Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Core English 1
Uploaded by
Keng PhearaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Core English 1
Uploaded by
Keng PhearaCopyright:
Available Formats
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
Grammar: ( The Tenses )
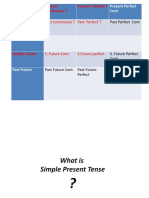
There are 24 main tenses in English:
There are 8 present tenses
Present Simple
Present Simple Passive
Present Continuous
Present Continuous Passive
Present Perfect
Present Perfect Passive
Present Perfect Continuous
Present Perfect Continuous Passive
There are 8 past tenses
Past Simple
Past Simple Passive
Past Continuous
Past Continuous Passive
Past Perfect
Past Perfect Passive
Past Perfect Continuous
Past Perfect Continuous Passive
There are 8 future tenses
Future Simple
Future Simple Passive
Future Continuous
Future Continuous Passive
Future Perfect
Future Perfect Passive
Future Perfect Continuous
Future Perfect Continuous Passive
I. Present Simple
1. Form: Subject+V1(present tense)
2. Examples
A. Positive Forms
I always get up at 5 a.m.
Your parents are active in the family.
Cambodian people always welcome King Norodom Sihamoni warmly.
Mary wants to play tennis with you.
Her brother is absent today.
Core English I 1 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
Life is a constant struggle.
I can help you. Please believe me.
Nurses take care of patients in hospital.
My students usually pay attention to A Special English Grammar.
The earth goes around the sun.
I‟m a government official, a researcher, and an English lecturer.
We are very happy because we can reach our destination.
The report does note that the government has made progress in recent years to
increase the amount of taxes it collects.
B. Negative Forms
David doesn‟t drink coffee very often.
I never drink coffee at night.
His uncle and aunt don‟t seem to be interested in him.
Danny‟s little brother isn‟t by himself.
It doesn‟t rain very much in summer.
They don‟t do foolish things because they are educated people.
You aren‟t responsible for her destiny.
We don‟t let destiny control our lives.
Your girlfriend isn‟t nasty now.
One document can take three months if I don‟t follow up and pay bribes.
I don‟t approach him anymore.
C. Question Forms
What time do you usually have dinner?
Does Mary look beautiful?
What time does she usually get home after work?
What does this word mean?
How long does it take from Phnom Penh to Takeo province?
Why is she so nasty?
Do you agree with my plans?
Does rice grow in Canada?
How often do you go to the dentist? You have a toothache.
Are you aware of the political and economic situation in Cambodia?
3. Definition
A. The first Definition
The Present Simple is used to express an action that happens again and again or
a present habit.
I go to work by motorcycle every day. (again and again)
He smokes twenty cigarettes a day. ( a present habit)
My daughter does the washing up every morning. ( Regular time)
She washes her hair twice a week.
My cousin does the washing on Sundays.
I usually get up at 5 o‟clock in the morning.
He always works from dawn to dusk.
Core English I 2 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
I rarely go for a walk at night.
We often pay attention to our course.
Mary doesn‟t often drink coffee.
We don‟t let other countries invade our land.
We don‟t ignore our environment.
Davy doesn‟t generally waste her time.
Are you always worried about your health?
What time do you usually have lunch?
You have a toothache. How often do you go to dentist?
Why do win-win situations always happen to you?
B. The Second Definition
The Present Simple is used to express a fact, which is always true.
The earth goes around the sun. ( all time)
Junichiro Koizumi comes from Japan. ( a fact)
My daughter has brown eyes. ( permanent)
I want $10. ( now)
Some birds fly south in winter.
You are tired. Why don‟t you go to bed early?
Vegetarians don‟t eat meat.
Where do you come from?
Where are you from?
The earth has a round shape.
The sun rises in the east.
The sun sets in the west.
Water boils at 100 centigrade.
C. The Third Definition
The Present Simple is used to express a fact, which stays the same for a long time.
I live in a flat in the center of town.
Nurses look after patients in hospital.
My elder brother works in an export and import company.
My father works in Ministry of Interior.
He prefers coffee to tea.
D. The Present Simple is often used with adverbs of frequency.
0% 50% 100%
never rarely not often sometimes often usually always
She‟s never late for work.
I rarely see Sophea these days.
My younger sister doesn‟t often go for a walk. She has a busy day.
Her younger brother often watches football matches on television.
I‟m usually in a hurry in the morning.
Being a student, I always pay attention to my courses.
Note:
Sometimes and usually can also go at the beginning or the end.
Core English I 3 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
Sometimes I‟m very happy when I‟m successful in my writing career.
My students understand an English grammar very clearly sometimes.
Never, always, rarely, and seldom cannot move their location. Every day, every night,
every week, every month, and every year go at the end.
I‟m never hopeless in my life.
Sad movie always makes girls cry
He phones me every night.
E. The Present Simple refers to a future event that is seen as unalterable
because it is based on a timetable or calendar.
My flight leaves at 10.00.
The second term starts on 4 April.
What time does the film start?
It is my birthday tomorrow.
You can meet me the day after tomorrow.
II. The Present Simple Passive
1. Form: Subject + am/is/are+ V3 (Past Participle)
2. Definition
The Present Simple Passive’s definition is the same as the Present Simple’s.
3. Examples
A. Positive Forms
Now I am forced to marry a girl whom I don‟t love.
His room is cleaned every day.
We are encouraged to study English in the evenings.
I am given two hours to do the first semester exam.
The Royal Government of Cambodia is sometimes accused of corruption.
My daughter is allowed to visit Pheah Vihea temple.
Your son is sometimes scolded because he doesn‟t listen to his teacher.
Your children are usually praised for their efforts.
B. Negative Forms
I am not accused of breaking a law.
Usually your daughter isn‟t helped by her co-workers.
All students aren‟t allowed to speak Khmer in the class.
I am not usually invited to take part in her birthday parties.
I am not taken to school on Fridays.
Your nephew isn‟t encouraged to do foolish things.
The National Assembly of Cambodia isn‟t completely admired by people
Make love, not war, violence shouldn‟t be used in the family and society.
Your family and you aren‟t given $200 a year by the government.
C. Question Forms
Why am I always encouraged to marry her? She‟s not my type.
Is he nominated to be the director general of your company?
Core English I 4 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
Are we forgiven now that we have admitted our mistakes?
What is David given $5,000 by the government every month?
What am I usually given to support her? Nothing, that‟s what.
They always rely on her. Is she expected to be a candidate for the Presidency?
Is your niece ordered to come here early or is it her own choice?
Who are you taken to work every day by?
Why are you motivated to study so hard?
Note:
Passive sentences move the focus from the subject to the object of active sentences.
The madam of a brothel forces her to be a prostitute.
She is forced to be a prostitute by the madam of a brothel.
by agent
The passive is not just another way of expressing the same sentences in the active. We
choose the active or the passive depending on what we are more interested in. In the first
sentence, we are more interested in the madam of the brothel; in the second sentences, she,
the prostitute, has moved to the beginning of the sentence because we are more interested in her.
By and the agents are often omitted in passive sentences if the agent:
is not known
This room is cleaned every morning. (Present Simple)
Children are usually praised for their efforts. (Present Simple Passive)
Her apartment was robbed last night. (Past Simple Passive)
Three suspects are being investigated rigorously. (Present Continuous Passive)
is not important
Pornographic film projection is suppressed and restrained. (Present Simple Passive)
English is spoken all over the world. (Present Simple Passive)
This bridge was built in 2001. (Past Simple Passive)
He has been convicted to a year in prison. (Present Perfect Passive)
is obvious
Vietnamese nationals who break the law in Cambodia are arrested promptly. (Present
Simple Passive) (obvious by the police)
He was fined £100 for speeding. (Past Simple Passive)
You will be fined £200 if you drive too fast. (Future Simple Passive)
The passive is associated with an impersonal, formal style. It is often used in notices and
announcements.
Customers are requested to refrain from smoking. (Present Simple Passive)
This proposal was forwarded to that company. (Past Simple)
It has been noticed that referent books have been removed from the library. (Present
Perfect Passive)
This case will have be solved next month. (Future Simple Passive)
In informal language, we often use „you‟, „we‟, and „they‟ to refer to people general. In this
way, we can avoid using the passive.
You can be responsible for your destiny.
You must never give up hope in your new life.
Core English I 5 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
We speak English in many countries.
They are building a new department store in the city centre.
By carefully! Many past participles are used as adjectives.
I‟m very interested in modern art.
We were extremely worried about you.
I‟m exhausted! I‟ve been working hard all day!
Are you excited today?
She is tired today. She has had a busy day.
I‟m bored today. I don‟t know where to go.
David is not getting better. He looks worried.
III. The Present Continuous
1. Form: Subject+ am/is/are +V1 +ing (Present Participle)
2. Examples
A. Positive Forms
Please be quiet. I‟m trying to concentrate.
The world is changing. Things never stay the same.
Don‟t make so much noise. I‟m studying English.
Excuse me. I‟m looking for my wallet. Do you know where it is?
The world is changing. Things never stay the same.
My friend is still ill, but he is getting better slowly.
The cost of living in Phnom Penh is increasing.
The Royal Government of Cambodia is reducing the Cambodian people‟s
poverty.
Everything in Phnom Penh is becoming more and more expensive.
John and Mary are marrying next year.
You are making a lot of noise. Can you be a bit quieter?
The poor in Cambodia are getting poorer and poorer, but the rich are getting
richer and richer.
The election is unlikely to end the Thai political standoff. The election was
called by Prime Minister Thaksin Shinawatra, who hopes to reassert his
popular mandate in the face of the strident, but so far peaceful, movement
that is working for his ouster, accusing him of corruption, abuse of power and
damaging the country‟s democratic institutions.
B. Negative Forms
I‟m not working today. I am on a holiday.
She isn‟t wearing jeans in the class.
I‟m not living in the countryside, but I grew up there.
I want to lose weight. I‟m not eating anything today.
John isn‟t listening to his teacher. He is thinking of his girlfriend.
