Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dungca, Julie Mae O. - ELP
Uploaded by
Julie Mae DungcaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dungca, Julie Mae O. - ELP
Uploaded by
Julie Mae DungcaCopyright:
Available Formats
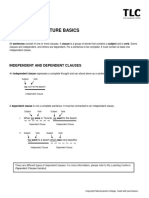
Sentence Structure Classification
Sentence structure
arrangement of words, phrases, and clauses in a sentence.
1. Simple sentence
one independent clause that ends with a period.
Note:
It compose of one subject and one predicate.
Independent clause– is
Example: Mary loves flowers. a clause that stand as
Subject predicate one sentence.
2. Compound sentence Coordinating conjunctions:
it has atleast two independent clauses. For, and, nor, but, or, yet, so
Uses coordinating conjunction, semi-colon Conjunctive adverb:
and conjunctive adverb to connect the Also, however, otherwise,
clauses. consequently, indeed,
similarly, finally, etc.
Example: Justine went to school but Maia went to plaza.
Independent clause conjunction Independent clause
3. Complex sentence Note:
It compose of one independent clause Dependent clause is a clause that
and one or more dependent clause. cannot stand on its own or it does
Uses subordinating conjunction to not have complete thought.
connect the clauses.
Example: I’m excited to try scuba diving, because they say it is fun.
Independent clause conjunction dependent clause
4. Compound-Complex sentence Subordinating
It compose of two or more independent clauses and conjunctions:
one dependent clause.
Although, after, before,
Uses coordinating conjunction, semi-colon and because, how, since,
conjunctive adverb to connect the independent until, so that, unless,
clauses; and uses subordinating conjunction to when, etc.
connect the dependent clause.
Example: I’m excited to try scuba diving, so I went to ask my friends on
Independent clause conjunction Independent clause
how to join their Diving Club, because they say it is fun.
Dependent clause
You might also like
- Types of Sentences 1Document5 pagesTypes of Sentences 1Babar HussainNo ratings yet
- Structure of SENTENCEDocument16 pagesStructure of SENTENCEBalraj Singh BatthNo ratings yet
- VAHO0203 - Grammar 3 - VA 3.4 - Theroy - Sentence Structure, Modifiers and ParallelismDocument8 pagesVAHO0203 - Grammar 3 - VA 3.4 - Theroy - Sentence Structure, Modifiers and ParallelismAbhishek KalaNo ratings yet
- Writing CivuDocument29 pagesWriting CivumarcosherrerauwuNo ratings yet
- Coordination PDFDocument3 pagesCoordination PDFTamer ObeidNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions & Conjunction AdverbsDocument2 pagesConjunctions & Conjunction AdverbsThảo HìnNo ratings yet
- Conjuction SDocument8 pagesConjuction SMothNo ratings yet
- Presentation Eng (Nabila)Document10 pagesPresentation Eng (Nabila)232370036No ratings yet
- Simple Sentence: This Is A A Remember, ItDocument3 pagesSimple Sentence: This Is A A Remember, Itjean wongNo ratings yet
- Sentence Structure Notes PDFDocument4 pagesSentence Structure Notes PDFjean wongNo ratings yet
- Sentence Types and FunctionsDocument6 pagesSentence Types and FunctionsMayank Aryanti Ar WhsNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions Part 2Document17 pagesConjunctions Part 2Carmen de ErazoNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 10 - SentenceDocument18 pagesKelompok 10 - SentenceErni WidiastutiNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2- CONNECTING IDEAS USING CONJUNCTIONS IN AN ARGUMENTATIVE TEXTDocument31 pagesWEEK 2- CONNECTING IDEAS USING CONJUNCTIONS IN AN ARGUMENTATIVE TEXTEicel PobleteNo ratings yet
- Lesson Exemplar 12Document13 pagesLesson Exemplar 12Virgelyu Urbesu JonyorNo ratings yet
- Compound Sentence 1.1 Definition of Compound SentenceDocument8 pagesCompound Sentence 1.1 Definition of Compound SentenceEfanTrisaktioNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Way To Crack Ielts Here Is A Video On Types of SentencesDocument49 pagesWelcome To Way To Crack Ielts Here Is A Video On Types of SentenceshorizonNo ratings yet
