Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Water Treatment Technology YCastro
Uploaded by
yovanny familian0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesThis document summarizes various water and wastewater treatment technologies including coagulation and flocculation to remove colloids, grit chambers to remove inorganic particles, sedimentation to separate suspended organics, filtration to remove residual solids, disinfection to eliminate pathogens, air floatation for wastewater containing emulsified oil, activated carbon absorption to remove certain organics and contaminants, aerobic treatment to convert organics to carbon dioxide and ammonia, and anaerobic digestion for sludge treatment and high strength wastewater.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes various water and wastewater treatment technologies including coagulation and flocculation to remove colloids, grit chambers to remove inorganic particles, sedimentation to separate suspended organics, filtration to remove residual solids, disinfection to eliminate pathogens, air floatation for wastewater containing emulsified oil, activated carbon absorption to remove certain organics and contaminants, aerobic treatment to convert organics to carbon dioxide and ammonia, and anaerobic digestion for sludge treatment and high strength wastewater.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesWater Treatment Technology YCastro
Uploaded by
yovanny familianThis document summarizes various water and wastewater treatment technologies including coagulation and flocculation to remove colloids, grit chambers to remove inorganic particles, sedimentation to separate suspended organics, filtration to remove residual solids, disinfection to eliminate pathogens, air floatation for wastewater containing emulsified oil, activated carbon absorption to remove certain organics and contaminants, aerobic treatment to convert organics to carbon dioxide and ammonia, and anaerobic digestion for sludge treatment and high strength wastewater.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
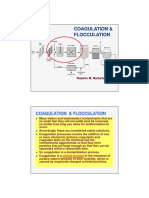
Coagulation and
Water Flocculation
and Wastewater Effective to form flocs
from colloids (1 -100 nm),
Treatment so that they can be
Technologies removed using
sedimentation or filtration.
Prof. Yessica Castro
Grit Chamber Sedimentation
Appropriate Separation of
technology to suspended organics
with particle size
separate inorganic
greater than 100 um
particles from water
from water, such as the
such as sand and
flocs formed during
metals. flocculation.
Filtration Disinfection
Removal of residual Elimination of most
suspended solids including pathogenic
minerals, fine flocs, and microorganisms from
microorganisms that cause water. The most popular
the water to be turbid. The disinfection methods are
main types of filters are free chlorine, Chlorine
slow and rapid sand filters. dioxide, UV, and Ozone.
Air Floatation Oil Separating Tank
Applicable to the treatment Suitable for the
of wastewater containing treatment of
emulsified oil such as in the
wastewater
petrochemical, machinery,
containing suspended
and food industries, as well as
oil, such as in the
the treatment of
petrochemical and
papermaking and dying
industries wastewaters. food industries.
Activated Ozonation
Carbon Oxidation process that not
only attack all
Absorption microorganisms
(disinfection), but also a
Effective in removing certain organics wide range of organic
(i.e. unwanted taste and odors, as well as and inorganic pollutants.
micropollutants), chlorine, fluorine, and Removes color, taste, and
radon from drinking or wastewater. odor.
Aerobic Treatment Anaerobic
Organic contaminants are
converted to carbon Digestion
dioxide, ammonia and some
additional gases in small Microorganisms convert organic matter
quantities, heat in large present in wastewater into a biofuel gas
quantities, and a final consisting of carbon dioxide, methane,
sludge product. and other end products. Used to treat
Eg. Activated sludge and aerobic lagoons sludge, and high strength wastewater.
