Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermal Engineering I - Lecture Plan
Uploaded by
kabbilaash kumarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thermal Engineering I - Lecture Plan
Uploaded by
kabbilaash kumarCopyright:
Available Formats
KARUNYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & SCIENCES
Depaertment of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
14ME2015 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I
TEACHING PLAN
Unit Lectur Book & Page Nos.
No. e Topic for reference Topic No.
No. (R at page bottom)
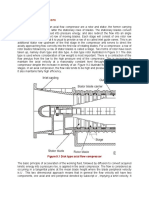
1 Introduction Syllabus
Unit
1
Classification of boilers, boiler R1 P.9.2
9.2
2 R2 p. 341 11.1-11.9
terms
R3 p. 416 10.2
3&4 Performance of steam R1 P.14.2-14.3 14.1 -14.3
generator - evaporator R2 p. 341 14.1-14.4
capacity, equivalent R3 p.432 10.2.11
evaporation, factor of
evaporation, boiler efficiency
5 Heat losses in a boiler plant R1 P.14.3-14.5 14.4
R2 p.342 14.5
R1 P.14.5-14.18 14.5
6-9 Heat balance calculations R2 p.404,405 16.18
R3 p.432 10.2.11
R1 P.17.2 17.2
10 Steam nozzles R2 p.440 18.1
R3 p.379 9.1
Unit
2
Flow through nozzles - R1 P.17.3 17.3
11 R2 p.440 18.2
Introduction
R3 p.379 9.1.1
12 General relation for adiabatic
flow
13 Effect of friction R1 P.17.9-17.10 17.4
14 &
Critical pressure ratio R1 P.17.4-17.9 17.3
15 R3 p.381 9.1.2
R2 p.448
16 Numericals - in steam nozzles
R3 p.294
Steam turbines - Advantages R1 P.18.1-18.2 18.1 & 18.2
17 R2 p.465 19.1-19.3
Unit of turbines
R3 p.438 10.4.1
3
R1 P.18.2-18.5 18.3
18 Impulse and reaction turbine R2 p.465 19.2,19.7-8
R3 p.439 10.4.2
19 & compounding of turbines R1 P.18.5-18.8 18.4
R2 p.468 19.5
20
R3 p.439 10.4.2
21 & velocity diagrams for simple R1 P.18.8-18.14 18.5
R2 p.469 19.7.1
22 turbines
R3 P.439 10.4.2
23 & R2 p.510
Numericals - in steam turbines
25 R3 p.451
R2 P.677 24.1 & 24.2
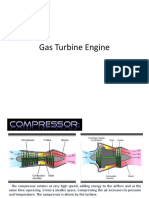
Air compressor, classification,
26 R3 p.234 6.1,6.2
working principle
R4 p.779 18.1
Unit
4
27 Work of compression without R1 P.24.4-24.5 24.4
and with clearance R2 p.678 24.3.2
R3 p.235 6.3-6.5
R4 p.779 18.2
Volumetric, Isothermal & R1 P.24.4-24.8 24.5 & 24.6
28 R3 p.241 6.4,6.6
Isentropic efficiencies
R4 p.784 18.4
Multistage air compressor and R1 P.24.8-24.10 24.8
29 R2 p.681 24.3.6
inter-cooling
R3 p.243 6.7
R1 P.24.10-24.13 24.9
Work in a multistage air R2 p.681 24.3.6
30
compressor R3 p.243 6.7
R4 p.786 18.5
Numericals - in air R3 p.249
31-35
compressors R4 p.797
36 Vapour compression 27.7
refrigeration cycle – working R1 P.27.7-27.10 26.3
principle R2 P.804 7.4
Unit R3 p.279 14.3
5 R4 p.617 3.2
R5 p.36
R2 p.808 26.3.7
37 Super heat, sub-cooling R3 P.282-284 7.4.1
R4 P.617 14.3
R1 P.27.32-27.43
38- 42 Performance calculations
R4 p.619 14.31
Working principle of vapour
43 absorption system-ammonia-
water system R1 P.27.10-27.12 27.10
R2 p.811 26.11
R3 p.292 7.8-7.8.1
R4 p.627 14.4
44 water-lithium bromide system
Comparison between vapour R1 P.27.13-27.14 27.12
45 compression and absorption R2 p.816
systems R3 p.288 7.5
REFERENCE BOOKS (621.402 – KU Library reference)
R1.Kothandaraman,C.P, DomkundwarS, “A course in Thermal
Engineering”DhanpatRai&Sons
R2.Rajput, R.K. “Thermal Engineering”,Laxmi Publications (P) Ltd., 2009
R3. Rudramoorthy, R. “Thermal Engineering”, Tata McGraw-Hill, 2010
R4. Nag P.K. Engineering Thermodynamics, Tata McGraw-Hill, 2002
R5. Arora, C.P. “Refrigeration and Air-conditioning, Tata McGraw-Hill, 2002
You might also like
- Air-To-Water Heat Pump: Shanghai Hezhong Carrier Air-Conditioning Equipment Co., LTDDocument7 pagesAir-To-Water Heat Pump: Shanghai Hezhong Carrier Air-Conditioning Equipment Co., LTDguy namNo ratings yet
