Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Shapes of Molecules and Molecular Ions
Shapes of Molecules and Molecular Ions
Uploaded by
jennie0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageThis document provides a chart for determining the shape of molecules and molecular ions based on the number of electron domains and non-bonding pairs around the central atom. It explains that electron domain geometry refers to the distribution of all electron pairs, while molecular geometry refers specifically to the arrangement of bonded atoms. The user draws a Lewis structure, counts electron domains on the central atom, and checks for non-bonding pairs to look up the expected shape in the provided chart.
Original Description:
Original Title
3 VSEPR Summary
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a chart for determining the shape of molecules and molecular ions based on the number of electron domains and non-bonding pairs around the central atom. It explains that electron domain geometry refers to the distribution of all electron pairs, while molecular geometry refers specifically to the arrangement of bonded atoms. The user draws a Lewis structure, counts electron domains on the central atom, and checks for non-bonding pairs to look up the expected shape in the provided chart.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageShapes of Molecules and Molecular Ions
Shapes of Molecules and Molecular Ions
Uploaded by
jennieThis document provides a chart for determining the shape of molecules and molecular ions based on the number of electron domains and non-bonding pairs around the central atom. It explains that electron domain geometry refers to the distribution of all electron pairs, while molecular geometry refers specifically to the arrangement of bonded atoms. The user draws a Lewis structure, counts electron domains on the central atom, and checks for non-bonding pairs to look up the expected shape in the provided chart.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Shapes of molecules and molecular ions
1. Draw Lewis structure
.
2. Count number of electron domains around the central atom.
An electron domain (i.e. 1 electron domian) refers to either one of the following:
1 non-bonding pair of electrons
1 single covalent (1 bonding pair) bond
1 double covalent bond (2 bonding pairs of electrons)
1 triple covalent bond (3 bonding pairs of electrons)
3. Check how many of the negative charge centres are non-bonding pairs there around the central atom and
then use the chart below.
Number Electron Number of Shape of Bond angles Examples
of domain non-bonding pairs molecule/ (in )
charge geometry around central atom molecular-ion
centers (electron arrangement) (molecular geometry)
2 Linear 0 Linear 180 BeCl2, CO2,
HCN, C2H2,
+
BeF2, NO2
3 0 Trigonal planar 120 BF3, BCl3,
2-
C2H4, CO3 ,
- +
Trigonal NO3 , CH3
planar
1 Bent Less than 120 O3, SO2 ,
-
HNO, NO2
0 Tetrahedral 109.5 CH4, CCl4,
Tetrahedral CF4, CBr4
4
-
1 Trigonal pyramidal Less than 109.5 NH3, CH3 ,
PCl3
2 Bent Much Less H2O, SF2,
than 109.5 SBr2, Cl2O
Electron pair domain geometry refers to how all electron pairs/negative charge centres (bonding and non-
bonding pairs) are distributed around the central atom; this is not necessarily the shape of the
molecule/molecular ion.
Shape of the molecule/molecular-ion or molecular geometry refers to how the atoms are arranged in the
molecule or ion. To determine the molecule/molecular-ion shape only consider the bonded pairs which are
distributed around the central atom.
