Professional Documents
Culture Documents
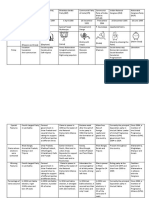
S.N O. Name Foundation Year Founding Members and Claim To Power Party Symbol Ideologies States/UT
Uploaded by
Ashwani Anand0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
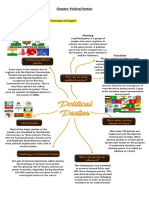
15 views4 pages1. The document lists 7 major political parties in India, providing information on their founding year, key leaders and ideologies, and states/regions where they have significant presence or support.
2. The three largest national parties are the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), Indian National Congress (INC), and Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP). The BJP and INC currently lead pre-election coalitions and the INC was in power from 2004-2019.
3. The political parties represent a range of ideological positions from left-leaning like the Communist Party of India (CPI) to centrist like the INC to right-leaning cultural nationalism associated with the BJP.
Original Description:
Original Title
National Parties of India
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document lists 7 major political parties in India, providing information on their founding year, key leaders and ideologies, and states/regions where they have significant presence or support.
2. The three largest national parties are the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), Indian National Congress (INC), and Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP). The BJP and INC currently lead pre-election coalitions and the INC was in power from 2004-2019.
3. The political parties represent a range of ideological positions from left-leaning like the Communist Party of India (CPI) to centrist like the INC to right-leaning cultural nationalism associated with the BJP.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views4 pagesS.N O. Name Foundation Year Founding Members and Claim To Power Party Symbol Ideologies States/UT
Uploaded by
Ashwani Anand1. The document lists 7 major political parties in India, providing information on their founding year, key leaders and ideologies, and states/regions where they have significant presence or support.
2. The three largest national parties are the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), Indian National Congress (INC), and Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP). The BJP and INC currently lead pre-election coalitions and the INC was in power from 2004-2019.
3. The political parties represent a range of ideological positions from left-leaning like the Communist Party of India (CPI) to centrist like the INC to right-leaning cultural nationalism associated with the BJP.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
S.
N Name Foundation Founding Party Ideologies States/UT
o. Year members Symbol
and claim
to power
1 All India 1 January Mamata The Committed to secularism West
Trinamool 1998 Banerjee party’s and federalism Bengal,
Congress symbol is Arunachal
(AITC) In the flowers Pradesh,
General and Manipur and
Elections grass. Tripura.
held in
2019, it got
4.07 per
cent votes
and won 22
seats,
making it
the fourth
largest
party in the
Lok Sabha.
2 Bahujan 1984 Kanshi 1. Seeks to represent and Uttar
Samaj Ram secure power for the Pradesh,
Party Came to bahujan samaj which Madhya
(BSP) power in includes the dalits, Pradesh,
1998 as the adivasis, OBCs and Chhattisgar,
leader of Elephant religious minorities. Uttarakhand,
the National 2. Draws inspiration from Delhi and
Democratic the ideas and Punjab.
Alliance teachings of Sahu
(NDA) Maharaj, Mahatma
including Phule, Periyar
several Ramaswami Naicker
regional and Babasaheb
parties. Ambedkar.
Emerged as 3. Stands for the cause of
the largest securing the interests
party with and welfare of the
303 dalits and oppressed
members in people.
the 2019
Lok Sabha
elections.
Currently
leads the
ruling NDA
government
at the
Centre.
3 Bharatiya 1980 by 1. Wants to build a strong All across
Janata reviving the and modern India by India
Party (BJP) erstwhile drawing inspiration
Bharatiya from India’s ancient Earlier
Jana Sangh culture and values; limited to
formed by Lotus 2. Draws inspiration from north and
Syama flower Deendayal west and to
Prasad Upadhyaya’s ideas of urban areas,
Mukherjee integral humanism and the party
in 1951 Antyodaya. expanded its
3. Cultural nationalism (or support in
Came to ‘Hindutva’) is an the south,
power in important element in its east, the
1998 as the conception of Indian north-east
leader of nationhood and and to rural
the National politics. areas.
Democratic 4. Wants full territorial
Alliance and political integration
(NDA) of Jammu and Kashmir
including with India,
several 5. a uniform civil code for
regional all people living in the
parties. country irrespective of
Emerged as religion,
the largest 6. ban on religious
party with conversions
303
members in
the 2019
Lok Sabha
elections.
Currently
leads the
ruling NDA
government
at the
Centre.
4 Communist 1925 1. Believes in Marxism- Kerala, West
Party of Leninism, secularism Bengal,
India (CPI) Its support and democracy. Punjab,
base had 2. Opposed to the forces Andhra
gradually of secessionism and Pradesh and
declined communalism. Tamil Nadu.
over the 3. Accepts parliamentary
years. It democracy as a
secured means of promoting
less than 1 the interests of the
per cent working class, farmers
votes and 2 and the poor.
seat s in the
2019 Lok
Sabha
elections.
