Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math g7 m3 Topic C Lesson 17 Teacher
Uploaded by
Angelina Uruchima-CabreraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Math g7 m3 Topic C Lesson 17 Teacher
Uploaded by
Angelina Uruchima-CabreraCopyright:
Available Formats
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 17 7•3
Lesson 17: The Area of a Circle
Student Outcomes
Students give an informal derivation of the relationship between the circumference and area of a circle.
Students know the formula for the area of a circle and use it to solve problems.
Lesson Notes
Remind students of the definitions for circle and circumference from the previous lesson. The Opening
Exercise is a lead-in to the derivation of the formula for the area of a circle.
Not only do students need to know and be able to apply the formula for the area of a circle, it is critical for
them to also be able to draw the diagram associated with each problem in order to solve it successfully.
Students must be able to translate words into mathematical expressions and equations and be able to
determine which parts of the problem are known and which are unknown or missing.
Classwork
Exercises 1–3 (4 minutes)
Exercises 1–3
Solve the problem below individually. Explain your solution.
1. Find the radius of a circle if its circumference is 𝟑𝟕. 𝟔𝟖 inches. Use 𝝅 ≈ 𝟑. 𝟏𝟒.
If 𝑪 = 𝟐𝝅𝒓, then 𝟑𝟕. 𝟔𝟖 = 𝟐𝝅𝒓. Solving the equation for 𝒓,
𝟑𝟕. 𝟔𝟖 = 𝟐𝝅𝒓
𝟏 𝟏
( ) 𝟑𝟕. 𝟔𝟖 = ( ) 𝟐𝝅𝒓
𝟐𝝅 𝟐𝝅
𝟏
(𝟑𝟕. 𝟔𝟖) ≈ 𝒓
𝟔. 𝟐𝟖
𝟔≈𝒓
The radius of the circle is approximately 𝟔 𝐢𝐧.
2. Determine the area of the rectangle below. Name two ways that can be used to find the area of the rectangle.
The area of the rectangle is 𝟐𝟒 𝐜𝐦𝟐. The area can be found by counting the square units inside the rectangle or by
multiplying the length (𝟔 𝐜𝐦) by the width (𝟒 𝐜𝐦).
Lesson 17: The Area of a Circle
252
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G7-M3-TE-1.3.0-08.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 17 7•3
3. Find the length of a rectangle if the area is 𝟐𝟕 𝐜𝐦𝟐 and the width is 𝟑 𝐜𝐦.
If the area of the rectangle is 𝐀𝐫𝐞𝐚 = 𝐥𝐞𝐧𝐠𝐭𝐡 ∙ 𝐰𝐢𝐝𝐭𝐡, then
𝟐𝟕 𝐜𝐦𝟐 = 𝐥 ∙ 𝟑 𝐜𝐦
𝟏 𝟏
⋅ 𝟐𝟕 𝐜𝐦𝟐 = ⋅ 𝒍 ⋅ 𝟑 𝐜𝐦
𝟑 𝟑
𝟗 𝐜𝐦 = 𝒍
Exploratory Challenge (10 minutes)
Complete the exercise below. Scaffolding:
Provide a circle divided into 16
Exploratory Challenge equal sections for students to
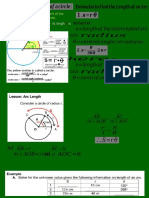
To find the formula for the area of a circle, cut a circle into 𝟏𝟔 equal pieces. cut out and reassemble as a
rectangle.
Arrange the triangular wedges by alternating the “triangle” directions and sliding them together to make a
MP.7 “parallelogram.” Cut the triangle on the left side in half on the given line, and slide the outside half of the triangle to the
other end of the parallelogram in order to create an approximate “rectangle.”
Move half to the other end.
The circumference is 𝟐𝝅𝒓, where the radius is 𝒓. Therefore, half of the circumference is 𝝅𝒓.
Lesson 17: The Area of a Circle
253
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G7-M3-TE-1.3.0-08.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 17 7•3
What is the area of the “rectangle” using the side lengths above?
The area of the “rectangle” is base times height, and, in this case, 𝑨 = 𝝅𝒓 ∙ 𝒓.
Are the areas of the “rectangle” and the circle the same?
Yes, since we just rearranged pieces of the circle to make the “rectangle,” the area of the “rectangle” and the area of the
circle are approximately equal. Note that the more sections we cut the circle into, the closer the approximation.
If the area of the rectangular shape and the circle are the same, what is the area of the circle?
The area of a circle is written as 𝑨 = 𝝅𝒓 ∙ 𝒓, or 𝑨 = 𝝅𝒓𝟐 .
