Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Individual Retirement Accounts - Roth IRAs 2021
Uploaded by
Finn KevinCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Individual Retirement Accounts - Roth IRAs 2021
Uploaded by
Finn KevinCopyright:
Available Formats
TAX YEAR
2021
Individual Retirement Accounts
Roth IRAs
Save $
And Experience
The Difference
+1-516-464-7444
info@cpaclinics.com
www.cpaclinics.com
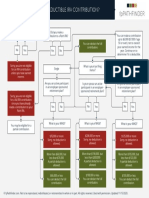
Roth IRAs Who Can Contribute to a Roth IRA?
Generally, you can contribute to a Roth IRA if you have
Roth IRA Contribution Limits—2021 taxable compensation and income less than the top of the
Lesser of: Taxable compensation for the year, or: phaseout range for your filing status, see Roth IRA Phaseouts
Under age 50. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ......................................................... $ 6,000 chart, below.
Age 50 or older. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .......................................................... $ 7,000
Roth IRA Phaseouts—2021
Filing Status MAGI Contribution Limit
What is a Roth IRA?
Single, Head of Less than $125,000. Up to $6,000 ($7,000, age 50 and
A Roth IRA is an individual retirement arrangement. It is a Household, or older).
personal savings plan that gives you tax advantages for set- Married Filing At least $125,000, but Contribution limit reduced.*
ting aside money for retirement. An account must be desig- Separately (lived less than $140,000.
apart from spouse
nated as a Roth IRA when opened. all year) $140,000 or more. Cannot contribute to Roth IRA.
Roth IRA tax advantages and rules compared to a tradi- Married Filing Less than $198,000. Up to $6,000 ($7,000, age 50 and
tional IRA: Jointly or Qualifying older).
Widow(er) At least $198,000, but Contribution limit reduced.*
• Contributions are not deductible. Being covered by an
employer retirement plan is irrelevant. less than $208,000.
• If certain requirements are satisfied for qualified distri- $208,000 or more. Cannot contribute to Roth IRA.
butions, distributions are tax free. Married Filing Zero. Up to $6,000 ($7,000, age 50 and
Separately (lived older).
• Can withdraw contributions any time for any reason
with spouse at any More than zero, but Contribution limit reduced.*
without owing taxes or penalties. time during the year) less than $10,000.
• The required minimum distribution (RMD) rules do not
$10,000 or more. Cannot contribution to Roth IRA.
apply. Distributions are not required until death of the
* To calculate reduced contribution limit: Example: Bob, age 35, Single,
participant.
1) Subtract the lower limit of the phaseout $ 127,000 MAGI:
• Contributions are not allowed when modified adjusted range from MAGI. 1) $ 127,000 – $ 125,000 = $2,000.
gross income (MAGI) is above certain limits. 2) Divide result by $ 10,000 (MFJ and MFS, 2) $ 2,000 / $ 15,000 = 0.133.
• Neither a SEP IRA nor a SIMPLE IRA can be set up as a lived with spouse) or $ 15,000 (all others). 3) 0.133 × $ 6,000 = $ 800.
3) Multiply result by maximum contribution 4) $ 6,000 – $ 800 = $ 5,200 (Bob’s
Roth IRA. amount. maximum contribution limit).
4) Subtract the result from the maximum
contribution limit.
Compensation. Compensation includes wages, salaries,
tips, professional fees, bonuses, and other amounts re-
ceived for providing personal services. It also includes
commissions, self-employment income, nontaxable com-
bat pay, military differential pay, and taxable alimony and
separate maintenance payments.
Qualified Distributions
Individual A nontaxable qualified distribution is any payment or
Retirement Accounts
distribution from a Roth IRA that meets the following
Roth IRAs requirements.
