Professional Documents
Culture Documents
National Institute of Technology, Raipur: Term Project
Uploaded by
Joshtyler 21Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
National Institute of Technology, Raipur: Term Project
Uploaded by
Joshtyler 21Copyright:
Available Formats
NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ,
RAIPUR
High Voltage Engineering
TOPIC :- Testing of Break down strength of
transformer oil
TERM PROJECT
Name - vineet chopra
Roll no. - 19117100
Branch - electrical eng. (6th sem)
Subject - HVE
Guided by - K. Chandrasekaran
Introduction
What is Transformer Oil?
Transformer oil (also known as insulating oil) is a special type of oil
which has excellent electrical insulating properties and is stable at high
temperatures. Transformer oil is used in oil-filled electrical power
transformers to insulate, stop arcing and corona discharge, and to
dissipate the heat of the transformer (i.e. act as a coolant).
Transformer oil is also used to preserve the transformer ’ s core and
windings – as these are fully immersed inside the oil. Another
important property of the insulating oil is its ability to prevent oxidation
of the cellulose-made paper insulation. The transformer oil acts as a
barrier between the atmospheric oxygen and the cellulose – avoiding
direct contact and hence minimizing oxidation. The level of transformer
oil is typically measured using a MOG (Magnetic Oil level Guage).
Transformer Oil Types :-
paraffin based transformer oil :- Paraffin oil has a lower oxidation
rate than Naphtha oil, the oxidation product (sludge) is insoluble and
precipitated at the bottom of the tank. This sludge acts as an obstruction
to the transformer cooling system.
Naphtha based transformer oil :- Naphtha oil is more easily
oxidized than paraffin oil. But the product of oxidation – i.e. sludge
– in the naphtha oil is more soluble than the sludge from the paraffin
oil. Thus sludge of naphtha-based oil is not precipitated in the bottom of
the transformer. Hence it does not obstruct convection circulation of the
oil, means it does not disturb the transformer cooling system.
Transformer Oil Properties :-
1. The dielectric strength of transformer oil is also known as the
breakdown voltage (BDV) of transformer oil. Breakdown voltage is
measured by observing at what voltage, sparking strands between
two electrodes immersed in the oil, separated by a specific gap. A low
value of BDV indicates presence of moisture content and conducting
substances in the oil.
2. For measuring BDV of transformer oil, portable BDV measuring kit
is generally available at site. In this kit, oil is kept in a pot in which
one pair of electrodes are fixed with a gap of 2.5 mm (in some kit it
4mm) between them. Now slowly rising voltage is applied between
the electrodes. The rate of rising voltage is controlled at 2 KV/s and
observe the voltage at which sparking starts between the electrodes.
That means at which voltage dielectric strength of transformer oil
between the electrodes has been broken down.
3. The specific resistance of oil is a measure of DC resistance
between two opposite sides of one cm3 block of oil. Its unit is
ohm-cm at a specific temperature. With increase in temperature the
resistivity of oil decreases rapidly
4. Minimum standard specific resistance of transformer oil at 90oC is
35 × 1012 ohm–cm and at 27oC it is 1500 × 1012 ohm–cm.
5. Dielectric dissipation factor is also known as loss factor or tan
delta of transformer oil. When a insulating materials is placed
between live part and grounded part of an electrical equipment,
leakage current will flow. As an insulating material is dielectric in
nature the current through the insulation ideally leads the voltage by
90o. Here voltage means the instantaneous voltage between live part
and ground of the equipment. But in reality, no insulating materials
are perfect dielectric in nature.
6. Moisture or water content in transformer oil is highly
undesirable as it affects the dielectric properties of the oil adversely.
The water content in oil also affects the paper insulation of the core
and winding of a transformer. Paper is highly hygroscopic.
7. Acidic transformer oil is a harmful property. If oil becomes acidic,
the water content in the oil becomes more soluble in the oil. The
acidity of oil deteriorates the insulation property of paper insulation
of winding. Acidity accelerates the oxidation process in the oil. Acid
also includes rusting of iron in the presence of moisture.
8. the viscosity of transformer oil can be said that viscosity is the
resistance of flow, in normal condition. Resistance to flow of
transformer oil means obstruction of convection circulation of oil
inside the transformer. Good oil should have a low viscosity so that
it offers less resistance to the conventional flow of oil thereby not
affecting the cooling of a transformer.
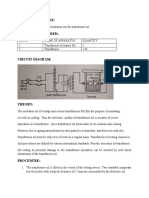
Transformer Oil Testing
Transformer oil needs to be tested to ensure that it works for today ’ s
standards. Testing standards and procedures are defined by various
international standards, and most of them are set by the ASTM.
Oil testing consists of measuring the breakdown voltage, and other
chemical and physical properties of the oil, either through portable test
equipment or in a laboratory. Through proper testing, the transformer’s
lifespan is increased, reducing the need to pay for replacement.