Advocates
the coming
together of
all left
parties to
build a
strong left
front.
5 Communist 1964 1. Believes in Marxism Enjoys
Party of After Leninism. strong
India - splitting with 2. Supports socialism, support in
Marxist the secularism and West
(CPI-M): Communist democracy and Bengal,
Party of opposes imperialism Kerala and
India (CPI) and communalism. Tripura,
3. Accepts democratic especially
Was in elections as a useful among the
power in and helpful means for poor, factory
West securing the objective workers,
Bengal of socio-economic farmers,
without a justice in India. agricultural
break for 34 4. Critical of the new labourers
years. In economic policies that and the
the 2019 allow free flow of intelligentsia
Lok Sabha foreign capital and
elections, it goods into the
won about country.
1.75 per
cent of
votes and 3
seats.
6 Indian 1885 1. Under the leadership All across
National of Jawaharlal Nehru, India
Congress Leader of the party sought to
(INC) the United build a modern
Progressive secular democratic
One of the Alliance republic in India. .
oldest (UPA) 2. A centrist party
parties of government (neither rightist nor
the world from 2004 leftist) in its
to 2019. In ideological orientation,
the 2019 the party espouses
Lok Sabha secularism and
election it welfare of weaker
won 52 sections and
seats. minorities.
3. The INC supports new
economic reforms but
with a human face.
7 Nationalist Formed in 1. Espouses democracy, A major
Congress 1999 Gandhian secularism, party in
Party following a equity, social justice Maharashtra
(NCP) split in the and federalism. and has a
Congress 2. Wants that high significant
party. offices in government presence in
be confined to natural Meghalaya,
A coalition born citizens of the Manipur and
partner in country. Assam
the state of
Maharashtr
a in alliance
with the
Congress.
Since 2004,
a member
of the
United
Progressive
Alliance.
You might also like
- Political PartiesDocument23 pagesPolitical PartiesPriyanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- The India I Know and of Hinduism: From a South Indian Woman WriterFrom EverandThe India I Know and of Hinduism: From a South Indian Woman WriterNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Social Science Political Parties in IndiaDocument2 pagesClass 10 Social Science Political Parties in IndiaS.RamasamyNo ratings yet
- Sa II Class X S.STDocument22 pagesSa II Class X S.STIvniaz Zoref DeysNo ratings yet
- All India Trinamool CongressDocument3 pagesAll India Trinamool CongressDiya R ShahNo ratings yet
- Polity Chapter 3Document34 pagesPolity Chapter 3Vitteshwar KamurtiNo ratings yet
- All India Trinamool Congress (AITC) : Mukharjee" in 1951Document2 pagesAll India Trinamool Congress (AITC) : Mukharjee" in 1951Zeyan SayeedNo ratings yet
- Political PartiesDocument28 pagesPolitical PartiesswethaNo ratings yet
- Mayawati English Bio-DataDocument4 pagesMayawati English Bio-Dataapi-3803039No ratings yet
- Unit 10Document12 pagesUnit 10Nabam Tazap HinaNo ratings yet
- Social Science Project Indian Political Parties: Vii B'Document7 pagesSocial Science Project Indian Political Parties: Vii B'Apu RvaNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Political Parties in India: Their Growth and Contribution To The Development of LawDocument16 pagesThe Effectiveness of Political Parties in India: Their Growth and Contribution To The Development of LawAbhipsha MohantyNo ratings yet
- Political Parties Meaning of Political PartyDocument4 pagesPolitical Parties Meaning of Political PartyAryan SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- SST - Revision (Civics)Document49 pagesSST - Revision (Civics)Gargi SapteNo ratings yet
- Igp Cia 3Document15 pagesIgp Cia 3jeevan t georgeNo ratings yet
- List of All Political Parties in India With Their Founder Presidents Check Here E8271660Document15 pagesList of All Political Parties in India With Their Founder Presidents Check Here E8271660Armaan GarnayakNo ratings yet
- 10 Pol Lesson 6 Notes 2023-24Document20 pages10 Pol Lesson 6 Notes 2023-24jokerbladed19No ratings yet
- Inside Narendra Modi's BattleDocument9 pagesInside Narendra Modi's Battlena09b042No ratings yet
