ Units to be produced weekly
Cycle time = (40 hrs x 60 mins) /50 = 48 minutes
c)
Minimum number of work stations = Total task time / Cycle time
Minimum number of work stations = 80 mins / 48 = 2 work stations
Efficiency = (sum of the task time) / [(number of work stations x (cycle time)]
Efficiency = 80 / (2x48) = 83,33%
Workstation Element Task Time
A 30
1
B 15
C 10
D 5
2
E 10
F 10
Course: Production Management
International University (IU) - VNU HCMC
d)
If 80 cases per week would be produced
Cycle time = (40 hours x 60 minutes) / 80 = 30 minutes
Number of work station = 80 mins / 30 mins = 3 work stations
Efficiency = 80 / (3x30) = 88,89%
Workstation Element Task Time
A 30
1
B 15
C 10
2
D 5
E 10
3
F 10
Course: Production Management
You might also like
- International University (IU) - VNU HCMC: ID NameDocument15 pagesInternational University (IU) - VNU HCMC: ID NameThu UyênNo ratings yet
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- Production Management: Composite Load Composite Load (Descending Order)Document12 pagesProduction Management: Composite Load Composite Load (Descending Order)Khánh Đoan Lê ĐìnhNo ratings yet
- Practical Question and AnswerDocument15 pagesPractical Question and AnswergracesachinrockNo ratings yet
- Tugas (UTS) ASPK - Andro Tri Julianda (95017019)Document4 pagesTugas (UTS) ASPK - Andro Tri Julianda (95017019)محمد عزيرNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio 1Document17 pagesEjercicio 1Carlos Sánchez NietoNo ratings yet
- 2122promana HW5 G5Document10 pages2122promana HW5 G5Minh TríNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENTDocument5 pagesASSIGNMENTKayNo ratings yet
- Load Summary Chart: Deparment 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 Composite LoadsDocument4 pagesLoad Summary Chart: Deparment 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 Composite LoadsOmachi ADOHANo ratings yet
- Desarrollo de La Tarea 1: Resolucion 1Document8 pagesDesarrollo de La Tarea 1: Resolucion 1Ronald ACNo ratings yet
- Syntax: " (" Cannot Be Followed by "0, 1) "Document10 pagesSyntax: " (" Cannot Be Followed by "0, 1) "mohitNo ratings yet
- Abdul Malik Tgs Mid StatistikDocument5 pagesAbdul Malik Tgs Mid StatistikDaif KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Driving Assignment (X-Xbar) 2 Miles Traveled (X) Travel Time (Y) X-Xbar (Mean) Y-Ybar (Mean)Document7 pagesDriving Assignment (X-Xbar) 2 Miles Traveled (X) Travel Time (Y) X-Xbar (Mean) Y-Ybar (Mean)Karen Kaye PasamonteNo ratings yet
- 2122promana HW5 G5Document12 pages2122promana HW5 G5Dương NgNo ratings yet
- Doroh Efemena Edu 821 Research and Statistics Course Note 3Document9 pagesDoroh Efemena Edu 821 Research and Statistics Course Note 3CelestineNo ratings yet
- Tugas 11 Statitiska - Ogi SaepulohDocument3 pagesTugas 11 Statitiska - Ogi SaepulohOgi SaepulohNo ratings yet
- Matematicas EjercicioDocument5 pagesMatematicas EjercicioJesus Arturo Arenzano RamosNo ratings yet
- Multiple Linear Regression 1Document8 pagesMultiple Linear Regression 1crossline093No ratings yet
- MT-T1 220211010058 ChelseaVirginiaNuahDocument6 pagesMT-T1 220211010058 ChelseaVirginiaNuahChelsea Virginia NuahNo ratings yet
- Josh Prob Cat 1Document6 pagesJosh Prob Cat 1Joshua MercyNo ratings yet
- Bms QuestionsDocument3 pagesBms Questionskavyaganesan0% (1)
- A Theoretical Study of The Performance of The Tanda Thread Wetting Device Based On A Mathematical ModelDocument9 pagesA Theoretical Study of The Performance of The Tanda Thread Wetting Device Based On A Mathematical Modelindex PubNo ratings yet
- ExamplesDocument8 pagesExamplesRohitNo ratings yet
- Tutorial #1 AnswersDocument9 pagesTutorial #1 Answersking AliNo ratings yet
- Basic Mathematical OperationsDocument4 pagesBasic Mathematical OperationsNithiyandran RajNo ratings yet
- Abacus HWDocument12 pagesAbacus HWsudiptamidyaNo ratings yet
- Solution 2223PrdMgmt HW5Document22 pagesSolution 2223PrdMgmt HW5Trung Đức HuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 SkewnessDocument9 pagesLecture 7 SkewnessDr-Ajay SinghNo ratings yet