- C Check Value) OT Outside Tolerance (X Is Set)Document4 pagesC Check Value) OT Outside Tolerance (X Is Set)Best Auto TechNo ratings yet
- S Setting Value, C Check Value) OT Outside Tolerance (X Is Set)Document4 pagesS Setting Value, C Check Value) OT Outside Tolerance (X Is Set)Екатерина Калашникова100% (1)
- Cha-K 524-PDocument4 pagesCha-K 524-PAnonymous KB3AksTpBNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Engineering Cycles: Power, Refrigerating and Gas Liquefaction PlantFrom EverandAnalysis of Engineering Cycles: Power, Refrigerating and Gas Liquefaction PlantNo ratings yet
- Effects of Variable Load On Power StationDocument3 pagesEffects of Variable Load On Power StationRasel Islam100% (1)
- Copeland Hermetic 2003Document20 pagesCopeland Hermetic 2003Alvaro DiazNo ratings yet
- Replacement of R22 by Gas Servei, SpainDocument6 pagesReplacement of R22 by Gas Servei, SpainDEMETRIOS 02No ratings yet
- Copeland Compressors JR, Re, RR, CR, CT, ZR, ZRT, BRDocument18 pagesCopeland Compressors JR, Re, RR, CR, CT, ZR, ZRT, BRTatu Brito100% (1)
- R401B Link PDFDocument2 pagesR401B Link PDFhihihiNo ratings yet
- Volantes Com CaboDocument2 pagesVolantes Com CaboHernane MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Quality DailyDocument76 pagesQuality Dailydilip matalNo ratings yet
- OT Outside Tolerance (X Is Set)Document4 pagesOT Outside Tolerance (X Is Set)carlos puertoNo ratings yet
- Daikin R32 Product 1Document29 pagesDaikin R32 Product 1joshuatamNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Valvulas de SeguridadDocument10 pagesDatasheet Valvulas de SeguridadEnderson OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Reece Compressor CatalogueDocument8 pagesReece Compressor Cataloguebookslover1No ratings yet
- P1 - Ion Exchange-A2-Process Data Sheet of SRP Feed Pump PDFDocument5 pagesP1 - Ion Exchange-A2-Process Data Sheet of SRP Feed Pump PDFsumit kumarNo ratings yet
- MacSpares - Samsung Lastest Price List PDFDocument3 pagesMacSpares - Samsung Lastest Price List PDFMacSparesNo ratings yet
- DS For Level SwitchDocument7 pagesDS For Level SwitchnathaNo ratings yet
- Ati - VolantesDocument2 pagesAti - VolantesEdson OliveiraNo ratings yet
- R290 Propane: AJ AE HG VTCDocument16 pagesR290 Propane: AJ AE HG VTCengmec12188No ratings yet
- SC12DL MBP/HBP Compressor R404A/R507 & R407C 220-240V 50Hz: GeneralDocument2 pagesSC12DL MBP/HBP Compressor R404A/R507 & R407C 220-240V 50Hz: GeneralDanieleNo ratings yet
- Final Drawings Marine Propulsion EngineDocument177 pagesFinal Drawings Marine Propulsion EngineHua Hidari Yang75% (4)
- Toro Nozzle ChartDocument2 pagesToro Nozzle Chartrichard_costaNo ratings yet
- Application r290 11-2000 cn60f102Document12 pagesApplication r290 11-2000 cn60f102Giorgio OlianasNo ratings yet
- S Setting Value, C Check Value) OT Outside Tolerance (X Is Set)Document4 pagesS Setting Value, C Check Value) OT Outside Tolerance (X Is Set)Best Auto TechNo ratings yet
- BOM GC-73 Preamp Rev3Document2 pagesBOM GC-73 Preamp Rev3MazaroNo ratings yet
- S Setting Value, C Check Value) OT Outside Tolerance (X Is Set)Document4 pagesS Setting Value, C Check Value) OT Outside Tolerance (X Is Set)OFFICE DANACNo ratings yet
- 新冷媒相关Document5 pages新冷媒相关ruoqi.chengNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet No. Ds-P-5984 Rev. 0: Centrifugal Pump Data Sheet U.S. Customary UnitsDocument10 pagesData Sheet No. Ds-P-5984 Rev. 0: Centrifugal Pump Data Sheet U.S. Customary Unitsrajindo1No ratings yet
- Component Parts ListDocument4 pagesComponent Parts ListVasilis RiderNo ratings yet
