Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Government Accounting
Uploaded by
Joody Catacutan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesbasic recording process
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentbasic recording process
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesGovernment Accounting
Uploaded by
Joody Catacutanbasic recording process
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
JOODY S.
CATACUTAN
BSA-3A
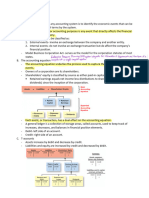
ACTIVITY #3: THE BASIC RECORDING IN GOVERNMENT ACCOUNTING
REVISED CHART OF ACCOUNTS IN GOVERNMENT ACCOUNTING
1. Codes are assigned to account groups to facilitate location of accounts in the general and
subsidiary ledgers, to provide systematic arrangement and classification of accounts and
facilitate preparation of the consolidated financial reports as follows:
Code Account Groups
1 Assets
2 Liabilities
3 Equity
4 Income
5 Expenses
2. The account code structure consists of eight (8) mandatory digits as follows:
0 00 00 00 0
Account Group
Major Account Group
Sub-Major Account Group
General Ledger Account
General Ledger Contra-Account
2.1 Account Group represents the accounts classification as to assets, liabilities, equity,
revenue/income and expenses.
2.2 Major Account Group classifies the account within an account group, e.g. for assets major
accounts: cash and cash equivalents, investments, receivables, inventories, investment
property, etc.
2.3 Sub-major Account Group further classifies the account within the major account group, e.g.
for cash and cash equivalents: Cash on Hand, Cash in Bank-Local Currency, Cash in Bank-Foreign
Currency, etc.
2.4 General Ledger Account represents the account to be presented in the detailed financial
statements, e.g. Cash-Collecting Officer, Petty Cash, etc. this is composed of two (2) segments:
The first two digits from left is the GL code and the last digit is reserved to indicate whether it is
a contra account like, Allowance for Impairment, Accumulated Depreciation, etc.
TYPES OF REGISTRIES IN GOVERNMENT ACCOUNTING (logbook)
1. Registries of Revenue and Other Receipts (RROR) – used to monitor the budgeted amounts,
actual collections, and remittances of revenue and other receipts.
- Dito nirerecord ung mga revenues and receipts
2. Registry of Appropriations and Allotments (RAPAL) – used to monitor appropriations and
allotments. This is to ensure that allotments will not exceed appropriations.
3. Registries of Budget, Utilization, and Disbursements (RBUD) – used to record the approved
special budget and corresponding utilizations and disbursements changed to retained income.
Separate RBUD shall be maintained for each object of expenditure.
- It’s like general ledger
RBUD – PS
RBUD – MOOE
RBUD – FE
RBUD - CO
4. Registries of Allotments, Obligations, and Disbursements (RAOD) – used to monitor the
allotment received, obligations incurred against the corresponding allotment, and the actual
disbursements made. This is to ensure that obligations incurred will not exceed allotments while
actual disbursements will not exceed the obligations incurred. Separate RBUD shall be
maintained for each object of expenditure.
RAOD – PS
RAOD – MOOE
RAOD – FE
RAOD – CO
Object of Expenditures
The classification of expenditures by object are as follows:
Personnel Services (PS) - pertain to all types of employee benefits, for example,
salaries, bonuses, allowances, cash gifts, etc.
Maintenance and Other Operating Expenses (MOOE) – pertain to various
operating expenses other than employee benefits and financial expenses, for
example, travel, utilities, supplies, etc.
Financial Expenses (FE) – pertain to finance costs, for example, interest
expense, bank charges, losses on foreign exchange transactions.
Capital Outlays (CO) – pertain to capitalizable expenditures, for example,
expenditures on the construction of public infrastructure, acquisition costs of
equipment, etc.
