Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mouth, Hands, Neck, Extremities.: Disease Assesment Findings Medications Nsg. Considerations Impetigo
Uploaded by
Yna RamiroOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mouth, Hands, Neck, Extremities.: Disease Assesment Findings Medications Nsg. Considerations Impetigo
Uploaded by
Yna RamiroCopyright:
Available Formats
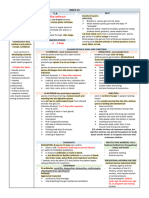
DISEASE ASSESMENT FINDINGS MEDICATIONS NSG.
CONSIDERATIONS
Impetigo - Vesicles or pustules - Antibiotic ointments - Use contact precautions
- Highly contagious bacterial surrounded by edema and - Apply warm water
infection of the skin redness compresses to the lesions
caused by beta-hemolytic - Lesions weeping cloudy 2 or 3 times daily, followed
streptococci, serous fluid by mild soap-and-water
staphylococcus aureus, or - Honey-colored crusts rinse to soften crusts for
both. - Pruritus and burning removal and promote
- Most common sites: healing
mouth, hands, neck, - Teach the parents to apple
extremities. antibiotic ointments and
explain that the infection is
communicable for 48
hours after antibiotic
ointment treatments Is
begun
- Separate use of towels,
linens, and dishes
- Linens and clothing should
be washed separately with
detergent in hot water
PEDIATRIC DISORDERS
I. INTEGUMENTARY
DISEASE ASSESMENT FINDINGS MEDICATIONS NSG. CONSIDERATIONS
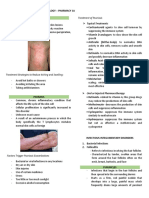
Pediculosis Capitis (Head Lice) - Intense pruritus - Pediculicide shampoo - Remove nits by back-
- Transmitted by way of - Small, gray specks that combing the child’s hair
direct and indirect contact. may crawl fast with a fine-tooth comb
- Most common site: - Nits, visible as tiny silver or after loosening nits with a
occipital area; less gray specks resembling mixture of half vinegar and
frequently, the eyebrows dandruff half water 1 hour before
and eyelashes are affected back combing.
- Teach the child not to
share clothing, headwear,
or brushes and combs.
DISEASE ASSESMENT FINDINGS MEDICATIONS NSG. CONSIDERATIONS
Scabies - Intense pruritus, especially - Scabicide is applied - Importance of
- Caused by infestation with at night topically. handwashing.
Sarcoptes scabiei, the itch - Pustules - Seal non-washable toys
mite. - Burrows, which appear as and other items in plastic
- Transmitted by way of fine grayish-red lines on bags for at least 4 days.
close personal contact the skin
with an infected person.
DISEASE ASSESMENT FINDINGS NSG. CONSIDERATIONS/ TREATMENT
Nephroblastoma (Wilms Tumor) - Abdominal swelling or Before Surgery:
- This tumor of the kidney mass (firm, nontender, - Monitor VS, particularly blood pressure.
may present unilaterally confined to one side, and - Avoid palpitation of abdomen, which could disrupt the tumor
and localized or bilaterally, deep within the flank) capsule, resulting in seeding elsewhere in the body.
sometimes with metastasis - Abdominal pain - Measure the client’s abdominal girth daily each morning.
to other organs. - Urine retention After Surgery:
- Treatment: is a - Hematuria - Monitor temperature for signs and symptoms of infection;
combination of surgery - Hypertension monitor the blood pressure for any changes.
(partial to total - Signs & symptoms of lung - Monitor for hemorrhage.
nephrectomy) and involvement if metastasis - Monitor intake and output closely, particularly urine production.
chemotherapy with or has occurred - Monitory gastrointestinal activity, bowel sounds, stool
without radiation. production, and abdominal distention.
- Avoid contact sports.
II. ONCOLOGICAL
DISEASE ASSESMENT FINDINGS NSG. CONSIDERATIONS/ TREATMENT
Neuroblastoma - Abdominal swelling or Before Surgery:
- An embryonal tumor mass (firm, nontender, - Monitor signs and symptoms related to the location of the
found in children, arises confined to one side, and tumor.
from the neural chest. deep within the flank) After Surgery:
- The abdomen is usually - Abdominal pain - Watch for complications related to the location of the surgery.
the primary site because - Urine retention
the tumor cells arise from - Hematuria
the adrenal gland or - Hypertension
retroperitoneal
sympathetic chain.
- Most presenting signs and
symptoms are caused by
tumor compression of
adjacent normal tissue and
organs.
- Surgery is performed to
remove the tumor as
possible and to obtain
biopsy specimens.
