Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is White Matter
Uploaded by
Abhay Iyer0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views1 pageOriginal Title
What-is-white-matter
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views1 pageWhat Is White Matter
Uploaded by
Abhay IyerCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
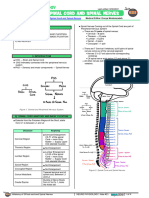
1 Different regions of the brain 2 A slice through the brain showing the left
and right cerebral hemispheres (a) and the
What is White Matter? distribution of white and grey matter (b).
X Y
White matter is a type of tissue in the brain that is white matter
X grey matter
made up of axons and a lot of a fatty substance frontal lobe parietal lobe (a) (b)
called myelin (fig 3a). The myelin is what makes the
tissue appear ‘white’ in some types of brain scans.
left right
What is white matter made of? occipital
lobe
• Neurons These are brain cells that carry temporal lobe
signals from one part of the brain to another (fig 3a).
An important part of a neuron, the long thin tubular cerebellum
structure called the axon, is wrapped in myelin,
which acts like the insulation layer that covers spinal cord
electrical wires. It helps the signals to travel quicker
down the axon. These neuron axons can group
together, travelling in the same direction to form
‘fibre bundles’ (fig 3b).
Y
• Connective pathways When fibre bundles 3 A neuron with myelin wrapped around the
are large enough, they are called white matter axon (a) and neuron axons grouped together
pathways (fig 4). They connect different regions of to form a ‘fibre bundle’ (b).
4 Brain slices showing the location of two white
the brain to each other. Some are very short and matter pathways, the Corpus Callosum (red)
connect neighbouring sections of the brain. Others X Y
(a) (b) and IFOF (green).
are much longer and might connect the front of the
brain to the back, or the left half of the brain to the X X
right half. Some pathways are small and thin, some
are very thick and large.
Two examples of white matter pathways are the
Inferior Fronto-Occipital Fasciculus (IFOF), which neuron
Y
body X
connects the front and back regions of the brain
and the Corpus Callosum pathway, which connects
the left and right cerebral hemispheres together dendrites
and is the biggest pathway in the brain (fig 4).
How do we measure white matter?
Scientists and doctors can look at these white neuron axon
wrapped in myelin
matter pathways in living brains. They use a type
of brain scan called an MRI (Magnetic Resonance
Imaging) scan to capture information and create
3D pictures of these white matter pathways. synaptic boutons
Y
This introductory information sheet was produced as part of This information sheet represents independent research part funded by the National Institute
a participatory research exercise in March 2019. For more for Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre at South London and Maudsley NHS
information please contact Anoushka.1.leslie@kcl.ac.uk Foundation Trust and King’s College London. The views expressed are those of the authors and
not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health and Social Care.
You might also like
- Excitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesFrom EverandExcitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computational Neuroscience: Lecture 3: Windows To The BrainDocument70 pagesIntroduction To Computational Neuroscience: Lecture 3: Windows To The BrainNAGAVARSHININo ratings yet
- Assessment of Neurologic Function 1827Document4 pagesAssessment of Neurologic Function 1827Mahendra PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Brain Functions Underlying SpeechDocument24 pagesBrain Functions Underlying SpeechHAKAN ÖZTEMÜRNo ratings yet
- Hu Bio Lecture 6a (Nervous Systen II)Document5 pagesHu Bio Lecture 6a (Nervous Systen II)Katie YeungNo ratings yet
