Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MDC Viva 3
MDC Viva 3
Uploaded by
Hitender Singh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pages1. Electronics deals with currents in semiconductor materials and vacuum tubes, while electrical deals with currents in conductors.
2. There are three types of materials - conductors with no energy gap, semiconductors with a narrow energy gap, and insulators with the widest energy gap. Semiconductors have 4 electrons in their valence band while conductors have more than 4.
3. Intrinsic semiconductors are pure while extrinsic are doped with impurities to create P-type or N-type materials. P-type are done with trivalent impurities and N-type with pentavalent impurities.
Original Description:
electromagnetic devices and circuit viva
Original Title
MDC VIVA 3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Electronics deals with currents in semiconductor materials and vacuum tubes, while electrical deals with currents in conductors.
2. There are three types of materials - conductors with no energy gap, semiconductors with a narrow energy gap, and insulators with the widest energy gap. Semiconductors have 4 electrons in their valence band while conductors have more than 4.
3. Intrinsic semiconductors are pure while extrinsic are doped with impurities to create P-type or N-type materials. P-type are done with trivalent impurities and N-type with pentavalent impurities.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesMDC Viva 3
MDC Viva 3
Uploaded by
Hitender Singh1. Electronics deals with currents in semiconductor materials and vacuum tubes, while electrical deals with currents in conductors.
2. There are three types of materials - conductors with no energy gap, semiconductors with a narrow energy gap, and insulators with the widest energy gap. Semiconductors have 4 electrons in their valence band while conductors have more than 4.
3. Intrinsic semiconductors are pure while extrinsic are doped with impurities to create P-type or N-type materials. P-type are done with trivalent impurities and N-type with pentavalent impurities.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
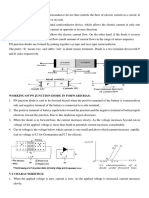
What is the difference b/w Electronics and Electrical?
Electronics is the science which deals with the currents in semiconductor materials,
Vacuum tubes.Where electrical deals with the currents in conductors
2.What are types of materials?
conductors (Energy gap is zero)
semiconductors (Energy gap is narrower) (si 1.1ev,ge 0.7ev)
Insulators (energy gap is widest).
3.What are the Semiconductor and conductors?
Semiconductor which has 4 electrons in its valance band, and conductors has more
than 4 electrons its valance band (best conductors: Ag,Al,Cu)
4. Difference b/w intrinsic and extrinsic Semiconductors?
Ans: intrinsic semiconductors are pure semiconductors, Extrinsic are impure, i.e.by
adding impurities (tri, pentavalent)Extrinsic semiconductors created(P,N Type).
5.What are the type in Extrinsic semiconductors and how the formed?
P-Type and N-Type
by adding trivalentimpurities (arsenic, antimony, phosphorus) P-Type
semiconductors created.by adding pentavalent impurities (aluminum, boron) N-
Type semiconductors created.
6.What is Doping?
The processes of adding impurities.
7.How the PN Junction will be formed?
In a piece of semiconductor material, if one half is doped by P type impurity and
the other half is doped by N type impurity
8.What is Barrier Potential (cut in voltage)?
The forward voltage at which the current through the junction starts increasing
rapidly
9.What is Forward bias and Reverse bias?
In diode’s anode(P) voltage is more than cathode(N) voltage its forward bias, if
anode voltage is less than cathode voltage its reverse bias.
10.What is Diffusion and Drift currents?
Drift current depends on the electric field applied, if there is no electric field there
is no drift current. Diffusion current occurs even though there is not an electric
field applied to the semiconductor.
11.What is mean by 1n4007?
1n – single junction
400x-is indicates the voltage, current and power
4007 reverse voltage from 50v to 1000v, max forward current is 1A
12.What is the Diode current Equation?
I=Io(e(V/nVT)-1), Io-Reverse saturation current,n=1,ge,2 si
13.Define PIV(Peak inverse voltage)?
It is the maximum reverse voltage that can be applied to the Diode. if the voltage
across the junction exceeds PIV, under reverse bias condition, the junction gets
damaged.
14.Define Reverse saturation current?
It is the current due to the diffusive flow of minority electrons from p- side to N-
side, and minority holes from N- side to P- side
15.How do we test a diode using a multimeter?