You might also like
- Student Exploration: Polarity and Intermolecular ForcesDocument10 pagesStudent Exploration: Polarity and Intermolecular ForcesLama Ashi86% (7)
- Chemistry WorksheetDocument5 pagesChemistry WorksheetGiezel MadurarNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Particle TestingDocument3 pagesMagnetic Particle TestingKurniawanNo ratings yet
- ANO4A-oxidation States-Nomenclatuur-2018 PDFDocument30 pagesANO4A-oxidation States-Nomenclatuur-2018 PDFJelte de WitNo ratings yet
- DGA Reference VALUESDocument6 pagesDGA Reference VALUESNisal AmarasingheNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding1Document39 pagesCovalent Bonding1Zheng JoeyNo ratings yet
- G.O.C. Iws-1Document50 pagesG.O.C. Iws-1Lakshya ChandakNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Chemistry Assignment #3 2018-2019 ANSWERSDocument5 pagesAromatic Chemistry Assignment #3 2018-2019 ANSWERSZoe NorvilleNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 With Ans Solution ChemistryDocument15 pagesPaper 2 With Ans Solution ChemistryKushagraNo ratings yet
- 1group and 2 Group Disconnections 04-Mar-2021Document10 pages1group and 2 Group Disconnections 04-Mar-2021Sowmya N DNo ratings yet
- Alkane PDFDocument5 pagesAlkane PDFRavi Kiran KoduriNo ratings yet
- Alkane Jee-Advance Level-1Document5 pagesAlkane Jee-Advance Level-1Ravi Kiran KoduriNo ratings yet
- CourseDocument18 pagesCourseflamepixerxNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 ANSWERDocument2 pagesWorksheet 3 ANSWERAna PavlovicNo ratings yet
- The Shapes of Molecules: AspartameDocument6 pagesThe Shapes of Molecules: AspartameABHISEK SAHUNo ratings yet
- Shapes of Covalent Molecules and Polarity LAB1Document5 pagesShapes of Covalent Molecules and Polarity LAB1Manal NasrallahNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument3 pagesAldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acidsbalaganesh1505No ratings yet
- Applications of Free Wilson AnalysisDocument26 pagesApplications of Free Wilson AnalysisSreenivas neeladri100% (1)
- Chemistry Paper With AnswerDocument11 pagesChemistry Paper With AnswerStunt RangersNo ratings yet
- CHEM1701 Formulas Periodictable 20202021Document2 pagesCHEM1701 Formulas Periodictable 20202021tomasNo ratings yet
- Chem1701 Formulas Periodictable 20202021Document2 pagesChem1701 Formulas Periodictable 20202021api-534461940No ratings yet
- JEE Main 2013 Question Paper With Answers - Paper 1Document24 pagesJEE Main 2013 Question Paper With Answers - Paper 1aashuchattNo ratings yet
- Fukuyama Group - Group Meeting Problems 2001/08/22: N N N HDocument2,429 pagesFukuyama Group - Group Meeting Problems 2001/08/22: N N N HGia PhướcNo ratings yet
- Neet Full Test-3Document21 pagesNeet Full Test-3vasteducationalNo ratings yet
- 10 Hydrocarbons: AssignmentDocument6 pages10 Hydrocarbons: AssignmentalarmbarbarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NMR Spectroscopy: Part II (C-NMR)Document21 pagesIntroduction To NMR Spectroscopy: Part II (C-NMR)andi evi febriantiNo ratings yet
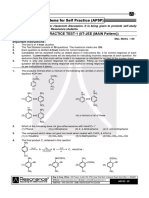
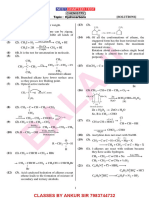
- Part - I: Practice Test-1 (Iit-Jee (Main Pattern) ) : Important InstructionsDocument22 pagesPart - I: Practice Test-1 (Iit-Jee (Main Pattern) ) : Important InstructionsKivilia EduventuresNo ratings yet
- Jee Advanced October 2021 Chemistry Paper 2 Solution - PHPDocument12 pagesJee Advanced October 2021 Chemistry Paper 2 Solution - PHPDeath RiderNo ratings yet
- Heating EffectDocument9 pagesHeating Effectshubhra.kuldeep2003No ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid & Acid Derivatives and Amines: Exercise - IDocument3 pagesCarboxylic Acid & Acid Derivatives and Amines: Exercise - ILifestyle BoomNo ratings yet