Example 1 (4 minutes)
Example 1
Use the shaded square centimeter units to approximate the area of the circle.
What is the radius of the circle?
𝟏𝟎 𝐜𝐦
What would be a quicker method for determining the area of the circle other than counting all of the squares in the entire
circle?
𝟏
Count of the squares needed; then, multiply that by four in order to determine the area of the entire circle.
𝟒
Using the diagram, how many squares were used to cover one-fourth of the circle?
The area of one-fourth of the circle is approximately 𝟕𝟗 𝐜𝐦𝟐.
What is the area of the entire circle?
𝑨 ≈ 𝟒 ∙ 𝟕𝟗 𝐜𝐦𝟐
𝑨 ≈ 𝟑𝟏𝟔 𝐜𝐦𝟐
Lesson 17: The Area of a Circle
254
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G7-M3-TE-1.3.0-08.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 17 7•3
Example 2 (4 minutes)
Example 2
A sprinkler rotates in a circular pattern and sprays water over a distance of 𝟏𝟐 feet. What is the area of the circular
region covered by the sprinkler? Express your answer to the nearest square foot.
Draw a diagram to assist you in solving the problem. What does the distance of 𝟏𝟐 feet represent in this problem?
The radius is 𝟏𝟐 feet.
What information is needed to solve the problem?
The formula to find the area of a circle is 𝑨 = 𝝅𝒓𝟐 . If the radius is 𝟏𝟐 𝐟𝐭., then 𝑨 = 𝝅 ∙ (𝟏𝟐 𝐟𝐭. )𝟐 = 𝟏𝟒𝟒𝝅 𝐟𝐭 𝟐, or
approximately 𝟒𝟓𝟐 𝐟𝐭 𝟐.
Make a point of telling students that an answer in exact form is in terms of 𝜋, not substituting an approximation of pi.
Example 3 (4 minutes)
Example 3
Suzanne is making a circular table out of a square piece of wood. The radius of the circle that she is cutting is 𝟑 feet. How
much waste will she have for this project? Express your answer to the nearest square foot.
Draw a diagram to assist you in solving the problem. What does the distance of 𝟑 feet represent in this problem?
The radius of the circle is 𝟑 feet.
What information is needed to solve the problem?
The area of the circle and the area of the square are needed so that we can subtract the area of the circle from the area of
the square to determine the amount of waste.
What information do we need to determine the area of the square and the circle?
Circle: just radius because 𝑨 = 𝝅𝒓𝟐 Square: one side length
Lesson 17: The Area of a Circle
255
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G7-M3-TE-1.3.0-08.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 17 7•3
How will we determine the waste?
The waste is the area left over from the square after cutting out the circular region. The area of the circle is
𝑨 = 𝝅 ∙ (𝟑 𝐟𝐭. )𝟐 = 𝟗𝝅 𝐟𝐭 𝟐 ≈ 𝟐𝟖. 𝟐𝟔 𝐟𝐭 𝟐 . The area of the square is found by first finding the diameter of the circle, which is
the same as the side of the square. The diameter is 𝒅 = 𝟐𝒓; so, 𝒅 = 𝟐 ∙ 𝟑 𝐟𝐭. or 𝟔 𝐟𝐭. The area of a square is found by
multiplying the length and width, so 𝑨 = 𝟔 𝐟𝐭. ∙ 𝟔 𝐟𝐭. = 𝟑𝟔 𝐟𝐭 𝟐 . The solution is the difference between the area of the
square and the area of the circle, so 𝟑𝟔 𝐟𝐭 𝟐 − 𝟐𝟖. 𝟐𝟔 𝐟𝐭 𝟐 ≈ 𝟕. 𝟕𝟒 𝐟𝐭 𝟐.
Does your solution answer the problem as stated?
Yes, the amount of waste is 𝟕. 𝟕𝟒 𝐟𝐭 𝟐 .
Exercises 4–6 (11 minutes)
Solve in cooperative groups of two or three.
Exercises 4–6
4. A circle has a radius of 𝟐 cm.
a. Find the exact area of the circular region.
𝐀 = 𝛑 ∙ (𝟐 𝐜𝐦)𝟐 = 𝟒𝛑 𝐜𝐦𝟐
b. Find the approximate area using 𝟑. 𝟏𝟒 to approximate 𝛑.
𝐀 = 𝟒 𝐜𝐦𝟐 ∙ 𝛑 ≈ 𝟒 𝐜𝐦𝟐 ∙ 𝟑. 𝟏𝟒 ≈ 𝟏𝟐. 𝟓𝟔 𝐜𝐦𝟐
5. A circle has a radius of 𝟕 cm.
a. Find the exact area of the circular region.