Connect anode of dide to + terminal of multimeter and cathode to Negative
terminal if voltage is 0.3 to 0.7 then diode is good.
16.Explain the capacitive effects in a junction.
.Explain the capacitive effects in a junction.
Diffusion capacitance occurs in Forward bias, Transition capacitance exist in
Reverse Bias.
17.What is mean by Break down, difference b/w avalanche Break down and Zener
Break down?
Avalanche breakdown occurs in PN diode due to impact ionization of electron-hole
pair, zener braek down occurs in Zener dioade due to electron hole pair break due
to reverse bias voltage
18.What is the temperature effect on reverse saturation current and barrier voltage?
Reverse saturation doubles for every 10 degrees increment in temperature
Barrier voltage decreases by 2.5mv for every 1 degree increment in temperature
19.What is mean by static and dynamic resistances?
Static resistance is the ratio of V,I at operating (Q) point, dynamic resistance is
inverse to the slope of the forward bias characteristics curve at operating point.
20.What are the PN Diode, Zener diode applications?
PN:rectifier,switch,clipper,clapper
Zener Diode:voltage regulator
21.Difference b/w PN, Zener Diode?
Pn is lightly doped, Zener heavily doped
22.Why is a Zener diode generally not connected in forward bias?
Zener gives the same response as pn diode in forward bias, so it uses in reverse
bias only with Zener break down
23.What is the effect of Temperature on Zener diode?
For Vz(Break down voltage) less than 6v Vz is inversely proportional to
temperature,For Vz(Break down voltage) more than 6v Vz is directly proportional
to temperature.
24. Why silicon is more preferred than germanium?
For Si break Down voltage Is more than Ge, reverse saturation current Is less in Si,
Si is cheap (raw material Is sand)
You might also like
- Is Starting A Business Right For YouDocument33 pagesIs Starting A Business Right For YouSorom ComputerNo ratings yet
- Find Your Partner As Per NumerologyDocument6 pagesFind Your Partner As Per NumerologyDilip Kininge100% (1)
- Electron DeviceDocument112 pagesElectron DevicekrishnaNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Drained Direct Shear Test: (IS: 2720 (Part 13) - 1986)Document1 pageConsolidated Drained Direct Shear Test: (IS: 2720 (Part 13) - 1986)Biplab dattaNo ratings yet
- Partnering With Dell EMC ServicesDocument20 pagesPartnering With Dell EMC ServicesAdnan JavaidNo ratings yet
- 1 PN Junction PDFDocument4 pages1 PN Junction PDFAbhishekh TiwariNo ratings yet
- D Lovett (Author) - Tensor Properties of Crystals-CRC Press (1989)Document181 pagesD Lovett (Author) - Tensor Properties of Crystals-CRC Press (1989)林丗育No ratings yet
- Bed Unit 1Document29 pagesBed Unit 1AravindNo ratings yet
- EDC Question BankDocument44 pagesEDC Question BankKRCT EEE HODNo ratings yet
- 2 Mark (ED Questions)Document26 pages2 Mark (ED Questions)Pradeep ravichanderNo ratings yet
- SR Inter IPE Question Bank Chapter-XV (SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS)Document12 pagesSR Inter IPE Question Bank Chapter-XV (SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS)sojakoj867No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Ver 0.50Document124 pagesBasic Electronics Ver 0.50Manoranjan Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- PN Junction Diode: Electronic Circuits (18NPC304) Assignment 2 Part - 1Document2 pagesPN Junction Diode: Electronic Circuits (18NPC304) Assignment 2 Part - 1Narendran SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Edc Lab ManualDocument35 pagesEdc Lab ManualYAMINI D SDECT013No ratings yet
- PN Diode and Zener Diode AS PER BEEE NOTES MainDocument17 pagesPN Diode and Zener Diode AS PER BEEE NOTES MainMohd AbrarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To DiodesDocument46 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To DiodesYazik DurdiyevNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors: DefinitionDocument10 pagesSemiconductors: DefinitionOnoda SakamichiNo ratings yet