- Theoretical and Experimental Research On The Performance of Twin Screw Compressor Using R513A As R134a ReplacementDocument8 pagesTheoretical and Experimental Research On The Performance of Twin Screw Compressor Using R513A As R134a ReplacementVicente Pérez GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Component Parts ListDocument4 pagesComponent Parts ListskyNo ratings yet
- Peavey XR600F PreampDocument19 pagesPeavey XR600F PreampDavid SomozaNo ratings yet
- R5 - FCC Main Fractionator: Process DataDocument24 pagesR5 - FCC Main Fractionator: Process Datanico123456789No ratings yet
- Coolant Pump PDFDocument32 pagesCoolant Pump PDFPravin SatheNo ratings yet
- Termostato Robertsaw AnsalDocument7 pagesTermostato Robertsaw Ansalcapacitacion bomberos voluntarios sarmientoNo ratings yet
- S Setting Value, C Check Value) OT Outside Tolerance (X Is Set)Document5 pagesS Setting Value, C Check Value) OT Outside Tolerance (X Is Set)carlos puertoNo ratings yet
- P4 - Ion Exchange-Process Data Sheet For Reject Water Transfer PumpDocument5 pagesP4 - Ion Exchange-Process Data Sheet For Reject Water Transfer Pumpsumit kumarNo ratings yet
- Circuit Maker Assignment - C.A.DDocument3 pagesCircuit Maker Assignment - C.A.DNakitare W. ErickNo ratings yet
- Fu-Sheng 324 HADocument8 pagesFu-Sheng 324 HAAnh Hoang PhamNo ratings yet
- Sample Calculations For PG Test - SCLDocument14 pagesSample Calculations For PG Test - SCLc s shekarNo ratings yet
- Chilled Brine Requirement in Pl. 5 & Pl. 4Document1 pageChilled Brine Requirement in Pl. 5 & Pl. 4westewrNo ratings yet
- Datasheet For Pressure Safety Valve - IfbDocument66 pagesDatasheet For Pressure Safety Valve - Ifbfathan fathullahNo ratings yet
- Ground Maneuvering: Airport Planning ManualDocument10 pagesGround Maneuvering: Airport Planning ManualKentNo ratings yet
- Gerencia de Proyectos de Refinacion Y Petroquimica Departamento de Ingeniería - PinDocument4 pagesGerencia de Proyectos de Refinacion Y Petroquimica Departamento de Ingeniería - PinGerencia Rigar Colombia SASNo ratings yet
- OT Outside Tolerance (X Is Set)Document4 pagesOT Outside Tolerance (X Is Set)Agus WijayadiNo ratings yet
- Emerson Automation Solutions 3950 Greenbriar Stafford TX, 77477 United States (281) 274-4400 Quote NumberDocument2 pagesEmerson Automation Solutions 3950 Greenbriar Stafford TX, 77477 United States (281) 274-4400 Quote Numberdiego veyzagaNo ratings yet
- Toshiba Rotary Compressor Catalog 1Document12 pagesToshiba Rotary Compressor Catalog 1paulquero8No ratings yet
- Electrical Manual of Asphalt Batch Mix PlantDocument45 pagesElectrical Manual of Asphalt Batch Mix Plantsami zaroufNo ratings yet
- Notice-Rotary-Compressors Eu enDocument28 pagesNotice-Rotary-Compressors Eu enzelko kovacevicNo ratings yet
- S Setting Value, C Check Value) OT Outside Tolerance (X Is Set)Document3 pagesS Setting Value, C Check Value) OT Outside Tolerance (X Is Set)Agus WijayadiNo ratings yet
- Bettis RPE Series PDFDocument31 pagesBettis RPE Series PDFJohn CruzNo ratings yet
- USA Gas Cycles Diesel DualDocument4 pagesUSA Gas Cycles Diesel DualRaymartNo ratings yet
- Advanced Materials For Land Based Gas TurbineDocument26 pagesAdvanced Materials For Land Based Gas TurbineEnary SalernoNo ratings yet
- FAA 2017 1122 0002 - Attachment - 3Document41 pagesFAA 2017 1122 0002 - Attachment - 3a0968973521No ratings yet
- Keywords: Refrigerant R134a, Refrigerant R1234yfDocument7 pagesKeywords: Refrigerant R134a, Refrigerant R1234yfAndrew CrawfordNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Engineering Cycles: Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics SeriesFrom EverandAnalysis of Engineering Cycles: Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics SeriesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Thermodynamic Design Data for Heat Pump Systems: A Comprehensive Data Base and Design ManualFrom EverandThermodynamic Design Data for Heat Pump Systems: A Comprehensive Data Base and Design ManualNo ratings yet