𝐀 = 𝛑 ∙ (𝟕 𝐜𝐦)𝟐 = 𝟒𝟗𝛑 𝐜𝐦𝟐
𝟐𝟐
b. Find the approximate area using to approximate 𝛑.
𝟕
𝟐𝟐
𝐀 = 𝟒𝟗 ∙ 𝛑 𝐜𝐦𝟐 ≈ (𝟒𝟗 ∙ ) 𝐜𝐦𝟐 ≈ 𝟏𝟓𝟒 𝐜𝐦𝟐
𝟕
c. What is the circumference of the circle?
𝐂 = 𝟐𝛑 ∙ 𝟕 𝐜𝐦 = 𝟏𝟒𝛑 𝐜𝐦 ≈ 𝟒𝟑. 𝟗𝟔 𝐜𝐦
6. Joan determined that the area of the circle below is 𝟒𝟎𝟎𝝅 𝐜𝐦𝟐 . Melinda says that Joan’s solution is incorrect; she
believes that the area is 𝟏𝟎𝟎𝝅 𝐜𝐦𝟐. Who is correct and why?
Melinda is correct. Joan found the area by multiplying 𝝅 by the square of 𝟐𝟎 𝐜𝐦 (which
is the diameter) to get a result of 𝟒𝟎𝟎𝝅 𝐜𝐦𝟐, which is incorrect. Melinda found that the
radius was 𝟏𝟎 𝐜𝐦 (half of the diameter). Melinda multiplied 𝝅 by the square of the
radius to get a result of 𝟏𝟎𝟎𝝅 𝐜𝐦𝟐.
Lesson 17: The Area of a Circle
256
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G7-M3-TE-1.3.0-08.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 17 7•3
Closing (4 minutes)
Strategies for problem solving include drawing a diagram to represent the problem and identifying the given
information and needed information to solve the problem.
Using the original circle in this lesson, cut it into 64 equal slices. Reassemble the figure. What do you notice?
It looks more like a rectangle.
Ask students to imagine repeating the slicing into even thinner slices (infinitely thin). Then, ask the next two questions.
What does the length of the rectangle become?
An approximation of half of the circumference of the circle
What does the width of the rectangle become?
An approximation of the radius
1
Thus, we conclude that the area of the circle is 𝐴 = 𝐶𝑟.
2
1 1
If 𝐴 = 𝐶𝑟, then 𝐴 = ∙ 2𝜋𝑟 ∙ 𝑟 or 𝐴 = 𝜋𝑟 2 .
2 2
Also see video link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YokKp3pwVFc
Relevant Vocabulary
CIRCULAR REGION (OR DISK): Given a point 𝑪 in the plane and a number 𝒓 > 𝟎, the circular region (or disk) with center 𝑪 and
radius 𝒓 is the set of all points in the plane whose distance from the point 𝑪 is less than or equal to 𝒓.
The boundary of a disk is a circle. The area of a circle refers to the area of the disk defined by the circle.
Exit Ticket (4 minutes)
Lesson 17: The Area of a Circle
257
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G7-M3-TE-1.3.0-08.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 17 7•3
Name ___________________________________________________ Date____________________
Lesson 17: The Area of a Circle
Exit Ticket
Complete each statement using the words or algebraic expressions listed in the word bank below.
1. The length of the
of
the rectangular region
approximates the length of
the
of the circle.
2. The
of the rectangle
approximates the length of
one-half of the
circumference of the
circle.
3. The circumference of the circle is _______________________.
4. The _________________ of the ___________________ is 2𝑟.
5. The ratio of the circumference to the diameter is ______.
1 1
6. Area (circle) = Area of (_____________) = ∙ circumference ∙ 𝑟 = (2𝜋𝑟) ∙ 𝑟 = 𝜋 ∙ 𝑟 ∙ 𝑟 = _____________.
2 2
Word bank
radius height base 𝟐𝝅𝒓
diameter circle rectangle 𝝅𝒓𝟐 𝝅
Lesson 17: The Area of a Circle
258
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G7-M3-TE-1.3.0-08.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 17 7•3
Exit Ticket Sample Solutions
Complete each statement using the words or algebraic expressions listed in the word bank below.
