Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Study On Antigravity Ijariie15405
Uploaded by
Gherghe BogdanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Study On Antigravity Ijariie15405
Uploaded by
Gherghe BogdanCopyright:
Available Formats
Vol-7 Issue-5 2021 IJARIIE-ISSN(O)-2395-4396
A Study on Antigravity
K.A. Khan1, Md. Anowar Hossain2, Md. Robiul Islam, Md. Abdul Mannan3
1
Department of Physics, Jagannath University, Dhaka-1100
2
Center for Research Reactor,Bangladesh Atomic Energy Commission
3
Center for Research Reactor, Bangladesh Atomic Energy Commission
4
Central Engineering Facilities, Bangladesh Atomic Energy Commission
Abstract
Antigravity means that Reducing, canceling, or protecting against the effect of gravity.Many people seem to think
NASA has secret training rooms in which gravity can be turned off. Aside from the long-running Anti Gravity
column in Scientific American, however, there is no such thing as antigravity. Gravity is a force arising among any
two masses in the universe.In this work you can discover 4 synonyms, antonyms, idiomatic expressions, and related
words for anti-gravity, like: antigravity, gyroscope, remote-controlled and propulsion.The antigravity device is not a
large object, maybe three square feet, and easily fits on a tabletop. They took their oxygen suits off and walked over
to their antigravity beds.
Kewwords: Gyroscope,remote-controlled and propulsion,antigravity,antigravity beds, Dark energy, Zero gravity
I. Introduction
Some researchers patented nanotechnology, antigravity devices, and genetic techniques of all sorts by my teenage
years.Physically, Sir Isaac Newton was not a large man. However, he had a large intellect, as shown by his
discoveries on gravity, light, motion, mathematics, and more. Legend has it that Isaac Newton came up with
gravitational theory in 1665, or 1666, after watching an apple fall.Dark energy is the name given to an unexplained
force that is drawing galaxies away from each other, against the pull of gravity, at an accelerated pace. Dark energy
is a bit like anti-gravity. Where gravity pulls things together at the more local level, dark energy tugs them apart on
the grander scale.Dark energy is the name given to an unexplained force that is drawing galaxies away from each
other, against the pull of gravity, at an accelerated pace.
Dark energy is a bit like anti-gravity. Where gravity pulls things together at the more local level, dark energy tugs
them apart on the grander scale. Its existence isn't proven, but dark energy is many scientists' best guess to explain
the confusing observation that the universe's expansion is speeding up. Experts still don't know what's driving this
force, but the quest to learn more about dark energy is one of cosmologists' top priorities.
II. Methods and Materials
The methods and materials have been discussed below:
15405 www.ijariie.com 871
Vol-7 Issue-5 2021 IJARIIE-ISSN(O)-2395-4396
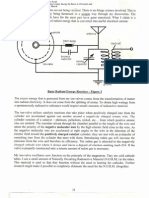
Fig.1 Antigravity seen by practically
Creation of Antigravity
In a new study, published in the journal Nature, researchers discovered they can create a similar anti-gravity effect
for buoyant objects by vibrating and levitating dense liquids in an enclosed glass chamber.
No Zero Gravity
Contrary to popular belief, there's no such thing as zero gravity. When astronauts orbit the earth, they're still subject
to gravity, but they're moving sideways so quickly that even though they're being pulled toward the earth, they're not
getting any closer to the planet's center.
Which country has no gravity?
Fig.2 The Faroe Islands
Well, there is one on the Faroe Islands, where the water seems to move upward, i.e., defying the law of gravity. In
fact, the waterfall, rather than defying gravity as the name suggests, goes upside down when strong gusts of wind
blows against the flow of the waterfall.
What would happen if Earth lost gravity?
If the Earth's gravity is lost, all items held to the Earth's surface by gravity would float away. That includes the
atmosphere, water, people, cars and animals. If you were lucky enough to be in a large building when gravity
disappeared, you would not drift away, but you also would not have air to breathe.
15405 www.ijariie.com 872
Vol-7 Issue-5 2021 IJARIIE-ISSN(O)-2395-4396
What will be happened if Earth stopped spinning?