• It is made after the 5-year period beginning with the first
Contributions. Total contributions are combined with tra- taxable year for which a contribution was made to a Roth
ditional IRA contributions to determine limits. For exam- IRA set up for your benefit, and
ple, a $1,000 contribution to a traditional IRA will reduce • The payment or distribution is:
total contributions allowable to a Roth IRA by $1,000. Em- – Made on or after the date you reach age 59½, or
ployer contributions under a SEP or SIMPLE IRA plan do – Made because you are disabled, or
not affect this limit. – Made to a beneficiary or to your estate after your death,
or
If your modified AGI is within the phaseout amounts, your
– Made to purchase a first home (up to a $10,000 lifetime
contribution limit is gradually reduced.
limit).
When Can You Make Contributions? Additional tax on early distributions. If you receive a
You can make contributions to a Roth IRA for a year at any nonqualified distribution, you must pay the 10% additional
time during the year or by the due date of your return for tax on early withdrawals penalty on the taxable part of any
that year (not including extensions). This means that most distributions. Exceptions apply.
people can make contributions for 2021 by April 15, 2022. Nonqualified distributions. A distribution from a Roth
IRA that is not qualified may be partly taxable or nontax-
Conversion Rules able as there is a set order in which contributions and earn-
There are no modified AGI limits or filing status require- ings are considered to be distributed from a Roth IRA. The
ments relating to rollovers from eligible retirement plans order is as follows:
into Roth IRAs. 1) Regular contributions.
Conversion contribution. Money distributed from a qual- 2) Conversion and rollover contributions, on a first-in first-
ified plan or IRA and reinvested within 60 days into a Roth out basis.
IRA is called a conversion contribution. The distribution is 3) Earnings on contributions.
taxable to the extent it does not represent a return of non- Distributions from a Roth IRA that are a return of regular
deductible basis. A conversion contribution is not subject to contributions are not subject to tax or penalty, no matter
the 10% early withdrawal penalty. A conversion contribu- when they are withdrawn. Only the portion of the nonqual-
tion can also be accomplished through a trustee-to-trustee ified distribution allocable to earnings may be subject to tax
transfer or a same trustee transfer where the trustee sim- and the 10% additional tax.
ply redesignates a traditional IRA as a Roth IRA rather than
open up a new account or issue a new contract. Are Distributions From Roth IRAs Required?
Income. In the year of conversion, the amount of the distri- You are not required to take distributions from your Roth
bution from a traditional IRA or employer plan converted IRA at any age. The required minimum distributions
to a Roth IRA is included in gross income. (RMD) rules that apply to traditional IRAs do not apply to
Roth IRAs while the owner is alive.
Employer plan conversions. Money in an employer-spon-
sored retirement plan, such as a 401(k), annuity, section
403(b) plan, government deferred compensation (§457
plan), or profit-sharing plan, may be directly converted to
Contact Us
There are many events that occur during the year that can affect
a Roth IRA. your tax situation. Preparation of your tax return involves sum-
marizing transactions and events that occurred during the prior
Inherited IRA. An inherited traditional IRA from someone year. In most situations, treatment is firmly established at the
other than a spouse cannot be converted into a Roth IRA. time the transaction occurs. However, negative tax effects can
be avoided by proper planning. Please contact us in advance
if you have questions about the tax effects of a transaction or
event, including the following:
• Pension or IRA distributions. • Retirement.
• Significant change in income or • Notice from IRS or other
deductions. revenue department.
• Job change. • Divorce or separation.
This brochure contains general information for taxpayers and • Marriage. • Self-employment.
should not be relied upon as the only source of authority. • Attainment of age 59½ or 72. • Charitable contributions
Taxpayers should seek professional tax advice for more information. • Sale or purchase of a business. of property in excess of
• Sale or purchase of a residence $5,000.
Copyright © 2021 Tax Materials, Inc.
or other real estate.