- Helen's Work. Do Not Delete !!Document6 pagesHelen's Work. Do Not Delete !!helen_huang123No ratings yet
- Sentence 1. An: HandoutDocument3 pagesSentence 1. An: HandoutAnglophile123No ratings yet
- Cordinating and Subordinating ConjuctionsDocument23 pagesCordinating and Subordinating ConjuctionsRajalakshmi GajapathyNo ratings yet
- Types of Conjunctions - Coordinating, Subordinating, Adverb, and CorrelativeDocument2 pagesTypes of Conjunctions - Coordinating, Subordinating, Adverb, and CorrelativeSkruzdelyte MielaNo ratings yet
- ClausesDocument5 pagesClausesMohamed GUERSNo ratings yet
- ClausesDocument5 pagesClausesBreeze BoukhrissNo ratings yet
- Complex Sentences ExplainedDocument22 pagesComplex Sentences ExplainedAnatasukiNo ratings yet
- English5 Q1 LP-6Document7 pagesEnglish5 Q1 LP-6Cher Z 2No ratings yet
- GrammarDocument14 pagesGrammarLogi CheminotNo ratings yet
- 2020-21 Sentence Structure NotesDocument2 pages2020-21 Sentence Structure Notesamogh.vinaykumarNo ratings yet
- Corrected Copy On English6 QTR 4 Mod 4 PDFDocument10 pagesCorrected Copy On English6 QTR 4 Mod 4 PDFRONA BUSTILLONo ratings yet
- Written Expression 2Document1 pageWritten Expression 2Cherrallah DjahidaNo ratings yet
- Sentence-Structure-Basics and PracticeDocument6 pagesSentence-Structure-Basics and Practicepablo Ortega100% (1)
- Sentence Structure: Improving YourDocument4 pagesSentence Structure: Improving YourVijaykumar D SNo ratings yet
- Clause and SentenceDocument13 pagesClause and SentenceAnonymous wFq3oKNo ratings yet
- Structure of English SentencesDocument6 pagesStructure of English Sentencesبوزيد OuleddahmaneNo ratings yet
- english project sem IDocument13 pagesenglish project sem Isanskrati116-20No ratings yet
- Sentence TeacherDocument33 pagesSentence Teacherbagus1313100% (1)
- A. Sentence Type (ST)Document10 pagesA. Sentence Type (ST)Ardian Kris BramantyoNo ratings yet
- Grammar AgriDocument13 pagesGrammar AgriYoussra FathiNo ratings yet
- ConjunctionDocument4 pagesConjunctionAliNo ratings yet
- Types of SentencesDocument17 pagesTypes of SentencesAhmed Raza TareenNo ratings yet
- GW SB2 Writer's Handbook 2Document16 pagesGW SB2 Writer's Handbook 2Mosab AlmazaydehNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in EnglishDocument11 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in EnglishAnnalyn NicolasNo ratings yet
- Conjunction SDocument18 pagesConjunction SLyka DarvinNo ratings yet
- Estructura Del Ingles PDFDocument21 pagesEstructura Del Ingles PDFShellys GomezNo ratings yet
- Exploring grammar - types of clause and how they are connectedDocument14 pagesExploring grammar - types of clause and how they are connectedTrần Thái Đình KhươngNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document2 pagesWeek 2vaishnave0625No ratings yet
- Coordination, Correlation, and Subordination ExplainedDocument3 pagesCoordination, Correlation, and Subordination ExplainedLidia StefNo ratings yet
- Conjunction Is A Word Used To ConnectDocument14 pagesConjunction Is A Word Used To ConnectSalome AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Avoiding Run-On Sentences, Comma Splices, and Fragments: Complete Sentence (Independent Clause)Document11 pagesAvoiding Run-On Sentences, Comma Splices, and Fragments: Complete Sentence (Independent Clause)juan umanzorNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions: For, And, Nor, But, Or, Yet, and SoDocument3 pagesConjunctions: For, And, Nor, But, Or, Yet, and SoamgiuntaNo ratings yet
- Conjucntion Group 6Document11 pagesConjucntion Group 6PAUL JUSTEIN SIA GRUEZO100% (1)
- Clause, Phrase, Sentence - Learn The Difference: What Is A Phrase?Document6 pagesClause, Phrase, Sentence - Learn The Difference: What Is A Phrase?WazalouaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Booklet 2Document10 pagesGrammar Booklet 2api-317227717No ratings yet