- Anshika IB10 MathTestDocument5 pagesAnshika IB10 MathTestRamit MoradiaNo ratings yet
- A Theoretical Study of The Performance of The Tanda Thread Wetting Device Based On A Mathematical ModelDocument9 pagesA Theoretical Study of The Performance of The Tanda Thread Wetting Device Based On A Mathematical Modelindex PubNo ratings yet
- CanalesDocument2 pagesCanalesAngela GsNo ratings yet
- Tarea2 Determinante de 6x6 Calculo GeneralDocument3 pagesTarea2 Determinante de 6x6 Calculo GeneralJeferson ChicayNo ratings yet
- Kizito Edu 821 Research and Statistics Assignment 01 - 2020.11Document9 pagesKizito Edu 821 Research and Statistics Assignment 01 - 2020.11CelestineNo ratings yet
- Wilcoxon Signed Rank TestDocument21 pagesWilcoxon Signed Rank TestRumaisyahNo ratings yet
- KORJENOVANJE ZadaciDocument4 pagesKORJENOVANJE ZadaciZODINo ratings yet
- PM THN3 - 2.0Document2 pagesPM THN3 - 2.0LING SU HUNG KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Business StatisticsDocument4 pagesBusiness StatisticskebNo ratings yet
- Statistical Techniques in Business and EconomicsDocument15 pagesStatistical Techniques in Business and EconomicsJesslyn Emmanuela Njoto PrawiroNo ratings yet
- 1 A 2022 7 Statictics OooDocument16 pages1 A 2022 7 Statictics OooHAMIDNo ratings yet
- Order Exponents 3 Operators P6Document2 pagesOrder Exponents 3 Operators P6Jemima Nicole FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Probstat2 PDFDocument34 pagesProbstat2 PDFYULIATU SYAIDDAH.M TEKNIK INFORMATIKANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Linear Regression and Correlation: I X y 14) 14) (Y 25.33)Document15 pagesChapter 11: Linear Regression and Correlation: I X y 14) 14) (Y 25.33)blu runner1No ratings yet
- Q3 Q4 Q5 Q6 Q8 Q11Document13 pagesQ3 Q4 Q5 Q6 Q8 Q11一No ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 5-Past Year Exam QuestionDocument2 pagesExercise Chapter 5-Past Year Exam QuestionDeelah MawarNo ratings yet
- Radical Worksheet With AnswersDocument2 pagesRadical Worksheet With AnswersRudyr BacolodNo ratings yet
- Taller RaicesDocument23 pagesTaller RaicesNathalia VallejoNo ratings yet
- Smart Edu 821 Research and Statistics Course NoteDocument9 pagesSmart Edu 821 Research and Statistics Course NoteCelestineNo ratings yet
- Class Frequency: 2 2 4 3 1 3 7 3 21 8 1 8 Total 7 36Document5 pagesClass Frequency: 2 2 4 3 1 3 7 3 21 8 1 8 Total 7 36dereje solomonNo ratings yet
- Võ Ngọc Kim Châu-Ielsiu18187 (Saturday Afternoon Class) : Homework 3Document14 pagesVõ Ngọc Kim Châu-Ielsiu18187 (Saturday Afternoon Class) : Homework 3Phuong Anh LuongNo ratings yet
- Partial Differences EDUC 471Document3 pagesPartial Differences EDUC 471Kasandra FoxNo ratings yet
- Uniminuto Administración Financiera: Estadistica DescriptivaDocument3 pagesUniminuto Administración Financiera: Estadistica DescriptivaYineth HENAO NAVALNo ratings yet
- CS19001: Programming and Data Structures Laboratory: Date: 23-August-2019Document4 pagesCS19001: Programming and Data Structures Laboratory: Date: 23-August-2019Shashank GautamNo ratings yet
- Metode Numerik: I Gede Putu Indra Maha Putra 1705511077Document39 pagesMetode Numerik: I Gede Putu Indra Maha Putra 1705511077Jnana PutraNo ratings yet
- Nama: Helmi Olpin Yunita NIM: 217 501 023 Tugas Statistik "TABEL 2"Document3 pagesNama: Helmi Olpin Yunita NIM: 217 501 023 Tugas Statistik "TABEL 2"Helmi Olpin YunitaNo ratings yet
- Nama: Helmi Olpin Yunita NIM: 217 501 023 Tugas Statistik "TABEL 2"Document3 pagesNama: Helmi Olpin Yunita NIM: 217 501 023 Tugas Statistik "TABEL 2"Helmi Olpin YunitaNo ratings yet
- QT Past Exam Question Papers. Topic by TopicDocument25 pagesQT Past Exam Question Papers. Topic by TopicalbertNo ratings yet
- MAthDocument28 pagesMAthrheynavarro24No ratings yet
- Excel 23Document20 pagesExcel 23El YizhanNo ratings yet
- Transshipment ProblemDocument2 pagesTransshipment ProblemTunahan AydınNo ratings yet