- RedoxDocument15 pagesRedoxInês AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- PKB IIT JEE 2010 Chemistry Paper 2 N SolutionDocument9 pagesPKB IIT JEE 2010 Chemistry Paper 2 N SolutionPawan BabelNo ratings yet
- MLP - UNIT 9 - Coordination ChemistryDocument9 pagesMLP - UNIT 9 - Coordination ChemistryJaspreet SinghNo ratings yet
- AlkanesDocument19 pagesAlkanesRahul deyNo ratings yet
- cs2c00307 Si 001Document16 pagescs2c00307 Si 001Dr. Suman Kalyan SahooNo ratings yet
- 4-Coordination Chemistry IDocument61 pages4-Coordination Chemistry Igunjan pratapNo ratings yet
- Reaction SheetDocument8 pagesReaction SheetKanika VyasNo ratings yet
- Q J Apx Py FX Q J Ap X P Y FX: For 1 Membrane Assume Binary System: Only Co and CHDocument3 pagesQ J Apx Py FX Q J Ap X P Y FX: For 1 Membrane Assume Binary System: Only Co and CHVõ Hồng HạnhNo ratings yet
- Copper Leaching Behavior From Waste Printed Circuit Board in Ammoniacal Alkaline SolutionDocument5 pagesCopper Leaching Behavior From Waste Printed Circuit Board in Ammoniacal Alkaline SolutionJhon Barzola PalominoNo ratings yet
- Reaction Mechanism IDocument15 pagesReaction Mechanism IFilmodeNo ratings yet
- 作業2 20170323Document1 page作業2 20170323曾瑋富No ratings yet
- Neet Full Test-1Document20 pagesNeet Full Test-1vasteducationalNo ratings yet
- 3Document3 pages3Fausto SalazarNo ratings yet
- Unit 10. Complexometric Titration: I. Complex Ion FormationDocument5 pagesUnit 10. Complexometric Titration: I. Complex Ion FormationRaymond R. SantosNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesChemical BondingChannappa C SNo ratings yet
- Stereo New 2Document23 pagesStereo New 2Upendrasenareddy KunduruNo ratings yet
- CHEM 203 Midterm Exam 2Document7 pagesCHEM 203 Midterm Exam 2pNo ratings yet
- XI-Chemistry Chapter test-13-Hydrocarbons-SolutionsDocument3 pagesXI-Chemistry Chapter test-13-Hydrocarbons-Solutionsprateek yadavNo ratings yet
- Coordinate CompoundsDocument5 pagesCoordinate Compoundsmandhareneel06No ratings yet
- Cemi - 321 - Lecture 12 - 2023Document21 pagesCemi - 321 - Lecture 12 - 2023VILLA KGAMADINo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundsDocument51 pagesCoordination CompoundsasdfNo ratings yet
- Full Syllabus Test: C Iit-JeeDocument8 pagesFull Syllabus Test: C Iit-JeeshrawantiyaNo ratings yet
- AQA 9 1 Revision Sheets Chemistry Unit 3 GCSEDocument4 pagesAQA 9 1 Revision Sheets Chemistry Unit 3 GCSEOviya VashisthNo ratings yet
- Master Card - Coordination CompoundsDocument2 pagesMaster Card - Coordination CompoundsgudiNo ratings yet
- OriginalDocument28 pagesOriginalNurain BalqisNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds - UnlockedDocument5 pagesCarbonyl Compounds - UnlockedHuda ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Iitian'S Hub: Assignment # 1 General Organic Chemistry ChemistryDocument11 pagesIitian'S Hub: Assignment # 1 General Organic Chemistry ChemistrySAHILI RANENo ratings yet
- Amines - Short Notes - Lakshya JEE 2024Document3 pagesAmines - Short Notes - Lakshya JEE 2024subhamwork2006No ratings yet
- AL Chemistry 2008 Paper I SolutionDocument17 pagesAL Chemistry 2008 Paper I SolutiondorachusinyanNo ratings yet
- Chem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 4Document1 pageChem 212 Alkyl Halide Problems 4kevinamyNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2021 16 March Shift 1 ChemistryDocument12 pagesJEE Main 2021 16 March Shift 1 ChemistryshmalwaysNo ratings yet
- XXIVth International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary and Main Section Lectures Presented at Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany, 2–8 September 1973From EverandXXIVth International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary and Main Section Lectures Presented at Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany, 2–8 September 1973No ratings yet