1. The length of the height of the rectangular region approximates the length of the radius of the circle.
2. The base of the rectangle approximates the length of one-half of the circumference of the circle.
3. The circumference of the circle is 𝟐𝛑𝐫.
4. The diameter of the circle is 𝟐𝐫.
5. The ratio of the circumference to the diameter is 𝝅.
𝟏 𝟏
6. Area (circle) = Area of (rectangle) = ∙ 𝐜𝐢𝐫𝐜𝐮𝐦𝐟𝐞𝐫𝐞𝐧𝐜𝐞 ∙ 𝒓 = (𝟐𝝅𝒓) ∙ 𝒓 = 𝝅 ∙ 𝒓 ∙ 𝒓 = 𝛑𝐫 𝟐 .
𝟐 𝟐
Problem Set Sample Solutions
𝟐𝟐
1. The following circles are not drawn to scale. Find the area of each circle. (Use as an approximation for 𝝅.)
𝟕
𝟒𝟓
𝐜𝐦
𝟐
𝟑𝟒𝟔. 𝟓 𝐜𝐦𝟐 𝟓, 𝟏𝟓𝟓. 𝟏 𝐟𝐭 𝟐 𝟏, 𝟓𝟗𝟏. 𝟏 𝐜𝐦𝟐
2. A circle has a diameter of 𝟐𝟎 inches.
a. Find the exact area, and find an approximate area using 𝝅 ≈ 𝟑. 𝟏𝟒.
If the diameter is 𝟐𝟎 𝐢𝐧., then the radius is 𝟏𝟎 𝐢𝐧. If 𝐀 = 𝛑𝐫 𝟐, then 𝐀 = 𝛑 ∙ (𝟏𝟎 𝐢𝐧. )𝟐 or 𝟏𝟎𝟎𝛑 𝐢𝐧𝟐 .
𝐀 ≈ (𝟏𝟎𝟎 ∙ 𝟑. 𝟏𝟒) 𝐢𝐧𝟐 ≈ 𝟑𝟏𝟒 𝐢𝐧𝟐 .
b. What is the circumference of the circle using 𝝅 ≈ 𝟑. 𝟏𝟒 ?
If the diameter is 𝟐𝟎 𝐢𝐧., then the circumference is 𝐂 = 𝛑𝐝 or 𝐂 ≈ 𝟑. 𝟏𝟒 ∙ 𝟐𝟎 𝐢𝐧. ≈ 𝟔𝟐. 𝟖 𝐢𝐧.
3. A circle has a diameter of 𝟏𝟏 inches.
a. Find the exact area and an approximate area using 𝝅 ≈ 𝟑. 𝟏𝟒.
𝟐
𝟏𝟏 𝟏𝟏 𝟏𝟐𝟏
If the diameter is 𝟏𝟏 𝐢𝐧., then the radius is 𝐢𝐧. If 𝐀 = 𝛑𝐫 𝟐, then 𝐀 = 𝛑 ∙ ( 𝐢𝐧. ) or 𝛑 𝐢𝐧𝟐 .
𝟐 𝟐 𝟒
𝟏𝟐𝟏
𝐀≈( ∙ 𝟑. 𝟏𝟒) 𝐢𝐧𝟐 ≈ 𝟗𝟒. 𝟗𝟖𝟓 𝐢𝐧𝟐
𝟒
b. What is the circumference of the circle using 𝝅 ≈ 𝟑. 𝟏𝟒?
If the diameter is 𝟏𝟏 inches, then the circumference is 𝐂 = 𝛑𝐝 or 𝐂 ≈ 𝟑. 𝟏𝟒 ∙ 𝟏𝟏 𝐢𝐧. ≈ 𝟑𝟒. 𝟓𝟒 𝐢𝐧.
Lesson 17: The Area of a Circle
259
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G7-M3-TE-1.3.0-08.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 17 7•3
4. Using the figure below, find the area of the circle.
In this circle, the diameter is the same as the length of the side of the square. The diameter is 𝟏𝟎 𝐜𝐦; so, the radius
is 𝟓 𝐜𝐦. 𝑨 = 𝝅𝒓𝟐 , so 𝑨 = 𝝅(𝟓 𝐜𝐦)𝟐 = 𝟐𝟓𝝅 𝐜𝐦𝟐.
5. A path bounds a circular lawn at a park. If the inner edge of the path is 𝟏𝟑𝟐 𝐟𝐭. around, approximate the amount of
𝟐𝟐
area of the lawn inside the circular path. Use 𝝅 ≈ .
𝟕
The length of the path is the same as the circumference. Find the radius from the circumference; then, find the area.