DISEASE ASSESMENT FINDINGS NSG. CONSIDERATIONS/ TREATMENT
Osteogenic Sarcoma - Signs and symptoms in the - May include surgical resection with limb salvage to remove
(Osteosarcoma) earliest stage are almost affected tissue or amputation.
- Found in metaphysis of always attributed to - Chemotherapy may be administered both before and after
long bones, especially the extremity injury or normal surgery.
legs; most cases occur in growing pains. - If amputation is performed, tell the child about phantom limb
the femur. - Localized pain at the site pain (burning aching, or cramping pain in the missing limb)
that may be attributed to - Prosthetic fitting
trauma or the vague
complaint of “growing
pains”; often relieved with
a flexed position.
- Palpable mass
- Limping
- Progressively limited range
of motion with curtailment
of physical activity
- Pathological fractures at
the tumor site
DISEASE ASSESMENT FINDINGS NSG. CONSIDERATIONS/ TREATMENTS
Retinoblastoma - A white reflection - Postoperative are of the enucleated orbit entails careful
- Malignant tumor of the (leukocoria) is seen in one observations for signs & symptoms of infection, hemorrhage,
embryonic neural retina. of the child’s eyes instead and edema.
- This tumor of the eye is of the normal red color - The child will wear a patch over the socket for approximately 1
found only in children. when a camera flash is week postoperatively.
- reflected off the retina.
DISEASE ASSESMENT FINDINGS NSG. CONSIDERATIONS/ TREATMENTS
Ewing Sarcoma - Pain - Nursing care is similar to osteosarcoma.
- The bone tumor is more - Swelling of soft tissue
often located in the around the affected bone
midshaft of a long bone, - Fever
especially the femur, ribs, - Anorexia malaise, fatigue,
and pelvic bones, or in the and weight loss if
vertebrae. metastasis has occurred
- Neurological signs and
symptoms if a vertebral
tumor is present
- Respiratory signs &
symptoms if a rib tumor is
present
III. METABOLIC & ENDOCRINE
DISEASE ASSESMENT FINDINGS NSG. CONSIDERATIONS/ TREATMENTS
Fever - Temperature of 38.0 C or - Monitor child’s temperature
- Abnormally high body higher - Administer antipyretics (acetaminophen, ibuprofen) as
temperature - Flushed skin prescribed.
- Diaphoresis - Do not administer aspirin unless prescribed, because it may
- Chills precipitate the development of Reye’s syndrome.
- Restlessness or lethargy - Provide adequate fluid intake.
- Monitor the child for dehydration and fluid and electrolyte
imbalances.
DISEASE ASSESMENT FINDINGS NSG. CONSIDERATIONS/ TREATMENTS
Dehydration - Dry skin and mucous
- Infants and children are membranes
more vulnerable to fluid- - Loss of skin elasticity and
volume deficit that adults. turgor
- Causes: decreased fluid - Tachycardia
intake, diaphoresis, - Sunken eyeballs ad
vomiting, diarrhea, fontanels
diabetic ketoacidosis, and - Weight loss
extensive burns. - Decreased urine output
and increased urine
specific gravity
- Thirst
- Absence of tears
- Changes in level of
consciousness
You might also like
- Nursing Aspect - Wound ManagementDocument54 pagesNursing Aspect - Wound ManagementBbieSyg Usagi Tsukino0% (1)
- 2004 - Number Series For Psychological Normalization - Book1Document208 pages2004 - Number Series For Psychological Normalization - Book1Carla Perin67% (3)
- NCLEX Mark K NotesDocument131 pagesNCLEX Mark K NotesRhika Mae ObraNo ratings yet
- Pediatric MCQsDocument34 pagesPediatric MCQsn100% (2)
- Gram Positive CocciDocument21 pagesGram Positive CocciRedelle Mae Nini100% (2)
- Nutrition Assessment Subject McqsDocument13 pagesNutrition Assessment Subject McqsNoorNo ratings yet
- Part I - Antibiotics and The Human MicrobiomeDocument5 pagesPart I - Antibiotics and The Human MicrobiomeRejean Isip100% (3)
- NCP NeuroDocument2 pagesNCP NeuroMarie Frances Lalican-RingelNo ratings yet
- Careplan Week2Document2 pagesCareplan Week2api-302138606No ratings yet
- O o o o o o O: DescriptionDocument34 pagesO o o o o o O: DescriptionDarren BalbasNo ratings yet
- Medical EmergenciesDocument71 pagesMedical EmergenciespinkgirljojiNo ratings yet
- ALMOETE Bullous ImpetigoDocument4 pagesALMOETE Bullous ImpetigoGail NamangdanNo ratings yet
