Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wake Up Human Development Pronouns: A Pronoun Is A Word That Refers To or Takes The Place of A Noun
Wake Up Human Development Pronouns: A Pronoun Is A Word That Refers To or Takes The Place of A Noun
Uploaded by
Le Magnefique Guiraguira NafielOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Wake Up Human Development Pronouns: A Pronoun Is A Word That Refers To or Takes The Place of A Noun
Wake Up Human Development Pronouns: A Pronoun Is A Word That Refers To or Takes The Place of A Noun
Uploaded by
Le Magnefique Guiraguira NafielCopyright:
Available Formats
WAKE UP
HUMAN DEVELOPMENT
LESSON 3
PRONOUNS
DEFINITION
WHAT IS A PRONOUN?
A pronoun is a word that refers to or takes the place of a noun. The noun being referred to is
called the antecedent. The identity of the pronoun is made clear by the antecedent.
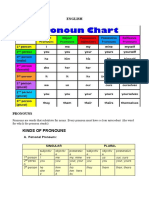
TYPES OF PRONOUNS
There are many types and subtypes of Pronouns in English.
1) Personal Pronouns: The personal Pronouns include: (I, you, he, him, we, us, me,
she, her, it, they and them). They are referred to as personal because refer to the
person speaking or being spoken to.
a) The doctor told me I will be fine
b) Leave us alone, we will survive the storm
c) She told her the secret
d) He rarely eats sugar
e) It is sunny today, I am sure they will go visit them
2) Possessive Pronouns: The possessive Pronouns include: (my, our, your, their, her, his
and mine, ours, yours, theirs, hers, his). They are referred to as possessive because
they function in genitive case.
a) Our teachers are working hard.
b) Theirs is to eat and mine, to buy.
c) Should the pen be his, the book is ours.
d) His mother is my friend
e) Her car is dirty, she needs yours.
Trainer: Saulino Bernardo Mulotoua
2) Relative Pronouns: Relative Pronouns are used to relate an adjectival or describing
clause to the noun or Pronoun it describes. They show relationship between two or
more sentence elements.
a) Look at the man who killed his mother.
b) Let me have the book that I asked you to buy.
c) The students lack the idea about how they failed the test.
d) Meet my son in whom I am well pleased.
3) Partitive Pronouns: These are Pronouns which refer to parts (not the whole) of the
antecedents (what they represent). They include: (any, some, something, no, nothing,
anything).
a) Please give me some plain sheets
b) There must be something wrong with Jane.
c) Students dont read anything lengthy.
5) Reflexive Pronouns: Reflexive Pronouns are those which refer directly to the nouns or
the noun phrase. They are: (myself, themselves, itself, yourself, himself, herself,
ourselves, yourselves). Examples of reflexive Pronouns include:
a) They themselves are the evil doers
b) If you come yourself, he may be lenient
c) She solved the problem herself
d) The goat delivered an offspring itself
e) I can drive the car myself
6) Demonstrative Pronouns: These Pronouns are used to indicate or point out the person or
thing being referred to. The English language has four basic demonstrative Pronouns.
They are: this, those, that and these. They can be classified on two basis nearness [this]
and distance [that] as well as singular [this] and plural [these]. Examples of are given
below:
a) Are these the gifts from John?
b) This is my pen.
c) That may not be my property.
d) Excuse me gentleman, those boots are not yours.
Trainer: Saulino Bernardo Mulotoua
7) Interrogative Pronouns: As the name implies, interrogative Pronouns are used to ask
questions. More often than not, they appear as the first words in sentences terminsting in
a question. Eka, (2008) observes that interrogative Pronouns have morphological shapes
suggestive of relative Pronouns. The difference between the duo, however, lies in the
structural and functional characteristics. For instance, interrogative Pronouns regularly
ask questions. They include: (who, what, which and who). Illustrations are provided
below.
a) What is your name?
b) When is the event?
c) Which of the clothes are yours?
d) Who provided you the keys?