Your younger sister isn‟t doing her homework. She‟s busy watching TV.
Core English I 6 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
His nephew„s illness isn‟t getting better but worse and worse.
George W. Bush and Tony Blair aren‟t starting wars any more.
My niece isn‟t doing her homework.
Her nephew and sister aren‟t shouting at each other.
We aren‟t drinking beer and smoking cigarettes because we are worried
about our health.
Helen and Michel aren‟t dancing at the moment. They are talking about their
lives.
C. Question Forms
Is Davaid building his own house?
Why are you looking at me like that? Have I said something wrong?
What am I doing tonight? Why don‟t you tell me?
Why am I working very hard? In fact, I want to achieve my goals.
Why are they shouting at each other?
Am I thinking about anything? Of course I am, I am always thinking.
Is your English getting better?
Is the population of the world rising rapidly?
Are your friends writing a tourism book?
What are you doing after this course?
Hello, Marline. Are you enjoying my birthday party?
Are you saving money to buy a brand-new motorcycle next month?
Are we reading a romantic story?
3. Definition
3.1The first Definition
The Present Continuous is used to express an activity happening now or at the
time of speaking.
My children are playing football in the garden.
My niece can‟t answer the phone because she‟s washing her hair.
Let‟s go out now. It isn‟t raining any more.
You are taking part in my birthday. Are you enjoying the party?
There are a lot of people here because the politician is making a speech.
What are they thinking about? They look happy.
The men near the window are drinking Tiger beer and talking to each other
happily.
Hello, Piseth. What are you doing now?
Be quiet! I‟m watching my favorite program.
A. Where is your son?
B. He‟s having a bath.
3.2The Second Definition
The Present Continuous is used to express an activity happening around now,
but perhaps not at the moment of speaking.
They are studying Tourism at the Royal Academy of Cambodia.
The number of people without jobs is increasing at the moment.
Core English I 7 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
My friend and I are writing a tourism book these days.
I‟m reading a good book by Henry James.
She‟s studying mathematics at university.
Have you heard about John? He‟s building his own house.
My brother and sister are learning English and Japanese at night school.
Hello, Marlene. I haven‟t seen you for ages. What are you doing these days?
I‟m working hard these days because I want to have enough money to marry.
We are taking an English grammar evening course this year.
Don‟t take that book to the library. Jane is reading it.
We have some lovely neighbors; we are making friends with them.
3.3The Third Definition
The Present Continuous is used to express a planned future arrangement. Also,
the Present Continuous is used to express personal arrangements and fixed
plans, especially when the time and place have been decided. A present tense is
used because there is some really in the present. The event is planned or
decided, and can see it coming. The event is usually in the near future.
I‟m having lunch with Brian tomorrow.
What time are they meeting him?
Where are you having lunch?
What are you doing tonight?
Are you coming to the dance tonight?
I‟m meeting the director tomorrow.
We‟re playing tennis this afternoon.
I‟m sorry I can‟t go with you. I‟m meeting my brother at 10 o‟clock
tomorrow.
What are you doing at the weekend?
He and she are getting married next year.
I‟m having dinner with Danny in the evening.
We‟re meeting at 3.00 outside the restaurant.
They are saving up to $10,000 next year with their new car.
Could you lend me $100? I‟m really paying you back the day after tomorrow.
She and I are walking along the river tomorrow evening.
They aren‟t playing football on August 12, 2009.
What are you doing after this course?
Note:
Sometimes there is little or no different between the Present Continuous and going to
refer to the future.
We‟re seeing Hamlet at the theatre tonight.
We‟re going to see Hamlet at the theatre tonight.
When there is a different, the Present Continuous emphasizes an arrangement with
some reality in the present; going to expresses a person‟s intentions.
I‟m seeing my girlfriend tonight.
I‟m going to ask her to marry me. (right)
I‟m asking her to marry me. (wrong, you have not asked her yet)
Core English I 8 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
What are you doing this weekend?
What are you going to do about the broken toilet? (=What have you decided to do?)
4. Present Simple versus Present Continuous
Some verbs are used in both simple and continuous forms. These are called actions verbs,
but some verbs are never used in the continuous form. These are called state verbs.
Examples
Marline usually drives to work, but today she isn‟t driving. (action verb)
Don‟t turn off the TV. I am watching it. (action verb)
Do you want to be a top student? (state verb)
Nary always walks to work. She is not walking to work tomorrow. (action verb)
I know his face, but I forget his name. (state verb)
Peter is working as a waiter during the holiday. (action verb)
Sometimes I don‟t care about what happened to him. (state verb)
Note:
Some verbs can be used in the Present Continuous, but with a change of meaning. In the
continuous, the verb expresses an activity, not a state. Compare:
I think you are polite. (opinion)
We are thinking of going on holiday. (mental activity a plan)
Helene has a lot of money. (possessive)
You cannot speak to Helene. She is having a bath. (activity)
I see what you mean. (understand)
Are you seeing Danny tomorrow? (activity-meeting)
The soup tastes awful. (state)
I am tasting the soup to see if it needs salt. (activity)
Comparisons of two sentences
Tony Blair is coming from England. (incorrect)
Tony Blair comes from England. (correct)
This is a great party. Everyone has a good time. (incorrect)
This is a great party. Everyone is having a good time. (correct)
I read a good book at the moment. (incorrect)
I am reading a good book at the moment. (correct)
I am understanding your mind well. (incorrect)
I understand your mind well. (correct)
I am liking orange juice. (incorrect)
I like orange juice. (correct)
IV. The Present Continuous Passive
1. Form: Subject+ am/is/are+ being+ V3(Past Participle)
2. Definition
The Present Continuous Passive’s definition is the same as the Present Continuous Active’s.
3. Examples
Core English I 9 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
A. Positive Forms
I am being accused of destroying her reputation.
I‟m being encouraged to get a PhD.
This room is being cleaned at the moment.
Our kitchen is being decorated at the moment.
This bridge is being built.
The political crisis in Cambodia is being solved day by day.
Corruption is being eliminated in some countries.
About one thousand people are being employed in that factory.
Lots of tulips are being grown in Holland.
Davy is being forced to marry next month.
B. Negative Forms
I‟m not being criticized like you.
I‟m not being taught tourism.
I‟m not being punished now.
That block of flats isn‟t being pulled down next week.
The girl isn‟t being forced to do what she doesn‟t want to do.
Our factory isn‟t being taken over by an American company.
The environment in some countries isn‟t being protected carefully.
These problems aren‟t being investigated thorough and rigirously.
We aren‟t being allowed to speak loudly here.
Latin isn‟t being spoken in any countries officially.
C. Question Forms
What am I being forced to do?
Why am I being ordered to do what I don‟t want to do?
Is Khmer Rouge‟s case being investigated rigorously and thoroughly?
Is your house being built at the moment?
Are Cambodian people‟s living standards being improved?
Why is she being encouraged to study at night school?
Is his crisis being solved today?
Are you being encouraged to marry her next month?
Why are they being detained in jail?
Is the bridge being built by your uncle?
V. The Present Perfect
1. Form: Subject+ have/has +V3(Past Participle)
In English, the Present Perfect is essentially a present tense, but it also expresses the effect
of past actions and activities on the present.
Past Present Perfect Present
Core English I 10 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
Present Perfect means „before now‟. The Present Perfect does not express when an action
happened. If we say the exact, we have to use the Past Simple.
2. Examples
A. Positive Forms
I have been a seller for five years.
He has lost my car key. Can you help him look for it?
You have found a new job. Are you happy now?
You‟ve been interested in her for months. Why don‟t you ask her to marry you?
She has already solved her personal problems.
We‟ve made up their mind to get married.
Do you know about John? He has gone to the United States.
Peter is back in Phnom Penh. He‟s been in Canada. (He‟s come back)
Mary has thought enough about her marriage for one week.
B. Negative Forms
I have never been out with a girl. I‟m always busy studying.
He has not understood her mind until now.
I have not made a girl cry in my entire life.
You haven‟t created a conflict with them. Don‟t worry yet.
She hasn‟t agreed to marry you yet. Don‟t be upset.
You haven‟t given her any money. She can‟t live without money any more.
You haven‟t traveled all over the world.
They haven‟t brought their dictionaries with them.
Our family hasn‟t allowed them to go with us.
The Royal Government of Cambodia hasn‟t eliminated its corruption.
C. Question Forms
Has your friend ever been to Siem Reap?
Have they returned your money yet?
They are looking at me strangely. Have I said something wrong?
Have they returned your money yet?
Have you had dinner yet? Please have dinner with me.
How many books has your father written in his entire life?
How long have you worked as a professor?
Have you forgotten the times you had with her since she left you?
Has she passed her driving test yet?
Have they learned about the political situation in Cambodia during the past two
weeks?
3. Definition
3.1The First Definition
The Present Perfect is used to express an activity which began in the past and
continues to the present. It possibly goes on into the future, as well.
I‟ve lived in the same flat for five years.
How long have you known each other?
David‟s worked as a teacher since 1991.
Core English I 11 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
My daughter has not lived at my house since she was 18 years old.
The work has been easy so far, but things may change.
I‟ve met a lot of famous people. ( before now)
My brother has lived here all his life. ( up to the present, and problem into the
future)
I have lived in Phnom Penh for twelve years. ( I still live in Phnom Penh)
I have bought a new car recently. ( I still have a new car)
My uncle and aunt have been married for fifteen years.
How long have you worked in an export and import company?
Note:
We realize that a sentence in the present perfect fits the first definition when we see other
words: for, how long, since, a lot of, so far, and all one’s life.
These time expressions are common with the first definition
for three years since 2003
a month the end of the class
a few minutes May
half an hour 9 o‟clock
ages Women‟s Day
Note:
We use for with a period of time and since with a point in time.
I have lived in the same flat for five years.
I have lived in the same flat since 2001.
since 2001 for five years 2006 (now)
3.2 The Second Definition
The Present Perfect is used to express a past action that has a present result. The
action is usually in the recent past.