Breakdown voltage is measured by observing at what
voltage, sparking strands between two electrodes
immersed in the oil, separated by a specific gap. A low
value of BDV indicates presence of moisture content
and conducting substances in the oil.
What Factors Are Tested :-
1. Standard Specification for Mineral Insulating Oil Used in
Electrical Apparatus
2. Acid number
3. Dielectric breakdown voltage
4. Liquid power factor
5. Interfacial tension
6. Specific resistance
7. Corrosive sulfur
8. Visual examination
These tests will help determine if the oils are clean and will create a
baseline of properties that need to be tested periodically. Although
there are a large number of tests that are available, they are
expensive. So it ’ s best to use them as diagnostics if an issue occurs
during primary testing.
What is the transformer BDV test of oil?
BDV test means the Breakdown Voltage Test. This test is performed for
verifying the dielectric strength of the oil of the transformer. Dielectric
Strength is the maximum capacity to resist the voltage of insulating oil.
This test demonstrates the dielectric Strength of Transformer Oil.
What is ppm in transformer oil?
PPM stands for Parts Per Million. It is used to measure the weight of
moisture divided by the value of oil. The moisture content in oil lowers
the insulating system dielectric strength that permits flashover to harm a
transformer. For example, for mineral oil, a generally accepted
maximum moisture content is 35 ppm.
What is the Colour of transformer oil?
Typically, oil is yellow, orange, or somewhat red when fresh and will
work as proposed. As the oil ages, it transforms into brown or black
colour, and its efficiency weakens.
Common Problems When Testing
Fault Key Gas Results
Corona Low energy discharges create methane and hydrogen and
Hydrogen
discharge smaller quantities of ethylene and ethane.
Large amounts of hydrogen or acetylene or minor quantities of
Arcing Acetylene
ethylene and methane can be produced.
Overheate Carbon
If cellulose is overheated, then it will produce carbon monoxide
d Cellulose Monoxide
Overheating oil will produce methane and ethylene (300 degrees
Methane
Overheate F) or methane and hydrogen (1,112 degrees F). Traces of
and
d Oil acetylene might be created if the unit has electrical contacts or if
Ethylene
the problem is severe.
Why is Transformer Oil Testing Important
Determine essential electrical properties of transformer oil
Identify if a certain oil is suitable for future use
Detect whether regeneration or filtration is needed
Reduce oil costs and enhance component life
Prevent untimely failures and maximize safety
You might also like
- Start DateDocument2 pagesStart DateHussainNo ratings yet
- Emulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingFrom EverandEmulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Solo Improv GamesDocument1 pageSolo Improv GamesEduardo Garcia Rajo100% (3)
- Oil TransformerDocument19 pagesOil TransformerNURDINNo ratings yet
- L2 - 3 - Transformer Insulating OilDocument4 pagesL2 - 3 - Transformer Insulating OilPartha RayNo ratings yet
- Transformer OilDocument4 pagesTransformer OilJohnParkerNo ratings yet
- Transformer OilDocument12 pagesTransformer OilHARIHARANNo ratings yet
- TF OIlDocument5 pagesTF OIlsagNo ratings yet
- Notestransformeroil 170617003020Document52 pagesNotestransformeroil 170617003020satish reddy100% (2)
- Transformer Oil 1Document57 pagesTransformer Oil 1Rahman Scholar100% (1)
- Dielectric Constant, Tan Delta & Resistivity of Ester Oils As Insulating Oils in TransformerDocument7 pagesDielectric Constant, Tan Delta & Resistivity of Ester Oils As Insulating Oils in Transformertaufiqishak09No ratings yet
- Transformer OilDocument14 pagesTransformer OilGeorgina SuleNo ratings yet
- What Is Transformar OilDocument6 pagesWhat Is Transformar OilAditya RautNo ratings yet
- MEE Unit 5Document21 pagesMEE Unit 5dipak1980No ratings yet
- Guide of Transformer Oil TestingDocument5 pagesGuide of Transformer Oil Testingoorja.sachinborkarNo ratings yet
- Transformer Oil&DgaDocument70 pagesTransformer Oil&DgaBasudev PatraNo ratings yet
- Transformer OilDocument8 pagesTransformer OilMohammad Ibnul HossainNo ratings yet
- Transformer Oil TestingDocument29 pagesTransformer Oil TestingMrunal Salve75% (4)