You might also like
- Financial Analysis 101: An Introduction to Analyzing Financial Statements for beginnersFrom EverandFinancial Analysis 101: An Introduction to Analyzing Financial Statements for beginnersNo ratings yet
- "The Language of Business: How Accounting Tells Your Story" "A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding, Interpreting, and Leveraging Financial Statements for Personal and Professional Success"From Everand"The Language of Business: How Accounting Tells Your Story" "A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding, Interpreting, and Leveraging Financial Statements for Personal and Professional Success"No ratings yet
- Acc Chapter 2 LSCMDocument80 pagesAcc Chapter 2 LSCMwoleliemekieNo ratings yet
- Co Chapter 2 Accounting Cycle RevisedDocument19 pagesCo Chapter 2 Accounting Cycle RevisedmikeNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two BAcc.Document22 pagesChapter Two BAcc.kefyalew T100% (1)
- CH 2 3Document18 pagesCH 2 3Eyuel SintayehuNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting - Review: HUL Q4 Misses Estimates, Profit Dips 1% To Rs 1,519 Crore, Volume Shrinks 7%Document10 pagesFinancial Accounting - Review: HUL Q4 Misses Estimates, Profit Dips 1% To Rs 1,519 Crore, Volume Shrinks 7%anishjoseph007No ratings yet
- Accounting For Government and Non-Profit OrganizationsDocument13 pagesAccounting For Government and Non-Profit OrganizationsPatricia ReyesNo ratings yet
- Unit .2 The Accounting CycleDocument29 pagesUnit .2 The Accounting CycleYonasNo ratings yet
- Acb3 01Document41 pagesAcb3 01lidetu100% (3)
- Budget 2Document45 pagesBudget 2Naveen MalikNo ratings yet
- RTI AccountingManual PDFDocument459 pagesRTI AccountingManual PDFVanita ValluvanNo ratings yet
- Accounting UNIT 2Document20 pagesAccounting UNIT 2newaybeyene5No ratings yet
- Week 1 .06 - Revised Chart of AccountsDocument19 pagesWeek 1 .06 - Revised Chart of AccountsElaineJrV-IgotNo ratings yet
- Acctg 322Document2 pagesAcctg 322Janine Remoroza Ü100% (1)
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3luzespinosa602No ratings yet
- Ale Aubrey Bsma 3 1.lguDocument6 pagesAle Aubrey Bsma 3 1.lguAstrid XiNo ratings yet
- Part Ii Review of The Accounting ProcessDocument26 pagesPart Ii Review of The Accounting Processአረጋዊ ሐይለማርያምNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 5e With AnswersDocument16 pagesChapter 1 5e With AnswersDiana Aeleen Mandujano Poblano100% (2)
- ACT 132 Lecture 2Document69 pagesACT 132 Lecture 2Muadz D. LucmanNo ratings yet
- Learning Guide: LevelDocument39 pagesLearning Guide: LevelAgat100% (1)
- CCC Agnpo Lesson3 2021 2022Document15 pagesCCC Agnpo Lesson3 2021 2022Hazel VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Asset AccountingDocument9 pagesAsset AccountingPrabhu Ramanathan R100% (1)
- Framework For Preparation of Financial StatementsDocument8 pagesFramework For Preparation of Financial StatementsGauri SinglaNo ratings yet
- Nefas Silk Poly Technic College: Learning GuideDocument39 pagesNefas Silk Poly Technic College: Learning GuideNigussie BerhanuNo ratings yet
- Accounting ChapterDocument22 pagesAccounting ChapterMamaru SewalemNo ratings yet
- Accounting CycleDocument9 pagesAccounting CycleSirfMujjuNo ratings yet
- Appropriation and ReappropriationDocument8 pagesAppropriation and ReappropriationNasir Nadeem100% (1)
- The Government Accounting ProcessDocument2 pagesThe Government Accounting ProcessrochNo ratings yet
- ACCT1002 U2-20150826nprDocument15 pagesACCT1002 U2-20150826nprSaintNo ratings yet
- 10 - MM - FI IntegrationDocument44 pages10 - MM - FI IntegrationAbhishek Agrawal100% (7)
- Punching MediumDocument42 pagesPunching Mediumnagarjuna_upscNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesLecture NotesLyaman TagizadeNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four FundDocument13 pagesChapter Four FundnaodbrtiNo ratings yet
- Acctg 1Document39 pagesAcctg 1Clarize R. MabiogNo ratings yet
- Module 9 - Government Accounting ProcessDocument10 pagesModule 9 - Government Accounting ProcessJeeramel TorresNo ratings yet
- Engleski I I II PDFDocument23 pagesEngleski I I II PDFvejnicNo ratings yet
- A Lecture6 9 29 22Document46 pagesA Lecture6 9 29 22Kawaii SevennNo ratings yet
- Hotel AccountingDocument30 pagesHotel AccountingTitem Ashenafi Berta50% (2)
- Accounting FinalDocument14 pagesAccounting FinalTeodora IrimiaNo ratings yet
- FAA - Unit 1 - 2021Document11 pagesFAA - Unit 1 - 2021Pranjal ChopraNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-xii-accountancy-CA-scert-Focused Area-Based-Quick-NotesDocument76 pagesHsslive-xii-accountancy-CA-scert-Focused Area-Based-Quick-Notes37 Riya ThomasNo ratings yet
- FABM 2 NotesDocument4 pagesFABM 2 NotesShiny Natividad100% (1)