𝑪 = 𝟐𝝅𝒓
𝟐𝟐
𝟏𝟑𝟐 𝐟𝐭. ≈ 𝟐 ∙ ∙𝒓
𝟕
𝟒𝟒
𝟏𝟑𝟐 𝐟𝐭. ≈ 𝒓
𝟕
𝟕 𝟕 𝟒𝟒
∙ 𝟏𝟑𝟐 𝐟𝐭. ≈ ∙ 𝒓
𝟒𝟒 𝟒𝟒 𝟕
𝟐𝟏 𝐟𝐭. ≈ 𝒓
𝟐𝟐
𝑨≈ ∙ (𝟐𝟏 𝐟𝐭. )𝟐
𝟕
𝑨 ≈ 𝟏𝟑𝟖𝟔 𝐟𝐭 𝟐
6. The area of a circle is 𝟑𝟔𝝅 𝐜𝐦𝟐. Find its circumference.
Find the radius from the area of the circle; then, use it to find the circumference.
𝑨 = 𝝅𝒓𝟐
𝟑𝟔𝝅 𝐜𝐦𝟐 = 𝝅𝒓𝟐
𝟏 𝟏
∙ 𝟑𝟔𝝅 𝐜𝐦𝟐 = ∙ 𝝅𝒓𝟐
𝝅 𝝅
𝟑𝟔 𝐜𝐦𝟐 = 𝒓𝟐
𝟔 𝐜𝐦 = 𝒓
𝑪 = 𝟐𝝅𝒓
𝑪 = 𝟐𝝅 ∙ 𝟔 𝐜𝐦
𝑪 = 𝟏𝟐𝝅 𝐜𝐦
7. Find the ratio of the area of two circles with radii 𝟑 𝐜𝐦 and 𝟒 𝐜𝐦.
The area of the circle with radius 𝟑 𝐜𝐦 is 𝟗𝝅 𝐜𝐦𝟐 . The area of the circle with the radius 𝟒 𝐜𝐦 is 𝟏𝟔𝝅 𝐜𝐦𝟐 . The ratio
of the area of the two circles is 𝟗𝝅 ∶ 𝟏𝟔𝝅 or 𝟗 ∶ 𝟏𝟔.
Lesson 17: The Area of a Circle
260
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G7-M3-TE-1.3.0-08.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 17 7•3
8. If one circle has a diameter of 𝟏𝟎 𝐜𝐦 and a second circle has a diameter of 𝟐𝟎 𝐜𝐦, what is the ratio of the area of
the larger circle to the area of the smaller circle?
The area of the circle with the diameter of 𝟏𝟎 𝐜𝐦 has a radius of 𝟓 𝐜𝐦. The area of the circle with the diameter of
𝟏𝟎 𝐜𝐦 is 𝝅 ∙ (𝟓 𝐜𝐦)𝟐, or 𝟐𝟓𝝅 𝐜𝐦𝟐. The area of the circle with the diameter of 𝟐𝟎 𝐜𝐦 has a radius of 𝟏𝟎 𝐜𝐦. The
area of the circle with the diameter of 𝟐𝟎 𝐜𝐦 is 𝝅 ∙ (𝟏𝟎 𝐜𝐦)𝟐 or 𝟏𝟎𝟎𝝅 𝐜𝐦𝟐. The ratio of the diameters is 𝟐𝟎 to 𝟏𝟎
or 𝟐: 𝟏, while the ratio of the areas is 𝟏𝟎𝟎𝝅 𝒕o 𝟐𝟓𝝅 or 𝟒: 𝟏.
9. Describe a rectangle whose perimeter is 𝟏𝟑𝟐 𝐟𝐭. and whose area is less than 𝟏 𝐟𝐭 𝟐 . Is it possible to find a circle
whose circumference is 𝟏𝟑𝟐 𝐟𝐭. and whose area is less than 𝟏 𝐟𝐭 𝟐? If not, provide an example or write a sentence
explaining why no such circle exists.
A rectangle that has a perimeter of 𝟏𝟑𝟐 𝐟𝐭. can have a length of 𝟔𝟓. 𝟗𝟗𝟓 𝐟𝐭. and a width of 𝟎 . 𝟎𝟎𝟓 𝐟𝐭. The area of
such a rectangle is 𝟎. 𝟑𝟐𝟗𝟗𝟕𝟓 𝐟𝐭 𝟐 , which is less than 𝟏 𝐟𝐭 𝟐. No, because a circle that has a circumference of 𝟏𝟑𝟐 𝐟𝐭.
has a radius of approximately 𝟐𝟏 𝐟𝐭.
𝑨 = 𝝅𝒓𝟐 = 𝝅(𝟐𝟏)𝟐 = 𝟏𝟑𝟖𝟕. 𝟗𝟔 ≠ 𝟏
10. If the diameter of a circle is double the diameter of a second circle, what is the ratio of the area of the first circle to
the area of the second?