If the Earth stopped spinning suddenly, the atmosphere would still be in motion with the Earth's original 1100 mile
per hour rotation speed at the equator.This means rocks, topsoil, trees, buildings, your pet dog, and so on, would be
swept away into the atmosphere.
What would happen if gravity stopped for 1 second?
Fig.3 Massive Explosions of stopped of gravity for 1 second
When gravity disappears for 1 second the outwards force balanced by the gravity would be released causing a
massive explosion. In other star systems with more immense stars and natural phenomena such as pulsars and and
especially black holes the explosions and expansions would be greater.
What would happen if we lost gravity for five seconds?
Fig.4 Effect of lost of gravity for 5 seconds
15405 www.ijariie.com 873
Vol-7 Issue-5 2021 IJARIIE-ISSN(O)-2395-4396
If our planet were to lose gravity for even five seconds, it would spell the end of life on Earth as we know it. Gravity
pulls objects toward one another. The more massive an object is, the stronger its gravitational pull. Without gravity,
humans and other objects would become weightless.
Do anti-gravity chambers exist?
Fig.5 Creation of anti-gravity chambers
Contrary to popular belief, NASA does not have "anti-gravity chambers" where people can float around like
astronauts on the space station. But we do use several facilities to recreate the weightless, or microgravity,
conditions of orbit.
Is gravity a wave or a particle?
If your question is about the force of gravity in relation to rest mass, the intermediating mechanism is not a wave
and not a particle. It is vector space and the velocity is instantaneously. If your question is in relation to mass (like
Dark matter), gravitation has wave properties and is bound to the speed of light.
What is gravity waves made of?
15405 www.ijariie.com 874
Vol-7 Issue-5 2021 IJARIIE-ISSN(O)-2395-4396
Fig.5 Creation of Gravity waves
Compact binary inspiral gravitational waves are produced by orbiting pairs of massive and dense ("compact")
objects like white dwarf stars, black holes, and neutron stars.
How fast is gravity?
Fig.5 Measurement of speed of gravity
The best results, at the present time, tell us that the speed of gravity is between 2.993 × 10^8 and 3.003 × 10^8
meters per second, which is an amazing confirmation of General Relativity and a terrible difficulty for alternative
theories of gravity that don't reduce to General Relativity!
Is artificial gravity real?
15405 www.ijariie.com 875
Vol-7 Issue-5 2021 IJARIIE-ISSN(O)-2395-4396
Fig.6 Creation of Artificial Gravity
Speculative or fictional mechanisms. In science fiction, artificial gravity (or cancellation of gravity) or "paragravity"
is sometimes present in spacecraft that are neither rotating nor accelerating. At present, there is no confirmed
technique that can simulate gravity other than actual mass or acceleration.
Fig.7 Real antigravity
The warping of spacetime, in the General Relativistic picture, by gravitational masses is what causes the
gravitational force. It is assumed, but not experimentally verified, that antimatter masses will behave the same as
matter masses in a gravitational field. LIGO/T. PYLE
15405 www.ijariie.com 876
Vol-7 Issue-5 2021 IJARIIE-ISSN(O)-2395-4396
Fig.8 Trajectories of antihydrogen atoms from the ALPHA experiment.
What is the anti-gravity element?
The hypothetical element with Z = 145 is the unique among all elements whose nucleus has only anti-gravity
property. It is proposed that this element be named Hawking, in honour of Stephen W. Hawking.
Can gravity be reversed?
Fig.9 Impossibility of anti-gravity
Under general relativity, anti-gravity is impossible except under contrived circumstances.
Does light cause gravity?
15405 www.ijariie.com 877
Vol-7 Issue-5 2021 IJARIIE-ISSN(O)-2395-4396
Light has energy, energy is equivalent to mass, and mass exerts gravitational force. Thus, light creates gravity, i.e.
the bending of space-time.Thus, in order for light to generate a gravitational field like that of the Earth, it would
need to have the mass (energy) of the Earth.
Can gravity bend sound?
Sound waves are pressure waves and depend on density so gravity which stratifies the atmospheric density affects
sound waves through that. In solids and liquids to the extent that gravity stratifies them it will change the behaviour
of sound waves.
How can we oppose gravity?
"One can imagine three ways of countering gravity. First, something can provide a force opposing that of gravity.