- Tests - Mechanical Properties: Material Brand, Source, Tests Etc. Units RequirementDocument6 pagesTests - Mechanical Properties: Material Brand, Source, Tests Etc. Units RequirementNandika MilindaNo ratings yet
- MIL-R-5031 - B (Rods and Wire, Welding, Corrosion and Heat Resistant Alloys) (Notice 1)Document1 pageMIL-R-5031 - B (Rods and Wire, Welding, Corrosion and Heat Resistant Alloys) (Notice 1)ccorp00890% (1)
- Boiler Water Treatment QuesDocument18 pagesBoiler Water Treatment QuesPintu KumarNo ratings yet
- 4-006 ExplanationDocument6 pages4-006 ExplanationAdam BehielsNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements 2 Jan 2014Document2 pagesDesign of Machine Elements 2 Jan 2014Prasad C M100% (1)
- Installation Manual: SYSTEM Inverter Air ConditionersDocument52 pagesInstallation Manual: SYSTEM Inverter Air ConditionersOscar DiazNo ratings yet
- Non Ferrous MaterialsDocument8 pagesNon Ferrous MaterialsSH1961No ratings yet
- Vendor List For Snider PDFDocument2 pagesVendor List For Snider PDFsitam_nitj4202No ratings yet
- Consistency Training: Contamination ControlDocument67 pagesConsistency Training: Contamination ControlMaerks KevinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 GasesL.RDocument64 pagesChapter 5 GasesL.ROsama AlshoubakiNo ratings yet
- Asif Uz Zaman (Lecturer) Civil Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering Rabigh King Abdulaziz UniversityDocument10 pagesAsif Uz Zaman (Lecturer) Civil Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering Rabigh King Abdulaziz Universityالجارح الجارحNo ratings yet
- Architectural Building Technology 1 ReviewerDocument2 pagesArchitectural Building Technology 1 ReviewerFrannie BorrasNo ratings yet
- Exergy Analysis of The Industrial Symbiosis ModelDocument12 pagesExergy Analysis of The Industrial Symbiosis ModelMarco ZubietaNo ratings yet
- Wps Vosl-Pl-1 Pipeline Rev.2 XDocument11 pagesWps Vosl-Pl-1 Pipeline Rev.2 XVijo Jose100% (1)
- Schedule of Finishes: Female CR Male CRDocument7 pagesSchedule of Finishes: Female CR Male CRadobo sinigangNo ratings yet
- Buisiness Communication and Ethics: SubjectDocument19 pagesBuisiness Communication and Ethics: SubjectAtharva KulkarniNo ratings yet
- NTN PRO 006 Glass Types Used in BuildingsDocument2 pagesNTN PRO 006 Glass Types Used in BuildingsMoren AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Nitocote EP405Document4 pagesNitocote EP405mangjitNo ratings yet
- Quantification of The Influence of Cracks in Concrete Structures On Carbonation and Chloride PenetrationDocument9 pagesQuantification of The Influence of Cracks in Concrete Structures On Carbonation and Chloride Penetrationsulluminu pattoziiNo ratings yet
- Heat ExamDocument2 pagesHeat ExamZahraa A. NadeemNo ratings yet
- Astm D 3174-04Document5 pagesAstm D 3174-04Servando LozanoNo ratings yet
- IndustryDocument14 pagesIndustryVivek JayantNo ratings yet
- Astm E7 2003Document30 pagesAstm E7 2003Salvador DíazNo ratings yet
- Technical Paper-WSD 2018Document6 pagesTechnical Paper-WSD 2018krbabu1969No ratings yet
- Tentative Specification Built-Up Spray GroutDocument9 pagesTentative Specification Built-Up Spray GroutharivennelaNo ratings yet
- Lyocell Fiber: Lenzing Fibers Inc. CelluloseDocument5 pagesLyocell Fiber: Lenzing Fibers Inc. CelluloseGrosu Marian CatalinNo ratings yet
- CatalogueTroubleshooting HY29 0022 UKDocument62 pagesCatalogueTroubleshooting HY29 0022 UKStroia Constantin MariusNo ratings yet
- Symbol RMDocument7 pagesSymbol RMSiti MaimunahNo ratings yet