Professional Documents
Culture Documents
METABOLISM-AQA-4 4 2 3 - (v3)
Uploaded by
judymw2000Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
METABOLISM-AQA-4 4 2 3 - (v3)
Uploaded by
judymw2000Copyright:
Available Formats
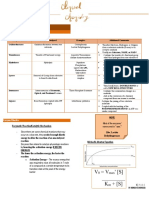
Carbon
+ Oxygen
Glucose
Dioxide +
Water
ENERGY The chemicals that take part
C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O Metabolic
in metabolic reactions
Enzymes:
are called metabolites
reactions use
Respiration is the chemical • Are specific
reaction that allows cells to
energy transferred
• Are a type of protein
release energy from food from
CELLULAR • Biological catalysts
Mitochondria in cells are the • Continually control the reactions
and it is specific to glucose
An example of a metabolic
RESPIRATION Metabolic pathways are a series of
enzyme is glucokinase
site of aerobic respiration Metabolic Rate: Is the enzyme controlled chemical reactions of metabolism
speed at which such that start with a substrate and finish • Reactions need energy from
chemical reactions take with an end product. Most are reversible. cellular respiration to take place
Metabolic rate varies because of several factors, including: place in the body Metabolic pathways can be • Work at an optimum temperature
* Age anabolic or catabolic • Change the substrate at each step in
METABOLISM
* Gender - male or female the metabolic pathway in order to get
* The proportion of muscle to fat in the body to the final product in the end
* The amount of exercise and other physical activity • Activity is affected by:
* Genetic traits • Substrate Type
Definition: Metabolism is the sum of all the reactions happening in a • Temperature
* The metabolic rate increases as we exercise and stays cell or organism, in which molecules are made or broken down • pH
high for a while afterwards
• Substrate Concentration
(up to saturation point)
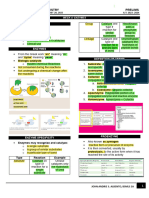
ENERGY
Required Anabolic Catabolic Releases
ENERGY
Endothermic
Reactions Reactions 'Degradation'
Exothermic
'Building Up' Large molecules break down
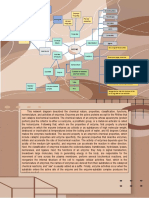
Glycogen Small molecules join to make larger ones to make smaller ones
is converted from glucose in the liver + ENERGY + ENERGY
and muscle cells. It is the storage form of
glucose in animals and humans
GLUCOSE
Starch A simple sugar (monosaccharride)
It is the major source of energy for a cell
is built from long chains of glucose
(produced in photosynthesis) and is the C6H12O6
main storage form of glucose in plants
Ammonia Urea
Cellulose NITRATE IONS
is made from chains of glucose. It is
used in plants and algal cells to
LIVER
strengthen their cell walls
LIPIDS do eins
AMINO ACIDS
en rot
wn
GLYCEROL
FATTY ACID 1
p
Excreted
ss
Sy
ce
nt
ok
he Expelled as waste
Ex
FATTY ACID 2
Br
sis Excretion: The removal of potentially
ed harmful or toxic substances from the body
FATTY ACID 3
(FATS & OILS)
PROTEINS
You might also like
- Test Bank For Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology 4th Edition by Pearl Solomon Isbn 10 0323239250 Isbn 13 9780323239257Document7 pagesTest Bank For Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology 4th Edition by Pearl Solomon Isbn 10 0323239250 Isbn 13 9780323239257carwynquanh4tuozNo ratings yet
- Biochimica MetabolicaDocument195 pagesBiochimica MetabolicaGianluca100% (1)
- ICAN White Paper With Cover PageDocument38 pagesICAN White Paper With Cover Pagejudymw2000No ratings yet
- (PPT) Cap. 10Document47 pages(PPT) Cap. 10Felito SifonteNo ratings yet
- BiocatalysisDocument10 pagesBiocatalysisazizrafeeqNo ratings yet
- Metabolism (Compatibility Mode)Document13 pagesMetabolism (Compatibility Mode)Dark_KiroNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MetabolismDocument49 pagesIntroduction To Metabolismmaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- CC Partii&III NotesDocument30 pagesCC Partii&III NotesAnielle Mongaya100% (1)