- Stunning TrailsDocument21 pagesStunning Trailskabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- European Student Accommodation Guide: SPRING 2018Document20 pagesEuropean Student Accommodation Guide: SPRING 2018kabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Equivalent EvaporationDocument21 pagesEquivalent Evaporationkabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Air CompressorsDocument26 pagesAir Compressorskabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Boilers - ClassificationDocument77 pagesBoilers - Classificationkabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Psychrometry - Part 1 of 2Document34 pagesPsychrometry - Part 1 of 2kabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Axial Flow CompressorsDocument8 pagesAxial Flow Compressorskabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Useful Websites of Pharmaceutical FieldDocument8 pagesUseful Websites of Pharmaceutical FieldVishnu ClickzNo ratings yet
- FAQ Visa For GermanyDocument1 pageFAQ Visa For Germanykabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Useful Websites of Pharmaceutical FieldDocument8 pagesUseful Websites of Pharmaceutical Fieldkabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- AaZ Englisch 2012 JenaDocument4 pagesAaZ Englisch 2012 JenaYassirBenNo ratings yet
- Block 2 Test 5Document1 pageBlock 2 Test 5kabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Suggested Packing ListDocument5 pagesSuggested Packing ListPranjali BidwaiNo ratings yet
- Useful Websites of Pharmaceutical FieldDocument8 pagesUseful Websites of Pharmaceutical FieldVishnu ClickzNo ratings yet
- Class 3Document19 pagesClass 3kabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine EngineDocument10 pagesGas Turbine Enginekabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Notes 1Document6 pagesNotes 1kabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Application For Statistical MeasuresDocument10 pagesApplication For Statistical Measureskabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- ARUMUKAM's Resume PDFDocument1 pageARUMUKAM's Resume PDFkabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Bewerbung Internationals enDocument6 pagesBewerbung Internationals enkabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Class 3Document19 pagesClass 3kabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Block 2 Test 5Document1 pageBlock 2 Test 5kabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Flowchart IDocument27 pagesFlowchart Ikabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Combuston ChamberDocument6 pagesCombuston Chamberkabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Class 2Document20 pagesClass 2kabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Class 3 - Normal DistributionDocument20 pagesClass 3 - Normal Distributionkabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Class 2 - Poisson DistributionDocument20 pagesClass 2 - Poisson Distributionkabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- ChartsDocument35 pagesChartskabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Class 1 - BinomialDocument25 pagesClass 1 - Binomialkabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Hastingsdiesel Catalog10202014Document37 pagesHastingsdiesel Catalog10202014cpaolinodNo ratings yet
- Solar Pile Drive Spare PartsDocument2 pagesSolar Pile Drive Spare PartsFrancis SalongaNo ratings yet