Such forces are known for instance, objects can be levitated using magnetic or electrostatic repulsion.
Does a paperclip have gravity?
The paperclips are being pulled toward the Earth by gravity, but they can't fall because the string is holding them in
the air. No matter which way we tilted the dowel rod, the paperclips were still being pulled straight toward the Earth
by gravity
Can a magnet defy gravity?
Magnetism can pass through the air! The iron in the paperclip is attracted to the magnet and when held at the right
distance, the magnet appears to “magically” defy the gravity of the paperclip.
Why is gravity so weird?
Why is gravity so weird? No force is more familiar than gravity- it's what keeps our feet on the ground, after all. If
these extra dimensions exist and if gravity is able to “leak” into them it could explain why gravity seems so weak
to us.
Is gravity affected by relativity?
Fig.10 gravity affected by relativity
GETTING A GRIP ON GRAVITY Einstein's general theory of relativity explains gravity as a distortion of space
(or more precisely, spacetime) caused by the presence of matter or energy. A massive object generates a
gravitational field by warping the geometry of the surrounding spacetime.
15405 www.ijariie.com 878
Vol-7 Issue-5 2021 IJARIIE-ISSN(O)-2395-4396
Did Einstein believe in gravity?
Einstein argued that gravity isn't a force at all. He described it as a curvature of time and space caused by mass and
energy. Their math, laid down in 10 equations, explained how gravity could move around objects via a warped
reality, accelerating without ever feeling any mysterious Newtonian forces.
Does anti matter have anti gravity?
The gravitational interaction of antimatter with matter or antimatter has not been conclusively observed by
physicists. Most methods for the creation of antimatter (specifically antihydrogen) result in high-energy particles
and atoms of high kinetic energy, which are unsuitable for gravity related study.
Why is gravity not a force?
Fig.11 Reason for why is gravity not a force
In general relativity, gravity is not a force between masses. Instead gravity is an effect of the warping of space and
time in the presence of mass. Without a force acting upon it, an object will move in a straight line.This explains why
all objects fall at the same rate.
III. Results and Discussion
One of the most astonishing facts about science is how universally applicable the laws of nature are. Every particle
obeys the same rules, experiences the same forces, and sees the same fundamental constants, no matter where or
when they exist. Gravitationally, every single entity in the Universe experiences, depending on how you look at it,
either the same gravitational acceleration or the same curvature of spacetime, no matter what properties it possesses.
At least, that's what things are like in theory. In practice, some things are notoriously difficult to measure. Photons
and normal, stable particles both fall as expected in a gravitational field, with Earth causing any massive particle to
accelerate towards its center at 9.8 m/s2. Despite our best efforts, though, we have never measured the gravitational
acceleration of antimatter. It ought to accelerate the exact same way, but until we measure it, we can't know. One
experiment is attempting to decide the matter, once-and-for-all. Depending on what it finds, it just might be the key
to a scientific and technological revolution.
IV. Conclussions
15405 www.ijariie.com 879
Vol-7 Issue-5 2021 IJARIIE-ISSN(O)-2395-4396
Many people seem to think NASA has secret training rooms in which gravity can be turned off. Aside from the
long-running Anti Gravity column in Scientific American, however, there is no such thing as antigravity. Gravity is
a force arising among any two masses in the universe
References
1. Thompson, Clive (August 2003). "The Antigravity Underground". Wired. Archivedfrom the original on 18
August 2010. Retrieved 23 July 2010.
2. "On the Verge of Antigravity". About.com. Retrieved 23 July 2010.
3. Department of Physics A Brief History of Isaac Newton's Apple Tree, University of York, Retrieved 2019-
07-20
4. Costas J. Papachristou (2 Mar 2016) - Electromagnetic waves, gravitational waves and the prophets who
predicted them, p.4, Department of Physical Sciences, Naval Academy of
Greece, https://arxiv.org/abs/1603.00871 Retrieved 2019-06-16
5. Albert Einstein Grundgedanken der allgemeinen Relativitätstheorie und Anwendung dieser Theorie in der
Astronomie (Preussische Akademie der Wissenschaften, Sitzungsberichte, 1915 (teil 1), 31), Zur
allgemeinen Relativitätstheorie (Preussische Akademie der Wissenschaften, Sitzungsberichte, 1915 (teil 2),
