Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Consolidate: Living Thing Winter Spring Summer Fall
Uploaded by
Hiếu LêOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Consolidate: Living Thing Winter Spring Summer Fall
Uploaded by
Hiếu LêCopyright:
Available Formats
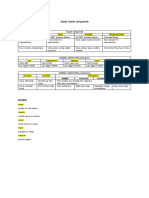
Living Thing Winter Spring Summer Fall
Blue Flag Iris dormant; rhizomes produces new blooms; produces upper portions of
remain under soil leaves; rhizomes seeds; continues to plants die back;
(underground spread via rhizomes goes dormant
roots) spread
Common Cattail dormant, usually breaks dormancy, grows; produces foliage dies; goes
still visible, brown grows leaves and seeds; produces dormant; usually
rushes flower heads new plants still visible, brown
asexually rushes
Fragrant Water Lily dormant breaks dormancy; grows leaves and foliage dies; goes
grows leaves and flowers (blooms); dormant
flowers (blooms) produces new
plants asexually
Lake Trout has very low eats and grows eats and grows; spawning; females
(*Labrador only) metabolism; stays spawning may lay eggs
in deeper regions begin late summer
below ice; does not
hibernate but does
not need food;
eggs hatch under
ice; young feeds off
yolk sac
Mink Frog tadpoles and adults wakes from breeding season; tadpoles and adults
hibernate, adults hibernation as females lay eggs enter hibernation,
underwater usually temperature that become adults underwater,
on top of mud increases; tadpoles usually on top
at pond bottom, overwintering of mud at pond
tadpoles in water tadpoles become bottom, tadpoles in
adults water
Ring-Necked Duck feeds migrates north; raises young; feeds migrates south
breeding season
Zigzag Darner nymphs may migrates north; nymphs may migrates south;
Dragon Fly metamorphose into breeds (eggs that metamorphose into breeds
adults; feeds and hatch into nymphs adults; feeds and
grows that live in the water) grows
CONSOLIDATE
My Wild Animal
Have students communicate their learning about an animal (or plant), either
from their own research or from Science Card 9 or 10, by creating an art
project that shows what the animal does in at least two different seasons.
For example, students might create a mobile, a drawing, or modelling clay
models.
64
You might also like
- 1 Lifecycles PDFDocument10 pages1 Lifecycles PDFMiss WandaNo ratings yet
- EntomologyDocument56 pagesEntomologyGwyneth Dane DangcatanNo ratings yet
- ENTOMOLOGYDocument56 pagesENTOMOLOGYGwyneth Dane DangcatanNo ratings yet
- Science Module 4A-CDocument10 pagesScience Module 4A-CRachelle Garobo BisaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 (Reproduction - Asexual Reproduction in Plants and Animals)Document7 pagesGeneral Biology 2 (Reproduction - Asexual Reproduction in Plants and Animals)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Wooly BearsDocument3 pagesWooly BearsyuniNo ratings yet
- K Strange PlantsDocument9 pagesK Strange PlantsNatalia IlhanNo ratings yet
- Types of ReproductionDocument18 pagesTypes of ReproductionCharm VergaraNo ratings yet
- NIE CT Nature Sept 2018 Revised 9-26-18Document1 pageNIE CT Nature Sept 2018 Revised 9-26-18Hartford CourantNo ratings yet
- Science Unit 4Document1 pageScience Unit 4kenneyma0204No ratings yet
- Activity Book Nov08Document24 pagesActivity Book Nov08jesrelljane.amperNo ratings yet
- Types of Reproduction: Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocument36 pagesTypes of Reproduction: Asexual and Sexual ReproductionMarievic DavidNo ratings yet
- Life CyclesDocument15 pagesLife Cyclesapi-521149724No ratings yet
- Bird Detective GuideDocument2 pagesBird Detective Guiderobld56No ratings yet
- PKR7Document1 pagePKR7nram8762No ratings yet
- Wildlife in WinterDocument1 pageWildlife in WinterHartford CourantNo ratings yet
- Life-Cycles & Families: Water and Land Animals: Adapted From Prairie Wetlands Learning Center SummaryDocument6 pagesLife-Cycles & Families: Water and Land Animals: Adapted From Prairie Wetlands Learning Center SummaryVladNo ratings yet
- Stages of Germination in A Seed.: Seed Coat Breaks and The Baby Plant GrowsDocument3 pagesStages of Germination in A Seed.: Seed Coat Breaks and The Baby Plant GrowsSri sai DuttNo ratings yet
- Mushrooms 2Document2 pagesMushrooms 2Nathan StrykerNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 5 - Chapter 01Document11 pagesExp SC 5 - Chapter 01megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Unit MDocument6 pagesUnit MMaddala NagendraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Life CyclesDocument15 pagesLesson 1 - Life CyclesIla NethercottNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument27 pagesChapter 7 How Do Organisms Reproducefortwitt18No ratings yet
- Body Snatchers: Flies, Wasps, and Other Creepy Crawly Zombie MakersFrom EverandBody Snatchers: Flies, Wasps, and Other Creepy Crawly Zombie MakersNo ratings yet
