Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Polymer:: Phenol Formaldehyde, Ureaformaldehyde, Etc
Polymer:: Phenol Formaldehyde, Ureaformaldehyde, Etc
Uploaded by
BYNAGARI KUSUMAOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Polymer:: Phenol Formaldehyde, Ureaformaldehyde, Etc
Polymer:: Phenol Formaldehyde, Ureaformaldehyde, Etc
Uploaded by
BYNAGARI KUSUMACopyright:
Available Formats
POLYMER :
A polymer is a large molecule which is essentially is a combination of many
subunits.
PROPERTIES OF POLYMER
Heat capacity
Thermal expansion
Permiability
Elastic modulus
Tensile strength
Resilience
Refractive index
Resistance to electric current
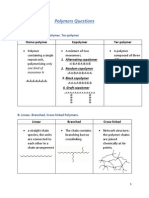
Difference between thermos plasic and thermosetting
plastics
Thermos plastic ploymer Thermosetting polymer
Formed by addition of Formed by condensation
polymerisation polymerisation
Low molecular weight High molecular weight
They are soft, weak and brittle They are hard , strong and more
brittle
They can softened , reshaped and They are not reshaped and
reused softened again and again
e.g. polystyrene, polyethelyne, e.g. phenol formaldehyde,
pvc etc ureaformaldehyde, etc
SEMI CONDUCTORS: a material which have a conductivity between conductors
and non-conductors or insulators.
INTERSTITIAL ATOMS:
An interstitial atom is one that occupies a site in a crystal structure that is normally
unoccupied by the atoms of the structure.
SELF INTERSTITIAL ATOMS:
If an atom leaves its lattice site and occupies some interstitial space then the defect is referred
as self -interstitial.
SUBSTITUTIONAL IMPURITY:
result from replacing the particle that should occupy a lattice site with a different
particle.
INTERSTITIAL IMPURITY:
An atom which is not normally found in a solid.
EDGE DISLOCATION:
An edge dislocation is a defect where an extra half-plane of atoms is introduced midway
through the crystal, distorting nearby planes of atoms.
DISLOCATION PROPERTIES:
Yield
Work hardening
Ductility
And other plastic properties
Dislocation:
disturbance from a proper, original, or usual place or state.
You might also like
- MEMSDocument21 pagesMEMSScientist SakthivelNo ratings yet
- Advanced Materials - JNTUK (R16)Document7 pagesAdvanced Materials - JNTUK (R16)uday kiran thagirchi50% (2)
- Polymer Notes 1Document23 pagesPolymer Notes 1catotheophilus18No ratings yet
- Green Vintage Illustration Laboratory Business PresentationDocument31 pagesGreen Vintage Illustration Laboratory Business Presentationmarcmaglaqui30No ratings yet
- PolymersDocument3 pagesPolymersnabeelbirdNo ratings yet
- Branched Polymers Occur When Groups of Units Branch Off From TheDocument2 pagesBranched Polymers Occur When Groups of Units Branch Off From ThedummyNo ratings yet
- Plastics Processing Technology Lecture 2Document13 pagesPlastics Processing Technology Lecture 2Davis TwinobusingyeNo ratings yet
- Unit V Polymers 5.1 PlasticsDocument38 pagesUnit V Polymers 5.1 PlasticsJustine joy cruzNo ratings yet
- Types of MaterialsDocument12 pagesTypes of MaterialsShione T MundawararaNo ratings yet
- Types of MaterialsDocument13 pagesTypes of MaterialsHaider ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Copolymers Are Polymers Composed of Two orDocument1 pageCopolymers Are Polymers Composed of Two orMatti NoNo ratings yet
- UNIT IV 20ME403 EMM (Non Metallic Materials) New 02.05.2022 (1) (2578)Document116 pagesUNIT IV 20ME403 EMM (Non Metallic Materials) New 02.05.2022 (1) (2578)Dark ranger YtNo ratings yet
- Extra Notes For PolymerDocument8 pagesExtra Notes For PolymerNHNo ratings yet
- 3.0 PolymersDocument8 pages3.0 PolymersKhaembaNo ratings yet
- Plastic (F1)Document32 pagesPlastic (F1)Brijesh VermaNo ratings yet
- Applications and Processing of PolymersDocument15 pagesApplications and Processing of PolymersRaymart Racoma MagdatoNo ratings yet
- Plastic Materials 1Document12 pagesPlastic Materials 1Anbu M S TNo ratings yet
- Thermosetting PrashantDocument11 pagesThermosetting PrashantSaloniNo ratings yet
- Composite MaterialsDocument6 pagesComposite Materialsashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- 3 Polymer TechnologyDocument65 pages3 Polymer TechnologySomu Aditya100% (1)