You might also like
- Nduba Landfil1Document6 pagesNduba Landfil1rrutayisire50% (2)
- Sewage TreatmentDocument24 pagesSewage TreatmentGemrex Breva100% (1)
- Wastewater TrainDocument3 pagesWastewater TrainLester Mercado100% (1)
- Environmental Management Plan (EMP)Document2 pagesEnvironmental Management Plan (EMP)Cloyd Richard La RosaNo ratings yet
- Effluent Treatment PlantDocument16 pagesEffluent Treatment PlantVishal guptaNo ratings yet
- Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) Design Calculations - S.I. UnitsDocument37 pagesSequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) Design Calculations - S.I. UnitsOn Gnios Ingeniería67% (6)
- Iloilo City Regulation Ordinance 2017-127Document10 pagesIloilo City Regulation Ordinance 2017-127Iloilo City CouncilNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Treatment PlantDocument102 pagesWaste Water Treatment Plantksbbs100% (5)
- Ion Exchange Resins and Adsorbents in Chemical Processing: Second EditionFrom EverandIon Exchange Resins and Adsorbents in Chemical Processing: Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Sweage Treatment Plant (STP)Document57 pagesSweage Treatment Plant (STP)pra311288No ratings yet
- Sludge Treatment and DisposalDocument16 pagesSludge Treatment and Disposalsandhya bhattiNo ratings yet
- Process of de Mineralization PlantDocument13 pagesProcess of de Mineralization Plantmoinulriad100% (4)
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument30 pagesWaste Water TreatmentFatima IffatNo ratings yet
- Annex IV - Explained & Sewage Treatment-1Document8 pagesAnnex IV - Explained & Sewage Treatment-1Gaurav ShresthNo ratings yet
- Textile EffluentDocument8 pagesTextile EffluentargentevesNo ratings yet
- Role of MicroOrganism in Waste Water TreatmentDocument32 pagesRole of MicroOrganism in Waste Water Treatmentamita kumari100% (1)
- Action Plan: Bagamanoc Rural Development High SchoolDocument3 pagesAction Plan: Bagamanoc Rural Development High SchoolJINCKYMAY FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment AssignmentDocument14 pagesWastewater Treatment AssignmentKanishka JayalathNo ratings yet
- 3.1 - Wastewater Treatment SystemDocument37 pages3.1 - Wastewater Treatment SystemPEARL ANGELIE UMBANo ratings yet
- Sydney Water TourDocument5 pagesSydney Water TourSeavMeng SengNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Potable and SewageDocument35 pagesTreatment of Potable and SewagemohitdesigntreeNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous of Water Treatment Methods FinalDocument26 pagesMiscellaneous of Water Treatment Methods FinalAvie BañaresNo ratings yet
- IGNTU EContent 673390684976 B.SC EnvironmentalSciences 2 PallaviDas EnvironmentalPollutionandHumanHealth 3Document34 pagesIGNTU EContent 673390684976 B.SC EnvironmentalSciences 2 PallaviDas EnvironmentalPollutionandHumanHealth 3Riyasath ahamedNo ratings yet
- SewageDocument34 pagesSewageMongolian MutuNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Part2 TreatmentDocument25 pagesWastewater Part2 Treatmentmee chuenNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Treatment Through BiotechnologyDocument4 pagesWaste Water Treatment Through BiotechnologySaba CHNo ratings yet
- Waste Water NewTreatmentDocument32 pagesWaste Water NewTreatmentQuant R&DNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument28 pagesWaste Water TreatmentRoseNavyaNo ratings yet
- Chem Unit 1Document34 pagesChem Unit 1Ismaeel ShamsiNo ratings yet
- Module 03 - Water Treatment MethodsDocument5 pagesModule 03 - Water Treatment MethodsTamika AguilarNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document19 pagesUnit 5Parth TripahiNo ratings yet