- Training Material On West Bengal Financial Rules and Office ProceduresDocument150 pagesTraining Material On West Bengal Financial Rules and Office Proceduresswarnendu_janaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - The Revised Chart of AccountsDocument16 pagesCHAPTER 3 - The Revised Chart of AccountsRafael VictoriaNo ratings yet
- 1 GovaccDocument2 pages1 Govaccyes yesnoNo ratings yet
- Ak HotelDocument16 pagesAk HotelDina RahayuNo ratings yet
- ChapterDocument9 pagesChapterVidia ProjNo ratings yet
- Repaso Capítulo 2 ContabilidadDocument9 pagesRepaso Capítulo 2 ContabilidadpaulaNo ratings yet
- ASP - 3H - 02 - Abdul Qodir - Tugas3Document5 pagesASP - 3H - 02 - Abdul Qodir - Tugas3abdul qodirNo ratings yet
- Overview of Business Processes: © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing As Prentice HallDocument20 pagesOverview of Business Processes: © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing As Prentice HallCharles MK ChanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Government Accounting SystemDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Government Accounting SystemSumeet Tiwary100% (1)
- LGU NGAS Chapter 1 and 2Document24 pagesLGU NGAS Chapter 1 and 2Lail PDNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: General Fund & Special Revenue Funds 3.1 General Fund IsDocument41 pagesChapter Three: General Fund & Special Revenue Funds 3.1 General Fund IsTamirat BashaaNo ratings yet
- ACT 132 Lecture 2Document69 pagesACT 132 Lecture 2Muadz D. LucmanNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument45 pagesClass NotesNaveed Whatsapp Status100% (1)
- Dmp3e Ch02 Solutions 04.13.10 FinalDocument56 pagesDmp3e Ch02 Solutions 04.13.10 Finalmichaelkwok1No ratings yet
- Sen Finance Sen Finance Sen Finance Sen Finance: CFA® Level IDocument31 pagesSen Finance Sen Finance Sen Finance Sen Finance: CFA® Level IPavel LahaNo ratings yet
- 201.10 Government AccountingDocument3 pages201.10 Government AccountingBiplob K. SannyasiNo ratings yet
- Final Output - Ais Elect 1Document18 pagesFinal Output - Ais Elect 1Joody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Marketing AspectsDocument2 pagesMarketing AspectsJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Process and Materials UsedDocument1 pageChapter 4 Process and Materials UsedJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document1 pageChapter 4Joody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Savon Heros Chapter 3Document18 pagesSavon Heros Chapter 3Joody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- GlowishDocument12 pagesGlowishJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- The Law On Partnership: Atty. Daryl G. Liangco, Cpa 1Document10 pagesThe Law On Partnership: Atty. Daryl G. Liangco, Cpa 1Joody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Savon HerosDocument15 pagesSavon HerosJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Front and Right ElevationDocument1 pageFront and Right ElevationJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Project Background: Don Honorio Ventura State University San Juan, Mexico, PampangaDocument44 pagesProject Background: Don Honorio Ventura State University San Juan, Mexico, PampangaJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Rear and Left ElevationDocument1 pageRear and Left ElevationJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 AnswersDocument1 pageChapter 3 AnswersJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Variants DescriptionDocument2 pagesVariants DescriptionJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Savon Heros-Stall-Floor-PlanDocument1 pageSavon Heros-Stall-Floor-PlanJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Project Background: Don Honorio Ventura State University San Juan, Mexico, PampangaDocument23 pagesProject Background: Don Honorio Ventura State University San Juan, Mexico, PampangaJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Multiple ChoiceDocument3 pagesMultiple ChoiceJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Disclaimer Audit ReportDocument2 pagesDisclaimer Audit ReportJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- AUDITING THEORY 2 Audit Reports.Document4 pagesAUDITING THEORY 2 Audit Reports.Joody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam - Acctg 115Document2 pagesMidterm Exam - Acctg 115Joody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Audprob Final Exam 1Document26 pagesAudprob Final Exam 1Joody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Consumption TaxesDocument11 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Consumption TaxesJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Adverse Audit ReportDocument2 