If I choose a diameter of 𝟐𝟒 𝐜𝐦 for the first circle, then the diameter of the second circle is 𝟏𝟐 𝐜𝐦. The first circle
has a radius of 𝟏𝟐 𝐜𝐦 and an area of 𝟏𝟒𝟒𝝅 𝐜𝐦𝟐. The second circle has a radius of 𝟔 𝐜𝐦 and an area of 𝟑𝟔𝝅 𝐜𝐦𝟐.
The ratio of the area of the first circle to the second is 𝟏𝟒𝟒𝝅 to 𝟑𝟔𝝅 , which is a 𝟒 to 𝟏 ratio. The ratio of the
diameters is 𝟐, while the ratio of the areas is the square of 𝟐, or 𝟒.
Lesson 17: The Area of a Circle
261
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G7-M3-TE-1.3.0-08.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
You might also like
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Math g7 m3 Topic C Lesson 22 TeacherDocument12 pagesMath g7 m3 Topic C Lesson 22 TeacherAzwa NadhiraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 21: Volume of Composite Solids: Student OutcomesDocument11 pagesLesson 21: Volume of Composite Solids: Student OutcomesIrene BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7: Creating and Solving Quadratic Equations in One VariableDocument8 pagesLesson 7: Creating and Solving Quadratic Equations in One VariableZeinab ElkholyNo ratings yet
- Math g7 m6 Topic D Lesson 20 TeacherDocument11 pagesMath g7 m6 Topic D Lesson 20 TeacherTylerShawNo ratings yet
- Class 22-Differentiation - Rates of Change and Stationary PointsDocument12 pagesClass 22-Differentiation - Rates of Change and Stationary PointsIndar SoochitNo ratings yet
- Plane AreasDocument16 pagesPlane AreasChristine Ann MumarNo ratings yet
- MATH 27 LECTURE GUIDE ON APPLICATIONS OF THE DEFINITE INTEGRALDocument22 pagesMATH 27 LECTURE GUIDE ON APPLICATIONS OF THE DEFINITE INTEGRALBryan Gerard GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Maximum Area of an Inscribed Rectangle in an EllipseDocument13 pagesMaximum Area of an Inscribed Rectangle in an EllipseRemalyn Villahermosa FajardoNo ratings yet
- Math g7 m6 Topic A Lesson 4 TeacherDocument11 pagesMath g7 m6 Topic A Lesson 4 TeacherENo ratings yet
- Volume of A Solid of RevolutionDocument14 pagesVolume of A Solid of RevolutionChristine Ann MumarNo ratings yet
- Circular Functions and TrigonometryDocument6 pagesCircular Functions and TrigonometryLorraine SabbaghNo ratings yet
- Surface Area of A ConeDocument15 pagesSurface Area of A ConeMyla Mae BalalaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 15: The Distance From A Point To A Line: Student OutcomesDocument10 pagesLesson 15: The Distance From A Point To A Line: Student OutcomeshakkensNo ratings yet
- 173414Document13 pages173414Inaaya MehboobNo ratings yet
- Detailed Trigonometry Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesDetailed Trigonometry Lesson Plangeorge taclobaoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Exam Example 1Document2 pagesEngineering Exam Example 1fahimsiddique.vfs2No ratings yet
- Electrodynamics & Optics: Tutorial# 10Document34 pagesElectrodynamics & Optics: Tutorial# 10TybuNo ratings yet
- 2023 G9 S6 CevasMenelaus-SCDocument8 pages2023 G9 S6 CevasMenelaus-SCMeme 2020No ratings yet
- Mensuration Formulas & ProblemsDocument14 pagesMensuration Formulas & ProblemsNot Ismdan100% (1)
- Q2W2 Lecture Precalculus FloresDocument16 pagesQ2W2 Lecture Precalculus FloresTroll HughNo ratings yet
- Math g7 m6 Topic D Lesson 22 TeacherDocument11 pagesMath g7 m6 Topic D Lesson 22 TeacherJeon JungkookNo ratings yet
- SLM 4 Trigonometric Ratios of Special Angles 22 23Document10 pagesSLM 4 Trigonometric Ratios of Special Angles 22 23Kate Megan ApuliNo ratings yet
- Q4 STEM Pre Caculus Week1Document4 pagesQ4 STEM Pre Caculus Week1Ykhay ElfanteNo ratings yet
- Math g8 m2 Topic C Lesson 12 Teacher PDFDocument9 pagesMath g8 m2 Topic C Lesson 12 Teacher PDFIsmail AbariNo ratings yet