- Waste TreatmentDocument36 pagesWaste TreatmentJiever Neil AustriaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Water TechnologyDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Water TechnologyGloria HicheNo ratings yet
- Publication - Drinking WaterDocument14 pagesPublication - Drinking WaterRavi JankarNo ratings yet
- Nanotech in Water RemediationDocument26 pagesNanotech in Water Remediationpriyadarsini parida100% (1)
- Water Resources: Part 3: DisinfectionDocument12 pagesWater Resources: Part 3: DisinfectionJohn KurongNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment NotesDocument13 pagesSewage Treatment Notesyashwanth h nNo ratings yet
- Waterwastewatertreatment 0Document24 pagesWaterwastewatertreatment 0Azka Januartrika100% (1)
- FullOzoneReport AclarusDocument32 pagesFullOzoneReport AclarusAdam FendrychNo ratings yet
- Watch Water® Initiative: Carbonblock - Titansorb 3 (Ts3)Document4 pagesWatch Water® Initiative: Carbonblock - Titansorb 3 (Ts3)Mehmet GülenerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19 Coagulation Flocculation B 2014Document49 pagesLecture 19 Coagulation Flocculation B 2014ProsperNo ratings yet
- Limbah Cair Dan PenanganannyaDocument89 pagesLimbah Cair Dan PenanganannyaDidit AhdiyatNo ratings yet
- Methods To Remove Dissolved and Colloidal Organic Matter: By: Ma. Ariela Mae V. RimbaoDocument25 pagesMethods To Remove Dissolved and Colloidal Organic Matter: By: Ma. Ariela Mae V. RimbaoarielaNo ratings yet
- Handout - Drinking WaterDocument12 pagesHandout - Drinking WaterRavi JankarNo ratings yet
- Table 1. Distillation: Distilled Water Herbicides PesticidesDocument9 pagesTable 1. Distillation: Distilled Water Herbicides Pesticidesgetahun esubalewNo ratings yet
- Water TreatmentDocument20 pagesWater TreatmentAnusha KumarasiriNo ratings yet
- Water TechnologyDocument2 pagesWater TechnologyVladimir Pascua CanaoNo ratings yet
- Screens: How Do Specific Water Purification Methods Work? 1 Physical Water PurificationDocument3 pagesScreens: How Do Specific Water Purification Methods Work? 1 Physical Water PurificationFhay BeeNo ratings yet
- SewageDocument43 pagesSewageyashwanth h nNo ratings yet
- Natural Organic Matter and Disinfection by Products 1Document5 pagesNatural Organic Matter and Disinfection by Products 1ooh daya IINo ratings yet
- Carbon FiltersDocument18 pagesCarbon FiltersAnabelle FernandezNo ratings yet
- Moduel 4 - SedimentationDocument28 pagesModuel 4 - SedimentationjagmalNo ratings yet
- OzoneDocument12 pagesOzoneAndreea GherghelNo ratings yet
- Technical PerformanceDocument19 pagesTechnical PerformanceMichael Huisa TaipeNo ratings yet
- IFI Ozonated Water (Feb 2017)Document3 pagesIFI Ozonated Water (Feb 2017)Vijay Rakesh Reddy SanikommuNo ratings yet
- gdwq4 With Add1 Annex5Document19 pagesgdwq4 With Add1 Annex5Keile Brugés PinedaNo ratings yet
- IGNTU Econtent 677113707754 M.SC EnvironmentalScience 2 PallaviDas EnvironmentalPollutionandControlTechnique I 5Document56 pagesIGNTU Econtent 677113707754 M.SC EnvironmentalScience 2 PallaviDas EnvironmentalPollutionandControlTechnique I 5vsumedhaNo ratings yet
- Alphabetical List of Water Treatment UnitsDocument4 pagesAlphabetical List of Water Treatment UnitsReena NasriNo ratings yet
- E. WWTP - TertiaryDocument10 pagesE. WWTP - Tertiaryzairulh7No ratings yet
- Tata Steel FRP VesselsDocument4 pagesTata Steel FRP VesselsR PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Topic3 Water Treatment Processes EffectsDocument124 pagesTopic3 Water Treatment Processes EffectsNUR ' AMIRAH BINTI ABDUL GHAFAR / UPMNo ratings yet
- Pollution & MicroorganismsDocument9 pagesPollution & MicroorganismshumeraNo ratings yet