8) Indefinite Pronouns: Indefinite Pronouns refer to unspecified referents. This category
of Pronouns often functions as adjectives. They include: each, every, anybody, anyone,
anything, both, nothing, another, all, any, anybody, everyone, everybody, everything, few,
many, some, nobody, none, no one, one(s), other, several, somebody, someone, something
etc. Illustrations are provided below.
a) Here are two ladies: an intelligent one and the rough one
b) Many are called but few are chosen.
c) I have another wife apart from this.
d) It is anyones whether or not I fail
e) Time will come, when no one will be poor
9) Distributive Pronouns: These are Pronouns used to talk about each and every person
separately. They include: each, either, none, both, everyone, every, neither, any, one,
everybody, everything). Examples of such Pronouns include:
a) Each of us has a car
b) Every Nigerian is corrupt
c) Everything good will come
d) Either of them is beautiful
e) Neither of my parents is educated
10) Reciprocal Pronouns: These are Pronouns used to talk about mutual relationship. They
are those Pronouns which demonstrated share or common relationship or action
Trainer: Saulino Bernardo Mulotoua
There are basically two types of reciprocal Pronouns in English namely: each other and one
another.
Example:
a) John and Mary love each other
b) The teacher talked about examination and the students looked at each other
c) They cheated one another in their business.
Trainer: Saulino Bernardo Mulotoua
You might also like
- Tips PDFDocument6 pagesTips PDFMiriam Mezesq0% (3)
- PronounDocument6 pagesPronounMei AnjaniNo ratings yet
- 1st Material - Nouns, Pronouns, AdjectivesDocument4 pages1st Material - Nouns, Pronouns, AdjectivesmelatiNo ratings yet
- PRONOUNS - Kelompok 12Document9 pagesPRONOUNS - Kelompok 12Meriliana Candra DeviNo ratings yet
- Sentences Using Pronouns:-2) The Coach Selected Several Key Points. He Wanted The Team To Memorize ThemDocument12 pagesSentences Using Pronouns:-2) The Coach Selected Several Key Points. He Wanted The Team To Memorize ThemRushiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 5 English Revision Worksheet (17) - PronounsDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 5 English Revision Worksheet (17) - PronounsJR100% (1)
- Summary Nouns: Name: Jusy Permata NPM: A1B019106 Lecturer: Wisma YunitaDocument4 pagesSummary Nouns: Name: Jusy Permata NPM: A1B019106 Lecturer: Wisma YunitaRetno Nurul AnnissaNo ratings yet
- Yellow Booklet - Revised 2013 PDFDocument42 pagesYellow Booklet - Revised 2013 PDFBabak EbrahimiNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Pronouns: Angela Sandiego Beed Ib PronounsDocument10 pagesKinds of Pronouns: Angela Sandiego Beed Ib Pronounskunta_kNo ratings yet
- Nota - PronounsDocument8 pagesNota - PronounsSukarni Bt PaimanNo ratings yet
- Pronouns. Types of Pronouns.: Personal Pronoun As Subject Personal Pronoun As ObjectDocument7 pagesPronouns. Types of Pronouns.: Personal Pronoun As Subject Personal Pronoun As ObjectMohd FaisNo ratings yet
- The Parts of SpeechDocument37 pagesThe Parts of Speechapi-397815258No ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument20 pagesParts of SpeechMuhammad TayyabNo ratings yet
- PRONOUNSDocument10 pagesPRONOUNSa_j_sanyalNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument9 pagesPart of SpeechJennifer PittmanNo ratings yet
- The Parts of Speech-2023Document15 pagesThe Parts of Speech-2023Jennifer CortezNo ratings yet
- 16th English cls9Document4 pages16th English cls9Jeff CadetNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 1N (Remedial English) The Parts of SpeechDocument9 pagesENGLISH 1N (Remedial English) The Parts of Speechnaldima06No ratings yet
- Internal Use Only - Part of Speech - LPDPDocument14 pagesInternal Use Only - Part of Speech - LPDPThamtham'nagh Djaiel BwangetzNo ratings yet
- The English PronounsandthierusageDocument9 pagesThe English PronounsandthierusageJervin MamoreNo ratings yet