778–786, 799–80) Retrieved 2019-06-16
6. Charles W. Misner, Kip S. Thorne, John Archibald Wheeler Gravitation, p. 1231, Princeton University
Press, 24 October 2017 ISBN 0691177791, ISBN 9780691177793, Retrieved 2019-06-16
7. Kaluza, Theodor (1921). "Zum Unitätsproblem in der Physik". Sitzungsber. Preuss. Akad. Wiss. Berlin.
(Math. Phys.): 966–
972. Bibcode:1921SPAW.......966K.https://archive.org/details/sitzungsberichte1921preussi
8. Einstein, Albert (1879-1955). Autograph manuscript, comprising calculations and arguments from the
Einheitliche theorie von Gravitation un Elektrizitt Christie's Retrieved 2019-06-16
9. Peskin, M and Schroeder, D.; An Introduction to Quantum Field Theory (Westview Press, 1995) ISBN 0-
201-50397-2
10. Wald, Robert M. (1984). General Relativity. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-
87033-5.
11. Polchinski, Joseph (1998). String Theory, Cambridge University Press. A modern textbook
12. Mooallem, J. (October 2007). "A curious attraction". Harper's Magazine. 315 (1889): 84–91.
13. List of winners Archived 28 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine
14. https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/physics/1999/summary/
15. Goldberg, J. M. (1992). US air force support of general relativity: 1956–1972. In, J. Eisenstaedt & A. J. Kox
(Ed.), Studies in the History of General Relativity, Volume 3 Boston, Massachusetts: Center for Einstein
Studies. ISBN 0-8176-3479-7
16. Mallan, L. (1958). Space satellites (How to book 364). Greenwich, CT: Fawcett Publications, pp. 9–10,
137, 139. LCCN 58-001060
17. Clarke, A. C. (1957). "The conquest of gravity". Holiday. 22 (6): 62.
18. Jump up to:a b Bondi, H. (1957). "Negative mass in general relativity". Reviews of Modern Physics. 29(3):
423–428. Bibcode:1957RvMP...29..423B. doi:10.1103/revmodphys.29.423.
19. Jump up to:a b Forward, R. L. (1990). "Negative matter propulsion". Journal of Propulsion and
Power. 6 (1): 28–37. doi:10.2514/3.23219.; see also commentary Landis, G.A. (1991). "Comments on
Negative Mass Propulsion". Journal of Propulsion and Power. 7 (2): 304. doi:10.2514/3.23327.
20. Supergravity and the Unification of the Laws of Physics, by Daniel Z. Freedman and Peter van
Nieuwenhuizen, Scientific American, February 1978
21. Jason Palmer, Antigravity gets first test at Cern's Alpha experiment, bbc.co.uk, 30 April 2013
22. Antigravity Batteries(https://antigravitybatteries.com)
15405 www.ijariie.com 880
You might also like
- 20 Things You Didnt Know About Gravity Discovery Magazine ArticleDocument4 pages20 Things You Didnt Know About Gravity Discovery Magazine Articleapi-293162935100% (1)
- Chapter 21 - Black Holes - The Ultimate Endpoint of Stellar EvolutionDocument12 pagesChapter 21 - Black Holes - The Ultimate Endpoint of Stellar EvolutionDodong RiderNo ratings yet
- Dark Energy and Dark MatterDocument26 pagesDark Energy and Dark MattersaphirehaelNo ratings yet
- Lec20 General RelativityDocument11 pagesLec20 General RelativitysjmpakNo ratings yet
- Special Relativity and Quantum Mechanics: Physics CentralDocument8 pagesSpecial Relativity and Quantum Mechanics: Physics CentralabuNo ratings yet
- 1704 0167v1 PDFDocument8 pages1704 0167v1 PDFBecerra SandovalNo ratings yet
- What Is AntigravityDocument2 pagesWhat Is AntigravitySameer SayyedNo ratings yet
- Gravitational Shielding: Hypothetical Process of Shielding Objects from GravityDocument3 pagesGravitational Shielding: Hypothetical Process of Shielding Objects from Gravitysigne.soderstrom1785No ratings yet
- Gravitational ForcesDocument7 pagesGravitational ForcesShoumik BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- NASA Scientists May Have Accidentally Created a Warp BubbleDocument5 pagesNASA Scientists May Have Accidentally Created a Warp Bubbletanay patekarNo ratings yet
