Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DCPD and Fatigue
Uploaded by
CHONKARN CHIABLAMOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DCPD and Fatigue
Uploaded by
CHONKARN CHIABLAMCopyright:
Available Formats
The Potential Drop Technique & Its Use
In Fatigue Testing
A Short Applications Note
The potential drop technique has been in use to measure and characterise the propagation of
defects in metallic specimens for many years. It is one of the few methods that directly
measures the depth of a defect or flaw providing this penetrates the surface of the material
under test.
BACKGROUND
The potential drop technique relies Both techniques have their Pulsed or interrupted DCPD units
upon the passage of a constant current protagonists and associated eliminate thermoelectric EMFs by
through a specimen and the subsequent advantages. taking two PD measure-ments, one
measurement of the voltage generated during a current pulse and one after
across an area (usually the crack site) ACPD provides a linear increase in (i.e. at zero current). By subtracting
on the specimen. voltage with crack depth and hence one from the other, the thermo-electric
permits simpler calibrations. It is also EMFs are removed.
Two forms of the technique exist; AC theoretically more sensitive than the
potential drop (ACPD) in which small DC technique since most of the current ACPD has always suffered from the
(ca. 1 amp) alternating currents are in the specimen is confined to the effect of pick-up (voltages induced in
passed through the specimen and DC surface regions via a pheno-menon the signal lead by the current supply
potential drop (DCPD) in which large known as the skin effect. lead).
(ca. 30 amp) direct currents are used.
These properties have lead to ACPD The pick-up signal is super-imposed
The techniques essentially measure being used to measure crack depth in upon the true ACPD and can
resistance (DCPD) or impedance the field in addition to its laboratory dramatically alter measured signal
(ACPD). The change in these role. DCPD is usually confined to the magnitudes.
quantities generated by a propagating materials testing and research
defect usually results in an increase in applications and is the more Pick up is not a problem in itself
the potential drop being measured. traditional, and hence accepted, of the except for the fact that altering the
potential drop methods. position of the leads during a test will
V V
I I change the measured PD value.
The major disadvantages of the DCPD
method have been the generation of Although the influence of the AC pick-
thermoelectric EMFs at the contact up phenomenon can be reduced by
points and the poor noise performance. careful test set-up, it is also possible to
These effects have been largely electronically remove the offending
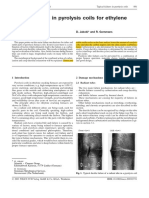
Typical DCPD and ACPD current overcome by the use of modern signal.
paths in CT specimens electronics and by pulsing the applied
currents.
FATIGUE TESTING
Both potential drop variants have extensively been used for fatigue testing by industry and
academia alike. They are now accepted as methods for the measurement of crack size by the
ASTM organisation (ref. 1).
In general, ACPD is suitable for both The rapid response of AC systems This phenomenon is often put to good
high and low frequency fatigue studies makes them ideal for high cycle use to characterise crack closure
whereas pulsed DCPD is only suitable studies. ACPD has even been used to effects but it can be problematic when
for low frequency work. obtain data during impact testing. static measurement of crack depth in
the field is performed since it causes
Modern pulsed DC systems permit the Both techniques suffer from the effect an effective underestimation of the
synchronisation of the current pulse to of crack shorting, whereby rough, crack depth.
the machine cycle waveform so that fresh crack surfaces can exhibit
measurements can be taken at, for alternative current paths that disappear Sometimes regarded as a complicating
example, peak tension. once the crack is opened after the factor, is the observed dependence of
Such operation is ideal for the study of application of a stress. both the DC and AC potential drop on
crack closure effects in metals. elastic and plastic strain.
