Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP 4
Uploaded by
ako at ang exo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesSandra, a 2 month old infant, was experiencing frequent vomiting and poor feeding. Her mother reported she looked skinny and sick. The nursing assessment identified a risk for deficient fluid volume. The nursing care plan was to monitor Sandra's potassium levels and provide supplemental potassium if needed. Fluids were to be given orally or intravenously as tolerated to replace lost volume. The family was taught to monitor fluid intake and output at home, and an emergency plan was established in case of worsening symptoms.
Original Description:
Original Title
ncp4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSandra, a 2 month old infant, was experiencing frequent vomiting and poor feeding. Her mother reported she looked skinny and sick. The nursing assessment identified a risk for deficient fluid volume. The nursing care plan was to monitor Sandra's potassium levels and provide supplemental potassium if needed. Fluids were to be given orally or intravenously as tolerated to replace lost volume. The family was taught to monitor fluid intake and output at home, and an emergency plan was established in case of worsening symptoms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesNCP 4
Uploaded by
ako at ang exoSandra, a 2 month old infant, was experiencing frequent vomiting and poor feeding. Her mother reported she looked skinny and sick. The nursing assessment identified a risk for deficient fluid volume. The nursing care plan was to monitor Sandra's potassium levels and provide supplemental potassium if needed. Fluids were to be given orally or intravenously as tolerated to replace lost volume. The family was taught to monitor fluid intake and output at home, and an emergency plan was established in case of worsening symptoms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
STUDENT NURSE’S NAME: Mixcy A.
Mabatid Date: March 8, 2022
Client’s Name: Sandra B. Age: 2 months old
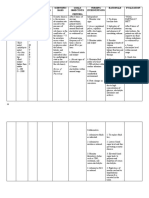
NURSING CARE PLAN
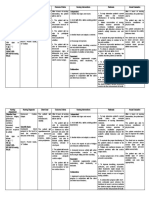
ASSESSMENT NURSING DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective: The mother Risk for deficient fluid Within 3 hours of nursing 1. Obtain specimens for 1. Urine and serum analysis After 3 hours of nursing intervention
of the patient verbalized volume related to intervention the patient will be able analysis of altered provides information about the patient has been able to
that Sandra breastfed vomiting to tolerated clear liquids without potassium levels as extracellular levels of tolerated clear liquids without
well for the first couple vomiting indicated. potassium. There is no vomiting
of weeks, but since then practical way to measure
“throws up all the time intracellular K.
like she’s forcing all her 2. Administer prescribed 2. Low potassium levels are
feedings out. She looks supplemental potassium dangerous and the patient
skinny and sick, and she (PO, NG, or IV) per policy. may require supplements.
cries and is fussy all the 3. Monitor for neurologic and 3. Potassium is a vital
time.” neuromuscular electrolyte for skeletal and
manifestations of smooth muscle activity.
Objective: hypokalemia.
- 4. Monitor for cardiac 4. Many cardiac rhythm
manifestations of disorders can result from
hypokalemia. hypokalemia. It is critical to
monitor cardiac function
with hypokalemia.
5. Maintain accurate intake 5. Accurate records are critical
and output record. in assessing the patient’s
fluid balance.
6. Monitor vital signs as 6. Vital sign changes such as
appropriate. increased heart rate,
decreased blood pressure,
and increased temperature
indicate hypovolemia.
7. Give fluids as appropriate. 7. As her nausea decreases
encourage her oral intake of
fluids as tolerated, again to
replace lost volume.
8. Administer IV therapy as 8. She will probably require
prescribed. intravenous replacement of
fluid. This is especially true
because her oral intake is
limited because of nausea
and vomiting
9. Teach family members how 9. An accurate measure of
to monitor output in the fluid intake and output is an
home. Instruct them to important indicator of
monitor both intake and patient’s fluid status.
output.
10. Identify an emergency plan, 10. Some complications of
including when to ask for deficient fluid volume
help. cannot be reversed in the
home and are life-
threatening. Patients
progressing toward
hypovolemic shock will need
emergency care.