- BasicDocument97 pagesBasicViviana Moreno NavarroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Word Class "Pronoun"Document23 pagesLecture 9 - Word Class "Pronoun"Ushna Shariq OfficialNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN in ENGLISH 4Document6 pagesLESSON PLAN in ENGLISH 4rolandgallo1234No ratings yet
- Another Three (3) Kinds of Noun!: Collective NounsDocument10 pagesAnother Three (3) Kinds of Noun!: Collective NounsRolan BulandosNo ratings yet
- English Assignment 1Document22 pagesEnglish Assignment 1katilabbuNo ratings yet
- Guidebook (Recuperado)Document44 pagesGuidebook (Recuperado)dylandavid987No ratings yet
- GuidebookDocument41 pagesGuidebookdylandavid987No ratings yet
- Pronoun ReportDocument17 pagesPronoun ReportKish GabrielNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument66 pagesPronounsJess WangNo ratings yet
- Pronouns and Verb Latest New 1647056114519Document102 pagesPronouns and Verb Latest New 1647056114519vivek singhNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Semantics NewDocument29 pagesGroup 1 Semantics NewMar Atul Latifah Jauharin NafiNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Semantics NewDocument29 pagesGroup 1 Semantics NewMar Atul Latifah Jauharin NafiNo ratings yet
- Week 3: Parts of Speech: PronounsDocument33 pagesWeek 3: Parts of Speech: PronounsVivian MwangiNo ratings yet
- Conjuction & Pronoun....Document13 pagesConjuction & Pronoun....Hafizh Nur WahyudiNo ratings yet
- Conjuction & Pronoun....Document13 pagesConjuction & Pronoun....Hafizh Nur WahyudiNo ratings yet
- English: Kinds of PronounsDocument9 pagesEnglish: Kinds of PronounsMarynell ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Pronoun Group 3Document5 pagesPronoun Group 3Moh. Ridho FauzanNo ratings yet
- 10 Kinds of Pronouns in EnglishDocument5 pages10 Kinds of Pronouns in EnglishRizal TambunanNo ratings yet
- Pronouns in EnglishDocument12 pagesPronouns in EnglishНастя ШепелеваNo ratings yet
- I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesI. ObjectivesAnonymous YwtZrxp100% (1)
- Study Material ENG.101Document61 pagesStudy Material ENG.101AsmaNo ratings yet
- The Paper of Adjectives: Lecturer: Dra. Nurrochmi, M.PDDocument7 pagesThe Paper of Adjectives: Lecturer: Dra. Nurrochmi, M.PDNanda Mutiara SopandiNo ratings yet
- GROUP 1-Nouns and PronounDocument29 pagesGROUP 1-Nouns and PronounAMA MUTTAHIZI AHADAN AUHANNo ratings yet
- GROUP 3 - Predicate, Referring Expressions and Discourse of UniverseDocument14 pagesGROUP 3 - Predicate, Referring Expressions and Discourse of Universemillatuz zulfaNo ratings yet
- Types of NounsDocument6 pagesTypes of NounsVan Angel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Eng Important NotesDocument24 pagesEng Important NotesArslanNo ratings yet
- Short QuestionsDocument15 pagesShort QuestionsNaeem AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDDocument41 pagesParts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDDenna Refnaldi SatryaNo ratings yet
- Pronouns Its TypesDocument6 pagesPronouns Its TypesMuhammad AdilNo ratings yet
- Personal PronounDocument6 pagesPersonal PronounRudi SaragihNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To EnglishDocument125 pagesAn Introduction To Englishuzmahanif253No ratings yet
- Hybrid English 4 Q2 M3 W3Document10 pagesHybrid English 4 Q2 M3 W3Jedasai PasambaNo ratings yet
- Types of Pronoun (Parts of Speech) Lec3Document7 pagesTypes of Pronoun (Parts of Speech) Lec3Hassam HaiderNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - PronounDocument18 pagesLecture Notes - PronounNur Jasmira Binti Jamil E22B0049No ratings yet
- Mid Term Test Hardianti (190105011) Ii ADocument6 pagesMid Term Test Hardianti (190105011) Ii AHARDIANTINo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 4 LESSON 3 Kinds of PronounsDocument21 pagesENGLISH 4 LESSON 3 Kinds of PronounsARLENE PINERANo ratings yet
- English Final EditDocument112 pagesEnglish Final EditSanathNo ratings yet