- Module1 RMYDocument28 pagesModule1 RMYpushpaNo ratings yet
- Be8253 - Unit 4Document28 pagesBe8253 - Unit 4balajiNo ratings yet
- EDC Question Bank 18Document33 pagesEDC Question Bank 18kalaiselvanNo ratings yet
- PN-junction ConstructionDocument13 pagesPN-junction Constructionمصطفى عدنان احمدNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document6 pagesExperiment 1srinathlalNo ratings yet
- Diode Applications.2Document47 pagesDiode Applications.2Shreyash SargarNo ratings yet
- AE Unit - 1Document12 pagesAE Unit - 1aamirnasirNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices & Practice: InstructorDocument33 pagesElectronic Devices & Practice: Instructorjavaid musaNo ratings yet
- Ec 8353 Edc 2018Document227 pagesEc 8353 Edc 2018gayathri yerukondaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Semiconductor Diodes ApplicsDocument27 pagesChapter 1-Semiconductor Diodes ApplicsRamyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Semiconductor Diodes & ApplicsDocument31 pagesChapter 1-Semiconductor Diodes & Applicsramya hegdeNo ratings yet
- Ec0221 Ed Lab ManualDocument68 pagesEc0221 Ed Lab ManualGoutham ShanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument20 pagesElectronic Devices and CircuitsjesudosssNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report Cover Sheet: 21Ecc211L - Devices and Digital Ic Lab Third Semester, 2023-24 (Odd Semester)Document12 pagesLaboratory Report Cover Sheet: 21Ecc211L - Devices and Digital Ic Lab Third Semester, 2023-24 (Odd Semester)nikunj sharmaNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital Electronics: S. M. Jahadun-NobiDocument39 pagesAnalog and Digital Electronics: S. M. Jahadun-NobiJune C. OsunaNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument3 pagesZener DiodeSaturn MoonNo ratings yet
- ED and CA Unit 1Document25 pagesED and CA Unit 1rsnagakumarNo ratings yet
- SemiconductorsDocument38 pagesSemiconductorssomarshidubeyNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics I: Dr. Abusabah I. A. AhmedDocument29 pagesAnalog Electronics I: Dr. Abusabah I. A. AhmedRachul heenimNo ratings yet
- P-N Junction DiodeDocument32 pagesP-N Junction Diodesashi_s2No ratings yet
- Analog ElectronicsDocument24 pagesAnalog ElectronicsDiptoNo ratings yet
- Exp5 2K20CO153Document7 pagesExp5 2K20CO153divye guptaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Ii YearDocument27 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits - Ii YearT ThirumuruganNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of P-N Junction DiodeDocument15 pagesCharacteristics of P-N Junction Diodehybe07jiminNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits NotesDocument89 pagesAnalog Circuits Notesgayathri-eceNo ratings yet
- EC 3353 Electronic Devices and Circuits: Unit 1: Semi Conductor DevicesDocument57 pagesEC 3353 Electronic Devices and Circuits: Unit 1: Semi Conductor DevicesAnusha PadmavathiNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Theory 1 YearDocument13 pagesElectrical and Electronic Theory 1 YearJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- Full Discription of Tunnel DiodeDocument30 pagesFull Discription of Tunnel Diodesahil6504No ratings yet
- DiodesDocument27 pagesDiodesamanuelfitsum589No ratings yet
- Transducers Unit IvDocument33 pagesTransducers Unit Ivsenthilku marNo ratings yet
- BEEER23 PartBDocument130 pagesBEEER23 PartBK S Ravi Kumar (MVGR EEE)No ratings yet
- Tunnel Diode - Definition, Symbol, and WorkingDocument16 pagesTunnel Diode - Definition, Symbol, and WorkingdevchandarNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Semiconductor Diodes and Their Applications: DiodeDocument35 pagesChapter-2 Semiconductor Diodes and Their Applications: DiodeYaregal ChalachewNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - Analog Electronics CBDocument47 pagesUnit-1 - Analog Electronics CBNagesh BhaviNo ratings yet