- Build An Electric Generator Model ProjectDocument2 pagesBuild An Electric Generator Model Projectapi-309043522No ratings yet
- (To Be Published in The Official Gazette of Kerala) : Boiler Operation Engineer'S Examination - 2021 BOE-2021Document8 pages(To Be Published in The Official Gazette of Kerala) : Boiler Operation Engineer'S Examination - 2021 BOE-2021Tamil VananNo ratings yet
- Gas Power Cycles The Carnot Gas Power CycleDocument6 pagesGas Power Cycles The Carnot Gas Power CycleAdnan Shahariar AnikNo ratings yet
- Jet Engine - 1Document21 pagesJet Engine - 1MuhammedNayeemNo ratings yet
- Datenblatt ULS Singapore Online AsDocument2 pagesDatenblatt ULS Singapore Online AsFaraj AlferjaniNo ratings yet
- List of Power Stations in Pakistan - WikipediaDocument27 pagesList of Power Stations in Pakistan - WikipediaMehmood WaniNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Kumpulan Contoh Makalah Teknik Mesin Sample Paper LengkapDocument8 pagesKumpulan Kumpulan Contoh Makalah Teknik Mesin Sample Paper Lengkapandino yogaNo ratings yet
- FWSSDocument2 pagesFWSSShwan SoraniNo ratings yet
- GETCO SubstationDocument1 pageGETCO SubstationAbhishek RajputNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbines: Associate Professor, Mech. Engg. Deptt. Head, Institute of Alternate Energy Research (IAER), R&D Coes, UpesDocument186 pagesGas Turbines: Associate Professor, Mech. Engg. Deptt. Head, Institute of Alternate Energy Research (IAER), R&D Coes, UpesPRAVEEN100% (1)
- Introduction To IC EnginesDocument43 pagesIntroduction To IC Engineswlkngs87No ratings yet
- Boiler - Components and FunctionsDocument49 pagesBoiler - Components and FunctionsAnonymous j5XYgIu100% (4)
- Combined Cycle Power Plant Combined Cycle Power Plant: Bydra Klilu T EsfamichaelDocument15 pagesCombined Cycle Power Plant Combined Cycle Power Plant: Bydra Klilu T EsfamichaelShafirNo ratings yet
- Turbines, Compressors and Fans - S. M. YahyaDocument170 pagesTurbines, Compressors and Fans - S. M. YahyaGt VaradharajanNo ratings yet
- Biomass Boiler - Buyers GuideDocument7 pagesBiomass Boiler - Buyers GuideMathias LeonNo ratings yet
- Solar UmbrellaDocument15 pagesSolar Umbrellaaniscartujo1989No ratings yet
- MQCs - EAM - Unit 6Document7 pagesMQCs - EAM - Unit 6Sayee DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- 07A52403 THERMALENGINEERING IIfr 6820Document8 pages07A52403 THERMALENGINEERING IIfr 6820Kenneth C.LinojNo ratings yet
- List of Power Stations in India - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument17 pagesList of Power Stations in India - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAnjali ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 27.6% Conversion Efficiency, A New Record For Single-Junction Solar Cells Under 1 Sun IlluminationDocument5 pages27.6% Conversion Efficiency, A New Record For Single-Junction Solar Cells Under 1 Sun IlluminationFernando DiasNo ratings yet
- Boiler Limits Rev2Document2 pagesBoiler Limits Rev2Ananth Kumar KNo ratings yet
- Potable Water Heaters: Main Features & Advantages Main Features & AdvantagesDocument2 pagesPotable Water Heaters: Main Features & Advantages Main Features & AdvantagesCarlos IzquierdoNo ratings yet
- Solar Panel RoofingDocument10 pagesSolar Panel RoofingAnandhu Anil100% (1)
- 1 - Hydro Power PlantsDocument54 pages1 - Hydro Power Plantsraghurmi100% (1)
- Renewable Energy ResourcesDocument3 pagesRenewable Energy ResourcesSandeep SunnyNo ratings yet
- P6112 Alstom PG9171E PowerPlant SpecificationsDocument1 pageP6112 Alstom PG9171E PowerPlant SpecificationsSunario YapNo ratings yet
- Drum Level ControlDocument16 pagesDrum Level ControlAakanksha GahlautNo ratings yet