I have lost my wallet. ( I haven‟t got it now)
The taxi hasn‟t arrived yet. (We‟re still waiting for it)
What have you done to your lip? (It‟s bleeding)
Tony has shaved his beard off! ( He looks different)
Has the postman brought any letter yet? ( Are there any letters on the mat now?)
I‟ve cut my finger. (It‟s bleeding)
Have you heard? The Prime Minister has registered. ( A present fact)
Mary has had her baby! ( A present fact)
I‟ve ruined my meal. It‟s burnt. ( A present fact)
I have not done my homework yet. (Negative form)
Have you posted my letter yet? (Question form)
A. Would you like something to eat?
B. No thanks. I‟ve just had lunch. ( Positive form)
I have already developed an interest in her. (Positive form)
You‟ve changed. What have you done to yourself?
He‟s lost his weight. He‟s worried about his health.
Core English I 12 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
German Chancellor Angela Merkel has clearly made an extremely good
impression in the four months since she took office.
Note
We realize that a sentence in the present perfect fits the second definition when we see other
words: yet, just, already, or other verbs in the recent past.
has has
Subject+ yet+ to +V1 = Subject+ + not + V3 +yet
have have
Marline has yet to do homework. (=Marline hasn‟t done her homework yet)
I have yet to think about getting married. (=I haven‟t thought about getting married yet)
She has yet to write her reports. (She hasn‟t written her reports yet)
He hasn‟t objected to your plan yet. (=I have yet to object to your plan)
I haven‟t given her money $50 yet. (=I have yet to give her $50)
I don‟t have the money, yet I really need the CD player. (Coordinating conjunction,
this sentence is not in the present perfect)
She doesn‟t have enough time, yet she wants to chat with me. (Coordinating
conjunction, this sentence is not in the present perfect)
We have yet to decide what to do with the money. (=We haven‟t decide what to do
with the money yet)
3.3The Third Definition
The Present Perfect is used to express an experience that happened at some time in
one’s life. The action is in the past and finished, but the effects of the actions are
still felt. When the action happened is not important.
I have been to Preah Vihear temple. (I still remember.)
He‟s written poetry and children‟s stories. (In his writing career)
Have you ever had an operation? ( At any time in your life up to now)
How many times has she been married? (In her life)
I haven‟t tried American food before.
Have you ever broken something expensive?
I have never tried Japanese food.
Have they ever been to Australia?
Has your girlfriend ever acted on stage?
They haven‟t flown in a helicopter.
He has never been to any foreign countries.
Note:
We realize that a sentence in the present perfect fits the third definition when we see other
words: been to, how many times, ever, never, and before
Be careful with „been‟ and „gone‟
David has been to the United States. (Experience- he isn‟t there now)
David has gone to the United States. (Present Result- he is there now)
Present Perfect versus Past Simple
The Present Perfect is not unfinished actions or refers to indefinite time. The Past
Simple is for completed actions or refers definite time by looking at the time expressions
used with the different tenses.
Examples
Core English I 13 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
Present Perfect
I have lived in Texas for six years. ( I still live there)
I‟ve written several books. (I can still write some more.)
I‟ve done it for a long time. (indefinite time)
She has known me since January. (indefinite time and she still knows me)
You haven‟t tried Japanese food before. (indefinite time)
I have loved a girl recently. (indefinite time and I still love the girl)
Past Simple
I lived in Texas for six years. (Now I live somewhere else)
Shakepeare wrote 30 plays. (He can‟t write any more)
I did it yesterday. (definite time)
I saw my best friend on the street the day before yesterday. (definite time)
Did you see your daughter last week? (definite time)
He found his person freedom two months ago. (definite time)
Danny talked to me at 9 o‟clock. (definite time)
I arrived in Phnom Penh in 1990. (definite time)
I had some difficult circumstances in my life when I was young. (definite time)
Police investigated this case for a long time before giving up. (definite time)
She resigned because she lost a vote of no confidence.
She had a baby boy this morning. I was a difficult birth.
I didn‟t watch it carefully enough.
When did you go to the United States?
I broke my leg once, but I didn‟t have to stay in the hospital.
He met his second wife in the dry cleaner‟s.
Compare with two sentences
When did you go to Japan? (Right)
When have you been to Japan? (Wrong)
I saw him yesterday. (Right)
I have seen him yesterday. (Wrong)
I have taught English for 15 years. (Right)
I teach English for 15 years. (Wrong)
Where did you buy your jumper? (Right)
Where have you bought your jumper? (Wrong)
I haven‟t brought my dictionary to class. (Right)
I didn‟t bring my dictionary to class. (Wrong)
Be careful with this morning/afternoon, etc.
Have you seen Helene this morning? ( It‟s still morning.)
Did you see Helene this morning? (It‟s the afternoon or evening.)
Core English I 14 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
Note:
American English is different from British English. In American English the simple past is
used more often in British English. In American English, the following sentences are correct.
Did you hear the news? The President resigned!
Did you do your homework yet?
Your father just called you.
I already had breakfast.
VI. The Present Perfect Passive
1. Form: Subject+ have/has+ been+ V3 (Past Participle)
2. Definition
The Present Perfect Passive’s definition is the same as the Present Perfect Active’s.
3. Examples
A. Positive Forms
I have been nominated as a director general.
We‟ve been allowed to stay at the hotel for five more days.
I‟ve been given $5,000 to buy a new car.
She has been bought a diamond ring for the wedding.
She‟s been transferred to teach English in the countryside.
Your dog has been taken for a walk already.
He has been assassinated because of his politics.
Your son has been admired because of his devotion to her.
You have been sentenced to two months in prison.
Popular singer Preap Sovath, well-known kick boxer Ei Pouthang, and film
star Tep Rindaro have been chosen as goodwill ambassadors by local
environmental NGO Wild Aid to educate the public about killing and trading
in wild animals. (newspaper)
B. Negative Forms
I haven‟t been appointed as a director general in her company.
You haven‟t been invited to join her auspicious marriage ceremony.
We haven‟t been given the chance to solve that problem.
She hasn‟t been doubted since I‟ve known her.
He hasn‟t been permitted to marry her. However, he always tries to meet
her.
Incompetent officials in the government haven‟t been removed yet.
Your parents haven‟t been forgiven because they are very rude to people.
John hasn‟t been respected because he‟s done nothing to deserve respect.
David and Mary have never been allowed to see each other.
Her nephew and niece haven‟t been selected to work in this organization.
C. Question Forms
How long have you been employed here?
Have you been given enough time to do the first semester exam?
Core English I 15 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
Has she been forced to vote for a specific political party?
Has your father been nominated to stand for election?
Who has been elected to be prime minister for the new term?
Why have Peter and David been allowed to work in this company all their
lives?
How long has his motorcycle been stolen?
Has the governor been removed from power?
Why has he been charged with corruption?
VII. The Present Perfect Continuous
1. Form: Subject+ have/has+ been+ V.ing (Present Participle)
2. Examples
A. Positive Forms
I have been teaching English for eleven years.
You have been working here for two months.
My sister has got paint in her hair because she has been decorating.
I‟ve been staying with my friends until I find my own place to live.
He‟s been cutting the grass.
I‟ve been living with them for two months.
You have been playing the piano since you were a child.
She‟s been reading all day. She‟ll take that book back to the library when she is
finished with it.
You have been working all day. (You‟re tired now)
He‟s been crying. (His eyes are red)
B. Negative Forms
John hasn‟t been feeling very well recently.
You haven‟t been reading for hours, so your eyes don‟t hurt.
I haven‟t been watching sad films recently, because right now I don‟t really like
them.
Kalyan hasn‟t been working in the garden, so her back doesn‟t hurt now.
We haven‟t been waiting for him. He is usually late.
Mary‟s not been shopping, so she has got a lot of money left.
Ellen hasn‟t been doing the housework. Everything is messy.
He hasn‟t been participating in the ceremony because he‟s ill now.
Darwin hasn‟t been giving the children a bath, so she‟s not taking wet.
They haven‟t been smoking ever since they were sick.
C. Question Forms
What have you been doing since I saw you?
Have they been sunbathing? They are a bit burnt.
Mary plays tennis quite often. How long has she been playing tennis?
Core English I 16 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
You are out of breath. Have you been running?
Why are your clothes so dirty? What has she been doing?
Mary lives in the countryside. How long has she been living there?
Your siblings learn English every day. How long have they been learning
English?
Tony wants to be rich soon. Has he been working hard?
Has your mother been cooking? The house smells of onions and garlic.
Has your girlfriend been waiting for hours? She looks furious.
3. Definition
3.1The Firs Definition
The Present Perfect Continuous expresses an activity, which began in the past and
is still continuing now. The Present Perfect Continuous is used to express an
activity that continues to the present.
I‟ve been staying with my friends until I find my own place to live. (Temporary
activity)
I‟ve been living with them for two weeks. (Temporary activity)
We have been living in this flat for the past few months. (Temporary activity)
Marline has been trying to lose weight for ages. She has lost five kilos so far.
We‟ve been looking for them for years, but I haven‟t found them yet.
I‟ve been learning English for four years.
It‟s been raining for days.
Sorry I‟m late. Have you been waiting long?
I‟ve been a teacher for five years. I‟ve been working at the same school all that time.
Chinese President Hu Jintao is due to visit Washington on April 24, and Beijing
has reportedly been preparing initiatives to ease trade tensions ahead of a
meeting with US President George W.Bush.
3.2The Second Definition
The Present Perfect Continuous is used to express a past activity that has caused a
present result.
I‟m hot because I‟ve been running.
Her shoes are muddy. She‟s been digging in the garden.
I‟m tired now. I‟ve been working all day.
Has she been crying? Her eyes are red.
You look hungry. What have you been eating?
Roger has been cutting the grass. I can smell it.
Look outside the window. It has been raining.
I have been writing this book for one year. It still isn‟t finished.
She‟s been decorating the bathroom. She has got paint in her hair.
She has been waiting for hours. She‟s furious.