- Ion-Valve Oscillators and Ion-Valve Converters Technologies (Who's Who in Free Energy)Document74 pagesIon-Valve Oscillators and Ion-Valve Converters Technologies (Who's Who in Free Energy)ernieespells1jtkl56100% (19)
- NASA Scientists Accidentally Discover World's First Warp Bubble!Document5 pagesNASA Scientists Accidentally Discover World's First Warp Bubble!tanay patekarNo ratings yet
- Weightlessness: Zero-G:-Zero GravityDocument12 pagesWeightlessness: Zero-G:-Zero GravityN PratyangiraNo ratings yet
- NASA May Have Achieved Faster Than Light Travel With Warp DrivesDocument11 pagesNASA May Have Achieved Faster Than Light Travel With Warp DrivesAlphonse DelagoenNo ratings yet
- What's The Big Idea?: Artificial Gravity Using Acceleration. As ADocument3 pagesWhat's The Big Idea?: Artificial Gravity Using Acceleration. As AkebarclaNo ratings yet
- 10 Strange Things About The Universe: Negative EnergyDocument10 pages10 Strange Things About The Universe: Negative EnergyYalın SümerNo ratings yet
- Aquarian Theospophist Vol-3-11Document33 pagesAquarian Theospophist Vol-3-11JohnVNo ratings yet
- AntigravityDocument3 pagesAntigravityapi-209357478No ratings yet
- Dynamical Friction of SMBH Binaries in Galactic NucleiDocument18 pagesDynamical Friction of SMBH Binaries in Galactic NucleiLuciano Del ValleNo ratings yet
- Negative Energy-WormHoles & Warp DriveDocument18 pagesNegative Energy-WormHoles & Warp DriveLaron ClarkNo ratings yet
- Troubled Times for Einstein's Gravity TheoryDocument9 pagesTroubled Times for Einstein's Gravity TheoryCK_2023No ratings yet
- The Warp Drive Could Become Science Fact: Skip To Main ContentDocument14 pagesThe Warp Drive Could Become Science Fact: Skip To Main ContentLuax01No ratings yet
- The Dark UniverseDocument5 pagesThe Dark UniverseLance LegelNo ratings yet
- Free Energy Database CDDocument2 pagesFree Energy Database CDxNo ratings yet
- What is Gravitation? Exploring Classical and Modern TheoriesDocument8 pagesWhat is Gravitation? Exploring Classical and Modern TheoriesJoufant ZedekianNo ratings yet
- WWW Astronomytoday ComDocument11 pagesWWW Astronomytoday ComneonavNo ratings yet
- Einstein's Gravitational Waves DetectedDocument4 pagesEinstein's Gravitational Waves DetectedPrakash HiremathNo ratings yet
- Science Assignment - Playground ForcesDocument2 pagesScience Assignment - Playground Forcesnevaehxm30No ratings yet
- The History of Physics and ScienceDocument5 pagesThe History of Physics and ScienceIvanbg03gdNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Modern Theory of GravitationDocument8 pagesLesson 6 Modern Theory of GravitationSherrie CasiaNo ratings yet
- Special Relativity and Quantum Mechanics: Physics CentralDocument8 pagesSpecial Relativity and Quantum Mechanics: Physics CentralabuNo ratings yet
- Anti-Gravity: Presented By-Naveen.L.GatlewarDocument12 pagesAnti-Gravity: Presented By-Naveen.L.GatlewarnaveenNo ratings yet
- Black, An Introduction To Signal Extraction in Interferometric Gravitational Wave Detectors-2-15Document14 pagesBlack, An Introduction To Signal Extraction in Interferometric Gravitational Wave Detectors-2-15marco ricciNo ratings yet
- Special Relativity and Quantum Mechanics: Physics CentralDocument8 pagesSpecial Relativity and Quantum Mechanics: Physics CentralabuNo ratings yet
- GPS clocks tick faster in space due to weaker gravityDocument13 pagesGPS clocks tick faster in space due to weaker gravityabuNo ratings yet
- Vacuum EnergyDocument4 pagesVacuum EnergyHKNo ratings yet
- Solar Radiation Pressure May Explain Peculiar Acceleration of Interstellar Object 'OumuamuaDocument5 pagesSolar Radiation Pressure May Explain Peculiar Acceleration of Interstellar Object 'OumuamuaAnonymous sQ9wLhhZNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 - Gravitational Force and FieldsDocument28 pagesChapter - 4 - Gravitational Force and FieldsViper PotNo ratings yet
- Gravity Part 2Document5 pagesGravity Part 2netname1No ratings yet