You might also like
- Anemia NCPDocument10 pagesAnemia NCPCharmz_asherah100% (9)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planmanu_gutierrez0891% (11)
- NCP 1Document7 pagesNCP 1Mark PabalanNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument13 pagesHypertensionkennedy1434450% (4)
- NCP GDMDocument10 pagesNCP GDMmishti94% (17)
- Pericare With Heat Lamp TreatmentDocument5 pagesPericare With Heat Lamp Treatmentako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Epidemiological TriadDocument1 pageEpidemiological Triadako at ang exo100% (1)
- Developing A Pharmaceutical Care PlanDocument2 pagesDeveloping A Pharmaceutical Care PlanRiga 'Azoe' AlrianiNo ratings yet
- Sop For Hemoglobin Determination by HPLCDocument13 pagesSop For Hemoglobin Determination by HPLCUMMID WashimNo ratings yet
- NCPs (ABRIAN)Document23 pagesNCPs (ABRIAN)Rouie Björn ABrianNo ratings yet
- Prado, Catherine BSN IIB (Activity 1 Case Scenario)Document52 pagesPrado, Catherine BSN IIB (Activity 1 Case Scenario)Catherine PradoNo ratings yet
- HYPONATREMIADocument3 pagesHYPONATREMIADienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- ROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPDocument6 pagesROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPkimberly quitonNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPLevyanne GsanchezNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharles Dave AgustinNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharles Dave AgustinNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationMargareth DandanNo ratings yet
- Group 47 NCP Bicarbonate DisordersHyperbicarbonatemia and HypobicarbonatemiaDocument6 pagesGroup 47 NCP Bicarbonate DisordersHyperbicarbonatemia and HypobicarbonatemiaAngel Joyce MontezaNo ratings yet
- NCP Drug Study 2, Ojoy Dan Joshua LDocument4 pagesNCP Drug Study 2, Ojoy Dan Joshua Ldan.ojoy18No ratings yet
- Unfolding Case StudyDocument3 pagesUnfolding Case StudyKeesha Mae Urgelles TimogNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveFreisanChenMandumotanNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Khyber Pukhtunkhwa, PeshawarDocument3 pagesAssignment: Khyber Pukhtunkhwa, PeshawarShafiq Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Octot, Angelica - NCPDocument2 pagesOctot, Angelica - NCPAngelica OctotNo ratings yet
- PNEUMONIADocument8 pagesPNEUMONIARica ParcasioNo ratings yet
- HYPOKALEMIADocument3 pagesHYPOKALEMIADienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Facto NCPDocument3 pagesFacto NCPkkd nyleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Submitted byDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Submitted byKarl Angelo MontanoNo ratings yet
- As Fluid Volume Deficit (FVD), Hypovolemia) Is ADocument2 pagesAs Fluid Volume Deficit (FVD), Hypovolemia) Is ATanya Alyssa Untalan AquinoNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPJet Ray-Ann GaringanNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument13 pagesHypertensionAbigail BascoNo ratings yet
- المستند (7) Document3 pagesالمستند (7) Mawadh AlsbhiNo ratings yet
- Postop Actual &potential NCPDocument12 pagesPostop Actual &potential NCPJohn Paul Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Ariane NCP 1Document2 pagesAriane NCP 1Kristian Ray EraulaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharles Dave AgustinNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationbambem aevanNo ratings yet
- Hypokalemia Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesHypokalemia Nursing Care PlanIan Lelis100% (1)
- Sedation For Icu Patients PresentationDocument8 pagesSedation For Icu Patients Presentationapi-736869233No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Artery Blockage May BeDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Artery Blockage May BeDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- NCP DM and HCVDDocument3 pagesNCP DM and HCVDMAYBELINE OBAOB100% (1)
- 6 NCPDocument8 pages6 NCPKlint IntervencionNo ratings yet
- NCP - DM - FatigueDocument12 pagesNCP - DM - FatigueJisel-Apple BulanNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPGinmarie Alcueno FabillarNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesAcute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanKrisianne Mae Lorenzo Francisco80% (5)
- NCP CKDDocument5 pagesNCP CKDDbktNo ratings yet
- NCP BeeaDocument3 pagesNCP BeeaKiko BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Management of Client With Hypokalemia ACTUAL 1Document4 pagesNursing Care Management of Client With Hypokalemia ACTUAL 1Angel Nieto PengsonNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPjsksNo ratings yet