- Be Com NotesDocument206 pagesBe Com NotesSiddharth MayyaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Analog ElectronicsDocument45 pagesUnit-1 Analog ElectronicsLodhaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document14 pagesUnit 3Manaswini PNo ratings yet
- What Is A Diode?Document48 pagesWhat Is A Diode?B SaiNo ratings yet
- Applied Electronics IDocument216 pagesApplied Electronics Iethio universeNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor NotesDocument4 pagesSemiconductor NotesADITYA MAHECHANo ratings yet
- Diode Valve Effect: Electrical and Electronics LabDocument4 pagesDiode Valve Effect: Electrical and Electronics LabLare ONo ratings yet
- Junction Diodes-I: Dr. Avinash ChandraDocument110 pagesJunction Diodes-I: Dr. Avinash Chandra10kRishabh GoelNo ratings yet
- 1.) What Are The Different Types of Semionductor Material?: A. Intrinsic B. EXTRENSIC (N and P Type Semiconductors)Document2 pages1.) What Are The Different Types of Semionductor Material?: A. Intrinsic B. EXTRENSIC (N and P Type Semiconductors)peter vanderNo ratings yet
- MHT PET-Broschuere 2013 KleinDocument8 pagesMHT PET-Broschuere 2013 Kleinchemikas8389No ratings yet
- C++ Question BankDocument19 pagesC++ Question BankChethanNo ratings yet
- Applications of Partial Derivatives in EconomicsDocument6 pagesApplications of Partial Derivatives in Economicsshahzeb afridiNo ratings yet
- Starry Landscape Stacker Procedure: David Swindler - Action Photo ToursDocument23 pagesStarry Landscape Stacker Procedure: David Swindler - Action Photo ToursAlfredo FinolNo ratings yet
- 06225768Document10 pages06225768Itjen SilabiNo ratings yet
- BAAO 2021 SolutionsDocument14 pagesBAAO 2021 SolutionsRadu Stoian100% (1)
- An Artificial Intelligence Based Neuro Fuzzy SymDocument6 pagesAn Artificial Intelligence Based Neuro Fuzzy SymbvinothhhNo ratings yet
- Investigation of 150/66 KV 100 MVA Transformer Internal FailureDocument6 pagesInvestigation of 150/66 KV 100 MVA Transformer Internal Failuredavid23281dNo ratings yet
- Integrated Dynamic Analysis of Floating Offshore Wind TurbinesDocument9 pagesIntegrated Dynamic Analysis of Floating Offshore Wind TurbinesSatish JadhavNo ratings yet
- Laboratory SafetyDocument30 pagesLaboratory SafetyEliana Nicole IbongNo ratings yet
- Geology 4th SemDocument2 pagesGeology 4th SemIkhlaq waniNo ratings yet
- Technical Data: Single-Pump System CO-1 Helix V 418/CE-01Document2 pagesTechnical Data: Single-Pump System CO-1 Helix V 418/CE-01karunagaren Ponien (kapo1705)No ratings yet
- Foundation Engineering II Course Outline 2016Document2 pagesFoundation Engineering II Course Outline 2016Ewnet YashenefalNo ratings yet
- Irvingia Gabonensis Seed Extract 10-1 IGSE-181011Document1 pageIrvingia Gabonensis Seed Extract 10-1 IGSE-181011Sophia XieNo ratings yet
- Automatic Railway Gate Control by Using Microcontroller - 24 PagesDocument44 pagesAutomatic Railway Gate Control by Using Microcontroller - 24 PagesSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 7 DLLDocument8 pagesMapeh 7 DLLFrancheska Venize Barola RevillosaNo ratings yet
- Lighting CalculationDocument21 pagesLighting CalculationEdwinDiane TandayuNo ratings yet
- Increase Resolution of Optical EncodersDocument6 pagesIncrease Resolution of Optical EncodersYoussef AbbasNo ratings yet
- 1 2 0 P 603c5c430612e File PDFDocument17 pages1 2 0 P 603c5c430612e File PDFNilesh WadhaveNo ratings yet
- Short Skirts (Thinkin) PDFDocument24 pagesShort Skirts (Thinkin) PDFKiana DizonNo ratings yet
- EMA Process ValidationDocument15 pagesEMA Process Validationdr3azzamNo ratings yet
- 【白细胞数据集】WBCAtt A White Blood Cell Dataset Annotated with Detailed Morphological AttributesDocument23 pages【白细胞数据集】WBCAtt A White Blood Cell Dataset Annotated with Detailed Morphological AttributesJeremy WayinNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument8 pagesResearch Proposalpearson cosmasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Interpret Plans and DrawingsDocument48 pagesLesson 4 Interpret Plans and Drawingsrf5h4h65n6No ratings yet