- Dark Matter, Dark Energy and Vacuum EnergyDocument7 pagesDark Matter, Dark Energy and Vacuum Energyapi-26470372100% (1)
- Contorting Reality - The Mystery of Black Holes and WormholesDocument12 pagesContorting Reality - The Mystery of Black Holes and WormholesFiladelfioNo ratings yet
- March 7, 2006 Astronomy 2010 1Document43 pagesMarch 7, 2006 Astronomy 2010 1Yousra ZrNo ratings yet
- Dark MatterDocument6 pagesDark MatterRanjit Edward100% (1)
- Physics of Artificial GravityDocument15 pagesPhysics of Artificial GravityWilliam RiveraNo ratings yet
- AntiGravity 2Document6 pagesAntiGravity 2Na ThanielNo ratings yet
- A Matter of Gravity: Breaking ThroughDocument3 pagesA Matter of Gravity: Breaking ThroughaaaaNo ratings yet
- Meyl Scalar Energy Longitudinal Waves Faraday-Or-MaxwellDocument16 pagesMeyl Scalar Energy Longitudinal Waves Faraday-Or-Maxwellhanon9100% (1)
- Gravity Falls 1Document15 pagesGravity Falls 1Athena May OmpalingNo ratings yet
- Gravity Remains a Puzzle Despite its UbiquityDocument2 pagesGravity Remains a Puzzle Despite its UbiquityAnthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Drop Test: Physicists Are Challenging Einstein's Theory in New Versions of The Most Famous Experiment That Never HappenedDocument4 pagesDrop Test: Physicists Are Challenging Einstein's Theory in New Versions of The Most Famous Experiment That Never HappenedKyle ThomsenNo ratings yet
- Gravity - NotesDocument2 pagesGravity - NotesAndrea MoniqueNo ratings yet
- New Energy AwakeningDocument19 pagesNew Energy AwakeningJoseph FlemingNo ratings yet
- Artificial Gravity in Theory and Practice: University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, 48109, USADocument20 pagesArtificial Gravity in Theory and Practice: University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, 48109, USALingMakaiNo ratings yet
- AnothDocument5 pagesAnothsagaegewNo ratings yet
- Dark Energy: Unit OverviewDocument42 pagesDark Energy: Unit Overviewfernando estradaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Aerospace PropulsionDocument57 pagesAdvanced Aerospace Propulsionsid676No ratings yet
- The One Thing You Need to Know: The Simple Way to Understand the Most Important Ideas in ScienceFrom EverandThe One Thing You Need to Know: The Simple Way to Understand the Most Important Ideas in ScienceRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Corporeality of Antigravity Volume One: An Antigravity Force, That Might Suddenly Become Incadescent in the Mind, Radiating Outward with Such Apocalyptic Power That Everything Would ChangeFrom EverandCorporeality of Antigravity Volume One: An Antigravity Force, That Might Suddenly Become Incadescent in the Mind, Radiating Outward with Such Apocalyptic Power That Everything Would ChangeNo ratings yet
- Physics of The Electromagnetic Control of Spacetime and GravityDocument17 pagesPhysics of The Electromagnetic Control of Spacetime and GravityGherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- Li-Baker EPJC Vol. 56, pp.407-423Document17 pagesLi-Baker EPJC Vol. 56, pp.407-423Gherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- GRAVITATIONAL WAVES by Robert Baker v8Document25 pagesGRAVITATIONAL WAVES by Robert Baker v8Gherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- ADA227121Document169 pagesADA227121Gherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- Seven UFO Crashes & Retrievals in New Mexico 1945-1948: Presented To Highlands Ranch Historical Society June 17, 2017Document33 pagesSeven UFO Crashes & Retrievals in New Mexico 1945-1948: Presented To Highlands Ranch Historical Society June 17, 2017Gherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- Faster-Than-Light Space Warps, Status and Next StepsDocument18 pagesFaster-Than-Light Space Warps, Status and Next StepsGherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- Archaeology Anthropology and Interstellar Communication TAGGEDDocument330 pagesArchaeology Anthropology and Interstellar Communication TAGGEDphphdNo ratings yet