MATELECT APPLICATION NOTE REFERENCE : FPD04
The strain effect has been used in better than DCPD as the low currents For further information on our
ACPD to detect the onset of crack employed in the former permit the products or if you just require advice
initiation (ref. 2) and has now been current lines to be multiplexed as well. on any aspect of potential drop
used to measure stress within a This ultimately leads to greater technology, please contact our offices
specimen (ref. 3). In fatigue studies, sensitivity and selectivity - essential if at the address below.
the change in PD with stress leads to a profiling is to be performed correctly.
cyclic variation in the PD signal that References:
mimics the load waveform. Multiplexing is, however, confined to
low frequency cycling studies where 1. ASTM E647 Guidlines for electrical
In general, for low frequency fatigue the time delay between readings on potential difference determination of crack
testing it is very important to use any one channel (caused by the size
equipment that offers high stability and necessity of scanning through other 2. Okumura et al. Application of the AC
low noise operation. channels) is not likely to prove a potential drop technique to the
problem. Determination of R curves. Eng. Frac.
Mech. 1981(14) 617
ACPD systems based on a single
3. M Saka et al. Measurement of Stress--
channel instrument need to incorporate For profiling during high frequency
intensity factor by means of AC Potential
a high stability current source if fatigue studies, specialist real time Drop Technique.
sensible long term measure-ments are multi-channel equipment is required. Experimental Mechanics vol 31 1991(3)
to be made. 209
Matelect have been established
It is possible to use poorer quality suppliers of potential drop
sources by using a second measuring instrumentation for over 10 years with 0$7(/(& /7'
channel to act as a reference. The sales extending world-wide.
33 Bedford Gardens
active channel is then normalised using London, W8 7EF, UK
the passive channel. Matelect supplies both standard single
Tel: +44 (0)20 7221 6784
channel ACPD and dual channel Fax: +44 (0)20 7727 9091
Increasing the number of signal pulsed DCPD systems together with Email: enquiry@matelect.com
channels by employing signal multiplexing equipment. Multi- Web: www.matelect.com
multiplexing makes it also possible to channel, real time (non-multiplexing) __________
obtain information on how a crack ACPD units are also fabricated to
profile alters during a fatigue test. For customer requirements.
this purpose the ACPD technique is far
A typical ACPD crack growth monitor
MATELECT APPLICATION NOTE REFERENCE : FPD04
You might also like
- Practical CS ProcessingDocument483 pagesPractical CS ProcessinganAMUstudent100% (2)
- Design of High Voltage Filter For Power Transformer TestingDocument6 pagesDesign of High Voltage Filter For Power Transformer TestingmayureshNo ratings yet
- Automated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsFrom EverandAutomated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsNo ratings yet
- Hilti TE 804 and 905avr PartsDocument13 pagesHilti TE 804 and 905avr PartsAqui Solo100% (1)
- BZY Series Tension Meter ManualDocument29 pagesBZY Series Tension Meter ManualJORGE SANTANDER0% (1)
- NDT and E International: Rollo Jarvis, Peter Cawley, Peter B. NagyDocument10 pagesNDT and E International: Rollo Jarvis, Peter Cawley, Peter B. NagyRafael FerraresiNo ratings yet
- 1348583100dielectric Diagnosis of EHV Current Transformer Using Frequency Domain Spectroscopy (Recovered)Document11 pages1348583100dielectric Diagnosis of EHV Current Transformer Using Frequency Domain Spectroscopy (Recovered)samrendraNo ratings yet
- Arduino Based Underground Cable Fault DetectionDocument5 pagesArduino Based Underground Cable Fault DetectionBikila DesalegnNo ratings yet
- Arduino Based Underground Cable Fault de PDFDocument5 pagesArduino Based Underground Cable Fault de PDFRana AbrarNo ratings yet