All Rights Reserved
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
You might also like
- Group Assigment CONCH PART1Document4 pagesGroup Assigment CONCH PART1BashirNo ratings yet
- Tax Free Retirement WebinarDocument28 pagesTax Free Retirement Webinarphillies1111No ratings yet
- Central Provident Fund Board: Ms Fikriah Binte Samani 767 Woodlands Circle #07 - 338 SINGAPORE 730767Document6 pagesCentral Provident Fund Board: Ms Fikriah Binte Samani 767 Woodlands Circle #07 - 338 SINGAPORE 730767Fikriah SamaniNo ratings yet
- John T. Reed - The Biggest Mistakes Real Estate Investors MakeDocument4 pagesJohn T. Reed - The Biggest Mistakes Real Estate Investors MakeDenis100% (1)
- Essentials of Economics 9Th Edition John Sloman Full ChapterDocument67 pagesEssentials of Economics 9Th Edition John Sloman Full Chapterpeter.voit454100% (5)
- High-Income Taxpayers 2021Document2 pagesHigh-Income Taxpayers 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Individual Retirement Accounts - Backdoor Roth IRA 2021Document2 pagesIndividual Retirement Accounts - Backdoor Roth IRA 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Ceesay Exp19 Word Ch04 CapAssessment RetirementDocument10 pagesCeesay Exp19 Word Ch04 CapAssessment RetirementcsaysalifuNo ratings yet
- Can I Make A Deductible IRA Contribution 2021Document1 pageCan I Make A Deductible IRA Contribution 2021JosephNo ratings yet
- Retirement Topics - IRA Contribution LimitsDocument3 pagesRetirement Topics - IRA Contribution LimitsSriniNo ratings yet
- Individual Retirement Account: For New Accounts OnlyDocument24 pagesIndividual Retirement Account: For New Accounts OnlyHeidi LopezNo ratings yet
- DWM Olt Trad LaDocument26 pagesDWM Olt Trad LaBullet GunnerNo ratings yet
- US Internal Revenue Service: f9452 - 1998Document2 pagesUS Internal Revenue Service: f9452 - 1998IRSNo ratings yet
- What Is An IRA? - RKB Accounting & Tax ServicesDocument6 pagesWhat Is An IRA? - RKB Accounting & Tax ServicesRKB AccountingNo ratings yet
- Tax-Friendly States For Retirees: Synergy Financial GroupDocument4 pagesTax-Friendly States For Retirees: Synergy Financial GroupgvandykeNo ratings yet
- 03 - Tax On AssetsDocument6 pages03 - Tax On Assetsmails4vipsNo ratings yet
- Who Must File Charts A B 4012Document1 pageWho Must File Charts A B 4012Jagmohan TeamentigrityNo ratings yet
- Synergy Financial Group: Your Personal CFODocument4 pagesSynergy Financial Group: Your Personal CFOgvandykeNo ratings yet
- How To Retire Rich PDFDocument6 pagesHow To Retire Rich PDFAra TaningcoNo ratings yet
- IRA Recharacterization Request: 1. Account OwnerDocument2 pagesIRA Recharacterization Request: 1. Account OwnersaranNo ratings yet
- 2012plan LimitsDocument4 pages2012plan LimitsAKTHOMNo ratings yet
- Distribution From IRAsDocument18 pagesDistribution From IRAsbhuang1No ratings yet
- It 12 DecDocument15 pagesIt 12 DecPuja PandaNo ratings yet
- Retirement CalculatorDocument1 pageRetirement CalculatorgunawanharijadiNo ratings yet
- OAS Allowance and GIS For Low Income Seniors ATB Financial 2Document1 pageOAS Allowance and GIS For Low Income Seniors ATB Financial 2Shoshana PellmanNo ratings yet
- Read This First:: Loan & General InfoDocument14 pagesRead This First:: Loan & General InfoJoannaNo ratings yet
- Tax-Free RetirementDocument8 pagesTax-Free RetirementYesy Amaya0% (1)
- SFG Newsletter December 2007Document4 pagesSFG Newsletter December 2007gvandykeNo ratings yet
- PK Tax News Jun 2008Document2 pagesPK Tax News Jun 2008PKTaxServicesNo ratings yet
- Mortgage and RRSPDocument2 pagesMortgage and RRSPmetaldwarfNo ratings yet
- Statement Redesign OnlineDocument2 pagesStatement Redesign OnlineJoshua LaporteNo ratings yet