pagesAdverse Audit ReportJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Unmodified Audit ReportDocument2 pagesUnmodified Audit ReportJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Auditing Problems SCFDocument7 pagesAuditing Problems SCFJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Joody S. Catacutan Activity #3: STRACOSMANDocument1 pageJoody S. Catacutan Activity #3: STRACOSMANJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- ExercisesComparative and Trend AnalysisDocument3 pagesExercisesComparative and Trend AnalysisJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Midterm ExamDocument4 pagesFinancial Management Midterm ExamJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Special Transactions Final Grading ExaminationDocument20 pagesAccounting For Special Transactions Final Grading ExaminationJoody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Research Title Group 7Document1 pageResearch Title Group 7Joody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- AUDITING PROB Activity 2Document4 pagesAUDITING PROB Activity 2Joody CatacutanNo ratings yet
- IFA Chapter 2Document17 pagesIFA Chapter 2Suleyman TesfayeNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 Caselette - Audit of LiabilitiesDocument27 pagesCHAPTER 8 Caselette - Audit of LiabilitiesNovie Marie Balbin Anit100% (1)
- Trial Balance PD Jaya Ban Motor Setelah PenyesuaianDocument1 pageTrial Balance PD Jaya Ban Motor Setelah PenyesuaianHimmalatul Aslami100% (1)
- Customs Vs Eastern Sea TradingDocument4 pagesCustoms Vs Eastern Sea TradingJP DCNo ratings yet
- 59025Document6 pages5902519epci022 Prem Kumaar RNo ratings yet
- Dipifr 2006 Jun Q PDFDocument11 pagesDipifr 2006 Jun Q PDFPiyal HossainNo ratings yet
- A-Financial Accounting - Midterm Exam QuestionsDocument8 pagesA-Financial Accounting - Midterm Exam QuestionsAmbra KoraNo ratings yet
- MerchandisingDocument11 pagesMerchandisingAIRA NHAIRE MECATE100% (1)
- Aggarwal Trading PDFDocument3 pagesAggarwal Trading PDFdipa ghondwalNo ratings yet
- Ledger Fee Charges - Balance - Requirement, Turnover - Credit and Turnover - DebitDocument22 pagesLedger Fee Charges - Balance - Requirement, Turnover - Credit and Turnover - DebitCHARLES TUMWESIGYENo ratings yet
- HAND OUT No. 3 FABM The Accounting EquationDocument9 pagesHAND OUT No. 3 FABM The Accounting Equationnatalie clyde matesNo ratings yet
- Assignment POSTING TO THE LEDGERDocument7 pagesAssignment POSTING TO THE LEDGERJie SapornaNo ratings yet
- Al n14 Corporate Reporting Exam PaperDocument18 pagesAl n14 Corporate Reporting Exam Paperzilchhour0% (1)
- Advanced Financial Accounting 10th Edition Christensen Cottrell Baker Solutions Chapter 15Document56 pagesAdvanced Financial Accounting 10th Edition Christensen Cottrell Baker Solutions Chapter 15renyNo ratings yet
- Practice Court - Joint Stipulation of FactsDocument5 pagesPractice Court - Joint Stipulation of FactsKio Paulo San AndresNo ratings yet
- Commercial StudiesDocument3 pagesCommercial StudiesChandu SagiliNo ratings yet
- Assume Smiling Springs Glass Company Uses The Perpetual Inventory SystemDocument1 pageAssume Smiling Springs Glass Company Uses The Perpetual Inventory Systemhassan taimourNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument65 pagesDocxAllana MierNo ratings yet
- Account StatementDocument3 pagesAccount StatementJamesNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Financial Accounting Global Edition 8th Edition by Libby and Short DownloadDocument32 pagesSolution Manual For Financial Accounting Global Edition 8th Edition by Libby and Short DownloadrahimNo ratings yet
- Audit of Cash Test BanksDocument270 pagesAudit of Cash Test BanksAldrin Zolina100% (2)
- Shelsy - 2142003 Tugas Pe 2-7a - PR 3-5BDocument5 pagesShelsy - 2142003 Tugas Pe 2-7a - PR 3-5BShelsy syNo ratings yet
- Basic Acctg 4th SatDocument11 pagesBasic Acctg 4th SatJerome Eziekel Posada PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Bank Reconciliation L2Document3 pagesBank Reconciliation L2C XNo ratings yet
- Oracle Apps Receivables Accounting EntriesDocument3 pagesOracle Apps Receivables Accounting Entrieskalpeshjain2004No ratings yet
- ACC 311 ReviewDocument2 pagesACC 311 ReviewMaricar DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Exercises With SolutionDocument5 pagesChapter 7 Exercises With Solutionmohammad khataybehNo ratings yet
- Notes CashbookDocument5 pagesNotes CashbookAdika Denish0% (1)
- H P I S T: IRE Urchase and Nstallment ALE RansactionsDocument46 pagesH P I S T: IRE Urchase and Nstallment ALE RansactionsJayant MittalNo ratings yet
- Sage 300 ERP 2012: Financial Reporter Quick ReferenceDocument23 pagesSage 300 ERP 2012: Financial Reporter Quick ReferencetrueNo ratings yet