- Fault Location in Power Transformers During Impulse TestsDocument6 pagesFault Location in Power Transformers During Impulse TestsMozar CostaNo ratings yet
- Fault Detection Methods For Three-Level NPC Inverter Based On DC Bus Electromagnetic SignaturesDocument13 pagesFault Detection Methods For Three-Level NPC Inverter Based On DC Bus Electromagnetic SignaturesBeto MayoNo ratings yet
- HVPD - CIRED 2013 - On-Line Partial Discharge Detection and Control On MV Cable Networks With Ground Fault NeutraliserDocument4 pagesHVPD - CIRED 2013 - On-Line Partial Discharge Detection and Control On MV Cable Networks With Ground Fault NeutraliserShady NasrNo ratings yet
- Monitoring of Dielectric Losses at Capacitor-Type Bushings: Dnedelcut@icmetDocument9 pagesMonitoring of Dielectric Losses at Capacitor-Type Bushings: Dnedelcut@icmetBlack JasmineNo ratings yet
- 2007 Korea Vasconcelos2Document7 pages2007 Korea Vasconcelos2Hamza RossafiNo ratings yet
- Kreuger 1993Document15 pagesKreuger 1993GerardoNo ratings yet
- Morris 2017Document4 pagesMorris 2017ismailNo ratings yet
- High Speed Multichannel Impedance Measuring System: Acta ImekoDocument6 pagesHigh Speed Multichannel Impedance Measuring System: Acta ImekoGoran MiljkovicNo ratings yet
- 1398 S2 Impedance Survey Full Final UploadDocument5 pages1398 S2 Impedance Survey Full Final UploaddougmadasNo ratings yet
- Scheme For Accelerated Trip For Faults in The SecoDocument3 pagesScheme For Accelerated Trip For Faults in The SecoSALAH SALLAMNo ratings yet
- Herold ISH 2007Document5 pagesHerold ISH 2007ismailNo ratings yet
- Egyed 2016Document4 pagesEgyed 2016fernandoquecaNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform-Based Modified Phasor Estimation Method Immune To The Effect of The DC OffsetsDocument9 pagesFourier Transform-Based Modified Phasor Estimation Method Immune To The Effect of The DC OffsetsWilliam_CoilungNo ratings yet
- Locating Underground Cable Faults A Review andDocument5 pagesLocating Underground Cable Faults A Review andcuntNo ratings yet
- Power System Relaying Committee 1981Document3 pagesPower System Relaying Committee 1981Abolfazl TayefehNo ratings yet
- Protection Strategy For Multi-Terminal DC Networks With Fault Current Blocking Capability of ConvertersDocument6 pagesProtection Strategy For Multi-Terminal DC Networks With Fault Current Blocking Capability of ConvertersShan JayamahaNo ratings yet
- Condition Monitoring For DC-link Capacitors Based On Artificial Neural Network AlgorithmDocument5 pagesCondition Monitoring For DC-link Capacitors Based On Artificial Neural Network AlgorithmMohan Kumar DashNo ratings yet
- ICMflex DatasheetDocument4 pagesICMflex DatasheetsunilNo ratings yet
- C-V Measurement Tips, Tricks, and Traps: Lee Stauffer Senior Staff Technologist Keithley Instruments, IncDocument14 pagesC-V Measurement Tips, Tricks, and Traps: Lee Stauffer Senior Staff Technologist Keithley Instruments, IncJoshua SmithNo ratings yet
- The Two-Winding Transformer: An Experimental Method To Obtain A Wide Frequency Range Equivalent CircuitDocument8 pagesThe Two-Winding Transformer: An Experimental Method To Obtain A Wide Frequency Range Equivalent Circuitjeos20132013No ratings yet
- Design of A Portable Low-Cost Impedance AnalyzerDocument6 pagesDesign of A Portable Low-Cost Impedance Analyzerjs590No ratings yet
- Partial Discharge Measurements On 110kV Current Transformers. Setting The Control Value. Case StudyDocument9 pagesPartial Discharge Measurements On 110kV Current Transformers. Setting The Control Value. Case StudyHafiziAhmadNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On The Partial Discharge Characteristics of Four Typical Defects in GISDocument5 pagesExperimental Study On The Partial Discharge Characteristics of Four Typical Defects in GISDebojyoti MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Cable Models For Time Domain SimulationsDocument5 pagesComparison of Cable Models For Time Domain SimulationsGokul VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Loop TestingDocument2 pagesLoop TestingVelitinelNo ratings yet