- Egyptian Tortoise: Life Cycle Size/Weight DietDocument1 pageEgyptian Tortoise: Life Cycle Size/Weight DietArmen HovhannisyanNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIONDocument8 pagesREPRODUCTIONTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet MarronDocument4 pagesFact Sheet MarronbernadethNo ratings yet
- Flowers!: Broad-Leaved Arrow-HeadDocument5 pagesFlowers!: Broad-Leaved Arrow-HeadĐinh Cẩm NhungNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Seed DispersalDocument9 pagesLesson 8 Seed DispersalJohany Gaona CruzNo ratings yet
- Heronfamilybychu 00 FergDocument4 pagesHeronfamilybychu 00 FergTere GómezNo ratings yet
- Salak TerbangDocument12 pagesSalak TerbangChelsica ChelsicaNo ratings yet
- Japanese Beetle: Quick FactsDocument6 pagesJapanese Beetle: Quick FactsTerryNo ratings yet
- ENGL202C Life Cycle of A Dragonfly 160ontfDocument7 pagesENGL202C Life Cycle of A Dragonfly 160ontfamrullah ksmNo ratings yet
- Goldfinch: A Bto Garden Birdwatch FactsheetDocument4 pagesGoldfinch: A Bto Garden Birdwatch FactsheetKoik KoikNo ratings yet
- Marijuana Horticulture: With A Little Care You Too Can Have A Beautiful Crop of 'Power Plant' Indoors or Outdoors!Document8 pagesMarijuana Horticulture: With A Little Care You Too Can Have A Beautiful Crop of 'Power Plant' Indoors or Outdoors!Scott Mertz ⎝⏠⏝⏠⎠100% (1)
- Asexual Reproduction Among AnimalsDocument11 pagesAsexual Reproduction Among AnimalsShan Taleah RealNo ratings yet
- Bot - New FamiliesDocument3 pagesBot - New Familiesatiyabegum282No ratings yet
- Franco 2014Document20 pagesFranco 2014Ariadne Cristina De AntonioNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument5 pagesTransport in PlantsJegatheesan KalirajanNo ratings yet
- Fugloy IslandsDocument3 pagesFugloy IslandsCarl PhilipNo ratings yet
- Introduction To VirologyDocument8 pagesIntroduction To VirologyBeck ParkerNo ratings yet
- Tachinidae Annu RevDocument35 pagesTachinidae Annu Revapi-3703629100% (1)
- Participant GMCKottayam KERALADocument193 pagesParticipant GMCKottayam KERALAKriti KumariNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII 2018 QUESTION PAPER BiologyDocument4 pagesCLASS XII 2018 QUESTION PAPER BiologyAnonymous f2rVBHlSuNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Note FotosintesisDocument4 pagesTeacher's Note Fotosintesisbijaksains2018No ratings yet
- E1.2 Homework - Biologos Exploration - LoG-2Document3 pagesE1.2 Homework - Biologos Exploration - LoG-2郭天阳No ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology P43 May2020 QPDocument17 pagesIGCSE Biology P43 May2020 QPPakorn WinayanuwattikunNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Quarter 4 PDFDocument51 pagesGrade 8 Quarter 4 PDFMJ Sol83% (6)
- Group 1: Asmira Athirah Iwani Cai Hua #AstipalDocument11 pagesGroup 1: Asmira Athirah Iwani Cai Hua #AstipalasyuraNo ratings yet
- Genomes With EnsemblDocument19 pagesGenomes With EnsemblCharu JoshiNo ratings yet
- Tea Mosquito BugDocument3 pagesTea Mosquito BugPrasad PullaNo ratings yet
- Tissues Notes Class IxDocument7 pagesTissues Notes Class Ixishaan singhNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science ViDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science ViJustin Ace MallorcaNo ratings yet
- Biomedik 2Document22 pagesBiomedik 2Fergi ListiawanNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Primary Production and Energy FlowDocument10 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Primary Production and Energy FlowAmaniNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology of Extremophiles Advances and ChallengesDocument731 pagesBiotechnology of Extremophiles Advances and ChallengesFernandoNo ratings yet
- B7 Sci WK5 PDFDocument4 pagesB7 Sci WK5 PDFDerick DadzieNo ratings yet
- Mitosis-Meiosis Comparison ChartDocument1 pageMitosis-Meiosis Comparison ChartSean CosepeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Atlas ADocument78 pagesChapter 1 Atlas Agabbs_123No ratings yet
- Blood Disease Bacterium: Husna Fikriya Baroroh, Luqman Qurata Aini, Abdul Latief AbadiDocument11 pagesBlood Disease Bacterium: Husna Fikriya Baroroh, Luqman Qurata Aini, Abdul Latief AbadiSefrilia JannahNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 BiologyDocument22 pagesChapter1 BiologyDanielle Kate MadridNo ratings yet
- Small Carnivore ConservationDocument56 pagesSmall Carnivore ConservationKhoirina Nur FadhilahNo ratings yet
- Transgenics For Abiotic StressDocument46 pagesTransgenics For Abiotic StressAmit BallaniNo ratings yet
- Desert BiomeDocument28 pagesDesert BiomeAlvin John ArconadoNo ratings yet
- Gametogenesis and Fertilization: The Circle of SexDocument85 pagesGametogenesis and Fertilization: The Circle of SexAdityanair RA1711009010128No ratings yet
- SpermatogenesisDocument31 pagesSpermatogenesiselzenyNo ratings yet
- Soal Pas Gasal Grow With English 6Document4 pagesSoal Pas Gasal Grow With English 6Rika Rumiati100% (1)