- 3 EnzymesDocument27 pages3 Enzymesharshit khareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-IDocument40 pagesChapter 4-ISifan MotumaNo ratings yet
- 2overview of MetabolismDocument16 pages2overview of MetabolismLeann RodriguezNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument7 pagesChemistryLee LuceroNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument10 pagesEnzymesAdri ChakraNo ratings yet
- Week 9 - EnzymesDocument5 pagesWeek 9 - Enzymesjvlegaspi7463valNo ratings yet
- Module 8: Enzymes & Metabolic Pathways MetabolismDocument4 pagesModule 8: Enzymes & Metabolic Pathways MetabolismThiody Hope Mongas100% (2)
- 9744 H2 Biology Lecture Notes - JC 1: EnzymesDocument43 pages9744 H2 Biology Lecture Notes - JC 1: EnzymesTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Enzymes: Metabolic Pathways Catalysts That Accelerate Chemical ReactionsDocument13 pagesBiochemistry Enzymes: Metabolic Pathways Catalysts That Accelerate Chemical ReactionsAnonymous 6L4f3LNo ratings yet
- Enzyme and Enzyme KineticsDocument7 pagesEnzyme and Enzyme KineticsSam Jeffrey100% (2)
- Activity 1 OrgchemDocument3 pagesActivity 1 OrgchemBASAY, HANNA RICA P.No ratings yet
- Cellular MetabolismDocument8 pagesCellular MetabolismShafique AhmadNo ratings yet
- CH 8 BOOK PDFDocument22 pagesCH 8 BOOK PDFAshlye LunaNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Energy Production HandoutsDocument5 pagesBiochemical Energy Production Handoutssilvestre bolosNo ratings yet
- EnzymologyDocument15 pagesEnzymologyhkrybmzxfbxbwnpfhnNo ratings yet
- General Biology Unit 4: Cellular Metabolism and Metabolic DisordersDocument13 pagesGeneral Biology Unit 4: Cellular Metabolism and Metabolic DisordersSultan AhimedNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Finals - Introduction To Microbial Metabolism-1Document40 pagesModule 3 - Finals - Introduction To Microbial Metabolism-1Mary Grace ClarosNo ratings yet
- SCE3204 Lecture 2Document31 pagesSCE3204 Lecture 2ainomugisha arnoldNo ratings yet
- Enzymes - Doc Version 1Document7 pagesEnzymes - Doc Version 1LALITH SAI KNo ratings yet
- BiocatalysisDocument8 pagesBiocatalysisHanithra AnanthanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Enzymes and Mechanism of Enzyme ActionDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Enzymes and Mechanism of Enzyme ActionAtif Amin BaigNo ratings yet
- Introducing Pharma (Drug) Cology..Document17 pagesIntroducing Pharma (Drug) Cology..monoj5859No ratings yet
- Enzymes: General Characteristics of EnzymesDocument10 pagesEnzymes: General Characteristics of EnzymesHamzullah KhanNo ratings yet
- 3 - Lec - MicroPara - Microbial MetabolismDocument33 pages3 - Lec - MicroPara - Microbial MetabolismFeona IgoroteNo ratings yet
- Integrated Cellular MetabolismDocument8 pagesIntegrated Cellular MetabolismPink MeNo ratings yet
- Enzymes PPTDocument39 pagesEnzymes PPTsunil patelNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument46 pagesEnzymesHighlifeNo ratings yet
- Biochem Mod 7 PDFDocument7 pagesBiochem Mod 7 PDFtheaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism and EnzymesDocument11 pagesMetabolism and Enzymessherylmatchado07No ratings yet
- Week 4 EnzymesDocument5 pagesWeek 4 EnzymesJOHAINA NORNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - The Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed ReactionsDocument18 pagesLecture 1 - The Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed ReactionsGenevive S. de VeraNo ratings yet
- Enzymes PPTDocument40 pagesEnzymes PPTJaisy PatelNo ratings yet
- ENZYMESDocument31 pagesENZYMESjuunisai6No ratings yet