- aspublishedonIEEEXplore TIE2349876Document10 pagesaspublishedonIEEEXplore TIE2349876josmelNo ratings yet
- Partial Discharge in Gas Insulated Sub-StationsDocument12 pagesPartial Discharge in Gas Insulated Sub-StationsAishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Using Eddy Current For Corrosion InspectionDocument3 pagesUsing Eddy Current For Corrosion InspectionEdAlmNo ratings yet
- Wyatt Na Ddg12Document6 pagesWyatt Na Ddg12Antonio BergnoliNo ratings yet
- Current Sensors Using Magnetic MaterialsDocument7 pagesCurrent Sensors Using Magnetic MaterialsSuttisak SuriyachanhomNo ratings yet
- Rough-Granular Approach For Impulse Fault Classification of Transformers Using Cross-Wavelet TransformDocument8 pagesRough-Granular Approach For Impulse Fault Classification of Transformers Using Cross-Wavelet TransformDebojyoti MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Real-Time Digital Compensation of Current Transformers Over A Wide Frequency RangeDocument8 pagesReal-Time Digital Compensation of Current Transformers Over A Wide Frequency RangeAlberto MedeirosNo ratings yet
- Effective Two-Terminal Numerical Algorithm For OveDocument9 pagesEffective Two-Terminal Numerical Algorithm For OveAbdallah AmroNo ratings yet
- Guide For Electrical Partial Discharge MDocument4 pagesGuide For Electrical Partial Discharge MvkNo ratings yet
- Paper 9145 Eurocorr 2010Document9 pagesPaper 9145 Eurocorr 2010weider11No ratings yet
- The Use of Absolute LimitsDocument11 pagesThe Use of Absolute LimitsMUSTAKUL ALAM BARLASKARNo ratings yet
- Mingkai Mu - New Core Loss Measurement Method For High-Frequency Magnetic MaterialsDocument8 pagesMingkai Mu - New Core Loss Measurement Method For High-Frequency Magnetic MaterialsNeha RajputNo ratings yet
- k1 FCL DigSilentDocument8 pagesk1 FCL DigSilentksg9731No ratings yet
- We Can Classify Test Failure Modes in Power Transformers Accord Ing To Transform Er Com Po NentsDocument8 pagesWe Can Classify Test Failure Modes in Power Transformers Accord Ing To Transform Er Com Po NentsShamil NiftaliyevNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation of Different Characterisitcs of PVC and XLPE CablesDocument11 pagesExperimental Investigation of Different Characterisitcs of PVC and XLPE CablesEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Fault Findings On Power Transformers: Presentation 10.1Document8 pagesDiagnosis and Fault Findings On Power Transformers: Presentation 10.1carlos suarezNo ratings yet
- Testing: Service LineDocument2 pagesTesting: Service LineVerónicaNo ratings yet
- Bandgap 1Document4 pagesBandgap 1sachin saxenaNo ratings yet
- Efficiency Based Design Flow For Fully-Integrated Class C RF Power Amplifiers in Nanometric CMOSDocument4 pagesEfficiency Based Design Flow For Fully-Integrated Class C RF Power Amplifiers in Nanometric CMOSHimanshu SardanaNo ratings yet
- CT Saturation Detection Based On Waveshape Properties of Current Difference FunctionsDocument10 pagesCT Saturation Detection Based On Waveshape Properties of Current Difference FunctionsAlberto MedeirosNo ratings yet
- A CMOS Bandgap ReferenceDocument10 pagesA CMOS Bandgap ReferencemeslonNo ratings yet
- Study On Partial Discharge Fault Diagnosis of High Voltage Switchboard Based On Ultrasound DetectionDocument8 pagesStudy On Partial Discharge Fault Diagnosis of High Voltage Switchboard Based On Ultrasound DetectionAM KANo ratings yet
- Fai Fer 2011Document5 pagesFai Fer 2011Tedy PradnyanaNo ratings yet
- Dependence of Over-V Oltage Level of Different V Oltage Class Surge Arrestors On Grounding Device Papameters. Experimental Study and SimulationDocument5 pagesDependence of Over-V Oltage Level of Different V Oltage Class Surge Arrestors On Grounding Device Papameters. Experimental Study and Simulationnam321985No ratings yet