Present Perfect and Continuous
A. Sometimes there is little or no difference in meaning between the Present Perfect and
Present Perfect Continuous.
How long have you worked here?
Core English I 17 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
How long have you been working here?
He has taught English for 12 years.
He has been teaching English for 12 years.
It has rained for days.
It has been raining for days.
B. Think of the verbs that have the idea of a long time, for example, wait, work, learn,
travel, play etc. These verbs can be found in the Present Perfect Continuous.
I‟ve been playing tennis since I was ten years old.
David has been working for the football team for over 10 years.
Danny has been waiting here for hours.
How long have you been learning at Asia Euro University?
Marlin‟s shoes are muddy. She has been digging in the garden.
They have been traveling abroad for two weeks.
C. Think of the verbs that only happen once and don‟t have the idea of a long time, for
example, find, start, buy, die, lose, break, stop etc. It is unusual to find these verbs in the
Present Perfect Continuous.
I‟ve bought a new car.
My dog has died.
My radio has broken.
Have you found your missing child?
Peter hasn‟t lost weigh so far.
My father has stopped smoking for a few months already.
I haven‟t decided to get married to her yet.
What have you bought her for her birthday?
Have you met your friend already?
D. Verbs that express a state, for example, like, love, know, have for possessions are not
found in the present Perfect Continuous.
We‟ve known each other for five years. (Right)
We‟ve been knowing each other for five years. (Wrong)
How long have you had your car? (Right)
How long have you been having your car? (Wrong)
How long has David loved Mary? (Right)
How long has David been loving Mary?(Wrong)
How long have you believed in Buddhism? (Right)
How long have you been believing Buddhism? (Wrong)
His living standard has depended on my support for years. (Right)
His living standard has been depending on my support for years. (Wrong)
E. The Present Perfect look at the completed action. That is why, if the sentence gives a
number or a quantity, the Present Perfect is used. The Present Perfect Continuous is for
actions that are continuing.
I‟ve written two letters in English today. (I have finished writing the two letters.
I‟ve been writing two letters in English today. (I am still writing the two letters)
The Royal Government of Cambodia has built 50 schools. (The schools are finished)
Core English I 18 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
The Royal Government of Cambodia has been building 50 schools. (The schools are
still being built.)
My family has raised ten cows. (The cows have already become full-grown)
My family has been raising ten cows. (The cows are still being raising)
The window has brought five children up. (She has finished bringing them up)
The window has been bringing five children up. (She is still bringing them up)
I have given my girlfriends $100 each. (I have given my girlfriends $100 only one
time)
I have been giving my girlfriends $100 each. (I have given my girlfriends $100 more
than once)
Note:
We use the Present Perfect Continuous when presenting evidence or reasons that
something happened.
She is hot because she‟s been running.
His back hurts because he‟s been digging in the garden.
He‟s got dirty hands because he‟s been fixing his car.
She‟s wet because she‟s been doing the washing up.
They are tired because they‟ve been playing tennis.
Her eyes hurt because she‟s been studying.
He smells like food because he‟s been cooking.
They have no money because they‟ve been shopping.
VIII. The Present Perfect Continuous Passive
1. Form: Subject+ have/has+ been+ being+ V3(Past Participle)
2. Definition
The Present Perfect Continuous Passive’s definition is the same as the Present Perfect
Continuous Active’s. This tense is not often used.
3. Examples
A. Positive Forms
This problem has been being worked on for two weeks.
We have been being allowed to study tourism at university.
I have been being encouraged to study for my PhD.
His sister has been being accused of breaking several laws lately.
This bridge has been being built for two months.
B. Negative Forms
I haven‟t been being greeted warmly by the people of this country.
We haven‟t been being intimidated by terrorists.
She hasn‟t been being compelled to be a prostitute.
He hasn‟t been being scolded strongly.
Darwin hasn‟t been being forced to do what she doesn‟t want to do.
C. Question Forms
Core English I 19 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
Have you been being admired for your famous achievements?
Have they been being considered good people by others?
Has she been being coerced to join that political party?
Has he been being given a fair chance to study overseas?
Has your boyfriend been being detained in jail?
IX. The Past Simple
1. Form: Subject+ V2(Past Tense)
2. Examples
A. Positive Forms
We played tennis last Sunday.
I worked as a teacher at Preah Sisowath High School from 1995 to 2001.
Mary left two minutes ago.
I invited my girlfriend to my party, but she decided not come.
The police stopped him for speeding.
David passed his exams because he had studied very hard.
I was angry because they had been late.
I slept well last night.
My cousin and I arrived in Phnom Penh in 1990.
We saw Helen a few days ago.
Philippine President Gloria Macapagal Arroyo said the coup conspiracy, joined
by left-wing and right-wing groups and quelled by the government on February
24, word have destroyed democracy in the Philippines if it had triumphed.
B. Negative Forms
They didn‟t invite me to the party, so I didn‟t go.
Denin and John weren‟t able to come because they were very busy.
I didn‟t buy that car because it was very expensive.
Marline didn‟t go with me, nor did I know where she went.
Cristina didn‟t forgive him although he admitted his mistakes.
We didn‟t go to university yesterday morning.
At midnight, last night your son wasn‟t at home. Perhaps he went to a nightclub.
We were hungry after the journey, but we weren‟t tired.
C. Question Forms
Where did you go last night?
Why didn‟t you buy that car the day before yesterday?
Was the weather good when you were on vacation?
Did you have suitable time to study English grammar?
Did he have free time to write a letter in English?
How many people did she use to cook for?
How much did your brother rent a car for?
How often did she stay at the hotel?
Core English I 20 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
Did you use to make girls cry?
Did you spend your time doing useful things?
Did you have any good dreams last night?
3. Definition
A. The Past Simple is used to express a finished action in the past.
Some of my friends and I arrived in Phnom Penh in 1990.
Columbus discovered America in 1492.
What time did you see Danny?
I played football last Saturday.
I worked as a teacher at Preah Sisowath High School from 1995 to 2001.
Cambodian Prime Minister Hun Sen on Wednesday, March 29, 2006, called on
UN Secretary-General Kofi Annan to replace special Representative for Human
Rights in Cambodia Yash Ghai, who he dismissed as a long term tourist.
British Prime Minister Tony Blair made an impassioned plea on Monday for an
international alliance to protect “global values” of fairness, justice, and freedom.
B. The Past Simple is used to express actions which follow each other in a
story.
I heard voices coming from downstairs, so I put on my dressing-gown and went
to investigate.
James came into the room. He took off his coat and sat down on the bed.
Suddenly, he noticed somebody behind the curtain. He stood up and walked
slowly across the room.
C. The Past Simple is used to express a past state or habit.
I knew her when we studied at the same high school.
I used to go to work by walking from 1995 to 1996.
He used to live in a large house.
Where did you use to go?
We didn‟t use to do anything interesting.
When I was a child, we lived in a small house by the sea. Every day I walked for
miles on the beach with my dog.
Note:
We cannot use “used to” with a time reference+ a number. In narrative, when expressing a
series of past actions it is common to begin with used to, then continue with would, for
reasons of style.
We used to have a holiday there for six years. (incorrect)
We used to go there every year. (correct)
When I was a child, we used to go on holiday on the seaside. We would play on
the beach, and then we would eat at a small restaurant at lunchtime.
Time Expression
last Monday last week when I was young
last month last year yesterday
one or two days ago weeks ago three months ago
five years ago in 2002 in winter
yesterday morning yesterday afternoon
Core English I 21 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
yesterday evening the day before yesterday
Examples
He was a teacher at Preah Sisowath High School for six years.
He has worked as an official at the Royal Academy of Cambodia for three years.
I have already written the letter in English.
My cousin and I arrived in Phnom Penh in 1990.
She had learned English before she went to England.
I had loved her before she loved me.
Miss Ellen was me at 9 a.m.
He just gave her a gold ring. She must feel very happy.
Hello, have you just arrived? We haven‟t seen each other for ages.
They got divorced three years ago. They have three children from their marriage.
Have you had dinner yet? What do you usually do after dinner?
I didn‟t see her cry when she left me three years ago.
I have never been to any foreign countries.
She has looked after his son since he was young.
Past Simple versus Past Simple
The Past Simple is used to express a finished action in the past, actions which follow each
other in a story, and a past situation or habit.
When I arrived home, my girlfriend started to cook a large dinner.
Yesterday, I went to the market where I was Helen.
When I was a child, I played the violin.
He got up when the alarm clock went off.
I said goodbye and left her house.
When David arrived, we had dinner. (David arrived and then we had dinner)
I walked home after the party last night. (A complete action)
John watching TV a lot when he was sick last year. (Not I was visiting...)
I went past her house everyday. (Not I was going...)
When Ratha was in hospital, we were visiting twice a day. (Or...we visited...)
Theary slept badly whenever she stayed with her grandparents. (Not...was sleeping..)
How did you cut your finger? (Not how were you cutting your finger?)
When Mary left University, she went to work for a bank. She left the bank after five
years, and she started working in another organization.
Compare these sentences
She lived in Rome. (But not any more)
I‟ve lived in Rome, Paris, and New York. (I know all these cities now.)
I‟ve been living in New York for ten years. (And I‟m living there now.)
She‟s been married three times. (She‟s dead)
She was married three times. (She‟s dead)
Did you see the Cambodia Trade Fair? (It‟s finished now)
Have you seen the Cambodia Trade Fair? (It‟s still on)
Did you see that programme on TV? (I‟m thinking of the one that on last night)
Did you enjoy the film? (Said as we‟re leaving the cinema)
Have you enjoyed the holiday? (Said near the end of the holiday)
Core English I 22 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
Where have I put my glasses? ( I want them now)
Where did I put my glasses? (I had them a minute ago)
It rained yesterday. (=past time)
It‟s been snowing. (There‟s snow still on the ground)
X. The Past Simple Passive
1. Form: Subject + was/were +V3 (Past Participle)
2. Definition
The Past Simple Passive’s definition is the same as the Past Simple Action’s.