- Network Diagram About EnzymeDocument2 pagesNetwork Diagram About EnzymeDURANO, ROSELLE Z.SCINo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Biocatalysis: SUBTOPIC: 4.1 Properties of Enzymes and Mechanism of Actions Learning OutcomesDocument8 pagesChapter 4: Biocatalysis: SUBTOPIC: 4.1 Properties of Enzymes and Mechanism of Actions Learning OutcomesNURUL HIDAYAH BINTI SAIFUL ANUAR MoeNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY LECTURE NotesDocument31 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY LECTURE NotesFREDRICK OUNDONo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document7 pagesChapter 5missmirachannel1No ratings yet
- Drug Metabolism PHASE 1 & PHASE 2Document36 pagesDrug Metabolism PHASE 1 & PHASE 2Kratika DanielNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument18 pagesEnzymesMarie Veatrice Jacomille100% (1)
- Enzyme Kinetics and Applications (Part 1a: Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed Reactions)Document26 pagesEnzyme Kinetics and Applications (Part 1a: Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed Reactions)Nur AishaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Microbial Physiology and GeneticsDocument47 pagesChapter 7 Microbial Physiology and Geneticsmarilyngalutera8No ratings yet
- Week 2 Lesson 2Document18 pagesWeek 2 Lesson 2Yury DesuNo ratings yet
- Enzmes and Activation EnergyDocument9 pagesEnzmes and Activation EnergydadjNo ratings yet
- Enzymes - BiochemistryDocument40 pagesEnzymes - Biochemistrysunil patelNo ratings yet
- 1FFF11B1BD16627EE05400144FEB5F70.pptDocument63 pages1FFF11B1BD16627EE05400144FEB5F70.pptNur AishaNo ratings yet
- 1 Enzyme Regulation in Biochemical PathwaysDocument29 pages1 Enzyme Regulation in Biochemical PathwayshadeelNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument44 pagesEnzymesYumul, Jewel B.No ratings yet
- Biochem NursingDocument144 pagesBiochem Nursingabukaritoyibu100No ratings yet
- Chapter 4C: Control of CellsDocument32 pagesChapter 4C: Control of CellsPikuNo ratings yet
- 3 Principles of Cell MetabolismDocument53 pages3 Principles of Cell MetabolismKristine Claire TarucNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry NCMA113 Midterm Notes PDocument3 pagesBiochemistry NCMA113 Midterm Notes PVaishnavi LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Materi 2Document34 pagesMateri 2siti purnamaNo ratings yet
- 5enzymes and Vitamins PDFDocument48 pages5enzymes and Vitamins PDFRomelyn AngelNo ratings yet
- Functional Metabolism: Regulation and AdaptationFrom EverandFunctional Metabolism: Regulation and AdaptationKenneth B. StoreyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Chronology of Education-Dennis Laurence Cuddy PhD-1994-143pgs-EDU - SMLDocument143 pagesChronology of Education-Dennis Laurence Cuddy PhD-1994-143pgs-EDU - SMLjudymw2000No ratings yet
- Affect of Sensory Processing Disorders On Learning Behavior and AttentionDocument53 pagesAffect of Sensory Processing Disorders On Learning Behavior and Attentionjudymw2000No ratings yet
- Daniel Cameron Asscoiates New Patient FormsDocument25 pagesDaniel Cameron Asscoiates New Patient Formsjudymw2000No ratings yet
- 21 Lessons For The 21st Century Summary - Four Minute BooksDocument4 pages21 Lessons For The 21st Century Summary - Four Minute Booksjudymw2000No ratings yet
- 25 Nov What Do I Mean by A Freedom PodDocument3 pages25 Nov What Do I Mean by A Freedom Podjudymw2000No ratings yet
- Cogs in The Machine - NewDocument92 pagesCogs in The Machine - Newjudymw2000No ratings yet
- Methylation - 04.2018Document72 pagesMethylation - 04.2018judymw2000No ratings yet
- Mike Adams Natural News Everyones Favorite à Ber-Quack 1 Anti-Science Websiteeven The Quacks Think HesDocument11 pagesMike Adams Natural News Everyones Favorite à Ber-Quack 1 Anti-Science Websiteeven The Quacks Think Hesjudymw2000No ratings yet
- Methylation - 04.2018Document72 pagesMethylation - 04.2018judymw2000No ratings yet
- 50 Studies Questioning Vaccine SafetyDocument5 pages50 Studies Questioning Vaccine SafetyshifanahmedNo ratings yet
- Kessinger (2007)Document6 pagesKessinger (2007)erisangelinNo ratings yet