- US Internal Revenue Service: f9452 - 1996Document1 pageUS Internal Revenue Service: f9452 - 1996IRSNo ratings yet
- 2022 Oregon EITC NoticeDocument1 page2022 Oregon EITC NoticeMan Tue ThaiNo ratings yet
- 2023 ReturnDocument2 pages2023 ReturnLuiNo ratings yet
- Building A Solid Financial FoundationDocument2 pagesBuilding A Solid Financial Foundationapi-25884993No ratings yet
- Understanding Roth IRA Jonathan BeckDocument10 pagesUnderstanding Roth IRA Jonathan BeckjonathanbeckadvisorNo ratings yet
- $26,000 Retirement OpportunityDocument2 pages$26,000 Retirement OpportunityRobert GrantNo ratings yet
- Lending Club Retirement GuideDocument8 pagesLending Club Retirement Guidecera66No ratings yet
- Ch4-Recordedlecture-Fall2023 17 5166787619170306Document38 pagesCh4-Recordedlecture-Fall2023 17 5166787619170306ronny nyagakaNo ratings yet
- Federal Budget 2021Document4 pagesFederal Budget 2021api-227304535No ratings yet
- Investment Environment & Securities MarketDocument28 pagesInvestment Environment & Securities MarketProf. Suyog ChachadNo ratings yet
- CPF Retirement Booklet PDFDocument24 pagesCPF Retirement Booklet PDFHadi Rosli100% (1)
- Windes 2021 Year End Year Round Tax Planning GuideDocument20 pagesWindes 2021 Year End Year Round Tax Planning GuideBrian SneeNo ratings yet
- F1040es 2018Document18 pagesF1040es 2018diversified1No ratings yet
- Tax Compliance, The IRS, and Tax Authorities: 2020 EditionDocument44 pagesTax Compliance, The IRS, and Tax Authorities: 2020 EditionAhmed AdamjeeNo ratings yet
- Ten Income and Estate Tax Planning Strategies For 2016Document4 pagesTen Income and Estate Tax Planning Strategies For 2016Humphrey Hessel-AppiahNo ratings yet
- Retirement Planning WorkbookDocument8 pagesRetirement Planning Workbooktwankfanny100% (3)
- Tax Cuts and Jobs Act Individuals 2018Document4 pagesTax Cuts and Jobs Act Individuals 2018godardsfanNo ratings yet
- US Individual RegulationDocument3 pagesUS Individual RegulationDarab AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Handbook To Investment DeclarationDocument17 pagesHandbook To Investment DeclarationMourya ChigurupatiNo ratings yet
- Ac00unting 2Document45 pagesAc00unting 2Hazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Schwab Individual 401 (K) : BenefitsDocument4 pagesSchwab Individual 401 (K) : BenefitsJames StampNo ratings yet
- US Master Tax Guide (PDFDrive)Document1,258 pagesUS Master Tax Guide (PDFDrive)sutan mNo ratings yet
- 2021 Tax Data Schedule v.3Document15 pages2021 Tax Data Schedule v.3Brian SneeNo ratings yet
- Nutmeg Lifetime ISA Information PackDocument12 pagesNutmeg Lifetime ISA Information PackNair YadukrishnanNo ratings yet
- F1040es 2020Document12 pagesF1040es 2020Job SchwartzNo ratings yet
- HTTPSWWW - Irs.govpubirs Pdff1040es PDFDocument12 pagesHTTPSWWW - Irs.govpubirs Pdff1040es PDFmark beattyNo ratings yet
- Roth Conversion Strategies To ConsiderDocument5 pagesRoth Conversion Strategies To Considerkj4892No ratings yet
- F 1040 EsDocument12 pagesF 1040 EsHyun SeonNo ratings yet
- Guide To Self Directed Investing - Equity Trust CompanyDocument24 pagesGuide To Self Directed Investing - Equity Trust CompanyEquityTrustNo ratings yet
- It's Not What You Earn - It's What You Keep: Synergy Financial GroupDocument4 pagesIt's Not What You Earn - It's What You Keep: Synergy Financial GroupgvandykeNo ratings yet
- Self-Help Guidebook for Retirement Planning For Couples and Seniors: Ultimate Retirement Planning Book for Life after Paid EmploymentFrom EverandSelf-Help Guidebook for Retirement Planning For Couples and Seniors: Ultimate Retirement Planning Book for Life after Paid EmploymentNo ratings yet