3. Examples
A. Positive Forms
I was forced to marry Miss Davy last month.
We were sent to teach English in the country yesterday afternoon.
You were accused of breaking a law the day before yesterday.
Dora and John were given $2,000 for their heroism.
Two Vietnamese nationals were arrested last night.
Miss Nary was sentenced to three months in prison in 2003.
Mr. David was allowed to take Miss Rita for a walk yesterday evening.
Miss Dayy was driven home yesterday.
His daughter‟s reputation was destroyed last month, so he was very upset.
Her son was nominated to be a vice director general two months ago.
CPP President Chea was reelected, in a 60-to-1 vote, as Senate President on
Monday at the first session of the institution‟s second term in office.
Russian President Vladimir Putin held talks Tuesday with counterpart, Chinese
President Hu Jintao, at the start of a visit that was expected to focus on plans for
a pipeline to carry Siberian oil to China‟s booming economy.
B. Negative Forms
I wasn‟t forced to marry her.
You weren‟t sent to study politics overseas.
They weren‟t freed from prison in 2002 as the government had promised.
We weren‟t allowed to smoke in the class.
Mara and Brown weren‟t invited to the party.
Your parents weren‟t given news about their daughter.
Miss Chinda wasn‟t blamed because she did nothing wrong.
Miss Lina wasn‟t punished yesterday morning.
Her niece wasn‟t done a favor.
His nephew wasn‟t robbed last night.
C. Question Forms
Why were you permitted to work there?
When were we given enough salary? We never got enough!
Was she bought a car?
Why were Henry and Boras arrested last Monday?
Core English I 23 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
How long before that problem was resolved?
Was the dog taken for a walk yesterday?
Was he freed from prison last year?
Was your girlfriend warmly welcomed when she visited you?
Was her son allowed to work in an export and import company?
Was your servant forgiven last week?
XI. The Past Continuous
1. Form:
Positive Form: I, He, She, It+ was+ V1+ ing
You, We, They+ were+ V1+ ing
Negative Form: I, He, She, It+ wasn‟t +V1+ing
You, We, They+ weren‟t+ V1+ ing
Question Form: Was+ I, He, She, It +V1+ing ?
Were+ You, We, They+ V1+ ing?
2. Definition
2.1 The First Definition
The Past Continuous is used to express an activity in progress before, and probably
after, a particular time in the past.
Example
I walked past your house last night. There was an awful lot of noise. What were you doing?
At 7:00 this morning. I was having breakfast.
last night 8p.m 9p.m 10p.m now
watching TV
What were you doing at 9:00 last night?
I was watching a football match on TV.
I was driving home from work.
This time in 1998 she was living in Japan. She lived there from 1997 to 2002.
Yesterday John and Jim played volleyball. They began at 2.00 and finished at 5.00. What
were they doing at 3.00?
They were playing volleyball at 3.00
2.2The Second Definition
The Past Continuous is used to express an interrupted past activity, an incomplete
activity in the past, or describing a situation or activity during a period in the past.
When the phone rang, I was having a bath.
We were playing tennis when it started to rain.
Police stopped him while he was driving his car.
I was reading a book during the flight. (I don‟t finish it)
I was watching a film during the flight. (The whole film)
Jenny looked lovely. She was wearing a green cotton dress. Her eyes were
shining in the light of the candles that were burning nearby.
Core English I 24 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
3. Past Continuous versus Past Simple
We often use the Past Simple and the Past Continuous together to say that something
happened in the middle of something else.
Example
Mary burned her hand while she was cooking dinner.
The second action The first action
Miss Davy was watching TV when I arrived at her house.
The first action The second action
I saw you in the park. You were sitting on the grass and reading a book.
While he was working in the garden, he hurt his back.
When Jackson arrived, we were watching TV.
When she realized I was looking at her, she turned away.
I dropped my bag while I was getting into her car.
When David arrived, we were having dinner. ( We have already started dinner)
I was walking home when I meet Dave. (In the middle of an action)
John was watching TV when the phone rang. (In the middle of an action)
What was Peter doing when the war broke out?
The sun was shining. People were sitting under the trees or walking around the park.
Suddenly a car drove into the middle of the park.
A. I didn‟t see you in the pub last night.
B. No, I stayed at home and watched the football match on the television.
A. I rang you last night, but there was no reply.
B. Sorry, I was watching football.
Note:
The Past Simple expresses past actions as simple facts. The Past Continuous gives past
activities time and duration.
I stayed at home and watched the football.
I phoned you last night, but there was no reply.
Oh, I was watching the football and I didn‟t hear the phone. Sorry.
Notice how the questions in the Past Continuous and Past Simple refer to different times.
When we arrived, Jan was ironing. She stopped ironing and made some coffee.
What was she doing when I arrived?
She was ironing.
What did you do when I arrived?
She made some coffee.
XII. The Past Continuous Passive
1. Form: Subject+ was/were +being+ V3(Past Participle)
2. Definition
The Past Continuous Passive’s definition is the same as the Past Continuous Active’s.
Core English I 25 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
3. Examples
A. Positive Forms
While this room was being cleaned, we couldn‟t go into it.
When I arrived, his house was being decorated.
While the bridge was being built, the Japanese Government provided us $50,000.
When you arrived here, many gangsters were being arrested and put in prison.
This romantic book was being read when you wanted to borrow it.
Peter and John were being driven home because they were drunk.
The political deadlock and economic crisis were being addressed by the
government.
Yesterday my friend, David gave me a lift to school because my motorcycle was
being repaired.
B. Negative Forms
The political deadlock and economic crisis weren‟t being solved properly.
Her reputation wasn‟t being destroyed because she was protected from villains.
Corruption wasn‟t being eliminated completely in some countries‟.
Her house wasn‟t being built because she was short of money.
His friends weren‟t being accused of anything because they didn‟t do anything
wrong.
Violence wasn‟t being used against women and children in my country at the
time.
Inactive people weren‟t being condemned by the law.
Judicial systems in some countries weren‟t being reformed properly.
C. Question Forms
Why was he being besieged by angry people when you walk past him?
Where was she being taken to when you saw her?
What color was your house being painted?
Were those schools being built when you asked me for $10,000?
Was your country‟s stagnant economy being improved during the 1990s?
Was Cambodian people‟s poverty being reduced in Cambodia during 1997?
Why was he being detained in jail?
XIII. The Past Perfect
1. Form: Subject + had+ V3(Past Participle)
2. Definition
The Past Perfect is used to express an action in the past which had happened before another
action in the past.
3. Examples
A. Positive Forms
The plants died because we had forgotten to water them.
My leg hurt because I had fallen over playing football.
I went to bed early because I had had a busy day.
When I returned with my camera, the bird had flown away.
I apologized to Miss Randy because I had been rude the day before.
When I met her, she had been married two times already.
We didn‟t need to queue because we had already bought the tickets.
At first I thought I‟d done the right thing, but I soon realized that I‟d made a mistake.
Core English I 26 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
When I got home, my lovely girlfriend had already cleaned the house and cooked a
meal.
B. Negative Forms
I was late for work because my alarm clock hadn‟t gone off.
My teacher was angry because I hadn‟t done the homework.
The house was in a mess because we hadn‟t tidied up after the party.
I was hungry because I hadn‟t had breakfast.
When I got home, I was starving. I hadn‟t had anything to eat all day.
I wasn‟t broke because I hadn‟t spent all my money on clothes.
I was very nervous as I waited in the department lounge. I had flown before.
The house was dirty. They hadn‟t cleaned it for weeks.
John was now a penniless beggar, but he hadn‟t always been poor. He had been a
millionaire, but his business had collapsed and he had lost everything.
C. Question Forms
What had you done before I arrived?
Why had she left the party before you arrived, wasn‟t she waiting for you?
Had you had breakfast before you decided to marry her?
Why hadn‟t you told me you were getting married before I left for Paris?
D. Past Perfect versus Past Simple
The Past Perfect is used to make clear that one action in the past happened before another
action in the past, but the Past Simple is used to express a finished action.
Examples:
She had been interested in me before I asked her to marry me.
The first action The second action
When he stopped laughing, everyone had left. (They left before he stopped laughing)
I had already gone to bed when the phone rang. (I went to bed and the phone rang)
Peter had wanted to visit the galley before he left Florence, but it‟s closed on Sundays.
Jack wanted new challenges in his work. He had been in the same job for ten years.
I had fallen in love with her before she knew me.
She had been interested in me before I asked her to marry me.
When I lent him $100, he had already lost $200.
Jane was furious because she had overslept and missed the bus.
Mary was very disappointed with her son. She had sent him to a good school, but he
hadn‟t done any work and had failed his exams.
When I got home, I found that someone had broken into my flat and stolen my stereo.
David had hoped to returned at 60, but he persuaded himself to stay on for a few more
years.
Brian was sent to prison for three years. He had stolen money from his employer and
spent it on drugs.
I didn‟t know his name, but his face was familiar. I was sure I had seen him somewhere
before.
Note:
We can use because, after, before, when or because with Past Perfect and Past Simple.
Subject+ Past Simple+ after+ Subject+ Past Perfect
After+ Subject+ Past Perfect,+ Subject+ Past Simple
Subject+ Past Simple+ before+ Subject+ Past Perfect
Before+ Subject+ Past Perfect,+ Subject+ Past Simple
Core English I 27 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
Subject+ Past Simple+ because+ Subject+ Past Perfect
Because+ Subject+ Past Perfect,+ Subject+ Past Simple
Examples
I met my girlfriend after I had finished doing my homework.
After David had bought a car, he felt very happy.
Mr. John had loved Miss Mary before he got married to her.
Before Marline went Japan, she had studied Japanese.
The house was in a mess because we hadn‟t tidied up after the party.
Because she had overslept and missed the bus, Jane was furious.
My mother had already cooked dinner when I arrived home.
When I had read the newspaper, I threw it away.
As soon as the guests had left, I started tidying up.
I sat outside until the sun had gone down.