- Lich Tong Mid212 - Dot1-Khoa IemDocument2 pagesLich Tong Mid212 - Dot1-Khoa IemThu UyênNo ratings yet
- CC $0.08 Per Yard Co $2,200 D 1,415,000 SQ - Yards A. The Optimal Order Size (Economic Order Quantity) IsDocument2 pagesCC $0.08 Per Yard Co $2,200 D 1,415,000 SQ - Yards A. The Optimal Order Size (Economic Order Quantity) IsThu UyênNo ratings yet
- 7.16: A) Precedence Diagram For Manufacturing of BriefcasesDocument4 pages7.16: A) Precedence Diagram For Manufacturing of BriefcasesThu UyênNo ratings yet
- HW1 - Formulating LPPDocument3 pagesHW1 - Formulating LPPThu UyênNo ratings yet
- Case Study Presentation - CGDocument37 pagesCase Study Presentation - CGapi-290866384No ratings yet
- QLD Plan Draft Review Raw DataDocument242 pagesQLD Plan Draft Review Raw DataRohit Jain100% (1)
- UniFi Quick GuideDocument2 pagesUniFi Quick GuideAndhika TharunaNo ratings yet
- Spike Magazine Cup PackDocument5 pagesSpike Magazine Cup PackBungle MarleyNo ratings yet
- SmoothWall Express 2.0 Quick-Start GuideDocument6 pagesSmoothWall Express 2.0 Quick-Start Guideinfobits100% (1)
- APS PresentationDocument32 pagesAPS PresentationRozack Ya ZhackNo ratings yet
- Police Cranston School Committee Member Stole PTO FundsDocument1 pagePolice Cranston School Committee Member Stole PTO FundsashaydelineNo ratings yet
- No ApprovedDocument154 pagesNo ApprovedAnnaNo ratings yet
- Panel Hospital List IGIDocument6 pagesPanel Hospital List IGIAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- 1.6 FSI Inlet Manifold Removal Guide - Audi A2 Owners' ClubDocument3 pages1.6 FSI Inlet Manifold Removal Guide - Audi A2 Owners' Clubdusan jovanovicNo ratings yet
- Analyse Bacterologique de L EauDocument6 pagesAnalyse Bacterologique de L Eaupeguy diffoNo ratings yet
- Bell Single-Sleeve Shrug Crochet PatternDocument2 pagesBell Single-Sleeve Shrug Crochet PatternsicksoxNo ratings yet
- Wind LoadingDocument18 pagesWind LoadingStephen Ogalo100% (1)
- Unit 4 Transistor Frequency ResponseDocument6 pagesUnit 4 Transistor Frequency ResponseShaina MabborangNo ratings yet
- 88 Year Old Man Missing in SC - Please ShareDocument1 page88 Year Old Man Missing in SC - Please ShareAmy WoodNo ratings yet
- CS1 Entity Level Controls SolutionsDocument16 pagesCS1 Entity Level Controls SolutionsPakistan Breaking News100% (6)
- Bubble SortDocument6 pagesBubble SortRollin RevieNo ratings yet
- Content Analysis of Tea BrandsDocument49 pagesContent Analysis of Tea BrandsHumaRiaz100% (1)
- RSM222.f22.CourseOutline v3 2022-09-05Document9 pagesRSM222.f22.CourseOutline v3 2022-09-05Kirsten WangNo ratings yet
- Bill - AKIJDocument3 pagesBill - AKIJm.tanjil2005No ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For ExcavationDocument6 pagesRisk Assessment For ExcavationAhmed GamalNo ratings yet
- Review Systems of Linear Equations All MethodsDocument4 pagesReview Systems of Linear Equations All Methodsapi-265647260No ratings yet
- Bank OD Account in Tally 1Document3 pagesBank OD Account in Tally 1yashusahu180No ratings yet
- BF254 BF255Document3 pagesBF254 BF255rrr2013No ratings yet
- FCC O Cials Denounce Lawmakers' Attempts To Censor NewsroomsDocument52 pagesFCC O Cials Denounce Lawmakers' Attempts To Censor NewsroomsKeithStewartNo ratings yet
- WHITE TOWN GROUP-4 FinalDocument112 pagesWHITE TOWN GROUP-4 Finalaswath manojNo ratings yet
- Definition Nature and Scope of Urban GeographyDocument4 pagesDefinition Nature and Scope of Urban Geographysamim akhtarNo ratings yet
- Impeller Velocity TrianglesDocument2 pagesImpeller Velocity TrianglesLorettaMayNo ratings yet
- Et200sp Im 155 6 PN ST Manual en-US en-USDocument47 pagesEt200sp Im 155 6 PN ST Manual en-US en-USayaz officeNo ratings yet
- General Arrangement, Isometric Views and B.O.M. A Midget Steam Car Using A Double Acting Oscillating EngineDocument3 pagesGeneral Arrangement, Isometric Views and B.O.M. A Midget Steam Car Using A Double Acting Oscillating EngineRobson Carlos0% (1)