- All India Majlis-e-Ittehadul Muslimeen - WikipediaDocument17 pagesAll India Majlis-e-Ittehadul Muslimeen - WikipediaKrishna SaiNo ratings yet
- Political PartiesDocument5 pagesPolitical PartiesShreya TyagiNo ratings yet
- Assignment - National Political PartiesDocument17 pagesAssignment - National Political PartiesMonishaNo ratings yet
- Indian Public School: Very Important Very-Very ImportantDocument10 pagesIndian Public School: Very Important Very-Very ImportantMithilesh JhaNo ratings yet
- Trends of Dalit Movements Post Independence:: Sanskritization ConversionsDocument6 pagesTrends of Dalit Movements Post Independence:: Sanskritization ConversionschethaemailsNo ratings yet
- Ijmrss 212Document4 pagesIjmrss 212SenthilKumarNo ratings yet
- Political Science..: Chapter - 6 Political Parties National Parties of IndiaDocument18 pagesPolitical Science..: Chapter - 6 Political Parties National Parties of IndiaRohit BhagtaniNo ratings yet
- Periyar in Justice PartyDocument34 pagesPeriyar in Justice Partypriya dharsiniNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Iv Emergence of Kapus in Andhra PoliticsDocument66 pagesChapter - Iv Emergence of Kapus in Andhra PoliticsMurali GurajalaNo ratings yet
- Key Concepts: Chapter 6 - Political Parties, Class 10, SST: What Is A Political Party?Document6 pagesKey Concepts: Chapter 6 - Political Parties, Class 10, SST: What Is A Political Party?Sandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- BJP (Bharatiya Janata Party)Document9 pagesBJP (Bharatiya Janata Party)tluanga kakaNo ratings yet
- 3.20 - Post Independence History Part 3Document20 pages3.20 - Post Independence History Part 3VedantNo ratings yet
- Political Parties HandoutDocument10 pagesPolitical Parties HandoutAvni PuriNo ratings yet
- A Study of The Politics and Role of Religion in Indian PoliticsDocument2 pagesA Study of The Politics and Role of Religion in Indian PoliticsLanupokyimNo ratings yet
- Maps Pol Sci Term 2Document5 pagesMaps Pol Sci Term 2tanushjaNo ratings yet
- Regional Parties in IndiaDocument5 pagesRegional Parties in IndiaRuat PuiiNo ratings yet
- National Parties inDocument22 pagesNational Parties invivekyashNo ratings yet
- Chapter: Political Parties: Mind-Map/Overview of ChapterDocument15 pagesChapter: Political Parties: Mind-Map/Overview of ChapterBinat SanghaniNo ratings yet
- HIndutvaDocument10 pagesHIndutvaAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Need Political Parties?Document6 pagesWhy Do We Need Political Parties?BEYOND GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Political Parties Notes For Term 2Document6 pagesPolitical Parties Notes For Term 2Renu YadavNo ratings yet
- Role of Caste in PoliticsDocument5 pagesRole of Caste in PoliticssalmanNo ratings yet
- Class - X Subject-Political Science Chapter-L6-Political Parties Handout & Q/A Name: .. Class/Section Roll NoDocument10 pagesClass - X Subject-Political Science Chapter-L6-Political Parties Handout & Q/A Name: .. Class/Section Roll NoParmeet SinghNo ratings yet
- BJP of IndiaDocument25 pagesBJP of Indiaansari naseem ahmadNo ratings yet
- IF10298Document3 pagesIF10298Dorjee SengeNo ratings yet
- Regional Parties Emergence and EvolutionDocument16 pagesRegional Parties Emergence and EvolutionPranshu VatsNo ratings yet
- Political Parties and Elections in India: An OverviewDocument62 pagesPolitical Parties and Elections in India: An OverviewSugunaNo ratings yet
- Rise of Congress Socialist Party - 1934 Onwards - GKTodayDocument2 pagesRise of Congress Socialist Party - 1934 Onwards - GKTodayankit_shakyawarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Social Science Civics Chapter 6 Political PartiesDocument8 pagesCBSE Notes Class 10 Social Science Civics Chapter 6 Political PartiesanzhiaxbNo ratings yet
- Vedika Kakar - CastePoliticsinContemporaryUttarPradeshDocument6 pagesVedika Kakar - CastePoliticsinContemporaryUttarPradeshOrange SnowNo ratings yet
- Role of Caste in Indian Politics: Social ScienceDocument3 pagesRole of Caste in Indian Politics: Social ScienceNaimish SinghNo ratings yet
- Regional Is MDocument25 pagesRegional Is MIlampariNo ratings yet
- Svu-Fc1em - BL2015 - TDocument4 pagesSvu-Fc1em - BL2015 - TAmanda BarkerNo ratings yet