- Unit Ii Polymer Matrix CompositesDocument121 pagesUnit Ii Polymer Matrix CompositesKarthick PrasadNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Polymer Matrix CompositesDocument121 pagesUnit Ii Polymer Matrix CompositesKarthick PrasadNo ratings yet
- Polymer: Auguste TrillatDocument8 pagesPolymer: Auguste TrillatMarvin LabajoNo ratings yet
- Nature of Chemical Attacks On Plastic and RubbersDocument7 pagesNature of Chemical Attacks On Plastic and RubberskayodeNo ratings yet
- Lecture40-40 - 16938 - Lecture 40Document16 pagesLecture40-40 - 16938 - Lecture 40Hozaan Najmi nFniwITMQmNo ratings yet
- 13 PolimerDocument54 pages13 PolimerJhonsonNo ratings yet
- Quibot, Mikaela (BSCE 1A) - Assignment #2Document3 pagesQuibot, Mikaela (BSCE 1A) - Assignment #2Mikaela QuibotNo ratings yet
- MEC 201 - MSM - Unit 3Document40 pagesMEC 201 - MSM - Unit 3Chandra Simha ReddyNo ratings yet
- BMECME 305 - MSM - Unit 3 - For SharingDocument40 pagesBMECME 305 - MSM - Unit 3 - For SharingMohamed SohaibNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete: Key CharacteristicsDocument13 pagesReinforced Concrete: Key CharacteristicsrisrizNo ratings yet
- Polymer Processing (Extrusion) 28.02.2020 PDFDocument35 pagesPolymer Processing (Extrusion) 28.02.2020 PDFEDISON OCHIENGNo ratings yet
- Polymer Science - Polymer Chemical PropertiesDocument11 pagesPolymer Science - Polymer Chemical Propertiesparrot TNo ratings yet
- (Chemistry) Polymers 2Document15 pages(Chemistry) Polymers 2Ashutosh TripathyNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv Part-ADocument7 pagesUnit-Iv Part-AParameswara RajaNo ratings yet
- Ceramic, Polymer and Composite MaterialsDocument39 pagesCeramic, Polymer and Composite MaterialsYasir ArafatNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument10 pagesPolymersConrado DirectoNo ratings yet
- Non Ferrous MaterialsDocument5 pagesNon Ferrous MaterialsSabirNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 and 2 Synthesis of Polymers - 2023Document106 pagesCHAPTER 1 and 2 Synthesis of Polymers - 2023abdisahurisa24No ratings yet
- Material 2 1Document76 pagesMaterial 2 1jeneneabebe458No ratings yet
- Structure Activity Relationship - Unit 2 25 04 2023Document43 pagesStructure Activity Relationship - Unit 2 25 04 2023ishaanmittalcollegeNo ratings yet
- PLASTICvs POLYMERSDocument12 pagesPLASTICvs POLYMERSjincy vargheseNo ratings yet
- MSE 413 Final Study GuideDocument11 pagesMSE 413 Final Study Guideharlow6winfield6adamNo ratings yet
- Thermoset Vs ThermoplasticDocument2 pagesThermoset Vs ThermoplasticMina Samy abd el zaherNo ratings yet
- Polymers IN Medicine AND SurgeryDocument18 pagesPolymers IN Medicine AND SurgeryShagun ChoudhariNo ratings yet
- 3 Structure Activity RelationshipDocument43 pages3 Structure Activity Relationshipbt21102047 Vishwajeet YadavNo ratings yet
- Rida Tahir Plastic 13Document10 pagesRida Tahir Plastic 13AyeshaNo ratings yet
- When Subjected To TemperatureDocument9 pagesWhen Subjected To TemperatureAnbu M S TNo ratings yet
- What Is A Polymer?: TL DR (Too Long Didn't Read)Document2 pagesWhat Is A Polymer?: TL DR (Too Long Didn't Read)SJia LimNo ratings yet
- Properties and Applications of MaterialsDocument59 pagesProperties and Applications of Materialssuryanarayandash100% (1)
- PolymersDocument33 pagesPolymerssundara ramanNo ratings yet
- 01 PlasticsDocument17 pages01 PlasticsVenkatesh BNo ratings yet
- Polymers QuestionsDocument15 pagesPolymers QuestionsOmar EzzatNo ratings yet
- Polymer FinalDocument38 pagesPolymer Finalإحسان خالد جودة الشحات ٣٥٧٣No ratings yet
- Thermoplastic, Thermoset and Elastomer: Technological Institute of The Philippines 363 P. Casal ST., Quiapo, ManilaDocument3 pagesThermoplastic, Thermoset and Elastomer: Technological Institute of The Philippines 363 P. Casal ST., Quiapo, ManilaMarvin ParasNo ratings yet
- Plastics, Wood Ad RubberDocument32 pagesPlastics, Wood Ad RubberPaul KagunyaNo ratings yet
- Modern Materials ChemicalsDocument19 pagesModern Materials ChemicalsUsama Majid100% (1)
- Polymers: 5.1 PlasticsDocument8 pagesPolymers: 5.1 PlasticsCh. Muhammad UsamaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Components, Tubes and Transistors: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandElectronic Components, Tubes and Transistors: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionNo ratings yet