- Non-Invasive Determination of Blood Glucose Concentration Using A Near-Field SensorDocument8 pagesNon-Invasive Determination of Blood Glucose Concentration Using A Near-Field SensorMouad JaouhariNo ratings yet
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 7 Blood Circulation - RBSE GuideDocument3 pagesRBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 7 Blood Circulation - RBSE GuideAlpine AcademiaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Quiz 3Document3 pagesGen Bio Quiz 3Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Ebook Ebook PDF Microbiology The Human Experience by John W Foster PDFDocument24 pagesFull Download Ebook Ebook PDF Microbiology The Human Experience by John W Foster PDFmicheal.cooper974100% (40)
- Athletes Medical Form 1Document2 pagesAthletes Medical Form 1JEZREEL HAVANANo ratings yet
- Setiawan D S, Tjahyono K, Afifah D N. 2016Document7 pagesSetiawan D S, Tjahyono K, Afifah D N. 2016Ismi WahyuniNo ratings yet
- Necropsy Guide For Dogs Cats and Small Mammals - 2016 - McDonough - Front MatterDocument17 pagesNecropsy Guide For Dogs Cats and Small Mammals - 2016 - McDonough - Front Matternabal22No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 DepEd Guidelines On Instructional PlanningDocument9 pagesLesson 1 DepEd Guidelines On Instructional PlanningJeanmae Omalyao MakilingNo ratings yet
- What Is Healing Energy - Part 4 Vibrational MedicineDocument9 pagesWhat Is Healing Energy - Part 4 Vibrational MedicineDianaNo ratings yet
- Lac Operon - Genetics-Essentials-Concepts-and-ConnectionsDocument15 pagesLac Operon - Genetics-Essentials-Concepts-and-ConnectionsDiandra AnnisaNo ratings yet
- Bioassay Systems: Quantichrom Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (D2No-100)Document1 pageBioassay Systems: Quantichrom Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (D2No-100)Avicenna AkbarNo ratings yet
- Case Study Bronchial Asthma - GROUP 2Document59 pagesCase Study Bronchial Asthma - GROUP 2Jimlord GarciaNo ratings yet
- Abdomen ProjectionsDocument4 pagesAbdomen Projectionsjr2zuzuarreguiNo ratings yet
- Human Inborn Errors of Immunity: An Expanding Universe: ReviewDocument17 pagesHuman Inborn Errors of Immunity: An Expanding Universe: ReviewCony GSNo ratings yet
- Fcps Guideline Vol.1: Perfect Time For PreparationDocument6 pagesFcps Guideline Vol.1: Perfect Time For PreparationFatima SagguNo ratings yet
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocument18 pagesWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsMahdi ChahrourNo ratings yet
- Brochure 1688575237139Document7 pagesBrochure 1688575237139RickNo ratings yet
- Theories of Motor ControlDocument33 pagesTheories of Motor ControlArslan Aslam100% (3)
- Pengesahan Ketua Jabatan: Universiti Pendidikan Sultan IdrisDocument14 pagesPengesahan Ketua Jabatan: Universiti Pendidikan Sultan IdrisserimawarNo ratings yet
- Physiology of MenopauseDocument20 pagesPhysiology of Menopauseindriyani makmunNo ratings yet
- AmphibiansDocument35 pagesAmphibianszubariaiqbal61No ratings yet
- Bala No Gloss UsDocument12 pagesBala No Gloss Usyayeg rajaNo ratings yet
- Nationality: Mexican Birth:: Vladimir Allex Martínez Rojas, PH.DDocument3 pagesNationality: Mexican Birth:: Vladimir Allex Martínez Rojas, PH.DIvan VillatoroNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestations and Treatment of Hypokalemia in AdultsDocument25 pagesClinical Manifestations and Treatment of Hypokalemia in Adultsr33realNo ratings yet
- UG Play - Session-7 - Theories-Of-Emotion - EdDocument24 pagesUG Play - Session-7 - Theories-Of-Emotion - EdDaniel Naawenkangua AbukuriNo ratings yet
- Nephron WTFDocument9 pagesNephron WTFCatherine AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Classification & Characteristics of CrustaceaDocument21 pagesClassification & Characteristics of CrustaceaSalma Afreen HussainNo ratings yet
- GRDA Intro Bony PelvisDocument5 pagesGRDA Intro Bony PelvisKingNo ratings yet