- Fluid Vol Deficit Secondary To Postpartum Hemorrhage Care PlanDocument3 pagesFluid Vol Deficit Secondary To Postpartum Hemorrhage Care PlanEllie GartungNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Trauma - 5Document12 pagesLower Limb Trauma - 5Renee RoSeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMiss GNo ratings yet
- Duty RequirementsDocument13 pagesDuty RequirementsRey Jean GarciaNo ratings yet
- Medical Diagnosis: Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5 Patient's NameDocument4 pagesMedical Diagnosis: Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5 Patient's NameHadeer Mahmoud Abuslima100% (1)
- NCP - Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesNCP - Activity IntoleranceRoyce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 2Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 2Fiona Xandra San JuanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Group 4-Open Wound Head Injury After Debris FallDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Group 4-Open Wound Head Injury After Debris FallNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- NCP and Drug Study (Isph-Gs Nursery)Document4 pagesNCP and Drug Study (Isph-Gs Nursery)Cristyl Shine BariaoNo ratings yet
- NCP Knowledge DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP Knowledge DeficitRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For HypertensionFranco Razon100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pregnancy Induced HypertensionMurugham DineshNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanDienizs Labini Tadena100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document4 pagesNursing Care Plan 1Kiko BernardinoNo ratings yet
- CVD HypertensionDocument15 pagesCVD HypertensionAbigail BascoNo ratings yet
- Webinar Reflection ManggaDocument1 pageWebinar Reflection Manggaako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Assessment KitDocument4 pagesPediatric Assessment Kitako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Treatment of Common Pediatric Sleep DisordersDocument1 pageAssessment and Treatment of Common Pediatric Sleep Disordersako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- End of Quiz: BSN2 N25 - Rizal's Life and Works (Summer 2022) RA 1425 QuizDocument3 pagesEnd of Quiz: BSN2 N25 - Rizal's Life and Works (Summer 2022) RA 1425 Quizako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Date/Hour of Shift Focus Note ProgressDocument2 pagesDate/Hour of Shift Focus Note Progressako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- NCP Form3Document2 pagesNCP Form3ako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- You Are Discussing Discharge Plans With Therese and His MotherDocument1 pageYou Are Discussing Discharge Plans With Therese and His Motherako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- According To The Video The Elohim Is A Category Title Not A NameDocument1 pageAccording To The Video The Elohim Is A Category Title Not A Nameako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Origami Dna: Folding InstructionsDocument1 pageOrigami Dna: Folding Instructionsako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Major Disease: Major Disease Frequency Percentage Diabetes Asthma Hypertension Ulcer Tuberculosis Anemia Kidney ProblemDocument1 pageMajor Disease: Major Disease Frequency Percentage Diabetes Asthma Hypertension Ulcer Tuberculosis Anemia Kidney Problemako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- 8 Wastes of Lean ManagementDocument1 page8 Wastes of Lean Managementako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Based On My Beginning Knowledge in Health AssessmentDocument1 pageBased On My Beginning Knowledge in Health Assessmentako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Changes The Symbol Probabilities During The Compression Process in Order To Adapt To The Changing Contexts During The ProcessDocument1 pageChanges The Symbol Probabilities During The Compression Process in Order To Adapt To The Changing Contexts During The Processako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Infant Tub BathDocument3 pagesInfant Tub Bathako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Sample Menu FormatDocument1 pageSample Menu Formatako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Meal Planning FormDocument2 pagesMeal Planning Formako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- CHN Home Visit PlanDocument2 pagesCHN Home Visit Planako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Evidence-Based ReportDocument1 pageEvidence-Based Reportako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Assessment