- Itemized Deductions - Homeowners 2021Document2 pagesItemized Deductions - Homeowners 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Business Use of Home 2021Document2 pagesBusiness Use of Home 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Short-Term Rentals 2021Document2 pagesShort-Term Rentals 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Individual Retirement Accounts - Required Minimum Distributions RMDs 2021Document2 pagesIndividual Retirement Accounts - Required Minimum Distributions RMDs 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Identity Theft and Your Taxes 2021Document2 pagesIdentity Theft and Your Taxes 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Recordkeeping For Tax Purposes 2021Document2 pagesRecordkeeping For Tax Purposes 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Household Employees 2021Document2 pagesHousehold Employees 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Rental Income and Expenses 2021Document2 pagesRental Income and Expenses 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Partnerships: Save $ and Experience The DifferenceDocument2 pagesPartnerships: Save $ and Experience The DifferenceFinn KevinNo ratings yet
- Small Business Health Care Tax Credit 2021Document2 pagesSmall Business Health Care Tax Credit 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Self-Employment Tax 2021Document2 pagesSelf-Employment Tax 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Health Savings Accounts HSAs 2021Document2 pagesHealth Savings Accounts HSAs 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Farm Income Worksheet 2021Document2 pagesFarm Income Worksheet 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Taxpayers Who Receive An IRS Notice 2021Document2 pagesTaxpayers Who Receive An IRS Notice 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Farm Vehicles and Fuels 2021Document2 pagesFarm Vehicles and Fuels 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Form 1099-MISC and Form 1099-NEC Reporting 2021Document2 pagesForm 1099-MISC and Form 1099-NEC Reporting 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Farm Expenses Worksheet 2021Document2 pagesFarm Expenses Worksheet 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Referrals Appreciated 2021Document2 pagesReferrals Appreciated 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Pandemic Relief: Save $ and Experience The DifferenceDocument2 pagesPandemic Relief: Save $ and Experience The DifferenceFinn KevinNo ratings yet
- Filing Status 2021Document2 pagesFiling Status 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- What Should You Do If You Cant Pay Your Taxes 2021Document2 pagesWhat Should You Do If You Cant Pay Your Taxes 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Estimated Taxes: Save $ and Experience The DifferenceDocument2 pagesEstimated Taxes: Save $ and Experience The DifferenceFinn KevinNo ratings yet
- Employee or Independent Contractor 2021Document2 pagesEmployee or Independent Contractor 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Dependent Support Worksheet 2021Document2 pagesDependent Support Worksheet 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Expense Reimbursements For Employees 2021Document2 pagesExpense Reimbursements For Employees 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Multi-State Taxation 2021Document2 pagesMulti-State Taxation 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Education Tax Benefits 2021Document2 pagesEducation Tax Benefits 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Starting A Business 2021Document2 pagesStarting A Business 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Lebanon's Economy An Analysis and Some Recommendations: Esther Baroudy & Hady Farah 20 January 2020Document17 pagesLebanon's Economy An Analysis and Some Recommendations: Esther Baroudy & Hady Farah 20 January 2020terryhadyNo ratings yet