Verbs in the Past Simple tell a story in chronological order:
John worked hard all day to prepare for the party. Everyone had a good time. Even the food
was all right. Unfortunately, Andy upset Peter, so Peter left early. Pat came looking for
Peter, but he wasn‟t there.
It was a great party. John sat and looked at all the mess. He felt tired. It was time for bed.
By using the Past Perfect, the speaker or writer can tell a story in a different order.
John sat and looked at all the mess. It had been a great party, and everyone had had a good
time. Even the food had been all right. Unfortunately, Andy upset Peter, so Peter left early.
Pat came looking for Peter, but he had already gone. John felt tired. He‟d been working all
day to prepare for the party. It was time for bed.
XIV. The Past Perfect Passive
1. Form: Subject + had+ been+ V3(Past Participle)
2. Definition
The Past Perfect Passive‟s definition is the same as Past Perfect Active‟s.
3. Examples
A. Positive Forms
Miss Anna wasn‟t happy after she had been forced to marry a man she didn‟t love.
Mr. Peter was sad because he had been convinced to once year in prison.
My son was very happy because he had been nominated to be a company director.
Darleen cried after all her money had been stolen.
After my friend had been sent to study overseas, he did his best to study English.
B. Negative Forms
The children were very hungry because they hadn‟t been given money to buy food.
Dishes were dirty because they hadn‟t been washed.
During Women‟s Day, she hadn‟t been bought anything.
We bought that the political deadlock hadn‟t been solved properly.
Pornographic film distribution throughout the city and province hadn‟t been restrained
and suppressed before the new law was issued.
Core English I 28 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
C. Question Forms
Had you been invited to her party on Sunday?
How had the problem been solved?
Had the serious case been investigated rigorously and thoroughly?
Why had the problem been solved unfairly?
Had he been forgiven when he ran into her?
Had deputy governors in all the cities and provinces been reported to about crack down
on pornographic video distribution?
XV. The Past Perfect Continuous
1. Form: Subject + had+ been+ V1(Present Participle)
2. Definition
The Past Perfect Continuous is used to express an activity that had been happening for a
period of time before something else happened
3. Examples
A. Positive Forms
I was very tired when I got home. I had been working hard all day.
We‟d been playing tennis for about half an hour when it started to rain heavy.
Jim quit drinking coffee two years ago. He‟d been drinking coffee for 20 years.
Helen woke up in the middle of the night. She was frightened and didn‟t know
where she was. She had been dreaming.
When the boys came into the house, their clothes were dirty, their hair was
messy, and one of them had a black eye. They had been fighting.
When I got home, my wife was sitting in front of the TV. She had just turned it
off. She‟d been watching TV.
John got a job in a factory. Five years later, the factory closed down. At the
time, the factory closed down, John had been working there for five years.
Yesterday morning I got up and looked out the window. The sun was shining,
but the ground was very wet because it had been raining. (It wasn‟t raining when
I looked out the window; the sun was shining. But it had been raining before)
B. Negative Forms
There was nobody in the room, but there was a smell of cigarette smoke.
Somebody had been smoking in the room.
Police hadn‟t been investigating the case. They said that they had no ability to
investigate properly.
Mary quit her job at the bank. She hadn‟t been working there for a long time.
Some officials hadn‟t been stopping corruption. They though that it was
acceptable, and they didn‟t need to prevent it.
The people in the countryside were unhappy because the government hadn‟t
been helping them during the economic crisis.
C. Question Forms
The two boy‟s clothes were dirty. Had they been fighting each other?
Why had the Supreme Court been charging an Australian national with having
sex with two underaged Cambodian girls?
An unidentified official stated, “Now body respects the laws in Cambodia. Not
even the courts respect our laws.” Had a lot of people been discussing the laws in
Cambodia before he said that? Not really.
Core English I 29 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
Had Mr. David been saving some money to marry her? He didn‟t earn much
money at his job so he must have saved for a long time.
Had she been getting on well with you? Perhaps you were interested in her.
D. Past Perfect Continuous versus Past Continuous
When I met David and Mary, they had been walking arm in arm. (I met after they
had finished.)
When I met David and Mary, they were walking hand in hand. (I met while they
were walking hand in hand.)
When I got home, I saw that water had been leaking through the roof. (It was no
longer leaking when I got there.)
When I got home, water was leaking through the roof. (It was leaking when I got
there)
I saw Miss Chinda on the way to Pochintong while she was driving her motorcycle.
E. Past Perfect Continuous versus Past Perfect.
We use the past perfect continuous when we talk about the continuity or duration of a
situation of a situation or activity, the past perfect to talk about the completion of a
situation or activity or its effects.
Examples
I had been working hard, so I felt that I deserved a holiday. (To emphasis the
activity)
I had worked hard, and the report was now finished. (To emphasis the result)
Mr. David had been saving since January to buy a new car.
Mr. David had saved enough money to buy the new car he wanted.
Mr. Peter had flown all the way from Tokyo to see me.
When the plane was diverted, it had been flying from London to Frankfurt.
Miss Marlene had applied for jobs, without success, since leaving university.
We had been looking at the painting for about ten minute before we realized who the
artist was.
XVI. The Past Perfect Continuous Passive
1. Form: Subject + had+ been+ being+ V3(Present Participle)
2. Definition
The Past Perfect Continuous Passive is used to express an action that had been happening for a
period of time before something else happened. The Past Perfect Continuous Passive is hardly
ever used, but we need to know it.
3. Examples
A. Positive Forms
This bridge had been being built all year. It was finally completed at the end of the year.
This case had been being investigated for about three years before it was solved.
Some Cambodian people‟s rights had been being violated before the 1993 elections
happened.
A nice girl‟s reputation had been being destroyed; we took pity on her very much.
Two Taiwanese men had been being accused of women trafficking until the real offenders
were caught.
Hospitals and schools had been being built in the area before the Khmer Rough came to
power.
Core English I 30 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
An innocent girl in Phnom Penh had been being forced to love the man who she hadn‟t
loved.
B. Negative Forms
My uncle hadn‟t been being accused of illegal logging, so he wasn‟t worried.
This problem hadn‟t been being solved by the proper people.
Women‟s Day in Cambodia hadn‟t been being celebrated throughout the country until the
government made it an official holiday.
Neak Loeung Bridge hadn‟t been being built when I went to visit there.
Some Cambodian people‟s living standard hadn‟t been being improved before the new law
was passed.
Human right hadn‟t been being practised throughout the country until other countries
started to criticize Cambodia.
C. Question Forms
Why had corruption been being accepted in Cambodia for such a long time?
Had violence against women been being fought all over the world before 1950?
Had the political deadlock been being solved in Cambodia? Or was it only after the UN got
involved?
Had the stagnant economy been being improved in Cambodia under the CPP?
How long had the dog been being taken out for a walk for before we arrived home?
Why had French been being spoken in some countries and not others during the 19th
century?
XVII. The Future Simple
1. Form: Subject + will/shall+ V1(Infinitive)
2. Definition
2.1. The future simple (Will) is used to express a future intention or decision made at the
moment of speaking. Also, the future simple (Will) can express a variety of meanings.
The meaning often depends on the meanings of the main verb.
Examples
I‟ll help you carry those bags. (=offer)
Will you marry me? (Willingness)
Will you open the window? (=request)
My car won‟t start. (=statement)
I‟ll love you forever. (=promise)
Will you shut the door, please? (Asking to do something)
That bag looks heavy. I‟ll help you with it. (Offering to do something)
Wait a moment, please. I‟ll open the door for you. (=offer)
Oh, I left the door open. I‟ll go and shut it. (=Willingness)
Will you please be quiet? I‟m trying to concentrate. (Asking to do something)
A. You know that book I lent you. Could I have it back if you‟re finished with it?
B. Of course. I‟ll give it to you this afternoon. (Promising to do something)
A. It‟s Jane‟s birthday.
B. Is it? I‟ll buy her some flowers.
A. Which one do you want? The blue or the red?
B. I‟ll take the red. Thank you.
A. What would you like to order?
B. I‟ll have a steak, please.
Core English I 31 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
A. I need my book to read more.
B. Ok, I‟ll give you your book back tomorrow.
A. Did you phone Helen?
B. Oh no, I forgot. I‟ll phone her now.
A. What would you like to drink?
B. I‟ll have some orange juice, please.
A. I‟m broke today.
B. Don‟t worry. I‟ll lend you some money.
A. What time will you leave here?
B. I‟ll leave here at 10 o‟clock.
A. Ok, wait for me here. I‟ll pick you up.
2.2.The future simple (Will) is used to express a future fact, certainly, or prediction at some
time in the future this event will happen. The speaker thinks; “This action is sure to
happen sometime in the future”.
Examples
I‟ll be thirty in a few days‟ time.
It will be cold and wet tomorrow, I‟m afraid.
Who do you think will win the match?
You‟ll feel better if you take this medicine.
I‟ll see you later.
Liverpool will win the cup.
The King will open the new hospital next Saturday.
Tom won‟t pass the exam. He hasn‟t studied hard enough.
That plate is very hot. If you touch it, you‟ll burn yourself.
A. Where will you be this time next year?
B. I‟ll be in Japan.
A. What time are we eating?
B. At 7 o‟clock. Don‟t worry. It‟ll be ready before your TV program.
2.3.Shall is found mainly in questions. It is used with I and we, and shall is used in the
questions Shall I…?/ Shall we…? to ask somebody‟s opinion (especially in offers or
suggestions).
Examples
Where shall I put your tea? (I‟m asking for instruction)
What shall we do tonight? (I‟m asking for a decision)
Shall I cook supper tonight? (I‟m offering to help)
Shall we eat out tonight? (I‟m making a suggestion)
Shall I open the window? (=Do you want me to open the window?)
Do you want me to open the window? (=Should I open the window?)
I shall be 35 years old next year. (We can‟t avoid it.)
It‟s Peter‟s birthday soon, and I have to buy him a present. What shall I buy him?