- Corepure1 Chapter 5::: Volumes of RevolutionDocument19 pagesCorepure1 Chapter 5::: Volumes of RevolutionJon HadleyNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Basic TrigonometryDocument47 pages5.1 Basic TrigonometrymonaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Conical PendulumDocument9 pagesExperiment 4 Conical PendulumKassy MondidoNo ratings yet
- Section 16 - 5 NotesDocument4 pagesSection 16 - 5 NotesAnonymous L21MIUqANo ratings yet
- 4A'S Lesson Plan - Solving Problems Involving KiteDocument9 pages4A'S Lesson Plan - Solving Problems Involving KiteJonel ValdezNo ratings yet
- The First Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Second Fundamental Theorem of CalculusDocument7 pagesThe First Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculuskierby sanbagrielNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document7 pagesModule 5shaina sucgangNo ratings yet
- 1 3 Guide Notes TE Converting Fractions and DecimalsDocument3 pages1 3 Guide Notes TE Converting Fractions and DecimalsSHAFFAF LATHEEFNo ratings yet
- Math g7 m6 Topic A Lesson 3 TeacherDocument12 pagesMath g7 m6 Topic A Lesson 3 TeacherKyra LewisNo ratings yet
- IGCSEFM TrigonometryII 3DTrigSineCosineDocument28 pagesIGCSEFM TrigonometryII 3DTrigSineCosinesreelakshmi100% (1)
- Multiple IntegralsDocument54 pagesMultiple IntegralsDK White LionNo ratings yet
- Volume of Prism, Cylinder and SphereDocument6 pagesVolume of Prism, Cylinder and SphereXlyth RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Optics Day2 (Tuition)Document32 pagesOptics Day2 (Tuition)Akdev SahaNo ratings yet
- Arc Length and Sector AreaDocument8 pagesArc Length and Sector AreaTroll HughNo ratings yet
- Math g6 m5 Topic A Lesson 4 TeacherDocument11 pagesMath g6 m5 Topic A Lesson 4 TeacherAfshiya AnjumNo ratings yet
- Basic Maths For Civil Engineering - Sandeep JyaniDocument45 pagesBasic Maths For Civil Engineering - Sandeep JyaniVenkata RamanaNo ratings yet
- Sco Supplementary OnewtwowayDocument18 pagesSco Supplementary OnewtwowayOkay SigNo ratings yet
- Notes On Trig Identities Part 3Document10 pagesNotes On Trig Identities Part 3dustinosugodNo ratings yet
- Rate of Change and Small ChangeDocument3 pagesRate of Change and Small ChangeIr_tuxedoNo ratings yet
- Math9 Q4 W8Document6 pagesMath9 Q4 W8Maria Eleonor BanaresNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Determining Volumes by Slicing, Mat 2280 2.3 Cylindrical Shells, Mat 2280Document15 pages2.2 Determining Volumes by Slicing, Mat 2280 2.3 Cylindrical Shells, Mat 2280Olivier UwamahoroNo ratings yet
- Finding the Definite Integral AreaDocument3 pagesFinding the Definite Integral AreaMA LEAH I ABADNo ratings yet
- Math 9 As Q2 Week 4Document2 pagesMath 9 As Q2 Week 4Jomar JamonNo ratings yet
- Lecture Seven: 1.derivatives of Exponential and Logarithm Functions 2. Applied OptimizationDocument8 pagesLecture Seven: 1.derivatives of Exponential and Logarithm Functions 2. Applied OptimizationEdi MuhammNo ratings yet
- Q3 LC39c Special Right TriangleDocument31 pagesQ3 LC39c Special Right TrianglePaul John PachecoNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus: Stokes TheoremDocument36 pagesVector Calculus: Stokes TheoremSiti HajarNo ratings yet
- 1 Calculus IDocument17 pages1 Calculus IArchie GardoceNo ratings yet
- Pattern Classification 10. Linear Perceptron, Least Squares & Multi-Layer NnsDocument38 pagesPattern Classification 10. Linear Perceptron, Least Squares & Multi-Layer NnsMostafa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Week 8Document65 pagesWeek 8sunil kumar sahNo ratings yet
- Tut 12 PostDocument13 pagesTut 12 PostYeeSun CheungNo ratings yet
- Math Internal Assessment: Comparing The Rate at Which A Popsicle and A Scoop of Ice Cream Melt SyllabusDocument19 pagesMath Internal Assessment: Comparing The Rate at Which A Popsicle and A Scoop of Ice Cream Melt SyllabusJayden OoiNo ratings yet
- MathsTraks: Geometry: A Collection of Blackline Masters for ages 11-14From EverandMathsTraks: Geometry: A Collection of Blackline Masters for ages 11-14No ratings yet