- Insulating Oils, Fluids, and GassesDocument15 pagesInsulating Oils, Fluids, and GassesUttog KaynamNo ratings yet
- Testing & Commissioning of Electrical EquipmentDocument16 pagesTesting & Commissioning of Electrical EquipmentAnkit YadavNo ratings yet
- Transformer Oil Analysis: Water ContentDocument12 pagesTransformer Oil Analysis: Water ContentSanjeev DhariwalNo ratings yet
- Transformer Health Monitoring SystemDocument10 pagesTransformer Health Monitoring SystemPavan Kumar A GNo ratings yet
- Trafo Oil Testing TypesDocument10 pagesTrafo Oil Testing TypesShrikanth SolaNo ratings yet
- Transformer Oil - WikipediaDocument22 pagesTransformer Oil - WikipediaGian CoderisNo ratings yet
- Transformer Oil - Wikipedia PDFDocument19 pagesTransformer Oil - Wikipedia PDFAkash SahaNo ratings yet
- Transformer Oil: ExplanationDocument8 pagesTransformer Oil: ExplanationshaikamirulhasanNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument2 pagesCase StudyAndrei HoNo ratings yet
- Transformer Oil TerminologyDocument7 pagesTransformer Oil TerminologyUtkarsh AnandNo ratings yet
- Transformer Oil & Its EvolutionDocument7 pagesTransformer Oil & Its EvolutionShrikanth SolaNo ratings yet
- Transformer Oil TestingDocument29 pagesTransformer Oil TestingDEADMAN100% (1)
- Transformer MaintenancDocument13 pagesTransformer MaintenancAnonymous m4MF1gNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of Liquid InsulationDocument4 pagesMaintenance of Liquid InsulationrodgerNo ratings yet
- Oil Diagnostics - Test InformationDocument12 pagesOil Diagnostics - Test InformationEscobar ValderramaNo ratings yet
- Study of Transformer Oil Purification: Shreya Salvi, Prof. A. P. ParanjapeDocument4 pagesStudy of Transformer Oil Purification: Shreya Salvi, Prof. A. P. Paranjapeamitranjan20No ratings yet
- Expt 06Document2 pagesExpt 06hod eeNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Transformer Oil AnalysisDocument13 pagesA Guide To Transformer Oil Analysiskrcdewanew100% (1)
- Seminar DocumentDocument26 pagesSeminar DocumentSaiNo ratings yet
- Transformer Oil-Article-Very NewDocument5 pagesTransformer Oil-Article-Very NewArshad AhmeedNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of TransformerDocument80 pagesMaintenance of Transformerajaynmenon100% (2)
- Classification of Insulating Materials As Per ISIDocument6 pagesClassification of Insulating Materials As Per ISIindranil das100% (2)
- Significance of Transformer Oil TestsDocument3 pagesSignificance of Transformer Oil Testscarlos albertoNo ratings yet
- NWsu09 HamrickDocument3 pagesNWsu09 HamrickNeha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Transformer Health & Condition MonitoringDocument23 pagesTransformer Health & Condition Monitoringchinnarao100% (1)
- Presentation DGADocument63 pagesPresentation DGAMuhammad Ahmed100% (2)
- Agging Effect in Insulating Oil of Power TransformerDocument5 pagesAgging Effect in Insulating Oil of Power TransformerKhaled Galal AhmedNo ratings yet
- TRF OilDocument47 pagesTRF Oilಶ್ರೀಕಾಂತ್ ತಿಪ್ಪೇರುದ್ರಪ್ಪNo ratings yet
- Transformer Oil Analysis For Maintenance ProgramsDocument10 pagesTransformer Oil Analysis For Maintenance Programskechaouahmed81No ratings yet
- Transformer Oil 1-24Document24 pagesTransformer Oil 1-24NikosNo ratings yet
- Transformer OilDocument14 pagesTransformer OilFaisal SoomroNo ratings yet
- Oil Breakdown TestingDocument5 pagesOil Breakdown TestingAshiq NafasNo ratings yet
- Refining Q&ADocument41 pagesRefining Q&Ashashwatchaurasia83No ratings yet
- Definition of A DIELECTRIC: Dielectrics... Are Not A Narrow Class of So-Called InsulatorsDocument12 pagesDefinition of A DIELECTRIC: Dielectrics... Are Not A Narrow Class of So-Called InsulatorsAF EYah MalikNo ratings yet
- University Teaching Department Rajasthan Technical University, KotaDocument29 pagesUniversity Teaching Department Rajasthan Technical University, Kotavershakhemka7193No ratings yet
- Transformer Oil TestDocument10 pagesTransformer Oil TestAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Coconut Oil Eru 2001Document11 pagesCoconut Oil Eru 2001Syafeeqah SaukiNo ratings yet
- Particle Effect On Breakdown Voltage of Mineral and Ester Based Transformer OilsDocument5 pagesParticle Effect On Breakdown Voltage of Mineral and Ester Based Transformer Oilsrasheed313No ratings yet
- Testing of TransformerDocument24 pagesTesting of TransformerObakoma JosiahNo ratings yet