A. Where shall we have lunch? (=Where should we have lunch?)
B. Let‟s go to Hong Lay‟s.
A. What time shall we meet each other?
B. At 6 p.m.
A. Let‟s go out tonight.
B. Ok, where shall we go?
Core English I 32 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
2.4.We often use will („ll) for a prediction that can be based more on an opinion than a fact
or evidence. It is often found with expressions such as probably, sure, think, don‟t think,
guess, suppose, hope and wonder.
Examples
I‟ll probably be home late tonight.
Don‟t worry about the exam. I’m sure you‟ll pass.
Do you think Mary will like the present we bought her?
I don’t think you will marry her because she‟s very nasty.
I guess you will go out with because you both spend a lot of time together.
When do you suppose Peter and Mary will get married?
I doubt you‟ll need much money, the restaurant is very cheap.
I wonder what will happen to us.
I hope you‟ll come and visit me one day.
3. Will and Going to
3.1. We use will when we decided to do something at the time of speaking.
Examples
Peter is drunk. Mary will take him home.
I‟ll phone you back in a minute.
Give me a ring some time. We‟ll go out together.
Just a minute! I‟ll make you a cup of tea.
You want to phone me. Don‟t worry. I‟ll give you my phone number.
Your homework is very difficult. Ok, I‟ll help you with it.
A. Which do you want? The blue or the red?
B. I‟ll take the red. Thank you.
3.2. We use going to when we have already decided to do something before the time of
speaking. Going to is used to express a future decision, intention, or plan made before
the moment of speaking.
Examples
When she grows up, she is going to be a ballet dancer.
We are going to get married in the spring.
We‟re going to move to London.
How long are they going to stay in Phnom Penh?
I‟m going to marry a beautiful girl in 2008.
We‟re going to move to Tokyo.
My girlfriend isn‟t going to have a birthday party.
A. Why can‟t you go to my wedding?
B. Because I‟m going to visit abroad.
3.3.We use going to when we can see or feel now that something is certain to happen in the
future. Going to can express a prediction based on a present fact. There is evidence now
that something is sure to happen. We can see the future from the present.
Examples
Careful! That glass is going to fall over. Too late!
Look at that blue sky! It is going to be a lovely day.‟
Look at those clouds! It‟s going to rain.
Watch out! That box is going to fall.
Core English I 33 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
Look out! We‟re going to crash!
You work so hard. You are going to be rich and successful.
I feel dizzy! The pile of plate is going to fall.
4. Will and Might
4.1. Might is used to express a future possibility. It contains with will, which, in the
speaker‟s opinion, expresses a future certainty.
Examples
Japan will win the match. ( I am sure they win)
Japan might win the match. (It‟s possible, but I don‟t know.)
It might not rain this afternoon. (=I don‟t think it‟ll rain this afternoon.)
Korean President Roth Moo-hyun said on Thursday South Korea won‟t sign a free trade
agreement with the US if it perceives it might get the short end of the bargain.
A. Where are you going to during Khmer New Year‟s Day?
B. I don‟t know. I might go to Sihanoukville, or I might go to Siam Reap.
A. What sort of car you going to buy?
B. I‟m not sure. I might buy a Camry, or I might buy a Corolla.
A. What are you doing tonight?
B. I don‟t know. I might go out, or I might stay at home.
XVIII. The Future Simple Passive
1. Form: Subject + will+ be+ V3(Past Participle)
Subject+ am/is/are+ going to+ be+ V3 (Past Participle)
2. Definition
The Future Simple Passive‟s definition is the same the Future Simple‟s.
3. Examples
A. Positive Forms
This problem will be solved soon if you take notice of it.
Our final exam results will be released on 23 April 2007.
He will be given a scholarship to study for his PhD next year.
I am going to be brought a new car next year.
The bridge is going to be built next month.
Marine wants to be married, so she is hoping that she is going to be asked to be married
soon.
John and Mary‟s parents want them to get married next. Therefore, John and Mary are going
to be pressured to get married by their parents.
B. Negative Forms
The politician deadlock‟s solution won‟t (will not) be found.
You won‟t be forced to marry her if you don‟t love her.
I am not going to be given $2,000 next week.
Our country‟s stagnant economy won‟t be improved.
This car isn‟t going to be sent to help poor people.
These bridges and schools aren‟t going to be built next month.
C. Question Forms
Core English I 34 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
What time shall they be picked up?
Why will he be removed from power?
Will Helen be sent to study abroad?
When are these bridges going to be built?
Why is he going to be condemned tomorrow?
What position am I going to be nominated for after this course?
XIX. The Future Continuous
1. Form: Subject + will+ be+ V1 +ing(Present Participle)
2. Definition
The Future Continuous is used to express an activity that will be in progress before and after
a time in the future. The Future Continuous is also used to refer to a future event that will
happen in the natural course of things. This use is uncoloured by ideas such as intention,
decision, arrangement, or willingness. As time goes by, this event will occur.
3. Examples
Don‟t phone me at 8.00. We‟ll be having supper.
This time tomorrow I‟ll be flying to New York.
Don‟t worry about our guests. They‟ll be arriving any minute now.
We‟ll be going right back to the football after the break. (said on the television)
I‟m leaving on vacation this Saturday. This time next week I‟ll be living on a beach or
swimming in the sea.
David loves football and tonight there is a big football game on TV. The game begins at
6.30 and ends at 8.20. Danny wants to see David tonight and wants to know what time to
come over.
+ Danny: Is it all right if I come at about 7.30?
+ David: No, I‟ll be watching the football match then.
+ Danny: Well, what about 8.30?
+ David: Fine. The game will have ended by then.
Remember about other continuous tense!
At 10.00 yesterday, Peter was in his office. He was working. (Past)
It is 10.00 now. Davy is in her office. She is working. (Present)
At 10.00 tomorrow, Mary will be in her office. She‟ll be working. (Future)
XX. The Future Continuous Passive
1. Form: Subject + will+ be+ being+ V3(Past Participle)
2. Definition
Its definition is the same as the Future Continuous Active‟s.
3. Examples
We will be being taught PhD lessons by the end of 2007.
That bridge will be being built next year during Khmer Year.
The tourism book will be being translated from English into Khmer next year.
$10,000,000 will be being saved investigated rigorously and thoroughly once you get
enough money to bribe the officials.
Core English I 35 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
XXI. The Future Perfect
1. Form: Subject + will+ have+ V3(Past Participle)
2. Definition
The Future Perfect is used to refer to an action that will be completed before a definite time
in the future. It is not a very common verb form.
3. Examples
I‟ll have done all my work by this evening.
Don‟t phone after 11.00 because I‟ll have gone to bed by then.
We‟re late. The movie will already have started by the time we get to the theatre.
John will have built his house next month.
Mary will have already been married to a handsome man by this time next year.
By the time I get home my girlfriend will have cleaned the house from top to bottom.
Helen always leaves for work at 7.00 in the morning, so she won‟t be at home at 7.30.
She‟ll have gone to work.
David loves football and tonight there is a big football game on TV. The game begins at
6.30 and ends at 8.20. Danny wants to see David tonight and wants to know what time to
come over.
+ Danny: Is it all right if I come at about 7.30?
+ David: No, I‟ll be watching the football match then.
+ Danny: Well, what about 8.30?
+ David: Fine. The game will have ended by then.
Notes
Mark and Danny have been married for 15 years. (Present Perfect)
Next year they will have been married for 16 years. (Future Perfect)
When their first child was born, they had been married for a year. (Past Perfect)
XXII. The Future Perfect Passive
1. Form: Subject + will have been+ V3(Past Participle)
2. Definition
Its definition is the same as the Future Perfect Active‟s.
3. Examples
By tomorrow evening John will have been asked to work here.
The political deadlock‟s solution will have been found by next year.
The school and hospital will have been completed by October.
Will the Khmer Rough leaders have been sentenced before they die?
The seminar won‟t have been finished by 9.30.
XXIII. The Future Perfect Continuous
1. Form: Subject + will+ have been+ V1 +ing
Nobody used the Future Perfect Continuous, so we just have the forms of the Future Perfect
Continuous.
XXIV. The Future Perfect Continuous Passive
Core English I 36 Tenses
Angkor Khemara University Assignment
1. Form: Subject + will have been being+ V3(Past Participle)
Nobody used the Future Perfect Continuous passive, so we just have the forms of the Future
Perfect Continuous passive.