- Dielectric and Electrical Properties of Lead Zirconate TitanateDocument11 pagesDielectric and Electrical Properties of Lead Zirconate TitanateGherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- New Energy Technologies Issue 10Document77 pagesNew Energy Technologies Issue 10blameitontherain9877100% (1)
- Formation of Cooper Pairs in Quantum Oscillations of Electrons in PlasmaDocument8 pagesFormation of Cooper Pairs in Quantum Oscillations of Electrons in PlasmaGherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- Top Secret Black Budget Projects and Special Access ProgramsDocument257 pagesTop Secret Black Budget Projects and Special Access ProgramsLeak Leaker100% (3)
- Advanced Space Propulsion Based On VacuumDocument17 pagesAdvanced Space Propulsion Based On VacuumMystery Wire100% (1)
- Donvblack AdvancedPropulsionSystems-V2b NovideoDocument71 pagesDonvblack AdvancedPropulsionSystems-V2b NovideoGherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- CapacitorEs Conicos GraVitaciOnDocument8 pagesCapacitorEs Conicos GraVitaciOnzorrinNo ratings yet
- Superluminal Near-Field Dipole Electromagnetic Fields: William D. WalkerDocument16 pagesSuperluminal Near-Field Dipole Electromagnetic Fields: William D. WalkerGherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- Khmelnik Force: A Previously Unknown ForceDocument7 pagesKhmelnik Force: A Previously Unknown ForceGherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- Metamaterial-Based Model of The Alcubierre Warp DriveDocument15 pagesMetamaterial-Based Model of The Alcubierre Warp DriveGherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- Magnetic and Electric Charges in Physics and TechnDocument18 pagesMagnetic and Electric Charges in Physics and TechnGherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- Experimental Realization of Simultaneous Negative Permittivity and Permeability in Ag/Y3Fe5O12 Random CompositesDocument6 pagesExperimental Realization of Simultaneous Negative Permittivity and Permeability in Ag/Y3Fe5O12 Random CompositesGherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- 15 - 2019g McCulloch June FISW Cotswolds2bDocument49 pages15 - 2019g McCulloch June FISW Cotswolds2bGherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- 87 - Men in Black V1Document55 pages87 - Men in Black V1Gherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- 1978 Mufon Symposium PDFDocument135 pages1978 Mufon Symposium PDFGherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- The Gravitational Levitation in Aerospace TechnoloDocument15 pagesThe Gravitational Levitation in Aerospace TechnoloGherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Accelerated Electrons Within Information Horizons Exert Bidirectional Propellant-Less ThrustDocument34 pagesElectrostatic Accelerated Electrons Within Information Horizons Exert Bidirectional Propellant-Less ThrustGherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- Top Secret Black Budget Projects and Special Access ProgramsDocument257 pagesTop Secret Black Budget Projects and Special Access ProgramsLeak Leaker100% (3)
- Dynamic Vacuum Model and Casimir Cavity ExperimentsDocument36 pagesDynamic Vacuum Model and Casimir Cavity ExperimentsGherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- Hassel Future Physics and Anti-Gravity PDFDocument17 pagesHassel Future Physics and Anti-Gravity PDFGherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- COFE StarShip 2018Document34 pagesCOFE StarShip 2018Gherghe BogdanNo ratings yet
- Dirac Equation-Sea of Negative Energy (Free Energy) - Hotson (David Sereda) - Pt1-2Document20 pagesDirac Equation-Sea of Negative Energy (Free Energy) - Hotson (David Sereda) - Pt1-2John Kuhles100% (2)