- Histology of the Nervous TissueDocument12 pagesHistology of the Nervous TissuenhcsmlmolNo ratings yet
- 3.1 CNS Histology 57Document57 pages3.1 CNS Histology 57Namomsa W.No ratings yet
- p88 99Document12 pagesp88 99Prasanna Venkhatesh VNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord (3 of 5)Document24 pagesSpinal Cord (3 of 5)j53934762No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Notes - The Central Nervous SystemDocument55 pagesUnit 5 Notes - The Central Nervous SystemValentina CaravelisNo ratings yet
- Histologi SarafDocument5 pagesHistologi SarafRama MaulidinNo ratings yet
- 8 Nervous SystemDocument7 pages8 Nervous Systemangel.loking10No ratings yet
- Assignment: Tissue Recognition /30: Part A: Epithelial TissueDocument5 pagesAssignment: Tissue Recognition /30: Part A: Epithelial Tissueapi-388753692No ratings yet
- Spinal CordDocument8 pagesSpinal CordPhantom of VeniceNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document7 pagesTopic 1Haotian gary LinNo ratings yet
- Internal Anatomy of The Spinal CordDocument5 pagesInternal Anatomy of The Spinal CordEijunNo ratings yet
- The Central Nervous System: Chapter 12 Part ADocument31 pagesThe Central Nervous System: Chapter 12 Part AMajdi AkNo ratings yet
- Nervous SYSTEM - 120721031607Document14 pagesNervous SYSTEM - 120721031607Drmhdh DrmhdhNo ratings yet
- Histology Neural Tissue IDocument5 pagesHistology Neural Tissue ImenschNo ratings yet
- Fish Brains Anatomy Functionality and Evolutionar-Wageningen University and Research 631234Document21 pagesFish Brains Anatomy Functionality and Evolutionar-Wageningen University and Research 631234Pep PepeNo ratings yet
- NUR11O1 Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityDocument5 pagesNUR11O1 Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityPrancheska Abigayle Peneyra SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ControlDocument10 pagesCoordination and ControlAJAYI PETERNo ratings yet
- Understanding Grey Matter in the Central Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Grey Matter in the Central Nervous SystemAbdallah El-ashriNo ratings yet
- Brain Anatomy PDFDocument37 pagesBrain Anatomy PDFPinto D. R PiliangNo ratings yet
- Modernpsychology00berriala PDFDocument61 pagesModernpsychology00berriala PDFMD SUJAN SEKHNo ratings yet
- Thehumancerebellum: A Review of Physiologic NeuroanatomyDocument11 pagesThehumancerebellum: A Review of Physiologic NeuroanatomyCan EkerNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To HistologyDocument60 pages01 Introduction To HistologyMartha Orendu Oche AttahNo ratings yet
- SG Sheep Brain Dissection+Document4 pagesSG Sheep Brain Dissection+ROHAN CHHABRANo ratings yet
- This Content Downloaded From 132.174.251.250 On Fri, 18 Jun 2021 23:05:00 UTCDocument19 pagesThis Content Downloaded From 132.174.251.250 On Fri, 18 Jun 2021 23:05:00 UTCJavieraNo ratings yet
- Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes: Mechanosensory PathwaysDocument8 pagesMedical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes: Mechanosensory PathwaysAnusha SebastianNo ratings yet
- White MatterDocument19 pagesWhite MatterZoya MoraniNo ratings yet
- Nerve Tissue & Nervous System: Assoc. Prof Dr. Karim Al-Jashamy IMS/MSU 2010Document27 pagesNerve Tissue & Nervous System: Assoc. Prof Dr. Karim Al-Jashamy IMS/MSU 2010Kaushik BhuvaNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document7 pagesModule 3fiids.castroNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt-19-20 XI Zoo Study-Package-1 Level-1 Chapter-1 PDFDocument20 pagesCLS Aipmt-19-20 XI Zoo Study-Package-1 Level-1 Chapter-1 PDFJainil PatelNo ratings yet
- Perception NotesDocument12 pagesPerception NotesAnu KNo ratings yet