- Types of Sentence 1Document2 pagesTypes of Sentence 1Ravesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Types of Sentence 1Document2 pagesTypes of Sentence 1Ravesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Guided Notes Compound and Complex SentencesDocument12 pagesGuided Notes Compound and Complex Sentenceshaleigh hiightNo ratings yet
- AvoidingRun OnsCommaSplicesFragmentsJuly08Document14 pagesAvoidingRun OnsCommaSplicesFragmentsJuly08Kirsten ManibogNo ratings yet
- Detailed Daily Lesson Plan in English FoDocument9 pagesDetailed Daily Lesson Plan in English Fomaria rebecca paroneNo ratings yet
- Seminar Linguistic Nurul Inayah BasarunDocument5 pagesSeminar Linguistic Nurul Inayah BasarunACPTTNo ratings yet
- Cissp NotesDocument83 pagesCissp NotesRobert Mota HawksNo ratings yet
- Industrial Radiography Image Forming Techniques English 4Document114 pagesIndustrial Radiography Image Forming Techniques English 4Narasimha Murthy InampudiNo ratings yet
- VKS INFRA DPR Submission for NHAI Bihar ProjectDocument1 pageVKS INFRA DPR Submission for NHAI Bihar ProjectamirNo ratings yet
- CA ruling on fertilizer disputeDocument16 pagesCA ruling on fertilizer disputeRuby Anna TorresNo ratings yet
- LAC Intraregional IRF GuideDocument81 pagesLAC Intraregional IRF GuideMario Cortez EscárateNo ratings yet
- AmikinDocument2 pagesAmikinLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- The Metacentric Height EX3Document3 pagesThe Metacentric Height EX3Edrees JamalNo ratings yet
- Solution:: Ex 3.3 Consider The Following Parallelograms. Find The Values of The Unknowns X, Y, ZDocument9 pagesSolution:: Ex 3.3 Consider The Following Parallelograms. Find The Values of The Unknowns X, Y, ZpadmaNo ratings yet
- San Diego Quick AssessmentDocument56 pagesSan Diego Quick AssessmentLizNo ratings yet
- Sbi KukkatpallyDocument2 pagesSbi KukkatpallyRavi Babu KonkatiNo ratings yet
- Methanol from Syngas Plant DesignDocument13 pagesMethanol from Syngas Plant DesignKhalidMadaniNo ratings yet
- Principle Principle PrincipleDocument12 pagesPrinciple Principle PrincipleDarshana JuvekarNo ratings yet
- Sakha DictionaryDocument14 pagesSakha DictionarySojeong MinNo ratings yet
- HER201 Flex Tiles Set 01 - VehiclesDocument3 pagesHER201 Flex Tiles Set 01 - VehiclesDouglas Mears100% (2)
- EPS: Electric Power Steering Components & ModesDocument9 pagesEPS: Electric Power Steering Components & ModesTilahun Worku100% (1)
- Music Business Chapter 9 Music PublishingDocument27 pagesMusic Business Chapter 9 Music Publishingcmk97No ratings yet
- GPSForex Robot V2 User GuideDocument40 pagesGPSForex Robot V2 User GuideMiguel Angel PerezNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary - Vocabulario de Salud y de Sintomas en InglesDocument4 pagesVocabulary - Vocabulario de Salud y de Sintomas en InglesCarlos MiguelNo ratings yet
- Activity 2EE56L FINALDocument6 pagesActivity 2EE56L FINALLUAÑA ALMARTNo ratings yet
- Hdpe Guide PDFDocument81 pagesHdpe Guide PDFbalotNo ratings yet
- IAC PPE and Intangible Students FinalDocument4 pagesIAC PPE and Intangible Students FinalJoyce Cagayat100% (1)
- Unit 1Document32 pagesUnit 1Viyat RupaparaNo ratings yet
- Pakistan'S Economy & The Role of Imf & World Bank On ITDocument15 pagesPakistan'S Economy & The Role of Imf & World Bank On ITAsaad Imtiaz100% (1)
- VsamDocument24 pagesVsamRodrigoNo ratings yet
- "Employee Payroll Management System": Miss - Priyanka Abhaynath YadavDocument31 pages"Employee Payroll Management System": Miss - Priyanka Abhaynath Yadavhabeb TubeNo ratings yet
- DQFAQsDocument8 pagesDQFAQsBhagyashree kawaleNo ratings yet
- Clarke 1973 Loss of InnocenceDocument13 pagesClarke 1973 Loss of InnocencePaula TralmaNo ratings yet
- ENGG378 - 948 HydroPower-Lecture - 1 - 2019 PDFDocument34 pagesENGG378 - 948 HydroPower-Lecture - 1 - 2019 PDFJ CNo ratings yet
- Solar Bloc DatasheetDocument2 pagesSolar Bloc DatasheetandresNo ratings yet
- Data CollectionDocument4 pagesData CollectionjochukoNo ratings yet