- People Vs Sindiong & PastorDocument4 pagesPeople Vs Sindiong & PastorErby Jennifer Sotelo-GesellNo ratings yet
- Cing - Common Interface For NMR Structure Generation: Results 1 - 10 of 978Document3 pagesCing - Common Interface For NMR Structure Generation: Results 1 - 10 of 978Judap FlocNo ratings yet
- Distribution and Production of Rice in IndiaDocument6 pagesDistribution and Production of Rice in IndiaZehan SheikhNo ratings yet
- Biraogo vs. Philippine Truth CommissionDocument3 pagesBiraogo vs. Philippine Truth CommissionJulesMillanarNo ratings yet
- MAXsys 2510 Meterin FamilyDocument52 pagesMAXsys 2510 Meterin FamilyAbel NinaNo ratings yet
- ICCT COLLEGES FOUNDATION INC. PHYSICAL EDUCATION DEPARTMENTDocument2 pagesICCT COLLEGES FOUNDATION INC. PHYSICAL EDUCATION DEPARTMENTmarites_olorvidaNo ratings yet
- Walo Dict 12 2007Document194 pagesWalo Dict 12 2007Yad ElNo ratings yet
- Compassionate Sciences - RedactedDocument184 pagesCompassionate Sciences - RedactedNew Jersey marijuana documentsNo ratings yet
- B IngDocument2 pagesB IngsyfnanyNo ratings yet
- (1902) The Centennial of The United States Military Academy at West Point New YorkDocument454 pages(1902) The Centennial of The United States Military Academy at West Point New YorkHerbert Hillary Booker 2nd100% (1)
- The Residents of The British East India Company at Indian Royal Courts, C. 1798-1818Document224 pagesThe Residents of The British East India Company at Indian Royal Courts, C. 1798-1818Ajay_Ramesh_Dh_6124No ratings yet
- Persons Choki MotobuDocument4 pagesPersons Choki MotobuHessabi max100% (1)
- Gabriel's Oboe String PartsDocument5 pagesGabriel's Oboe String Partshekerer50% (2)
- The Tibetan Weather Magic Ritual of A MoDocument13 pagesThe Tibetan Weather Magic Ritual of A MoYORDIS PCNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7Document29 pagesLesson 7Khelly Joshua UyNo ratings yet
- Use of VariablesDocument5 pagesUse of VariablesJohn Clyde RanchezNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Notes - Dividend Decision - Dynamic Tutorials and ServicesDocument10 pagesFinancial Management Notes - Dividend Decision - Dynamic Tutorials and Servicessimranarora2007No ratings yet
- 39.prof. Ketaki Yadav 2 SRJISDocument2 pages39.prof. Ketaki Yadav 2 SRJISAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNo ratings yet
- Katherine Keesling - The Votive Statues of The Athenian Acropolis - (2003, Camb)Document302 pagesKatherine Keesling - The Votive Statues of The Athenian Acropolis - (2003, Camb)vadimkoponevmail.ru100% (2)
- Clarifying Oracle EPM Versioning - PatchesDocument3 pagesClarifying Oracle EPM Versioning - PatchesSathish BalaNo ratings yet
- Family Creation WorkflowDocument2 pagesFamily Creation Workflowzax418No ratings yet
- Course Registration Slip MBA 2023Document3 pagesCourse Registration Slip MBA 2023Piyush RaghuwanshiNo ratings yet
- Refunds Maceda Law and PD957Document2 pagesRefunds Maceda Law and PD957QUINTO CRISTINA MAENo ratings yet
- Advanced Engineering Mathematics 10th EditionDocument7 pagesAdvanced Engineering Mathematics 10th EditionsamuelNo ratings yet
- Society of Radiographers - PDFDocument9 pagesSociety of Radiographers - PDFOsama AhmedNo ratings yet
- Present Simple and Present Progressive TensesDocument4 pagesPresent Simple and Present Progressive TensesHân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- AUMUND Bucket Elevators 180801Document16 pagesAUMUND Bucket Elevators 180801Tino TorehNo ratings yet
- Effects of The Sugar RevolutionDocument9 pagesEffects of The Sugar RevolutionSusan BarriotNo ratings yet
- Administrator Guide: Document Version 3.6.1Document76 pagesAdministrator Guide: Document Version 3.6.1App PackNo ratings yet
- 1 The Importance of Business ProcessesDocument17 pages1 The Importance of Business ProcessesFanny- Fan.nyNo ratings yet