- (Addison-Wesley Data & Analytics Series) Krohn, J. - Beyleveld, G. - Bassens, A. - Deep Learning Illustrated - A Visual, Interactive Guide To Artificial Intelligence-Pearson Education (2019)Document192 pages(Addison-Wesley Data & Analytics Series) Krohn, J. - Beyleveld, G. - Bassens, A. - Deep Learning Illustrated - A Visual, Interactive Guide To Artificial Intelligence-Pearson Education (2019)Valencia Carlos100% (4)
- Architectonic Mapping Amunts 2015Document22 pagesArchitectonic Mapping Amunts 2015Andra-Amalia ArmulescuNo ratings yet
- ANA113 Lecture 16 NS IV - BrainDocument3 pagesANA113 Lecture 16 NS IV - BrainSueNo ratings yet
- Saladin 13 Anatomy and Physiology OutlineDocument12 pagesSaladin 13 Anatomy and Physiology OutlineAnn Dahng100% (1)
- Organization of Nervous System - MBBS NewDocument53 pagesOrganization of Nervous System - MBBS NewDorin PathakNo ratings yet
- Hemispheric Structure and FuctionDocument4 pagesHemispheric Structure and FuctionDebby RizkyNo ratings yet
- Kimura Chapter 4Document66 pagesKimura Chapter 4Mio FaraoneNo ratings yet
- International Standards For Neurological and Functional Classification of Spinal Cord InjuryDocument14 pagesInternational Standards For Neurological and Functional Classification of Spinal Cord InjuryVijay IyerNo ratings yet
- 4 White MatterDocument8 pages4 White MatterMiguelNo ratings yet
- Lec Activity8 Jbillones 101221Document15 pagesLec Activity8 Jbillones 101221Jayvee BillonesNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument5 pagesAnatomyBRENDA VALDEZ 190291No ratings yet
- Module 2Document5 pagesModule 2Niezl Jia OlarioNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Human Body CareDocument13 pagesActivity 1 Human Body CareEduardoNo ratings yet
- Cortex 2012 Catani-2Document26 pagesCortex 2012 Catani-2edgarNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Laboratory Exercise 5 Different Tissues of The Human Body Tissues BETITO ABELLO ADRICULA ARTICULO BERGANTINOSDocument8 pagesModule 3 Laboratory Exercise 5 Different Tissues of The Human Body Tissues BETITO ABELLO ADRICULA ARTICULO BERGANTINOSDainah ArticuloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument18 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyMaggyNo ratings yet
- Macroscopic Neuroanatomy: Neuroanatomy Deals With The Structure of TheDocument14 pagesMacroscopic Neuroanatomy: Neuroanatomy Deals With The Structure of TheRoziel Anne BasaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BrainDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The BraineriannajNo ratings yet
- Medial Longitudinal FasciculusDocument5 pagesMedial Longitudinal FasciculussakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience Fundamentals: CNS Anatomy and NeurotraumaDocument23 pagesNeuroscience Fundamentals: CNS Anatomy and NeurotraumaChloe AnnNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument11 pagesNeuroscience: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDaniela BurceaNo ratings yet
- HLA7 - Nervous SyStemDocument25 pagesHLA7 - Nervous SyStemMichael UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- Unit XIII - Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesUnit XIII - Lecture NotesSteve SullivanNo ratings yet
- Sheep Brain Observation LAB 2015Document4 pagesSheep Brain Observation LAB 2015Leo MatsuokaNo ratings yet
- Executive Functions Review PDFDocument21 pagesExecutive Functions Review PDFMaría Fernanda Delgado RojasNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Extracts in CNS DisordersDocument13 pagesAyurvedic Extracts in CNS DisordersAbhay IyerNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Deficits-CovidDocument10 pagesCognitive Deficits-CovidAbhay IyerNo ratings yet
- What Is Diffusion Tensor Imaging?: How Does DTI Work?Document1 pageWhat Is Diffusion Tensor Imaging?: How Does DTI Work?Abhay IyerNo ratings yet
- Biological Wastewater Treatment: Aerobic & AnaerobicDocument8 pagesBiological Wastewater Treatment: Aerobic & Anaerobic007_pppqqqNo ratings yet
- Neurology Mnemonics Memory AidsDocument27 pagesNeurology Mnemonics Memory AidsMuhammad Luqman Nul Hakim100% (1)