of ToddlersDocument2 pagesAssessment of Toddlersako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Sample Menu FormatDocument1 pageSample Menu Formatako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Meal Planning FormDocument2 pagesMeal Planning Formako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Home Visit PlanDocument2 pagesHome Visit Planako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Appliation of HPM 2Document1 pageAppliation of HPM 2ako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- 250 WordsDocument1 page250 Wordsako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReportinggDocument4 pagesAnaphy Reportinggako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- A Fetal PositionDocument1 pageA Fetal Positionako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Group 4Document1 pageGroup 4ako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Tpoic #3 Roles and Responsibilities of MCNDocument11 pagesTpoic #3 Roles and Responsibilities of MCNMary Faith MadayagNo ratings yet
- Acupuncture For TinnitusDocument4 pagesAcupuncture For Tinnitussrimaauro5123No ratings yet
- Use of Occipital Nerve BlocksDocument5 pagesUse of Occipital Nerve BlocksMilton quisbert paredesNo ratings yet
- Christian Medical College VelloreDocument167 pagesChristian Medical College VelloreElisa 1209No ratings yet
- Pharma 1.13 CASE 1Document2 pagesPharma 1.13 CASE 1Aesthetics MinNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Estrogens and ProgesteroneDocument7 pagesThe Effects of Estrogens and ProgesteroneTinke WinkeNo ratings yet
- Parameters of Automated Cell Counter Automation in Hematology Laboratory and CBC Via Automated Blood AnalyzerDocument40 pagesParameters of Automated Cell Counter Automation in Hematology Laboratory and CBC Via Automated Blood AnalyzerArslan Arshad100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Central Venous CathetersDocument6 pagesChapter 1 - Central Venous CathetersParth PatelNo ratings yet
- A Study of Cisplatin Chemoteraphy and Hearing LossDocument4 pagesA Study of Cisplatin Chemoteraphy and Hearing LossPriska AmeliaNo ratings yet
- MedicineDocument53 pagesMedicineapi-25984682100% (1)
- Ovarian Cancers The National Academies Press PDFDocument397 pagesOvarian Cancers The National Academies Press PDFnersitiulfahNo ratings yet
- Msds of Copper TurningDocument3 pagesMsds of Copper TurningbabeNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Students Module 6 and 7Document4 pagesGuidelines For Students Module 6 and 7JasellePanteNo ratings yet
- Jl. Pulo Mas Timur K No.2 RT4/RW.14, Kayu Pu H, Kec. Pulo Gadung, Kota Jakarta Timur, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta 13210Document1 pageJl. Pulo Mas Timur K No.2 RT4/RW.14, Kayu Pu H, Kec. Pulo Gadung, Kota Jakarta Timur, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta 13210suherman paleleNo ratings yet
- Mrs Parveen Inamdar 29 02 2020 06 16 15 AM PDFDocument3 pagesMrs Parveen Inamdar 29 02 2020 06 16 15 AM PDFmalhari katakdoundNo ratings yet
- Sliding Bone Graft JournalDocument3 pagesSliding Bone Graft Journalapi-310305222No ratings yet
- CHO Special MCQs #1Document7 pagesCHO Special MCQs #1Praveen LaxkarNo ratings yet
- A Review - Dosing Issues When Using Minocin/Minocycline To Treat SarcoidosisDocument3 pagesA Review - Dosing Issues When Using Minocin/Minocycline To Treat SarcoidosisIonpropulsionNo ratings yet
- Antibiotik Dan Antiseptik Saluran KemihDocument14 pagesAntibiotik Dan Antiseptik Saluran KemihPuterinugraha Wanca ApatyaNo ratings yet
- Orthokeratology: Orthokeratology (Ortho-K) Is The Fitting of Specially Designed GasDocument4 pagesOrthokeratology: Orthokeratology (Ortho-K) Is The Fitting of Specially Designed GasPUSHPAK DASGUPTANo ratings yet
- Soal Ujian R2 FixedDocument9 pagesSoal Ujian R2 Fixedprakoso jatiNo ratings yet
- DUE of PIPERACILLIN and TazobactumDocument73 pagesDUE of PIPERACILLIN and Tazobactumanup jagarlamudiNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Nausea and VomitingDocument15 pagesJurnal Nausea and VomitingRisa KarmeylithaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment: Physiological Psychological Sociological SpiritualDocument5 pagesNursing Assessment: Physiological Psychological Sociological SpiritualFay DalanonNo ratings yet
- Orias DS PropofolDocument2 pagesOrias DS PropofolKyla OriasNo ratings yet
- Eurican Technicalsheet 12-08-2019Document2 pagesEurican Technicalsheet 12-08-2019dzulfikarfaizin romasNo ratings yet
- Etiqa PDFDocument39 pagesEtiqa PDFClifford LedesmaNo ratings yet
- 9851 BCG Vaccine Professional HCWDocument4 pages9851 BCG Vaccine Professional HCWIuliana PanaitNo ratings yet