- Basic Financial Statement AnalysisDocument34 pagesBasic Financial Statement AnalysisArpit SidhuNo ratings yet
- 2 Tips & Tricks For MSMEs Tax Compliance Handouts PDFDocument79 pages2 Tips & Tricks For MSMEs Tax Compliance Handouts PDFGetty Reagan DyNo ratings yet
- Research Memorandum Re Usec Dela GuardiaDocument5 pagesResearch Memorandum Re Usec Dela GuardiaJohn Kevin Carmen SamsonNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Concepts Competitiveness and Globalization Hitt 11th Edition Solutions ManualDocument29 pagesStrategic Management Concepts Competitiveness and Globalization Hitt 11th Edition Solutions ManualJohnny Adams100% (28)
- Self Assessment Plan 2024Document1 pageSelf Assessment Plan 2024fatima.razaNo ratings yet
- Meghmani Organics Limited Annual Report 2019 PDFDocument254 pagesMeghmani Organics Limited Annual Report 2019 PDFmredul sardaNo ratings yet
- University of Delhi: Semester Examination TERM I MARCH 2023 Statement of Marks / GradesDocument2 pagesUniversity of Delhi: Semester Examination TERM I MARCH 2023 Statement of Marks / GradesDev ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Dabur India Limited (Marketing)Document86 pagesProject Report On Dabur India Limited (Marketing)Avanikant VidyarthyNo ratings yet
- (Solution Answers) Advanced Accounting by Dayag, Version 2017 - Chapter 2 (Partnership - Continuation) - Solution To Multiple Choice (Part A)Document2 pages(Solution Answers) Advanced Accounting by Dayag, Version 2017 - Chapter 2 (Partnership - Continuation) - Solution To Multiple Choice (Part A)John Carlos DoringoNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis of Suzuki MotorsDocument21 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis of Suzuki MotorsMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Mooe School Forms 2020Document48 pagesMooe School Forms 2020KrisPaulineSantuaNo ratings yet
- Godda: 1. District AT A GlanceDocument8 pagesGodda: 1. District AT A GlanceNaina JhaNo ratings yet
- Baroda e GatewayDocument7 pagesBaroda e GatewayRajkot academyNo ratings yet
- Sport Odyssey AffiliateDocument2 pagesSport Odyssey AffiliateKimberly Solomon JavierNo ratings yet
- Registration Form 16TH Wsho Conference 2018 FinalDocument1 pageRegistration Form 16TH Wsho Conference 2018 FinalSuresh ThevanindrianNo ratings yet
- Past Year Question Group 6Document9 pagesPast Year Question Group 6Its AnnaNo ratings yet
- Complaint Escape From AlcatrazDocument19 pagesComplaint Escape From AlcatrazmschwimmerNo ratings yet
- RAD TorqueDocument16 pagesRAD TorqueRaziel Postigo MezaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior On Tata MotorsDocument78 pagesConsumer Behavior On Tata MotorsAkshitha MadishettyNo ratings yet
- 1330 Sarevsh Shinde Pptx. HRM IIDocument9 pages1330 Sarevsh Shinde Pptx. HRM IIsarvesh shindeNo ratings yet
- Steps Approach Coopsoc Audit 30062018Document150 pagesSteps Approach Coopsoc Audit 30062018Ritesh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Internet Marketing 4th Edition Debra Zahay Mary Lou Roberts 2Document13 pagesTest Bank For Internet Marketing 4th Edition Debra Zahay Mary Lou Roberts 2amberperezrqemidcbyx100% (25)
- 7 Steps To Building Your Personal BrandDocument5 pages7 Steps To Building Your Personal BrandGladz C CadaguitNo ratings yet
- PROPERTYDocument8 pagesPROPERTYHyder KhanNo ratings yet
- Riello Ups CatalogDocument109 pagesRiello Ups CatalogJose LopezNo ratings yet
- Hapus - Citi - Employee - Referral - Program - 2014Document80 pagesHapus - Citi - Employee - Referral - Program - 2014JoeNo ratings yet