- Definition of A - Dielectric: by Roger KernDocument7 pagesDefinition of A - Dielectric: by Roger Kernnaque94No ratings yet
- Transformer Oil BDV TestDocument12 pagesTransformer Oil BDV TestHameeda BanuNo ratings yet
- Machinery Oil Analysis & Condition Monitoring : A Practical Guide to Sampling and Analyzing Oil to Improve Equipment ReliabilityFrom EverandMachinery Oil Analysis & Condition Monitoring : A Practical Guide to Sampling and Analyzing Oil to Improve Equipment ReliabilityRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (4)
- Naval Diesel Engineering: The Fundamentals of Operation, Performance and EfficiencyFrom EverandNaval Diesel Engineering: The Fundamentals of Operation, Performance and EfficiencyNo ratings yet
- Assignment On I.T & Pharma IndustryDocument11 pagesAssignment On I.T & Pharma IndustryGolu SinghNo ratings yet
- REC4281GDocument307 pagesREC4281GadrianahoukiNo ratings yet
- Final ResearchDocument36 pagesFinal Researchralph jansen makabentaNo ratings yet
- Business Partner Application Form: Bintang Arif Kurniawan 08119002384Document1 pageBusiness Partner Application Form: Bintang Arif Kurniawan 08119002384Bintang ArifNo ratings yet
- 4 Insurance Sales Incentive Program Ideas That WorkDocument3 pages4 Insurance Sales Incentive Program Ideas That Workgeorge akamaNo ratings yet
- Beamray 50R100R Data SheetDocument2 pagesBeamray 50R100R Data Sheethassan elgamriNo ratings yet
- Simulación de Eventos Discretos Eduardo García Dunna May 4, 2015Document22 pagesSimulación de Eventos Discretos Eduardo García Dunna May 4, 2015Andrea GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Importance of Being Hydrated To Weight ManagementDocument3 pagesImportance of Being Hydrated To Weight ManagementAlastair MoltenNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Foundation For Large-Scale Computations For Nonlinear Material BehaviorDocument411 pagesTheoretical Foundation For Large-Scale Computations For Nonlinear Material BehaviorDalelAzaiezNo ratings yet
- What Is OLAP? Cube, Operations & Types in Data WarehouseDocument7 pagesWhat Is OLAP? Cube, Operations & Types in Data WarehouseGabrielAlexandruNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Cybercrime in IndiaDocument8 pagesThesis On Cybercrime in Indiakarinathomasdenver100% (2)
- Union Feb. 10, 2016Document16 pagesUnion Feb. 10, 2016Your News. When You Want It.No ratings yet
- QuestionDocument9 pagesQuestionIman ShahrizanNo ratings yet
- Revealed Comparative AdvantageDocument5 pagesRevealed Comparative AdvantageiamrahulkumarNo ratings yet
- Sample Size Determination and Confidence Interval Derivation For Exponential DistributionDocument6 pagesSample Size Determination and Confidence Interval Derivation For Exponential DistributionIsmael NeuNo ratings yet
- Sag: Sag Is A Vertical Distance From The Horizontal Line Between The Tops of TheDocument6 pagesSag: Sag Is A Vertical Distance From The Horizontal Line Between The Tops of TheMd. Ruhul AminNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 and Chapter 2 PowerpointDocument14 pagesChapter 1 and Chapter 2 Powerpointapi-252892423No ratings yet
- Delta Background-Group AssignmentDocument2 pagesDelta Background-Group AssignmentTinashe100% (2)
- Fundraising Guide For Rescue TeamsDocument5 pagesFundraising Guide For Rescue TeamsDecisions For HeroesNo ratings yet
- Reasearch ProposalDocument9 pagesReasearch Proposalamel amoulaNo ratings yet
- Panasonic SC BT200Document60 pagesPanasonic SC BT200Mark CoatesNo ratings yet
- Anh 7 Cum 1 (2017-2018)Document6 pagesAnh 7 Cum 1 (2017-2018)anhthunoban2011No ratings yet
- Lab 9Document3 pagesLab 9Tâm NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Oil and Gas - Black Gold!Document32 pagesOil and Gas - Black Gold!tabithapangNo ratings yet
- Dual 15A/Single 30A Step-Down Power Module: ISL8225MDocument34 pagesDual 15A/Single 30A Step-Down Power Module: ISL8225MAnonymous QakmLc3kTINo ratings yet
- Steel Fence CatalogDocument4 pagesSteel Fence CatalogtempfencingNo ratings yet
- Process-to-Process Delivery: Udp and TCP: (Chapter 23)Document41 pagesProcess-to-Process Delivery: Udp and TCP: (Chapter 23)Giri Tharan RockNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages. Personal Blogging TestDocument2 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages. Personal Blogging TestLaura, GarciaNo ratings yet