- An Improved Transformer For LLC Resonant Inverter For Induction Heating ApplicationsDocument8 pagesAn Improved Transformer For LLC Resonant Inverter For Induction Heating ApplicationsIvan PopovicNo ratings yet
- Partial Discharge Testing of Gas Insulated Substations: Group K4, KeyDocument8 pagesPartial Discharge Testing of Gas Insulated Substations: Group K4, KeyAishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Near-Field Antenna As A Scanning Microwave Probe For Characterization of Materials and DevicesDocument3 pagesNear-Field Antenna As A Scanning Microwave Probe For Characterization of Materials and DevicesClenaNo ratings yet
- Capacitive Sensor Interfacing Using Sigma-Delta TechniquesDocument4 pagesCapacitive Sensor Interfacing Using Sigma-Delta TechniquesAlex WongNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Portable Impedance AnalyzersFrom EverandDesign and Implementation of Portable Impedance AnalyzersNo ratings yet
- Otegui 2015Document18 pagesOtegui 2015CHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- Patil 2017Document6 pagesPatil 2017CHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- Skin Daras 2014Document6 pagesSkin Daras 2014CHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- Deepak 2021Document6 pagesDeepak 2021CHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- Reihani 2015Document12 pagesReihani 2015CHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- Paktiawal 2021Document8 pagesPaktiawal 2021CHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- 1Document6 pages1anon_234519022No ratings yet
- Fuyang2021 (Micro)Document11 pagesFuyang2021 (Micro)CHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S187770581504182X MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S187770581504182X Mainanwar ansariNo ratings yet
- 10.1016@j.engfailanal.2020.105122 (Ref.m23c6)Document32 pages10.1016@j.engfailanal.2020.105122 (Ref.m23c6)CHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- Michler2016 (Austenitic Steel)Document6 pagesMichler2016 (Austenitic Steel)CHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- 19.-Pyrolysis FurnaceDocument5 pages19.-Pyrolysis FurnaceWilfredo PastranaNo ratings yet
- Pourmohammad 2019Document11 pagesPourmohammad 2019CHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Engfailanal 2020 104610Document21 pages10 1016@j Engfailanal 2020 104610CHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- Engineering Failure Analysis: A. Goswami, S. KumarDocument7 pagesEngineering Failure Analysis: A. Goswami, S. KumarCHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- Ferrite Fraction and PermeabilityDocument5 pagesFerrite Fraction and PermeabilityCHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- Crystallographic Characterizations of Eutectic and Secondary Carbides in A Fe-12Cr-2.5Mo-1.5W-3V-1.25C AlloyDocument7 pagesCrystallographic Characterizations of Eutectic and Secondary Carbides in A Fe-12Cr-2.5Mo-1.5W-3V-1.25C AlloyCHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- Engineering Failure Analysis: M. Santos, M. Guedes, R. Baptista, V. Infante, R.A. CláudioDocument10 pagesEngineering Failure Analysis: M. Santos, M. Guedes, R. Baptista, V. Infante, R.A. CláudioCHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- AD0820780Document104 pagesAD0820780CHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- Materials: Alumina-Based Coating For Coke Reduction in Steam CrackersDocument19 pagesMaterials: Alumina-Based Coating For Coke Reduction in Steam CrackersCHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: 10.1016/j.energy.2017.12.163Document33 pagesAccepted Manuscript: 10.1016/j.energy.2017.12.163CHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- Wang 2014Document21 pagesWang 2014CHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- Acta Technica Corviniensis: - Bulletin of EngineeringDocument7 pagesActa Technica Corviniensis: - Bulletin of EngineeringCHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- DCPD Lu2012Document9 pagesDCPD