- 03 Module 4 Lesson 2 Treatment and Disposal of Sewage and Industrial WastewaterDocument1 page03 Module 4 Lesson 2 Treatment and Disposal of Sewage and Industrial WastewaterBruce GreenNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Treatment and Sludge ManagementDocument27 pagesWaste Water Treatment and Sludge ManagementSujith KumarNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment ProcessesDocument9 pagesWater Treatment ProcessesMildred GwasiraNo ratings yet
- Test PortionsDocument34 pagesTest PortionsnickNo ratings yet
- Tertiary TreatmentDocument24 pagesTertiary TreatmentHrithik BaradiaNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Clean Water Act - RA 9275Document3 pagesThe Philippine Clean Water Act - RA 9275Kathleen Kaye CastilloNo ratings yet
- SWM Notes IIDocument8 pagesSWM Notes IIBeast gaming liveNo ratings yet
- Septic GuidelineDocument26 pagesSeptic Guidelinedzari6738No ratings yet
- 14 DohDocument27 pages14 DohAlex OppusNo ratings yet
- Carbonized Rice Hull As Water PurifierDocument10 pagesCarbonized Rice Hull As Water PurifierMariel JurillaNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste ManagementDocument10 pagesSolid Waste Managementammar sangeNo ratings yet
- Field Assignment On Feacal Sludge ManagementDocument10 pagesField Assignment On Feacal Sludge ManagementSarah NamyaloNo ratings yet
- Comparing Technologies - Conventional ASP, SBR, MBBR, MBRDocument3 pagesComparing Technologies - Conventional ASP, SBR, MBBR, MBRJanakiram GoudNo ratings yet
- Yeshwantrao Chavan College of Engineering: (Accredited 'A' Grade by NAAC With A Score of 3.25)Document47 pagesYeshwantrao Chavan College of Engineering: (Accredited 'A' Grade by NAAC With A Score of 3.25)Utkarsh GohatreNo ratings yet
- Hydrology - Civil Engineering - Ace Engineering Academy Study Material Free Download PDFDocument74 pagesHydrology - Civil Engineering - Ace Engineering Academy Study Material Free Download PDFPrashant YadavNo ratings yet
- Guideline For Safe Closure and Rehabilitation of MSW Landfill SitesDocument126 pagesGuideline For Safe Closure and Rehabilitation of MSW Landfill Sitesmohd farhan ariff zaitonNo ratings yet
- MBBR Wastewater Treatment ProcessesDocument48 pagesMBBR Wastewater Treatment Processesmanuel.hernandezNo ratings yet
- Pengolahan Limbah Cair Industri Karet Dengan Kombinasi Proses Pretreatment Dan Membran UltrafiltrasiDocument10 pagesPengolahan Limbah Cair Industri Karet Dengan Kombinasi Proses Pretreatment Dan Membran UltrafiltrasiTiara Indah Fitrianingrum 1907155142No ratings yet
- Case Study 1Document6 pagesCase Study 1jitenderNo ratings yet
- Leachate Generation and Treatment at A LandfillDocument10 pagesLeachate Generation and Treatment at A Landfillbidonejack100% (2)
- Date of Application For BMWA BMWA Type Authorisation No Issued Date Valid DateDocument3 pagesDate of Application For BMWA BMWA Type Authorisation No Issued Date Valid DateRøhïth RøhãñNo ratings yet
- Strategic Sawege Disposal Hong KongDocument4 pagesStrategic Sawege Disposal Hong KongSebastian Martinez100% (1)
- Environmental Engineering IDocument3 pagesEnvironmental Engineering IPartha PratimNo ratings yet
- Soak Pits: What Is A Soak Pit?Document1 pageSoak Pits: What Is A Soak Pit?ascensionNo ratings yet
- MyFAST DataDocument3 pagesMyFAST DatadkdavorkalcNo ratings yet
- English Minat Burning Rubbish and Making The Air Bad SoulutionDocument4 pagesEnglish Minat Burning Rubbish and Making The Air Bad SoulutionReza AdhitiawanNo ratings yet
- Bioprocess - Activated SludgeDocument23 pagesBioprocess - Activated SludgeYunji LUNo ratings yet
- Eluru DPR - ULB On 17-09-2022Document10 pagesEluru DPR - ULB On 17-09-2022Sasidhar KatariNo ratings yet