- Biology Notes Human Digestive System For SSC Exam PDFDocument2 pagesBiology Notes Human Digestive System For SSC Exam PDFनितीन लाठकरNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy 5th Edition Saladin Test BankDocument16 pagesHuman Anatomy 5th Edition Saladin Test BankGregoryStricklandgtak100% (54)
- Bleeding Disorders in Children: Abdulhadi Alzaben, MD Pediatric Hematology Oncology and Stem Cell TransplantDocument51 pagesBleeding Disorders in Children: Abdulhadi Alzaben, MD Pediatric Hematology Oncology and Stem Cell TransplantRasha Al MousaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of Smooth and Rough Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument4 pagesStructure and Functions of Smooth and Rough Endoplasmic Reticulumjahp_13625% (4)
- Panik Poli Obgyn RS USU Mei 9 - 15.Document43 pagesPanik Poli Obgyn RS USU Mei 9 - 15.Zulfindra Arifin93No ratings yet
- BIOMECHANICS (30 MCQ 3 Saq) : StudyDocument7 pagesBIOMECHANICS (30 MCQ 3 Saq) : Studyronwest1990No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Female Genital OrgansDocument7 pagesAnatomy of Female Genital OrgansAyurveda PgNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System For MBBSDocument20 pagesAutonomic Nervous System For MBBSjacobsNo ratings yet
- Lab Worksheet 4 1 AnswersDocument5 pagesLab Worksheet 4 1 Answersjames bulawinNo ratings yet
- Maternal Child Health NursingDocument5 pagesMaternal Child Health NursingLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Yusi - Anatomy of The Urinary Tract 2009 12-7Document129 pagesYusi - Anatomy of The Urinary Tract 2009 12-7abstabsNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy and Delivery NotesDocument7 pagesPregnancy and Delivery NotesJae-Moy KeymistNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Autoimmune DiseasesDocument21 pagesThyroid Autoimmune Diseasesmicheal1960No ratings yet
- Infusion Therapy CompleteDocument93 pagesInfusion Therapy CompleteRafaelFreitasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Immune SystemDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Immune SystemKathzkaMaeAgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Auditory pathway: From cochlea to auditory cortexDocument16 pagesAuditory pathway: From cochlea to auditory cortexDrsreeram ValluriNo ratings yet
- Physio CAT 2 AnsweredDocument34 pagesPhysio CAT 2 AnsweredJohn KennedyNo ratings yet
- Ghafoor SalivaryGlandsDocument6 pagesGhafoor SalivaryGlandsMamadou DIENENo ratings yet
- Pulp & Periapical Disease GuideDocument195 pagesPulp & Periapical Disease GuideRebecca SephoraNo ratings yet
- The Functions of Vacuoles in Plant and Animal Cells (39 charactersDocument3 pagesThe Functions of Vacuoles in Plant and Animal Cells (39 charactersAmber L.No ratings yet
- Worksheet #1 4THDocument8 pagesWorksheet #1 4THrussellrada135No ratings yet
- Mark Scheme F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport June 2016Document10 pagesMark Scheme F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport June 2016vanessabrauneisNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Reading ArticlesDocument1 pageWeek 4 - Reading ArticlesKath MagtanongNo ratings yet
- Periodontal LigamentDocument37 pagesPeriodontal LigamentkeecancerNo ratings yet
- Bionetix Extra Vol - IIDocument125 pagesBionetix Extra Vol - IIJ.A.N ISNARD100% (3)
- Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionDocument112 pagesBasic Principles of Animal Form and Function: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionRauven Jean Erodias FadriquelaNo ratings yet
- Frcpath Part 1 Previous Questions: Document1Document11 pagesFrcpath Part 1 Previous Questions: Document1Ali LaftaNo ratings yet
- BSC Zoology SyllabusDocument72 pagesBSC Zoology SyllabusAnup KumarNo ratings yet
- Tissue Types and FunctionsDocument30 pagesTissue Types and FunctionsEspinosa Mary Dianne V.No ratings yet