- Democracy and Regional PartiesDocument37 pagesDemocracy and Regional PartiesTaronish IraniNo ratings yet
- Era of One Party DominanceDocument8 pagesEra of One Party DominanceRamita Udayashankar86% (14)
- REASON AND ASSERTION Class IxDocument3 pagesREASON AND ASSERTION Class Ixakhilyadav192009No ratings yet
- Political Parties (Prashant Kirad)Document13 pagesPolitical Parties (Prashant Kirad)jainanony844No ratings yet
- Vaishnav and Hintson - India's New Fourth Party SystemDocument8 pagesVaishnav and Hintson - India's New Fourth Party Systemmv011980No ratings yet
- Do This One Day Before SST ExamDocument112 pagesDo This One Day Before SST ExamabNo ratings yet
- Std. X Civics Chapter-6Document5 pagesStd. X Civics Chapter-6Priyanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Syndicate Group Presentation Group 11Document47 pagesSyndicate Group Presentation Group 11sonali malaviNo ratings yet
- ADocument2 pagesAẄâQâŗÂlïNo ratings yet
- AMAZONS StategiesDocument2 pagesAMAZONS StategiesPrachi VermaNo ratings yet
- Report - Fostering The Railway Sector Through The European Green Deal PDFDocument43 pagesReport - Fostering The Railway Sector Through The European Green Deal PDFÁdámHegyiNo ratings yet
- Torque Converter Lock-Up FunctionDocument2 pagesTorque Converter Lock-Up Functioncorie132100% (1)
- 99990353-Wsi4-2 C1D2-7940022562 7950022563 7940022564Document2 pages99990353-Wsi4-2 C1D2-7940022562 7950022563 7940022564alltheloveintheworldNo ratings yet
- CreatorsXO JuneDocument9 pagesCreatorsXO JuneGaurav KarnaniNo ratings yet
- OD426741449627129100Document1 pageOD426741449627129100SethuNo ratings yet
- AWS Migrate Resources To New RegionDocument23 pagesAWS Migrate Resources To New Regionsruthi raviNo ratings yet
- Effect of End Blocks On Anchorage Zone Stresses in Prestressed Concrete GirdersDocument15 pagesEffect of End Blocks On Anchorage Zone Stresses in Prestressed Concrete Girdersrohit kumarNo ratings yet
- BS351: Financial Reporting: Learning ObjectivesDocument3 pagesBS351: Financial Reporting: Learning ObjectivesMajeed Ullah KhanNo ratings yet
- General Director AdDocument1 pageGeneral Director Adapi-690640369No ratings yet
- Natures CandyDocument19 pagesNatures CandyFanejegNo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTS Foundation Paper1Document336 pagesACCOUNTS Foundation Paper1mukni613324100% (1)
- The 8051 Microcontroller & Embedded Systems: Muhammad Ali Mazidi, Janice Mazidi & Rolin MckinlayDocument15 pagesThe 8051 Microcontroller & Embedded Systems: Muhammad Ali Mazidi, Janice Mazidi & Rolin MckinlayAkshwin KisoreNo ratings yet
- BroucherDocument2 pagesBroucherVishal PoulNo ratings yet
- Slope Stability Analysis Using FlacDocument17 pagesSlope Stability Analysis Using FlacSudarshan Barole100% (1)
- Case Study 05 PDFDocument5 pagesCase Study 05 PDFSaltNPepa SaltNPepaNo ratings yet
- In The High Court of Delhi at New DelhiDocument3 pagesIn The High Court of Delhi at New DelhiSundaram OjhaNo ratings yet
- Python BarchartDocument34 pagesPython BarchartSeow Khaiwen KhaiwenNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Killamsetty Rasmita Scam 1992Document8 pagesAssignment of Killamsetty Rasmita Scam 1992rkillamsettyNo ratings yet
- Feed Water Heater ValvesDocument4 pagesFeed Water Heater ValvesMukesh AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Np2 AnswerDocument13 pagesNp2 AnswerMarie Jhoana100% (1)
- PDS Air CompressorDocument1 pagePDS Air Compressordhavalesh1No ratings yet
- Cortex - M1: Technical Reference ManualDocument174 pagesCortex - M1: Technical Reference ManualSzilárd MájerNo ratings yet
- Role of SpeakerDocument11 pagesRole of SpeakerSnehil AnandNo ratings yet
- MAC120 PartsDocument23 pagesMAC120 PartspRAMOD g pATOLENo ratings yet
- Project Management PDFDocument10 pagesProject Management PDFJamalNo ratings yet
- AMC Mining Brochure (A4 LR)Document2 pagesAMC Mining Brochure (A4 LR)Bandung WestNo ratings yet
- Bangalore University: Regulations, Scheme and SyllabusDocument40 pagesBangalore University: Regulations, Scheme and SyllabusYashaswiniPrashanthNo ratings yet
- Video Case 1.1 Burke: Learning and Growing Through Marketing ResearchDocument3 pagesVideo Case 1.1 Burke: Learning and Growing Through Marketing ResearchAdeeba 1No ratings yet