Core English I 37 Tenses
You might also like
- Unit 2: How Do You Spend Your Days?: ContentsDocument22 pagesUnit 2: How Do You Spend Your Days?: ContentsHirai MomoNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Vs ContinuousDocument2 pagesPresent Simple Vs ContinuousVictoria Prieto100% (1)
- Arabic ConjugationDocument55 pagesArabic ConjugationakhtarNo ratings yet
- Present Tense - Types of Present Tense, Examples & ExercisesDocument6 pagesPresent Tense - Types of Present Tense, Examples & ExercisesDard TongNo ratings yet
- Getting Started On Classical Latin PrintableDocument34 pagesGetting Started On Classical Latin PrintableJack BlackNo ratings yet
- English ModulDocument66 pagesEnglish ModulAkungameNo ratings yet
- 5.1 11. (Textbook) Present Simple PDFDocument4 pages5.1 11. (Textbook) Present Simple PDFUDAYAN SHAHNo ratings yet
- Nuevo Manual-Exani-II-Enero - 2023 PDFDocument52 pagesNuevo Manual-Exani-II-Enero - 2023 PDFluisDanielNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 English Final Module 3Document23 pagesGrade 7 English Final Module 3AmberNo ratings yet
- English, Fifty Topics for Beginners, Elementary LevelFrom EverandEnglish, Fifty Topics for Beginners, Elementary LevelRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson PlanRichelle PeñaflorNo ratings yet
- Review of TensesDocument17 pagesReview of TensesStefany Serret Trejo100% (1)
- 1revisiting Aspect and - AktionsartDocument313 pages1revisiting Aspect and - Aktionsartjaansegus100% (1)
- Simple Present TenseDocument6 pagesSimple Present Tensekuliah inggris100% (1)
- Seminarski Rad-Present Simple and Present ContinousDocument11 pagesSeminarski Rad-Present Simple and Present ContinousElmma28No ratings yet
- Lab Bhs Inggris 1 (Grammar and Speaking)Document42 pagesLab Bhs Inggris 1 (Grammar and Speaking)aphroditeNo ratings yet
- Clasa A VIII A B 4.05.2020 Present TensesDocument7 pagesClasa A VIII A B 4.05.2020 Present TensesLiliana GheorgheNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Vs Present ProgressiveDocument13 pagesSimple Present Vs Present ProgressiveVivian Carolina RAMOS SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Present Simple and Present Continuous CorrectionDocument2 pagesLesson 3 Present Simple and Present Continuous Correctionkuliah inggrisNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Form of Simple Present TenseDocument34 pages1.1 Form of Simple Present TenseimamNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Vs ContinuousDocument2 pagesPresent Simple Vs ContinuousVictoria PrietoNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Vs Present ContinuosDocument30 pagesSimple Present Vs Present ContinuosCynthia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 12 TensesDocument82 pages12 TensesXerxNo ratings yet
- Colegio de Las Americas English Guide 6 Grade: - Express Frequency in The Different Activities Done in A DayDocument10 pagesColegio de Las Americas English Guide 6 Grade: - Express Frequency in The Different Activities Done in A DayJeissonTrianaANo ratings yet
- The Present Continous TenseDocument3 pagesThe Present Continous TenseBRIYITH SIRLEY ROJAS TOBARNo ratings yet
- Life Vision Pre Intermediate WorkbookDocument2 pagesLife Vision Pre Intermediate WorkbookBanananecraftNo ratings yet
- Taller de Adverbios de FrecuenciaDocument5 pagesTaller de Adverbios de FrecuenciaCarlos Daniel Bolaño RuaNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Vs Present Continuous Worksheet Templates Layouts 46216Document26 pagesPresent Simple Vs Present Continuous Worksheet Templates Layouts 46216mrNo ratings yet
- Present Simple and Present ContinuousDocument20 pagesPresent Simple and Present ContinuousEsteban Martin Chiotti Kaneshima100% (1)
- Present Simple Vs Present Continuous Worksheet Templates Layouts - 46216Document27 pagesPresent Simple Vs Present Continuous Worksheet Templates Layouts - 46216ZULAY FERNANDA GONZALEZ PRADANo ratings yet
- Presentation Present Simple-Present ContinuousDocument26 pagesPresentation Present Simple-Present ContinuousElena GudzNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Present ContinuousDocument26 pagesPresent Simple Present ContinuousVelika KaradjovaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TenseDocument14 pagesSimple Present TenseSINDI 222151070No ratings yet
- Common MistakesDocument6 pagesCommon MistakesAhmad AkNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous vs. Present SimpleDocument4 pagesPresent Continuous vs. Present SimplePhạm ĐăngNo ratings yet
- Learning English: Present Continuous Vs Present SimpleDocument25 pagesLearning English: Present Continuous Vs Present SimpleLệ NguyễnNo ratings yet
- English Modul For SmaDocument70 pagesEnglish Modul For SmaYusran BakriNo ratings yet
- TMCDocument6 pagesTMClimnengliNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous.: How Do We Make The Present Continuous Tense?Document11 pagesPresent Continuous.: How Do We Make The Present Continuous Tense?RANDY NAYID PADILLA BELENONo ratings yet
- 1 001 PDFDocument25 pages1 001 PDFlubna nooraniNo ratings yet
- Meeting 12 - M.Aidil Irawan - 2022210067Document3 pagesMeeting 12 - M.Aidil Irawan - 2022210067M AidilNo ratings yet
- I Do Vs I Am DoingDocument4 pagesI Do Vs I Am DoingVũ VũNo ratings yet
- English Grammar in UseDocument5 pagesEnglish Grammar in UseLidiaNo ratings yet
- Used To Used ToDocument5 pagesUsed To Used ToRawda DamraNo ratings yet
- Present Simple vs. Present Continuous - Murphys 5th EdDocument4 pagesPresent Simple vs. Present Continuous - Murphys 5th EdNandaNo ratings yet
- Adverbs of FrequencyDocument6 pagesAdverbs of FrequencyJoana PereiraNo ratings yet
- SSM II Inglés Sem 02Document4 pagesSSM II Inglés Sem 02Susana Yarleque MejiaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet HeadwayDocument0 pagesWorksheet HeadwayUkicku CajcinuNo ratings yet
- Write A Paragraph. Tell Me About Your Daily Routine.: Valentina Pedraza Triana Grupo 1Document4 pagesWrite A Paragraph. Tell Me About Your Daily Routine.: Valentina Pedraza Triana Grupo 1Vale PedrazaNo ratings yet
- My Daily Routine: Morning FORDocument7 pagesMy Daily Routine: Morning FORОксана ТоткалоNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous and Present Simple 1 (I Am Doing and I Do)Document2 pagesPresent Continuous and Present Simple 1 (I Am Doing and I Do)DaryaNo ratings yet
- 12present Simple and Present Continuous Grammar Guides - 50777Document15 pages12present Simple and Present Continuous Grammar Guides - 50777Asmolova OlenaNo ratings yet
- Practice 1 - Dan Andra - 20182Document4 pagesPractice 1 - Dan Andra - 20182Dan AndraNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Vs Present Continuous Worksheet Templates Layouts - 46216Document26 pagesPresent Simple Vs Present Continuous Worksheet Templates Layouts - 46216jocelyn perez villarrealNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 PMDDocument6 pagesUnit 6 PMDDominicus GagarinNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous: Worksheet - Week 2Document6 pagesPresent Continuous: Worksheet - Week 2Alexa Fernanda Ponce LagunasNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous T Past Perfect TDocument17 pagesPast Continuous T Past Perfect TAnime Tv ChannelNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Vs Present ContinuousDocument4 pagesPresent Simple Vs Present ContinuousSorana PaleuNo ratings yet
- Buku Bahasa Inggris SD Kelas 4Document27 pagesBuku Bahasa Inggris SD Kelas 4SulmindahNo ratings yet
- Exam Handouts A 3Document21 pagesExam Handouts A 3Jehdad MoustafaNo ratings yet
- A1 Grammar List FinalDocument2 pagesA1 Grammar List FinalKazhaw IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Present Time 1Document11 pagesChapter 1 Present Time 1Muhamad Cesar Fajar100% (1)
- English, Fifty Topics for Beginners, Elementary Level: English, Fluency Practice, Elementary Level, #2From EverandEnglish, Fifty Topics for Beginners, Elementary Level: English, Fluency Practice, Elementary Level, #2Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (6)
- Mending Broken Lives: One Woman’s Journey with Bipolar DisorderFrom EverandMending Broken Lives: One Woman’s Journey with Bipolar DisorderNo ratings yet
- Class 6 English Grammar Ncert Solutions Verbs and Their FormsDocument6 pagesClass 6 English Grammar Ncert Solutions Verbs and Their Formstpiyush21No ratings yet
- GRAMMAR Narrative TensesDocument1 pageGRAMMAR Narrative TensesParisa BehboodiNo ratings yet
- BeLiDa1 (2022) - Tematski ZbornikDocument470 pagesBeLiDa1 (2022) - Tematski Zbornikmilena milenaNo ratings yet
- Go Billy Korean Episode 129Document4 pagesGo Billy Korean Episode 129kuyaharry02No ratings yet
- BARASOLIA - Final Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesBARASOLIA - Final Lesson PlanELLEN JANE BARASOLIANo ratings yet
- Ba English: Course PlanDocument24 pagesBa English: Course PlanSwathi KrishnadasNo ratings yet
- Arabic Dependency Treebank-A Word On The Million WordsDocument8 pagesArabic Dependency Treebank-A Word On The Million WordsNajlaNo ratings yet
- The Past and Present Perfect Continuous TenseDocument9 pagesThe Past and Present Perfect Continuous TenseBrenda KimNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Present TensesDocument10 pagesUnit 4 - Present TensesmaNo ratings yet
- American Headway - Book 3Document162 pagesAmerican Headway - Book 3camilaNo ratings yet
- EngLish QuestionDocument8 pagesEngLish QuestionAkmal RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Perfect and Progressive Verb FormsDocument1 pagePerfect and Progressive Verb FormsStavros86No ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument4 pagesThis Study Resource WasHadi Satria GanesaNo ratings yet
- 16 Tenses Dalam Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pages16 Tenses Dalam Bahasa InggrisJonash C. Murdiny TulisNo ratings yet
- HS8151 Communicative English MCQDocument54 pagesHS8151 Communicative English MCQsankar sNo ratings yet
- Book Level 1Document25 pagesBook Level 1Vlado PetricNo ratings yet
- English Tenses Examples and Flow Chart PDFDocument1 pageEnglish Tenses Examples and Flow Chart PDFsamanNo ratings yet
- Unit15 Verbs PDFDocument28 pagesUnit15 Verbs PDFGabriela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Engleza CPDocument45 pagesEngleza CPcatandryNo ratings yet
- Tugas Mandiri Teoic Preparation Passive VoiceDocument8 pagesTugas Mandiri Teoic Preparation Passive VoiceRika AmbaritaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Fourteen: Double Infinitive ConstructionDocument21 pagesChapter Fourteen: Double Infinitive Constructionvarshasdm1987No ratings yet
- The Future: Chrisnarita A/P Kanesuvaran M20201000534Document52 pagesThe Future: Chrisnarita A/P Kanesuvaran M20201000534sivanNo ratings yet
- Level A1 KyrgyztestDocument72 pagesLevel A1 Kyrgyztestslz0No ratings yet
- Class Six Schemes of Work 15 DecDocument87 pagesClass Six Schemes of Work 15 DecAkere100% (1)
- Simple Present Tense (Subj + Verb I/+s or Es)Document25 pagesSimple Present Tense (Subj + Verb I/+s or Es)Darius GanNo ratings yet