Lu2012CHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Pyrolysis Coil Failure: Rob Gommans M.SCDocument10 pagesDifferent Types of Pyrolysis Coil Failure: Rob Gommans M.SCCHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- Environmental Damage at High Temperature: 25.1 OxidationDocument19 pagesEnvironmental Damage at High Temperature: 25.1 OxidationCHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- Wang 2014Document21 pagesWang 2014CHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- 07.analysis of The Grain Boundary Microstructure and DegradationDocument4 pages07.analysis of The Grain Boundary Microstructure and Degradationhassan ghorbaniNo ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: 10.1016/j.energy.2017.12.163Document33 pagesAccepted Manuscript: 10.1016/j.energy.2017.12.163CHONKARN CHIABLAMNo ratings yet
- Bill - AKIJDocument3 pagesBill - AKIJm.tanjil2005No ratings yet
- Full Download Human Biology 11th Edition Starr Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Human Biology 11th Edition Starr Solutions Manualsheathe.zebrinny.53vubg100% (41)
- Celestino vs. CIRDocument6 pagesCelestino vs. CIRchristopher d. balubayanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Object Oriented Database: Unit-IDocument67 pagesIntroduction To Object Oriented Database: Unit-Ipreetham rNo ratings yet
- 2019q123.ev3-Descon Engro Level Gauges-QDocument7 pages2019q123.ev3-Descon Engro Level Gauges-Qengr_umer_01No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE Physics 0625 Complete Notes PDocument5 pagesCambridge IGCSE Physics 0625 Complete Notes PYamikani ManthandoNo ratings yet
- JAMB Syllabus For BiologyDocument27 pagesJAMB Syllabus For BiologyOluebube UchennaNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of Ashok LeylandDocument120 pagesFinancial Analysis of Ashok LeylandSiva Kumaravel0% (1)
- L15 PDFDocument15 pagesL15 PDFlesNo ratings yet
- PLX Model OfficialDocument105 pagesPLX Model OfficialBảo Ngọc LêNo ratings yet
- AMX Prodigy Install ManualDocument13 pagesAMX Prodigy Install Manualsundevil2010usa4605No ratings yet
- Light Dimmer CircuitsDocument14 pagesLight Dimmer CircuitskapilasriNo ratings yet
- Catphan®604 ManualDocument34 pagesCatphan®604 ManualTold Told LeungNo ratings yet
- CE Laws L8 L15Document470 pagesCE Laws L8 L15Edwin BernatNo ratings yet
- Program Logic FormulationDocument69 pagesProgram Logic FormulationIan OffemariaNo ratings yet
- GCG Damri SurabayaDocument11 pagesGCG Damri SurabayaEndang SusilawatiNo ratings yet
- MT4 EA Installation Guide Digital - EnglishDocument7 pagesMT4 EA Installation Guide Digital - EnglishThe Trading PitNo ratings yet
- Loan Agreement: Acceleration ClauseDocument2 pagesLoan Agreement: Acceleration ClauseSomething SuspiciousNo ratings yet
- Introductions and Basic Personal Information (In/Formal Communication)Document6 pagesIntroductions and Basic Personal Information (In/Formal Communication)juan morenoNo ratings yet
- Episode Transcript: Episode 34 - Chinese Han Lacquer CupDocument2 pagesEpisode Transcript: Episode 34 - Chinese Han Lacquer CupParvathy SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Hotel Voucher: Itinerary ID Hotel Santika Taman Mini Indonesia IndahDocument2 pagesHotel Voucher: Itinerary ID Hotel Santika Taman Mini Indonesia IndahSyukron PribadiNo ratings yet
- Castle CrashesDocument21 pagesCastle Crasheswicked wolfNo ratings yet
- Keira Knightley: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument12 pagesKeira Knightley: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchCrina LupuNo ratings yet
- Titus Selection of DiffuserDocument14 pagesTitus Selection of DiffuserhanyassawyNo ratings yet
- 30xa 100t PDFDocument162 pages30xa 100t PDFleung ka kitNo ratings yet
- WebMethods System Requirements 8xDocument7 pagesWebMethods System Requirements 8xmaxprinceNo ratings yet
- SOP For Operation & Calibration of PH Meter - QualityGuidancesDocument9 pagesSOP For Operation & Calibration of PH Meter - QualityGuidancesfawaz khalilNo ratings yet