- THENOUNPHRASEDocument9 pagesTHENOUNPHRASEEmely GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDDocument42 pagesParts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDFirda JinanNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive English Grammar Guide: From Basics to Competitive ExcellenceFrom EverandComprehensive English Grammar Guide: From Basics to Competitive ExcellenceNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive English Learning: Your All-in-One Guide for ESL SuccessFrom EverandComprehensive English Learning: Your All-in-One Guide for ESL SuccessNo ratings yet
- Female Bengali Freedom FightersDocument17 pagesFemale Bengali Freedom FightersMohan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology For Examination From 2023Document4 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Biology For Examination From 2023Valentina PorrasNo ratings yet
- Aodv.h File Sensor-Agent.h File: Timer Usage (In NS2) AODV Method: Another MethodDocument3 pagesAodv.h File Sensor-Agent.h File: Timer Usage (In NS2) AODV Method: Another MethodAvinash AvuthuNo ratings yet
- The Linguistic Structure of Modern English Sentence SemanticsDocument30 pagesThe Linguistic Structure of Modern English Sentence SemanticsGeorgiana Argentina DinuNo ratings yet
- SQL QueryDocument9 pagesSQL QuerynnandhaNo ratings yet
- R.V. College of Engineering, BangaloreDocument4 pagesR.V. College of Engineering, BangaloreSri Chandana KaruturiNo ratings yet
- 2003 AllochrtDocument1 page2003 Allochrtam1liNo ratings yet
- Lindquist Exercises Chapter 1Document1 pageLindquist Exercises Chapter 1Yolande CoetzeeNo ratings yet
- ID Leadership Communication Editorial Improving The Performance of Journalist in THDocument15 pagesID Leadership Communication Editorial Improving The Performance of Journalist in THLinda AsmaraNo ratings yet
- Ielts General Training Writing - Sample Scripts and Examiner CommentsDocument18 pagesIelts General Training Writing - Sample Scripts and Examiner CommentsMiryam DiabNo ratings yet
- ID 1610280.1Document3 pagesID 1610280.1NDONG1404No ratings yet
- 2ND Pu Kcet Mathematics Vector AlgebraDocument4 pages2ND Pu Kcet Mathematics Vector AlgebraROOPESH KunigalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CUDA C 3Document67 pagesIntroduction To CUDA C 3Tarun RamNo ratings yet
- Lecture MidtermDocument13 pagesLecture MidtermRica DiguinatNo ratings yet
- 09 - Chapter 3 PDFDocument61 pages09 - Chapter 3 PDFAshish AroraNo ratings yet
- English2 q4 Mod8Document9 pagesEnglish2 q4 Mod8Mely DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Explorer Ella's Magic ForestDocument12 pagesExplorer Ella's Magic ForestFrank KerzenmacherNo ratings yet
- 5 - Urdu and Regional Languages PAKISTAN STUDIESDocument3 pages5 - Urdu and Regional Languages PAKISTAN STUDIESSam ManNo ratings yet
- Ibibio PeopleDocument4 pagesIbibio PeopleSarvagya100% (1)
- Unit I.Building Business Administration LanguageDocument30 pagesUnit I.Building Business Administration LanguageCassey GandaNo ratings yet
- DumbDocument6 pagesDumbbita321No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Unix - Comp 206Document6 pagesAssignment 1 - Unix - Comp 206kitaNo ratings yet
- Ijpb v14n1p59 FaDocument24 pagesIjpb v14n1p59 Fahamed mollazadehNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous G&EDocument1 pagePresent Continuous G&ELucas GarinNo ratings yet
- Label3.Text Val (Textbox1.Text) - Val (Textbox2.Text)Document6 pagesLabel3.Text Val (Textbox1.Text) - Val (Textbox2.Text)劉又齊No ratings yet
- Burt Economic LocationDocument871 pagesBurt Economic LocationБямбаханд ӨлзийсайханNo ratings yet
- 11 Chapter 6Document31 pages11 Chapter 6S sharmaNo ratings yet
- Aveva Intouch Access Anywhere Server Administrator ManualDocument47 pagesAveva Intouch Access Anywhere Server Administrator Manualel misNo ratings yet
- 2 - How To Create A Personal Access Token in GitHubDocument4 pages2 - How To Create A Personal Access Token in GitHubKashif KamalNo ratings yet