- Temple Entry Movement and Nationalist Agitation in KeralaDocument25 pagesTemple Entry Movement and Nationalist Agitation in Keralahodhistory100% (4)
- Project Management Using Critical Path Method (CPM) - Apragmatic StudyDocument11 pagesProject Management Using Critical Path Method (CPM) - Apragmatic StudyNizam HasniNo ratings yet
- SHDP TizonDocument29 pagesSHDP TizonRonnel Alegria RamadaNo ratings yet
- Paschal CHAPTER TWODocument20 pagesPaschal CHAPTER TWOIdoko VincentNo ratings yet
- 03 Petroleum Basins of Southern South America - An OverviewDocument15 pages03 Petroleum Basins of Southern South America - An Overviewfiorela anait vera parqueNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Cancer ChemotherapyDocument2 pagesBasic Principles of Cancer ChemotherapyGerardLum100% (2)
- 07Document30 pages07David MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics 1st Edition Ebook or PaperbackDocument1 pageMacroeconomics 1st Edition Ebook or PaperbackSurya DarmaNo ratings yet
- Advocate - Conflict of InterestDocument7 pagesAdvocate - Conflict of InterestZaminNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis of Performance Management in Football ClubDocument5 pagesCase Analysis of Performance Management in Football ClubShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- The Multi-Objective Decision Making Methods Based On MULTIMOORA and MOOSRA For The Laptop Selection ProblemDocument9 pagesThe Multi-Objective Decision Making Methods Based On MULTIMOORA and MOOSRA For The Laptop Selection ProblemAnkushNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Constitution of IndiaDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Constitution of IndiaCHRISTINA GAYEN MONDAL100% (1)
- Priniciples of Income Tax LawDocument646 pagesPriniciples of Income Tax LawRashid Hussain Wadho100% (1)
- Slingfox RC NotesDocument2 pagesSlingfox RC NotesgauravwordsNo ratings yet
- Ethics Performance Task RevisedDocument4 pagesEthics Performance Task Revisedapi-337051062No ratings yet
- CMRIT R18 Syllabus ME PDFDocument142 pagesCMRIT R18 Syllabus ME PDFMaddipudi RamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- PalosliosDocument12 pagesPalosliossuwijak76797679No ratings yet
- R69 Sepulveda V PelaezDocument2 pagesR69 Sepulveda V PelaezfranceheartNo ratings yet
- Imam Mahdi and Jesus Christ - 2023 ADDocument290 pagesImam Mahdi and Jesus Christ - 2023 ADSyed AbidiNo ratings yet
- Professional EthicsDocument2 pagesProfessional EthicsKoushik MeduriNo ratings yet
- 05 AHP and Scoring ModelsDocument32 pages05 AHP and Scoring ModelsIhjaz VarikkodanNo ratings yet
- Dawn Ullmann - ReferenceDocument1 pageDawn Ullmann - Referenceapi-418750957No ratings yet
- Question Text Please Refer To Figure 2 To Answer The Question Below: The Error in Figure 2 IsDocument32 pagesQuestion Text Please Refer To Figure 2 To Answer The Question Below: The Error in Figure 2 IsJohn Dexter Lanot100% (1)
- HRM - Final Project PresentationDocument9 pagesHRM - Final Project PresentationJeenifer SteavenNo ratings yet
- The Innovator's Secret WeaponDocument9 pagesThe Innovator's Secret WeaponNaval VaswaniNo ratings yet
- The State Historical Society of Missouri-Research Center, Kansas City Shsofmo-Kc@umsystem - EduDocument2 pagesThe State Historical Society of Missouri-Research Center, Kansas City Shsofmo-Kc@umsystem - Eduapi-302393994No ratings yet
- Ulep vs. Legal Clinic, Inc., 223 SCRA 378, Bar Matter No. 553 June 17, 1993Document19 pagesUlep vs. Legal Clinic, Inc., 223 SCRA 378, Bar Matter No. 553 June 17, 1993CherNo ratings yet
- Sept 2013 NewsletterDocument6 pagesSept 2013 NewsletterBKU1965No ratings yet
- InequalitiesDocument6 pagesInequalitiesapi-235135985No ratings yet
- Csir Ugc Net - Life Sciences - Free Sample TheoryDocument12 pagesCsir Ugc Net - Life Sciences - Free Sample TheorySyamala Natarajan100% (1)