- GENERAL NURSING CARE PLAN FOR SKIN DISORDERS sgk-1Document2 pagesGENERAL NURSING CARE PLAN FOR SKIN DISORDERS sgk-1fxbukenyaNo ratings yet
- Pain Nursing Care Plan and Bactrobran Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPain Nursing Care Plan and Bactrobran Drug StudyAnni BarbaNo ratings yet
- Understand Scabies - 10112023Document2 pagesUnderstand Scabies - 10112023Nazli MassihiNo ratings yet
- DiseasesDocument7 pagesDiseasesPermalino Borja Rose AnneNo ratings yet
- Drugs ReviewedDocument7 pagesDrugs ReviewedJamil LorcaNo ratings yet
- Circumcision TeachingDocument3 pagesCircumcision Teachingapi-341263362No ratings yet
- Bed Bath and ShampooingDocument1 pageBed Bath and ShampooingJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyNicole Rachelyn MartinNo ratings yet
- Scabies Simplified CPGDocument3 pagesScabies Simplified CPGAliaSyafiqaNo ratings yet
- HYGIENEDocument3 pagesHYGIENECHRISTIAN ROY MAXINONo ratings yet
- High Risk School Age and AdolescentDocument6 pagesHigh Risk School Age and AdolescentRamos, Janica De VeraNo ratings yet
- Scabies: Dr. Atul Jain MD, Dermatology, SR, Santosh Medical College, GhaziabadDocument38 pagesScabies: Dr. Atul Jain MD, Dermatology, SR, Santosh Medical College, GhaziabadMaria GharuNo ratings yet
- ARTHROPODSDocument5 pagesARTHROPODSAis AbulNo ratings yet
- Candidiasis: 1. Thrush-Causes Curd-Like White Patches Inside TheDocument2 pagesCandidiasis: 1. Thrush-Causes Curd-Like White Patches Inside ThekyawNo ratings yet
- ElsieDocument4 pagesElsieFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Surface Infections 1st & 3rd Sept-2022Document7 pagesSurface Infections 1st & 3rd Sept-2022Doctor iVJNo ratings yet
- AnthraxDocument1 pageAnthraxsaint_peter_03No ratings yet
- Middle Age and Older AdultDocument2 pagesMiddle Age and Older AdultRAYANA UBASNo ratings yet
- System Disorder ADDocument1 pageSystem Disorder ADSariahNo ratings yet
- wk13 ValerianoDocument5 pageswk13 ValerianoVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveLen meloNo ratings yet
- TMC OrientationDocument4 pagesTMC OrientationJennifer HerediaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ColostomyDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan ColostomyCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- L05 Malaria, ThreadwormDocument3 pagesL05 Malaria, ThreadwormdeeyungcocoNo ratings yet
- Parasit IntegumenDocument43 pagesParasit Integumenandi mutiah armusNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management For CancerDocument6 pagesNursing Management For CancerL Rean Carmelle MAGALLONESNo ratings yet
- Annotated Group 2 Impetigo Concept Mapping 1Document30 pagesAnnotated Group 2 Impetigo Concept Mapping 1DHANE ANN CAMPOSANONo ratings yet
- First Aid Part - 3 - 201023 - 132951Document13 pagesFirst Aid Part - 3 - 201023 - 132951VishnuNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy - 01 02 24Document3 pagesDrugStudy - 01 02 24Laurente, Patrizja Ysabel B. BSN-2DNo ratings yet
- Scabies Information: What About Mites in Clothing and Bedding?Document2 pagesScabies Information: What About Mites in Clothing and Bedding?DreamNo ratings yet
- Handouts in HYGIENE Hygiene - Is The Science of Health and Its MaintenanceDocument9 pagesHandouts in HYGIENE Hygiene - Is The Science of Health and Its MaintenanceTweetie Borja DapogNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 First AidDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 First AidEmma PataNo ratings yet
- Classification Drugs Pharmaco-Dynamics Pharmaco-Kinetics Indications Side Effects/ Interactions Nursing Considerations RationaleDocument11 pagesClassification Drugs Pharmaco-Dynamics Pharmaco-Kinetics Indications Side Effects/ Interactions Nursing Considerations RationalePeter Emmil GonzalesNo ratings yet
- WEEK 14 CD Vidlec 1-3 (+ Module Info)Document24 pagesWEEK 14 CD Vidlec 1-3 (+ Module Info)jmmacar19No ratings yet
- Del Rosario Ryan D. BSN 4C1-7 Mr. Daniel Mon Mamanao: Measles Pre-Eruptive StageDocument5 pagesDel Rosario Ryan D. BSN 4C1-7 Mr. Daniel Mon Mamanao: Measles Pre-Eruptive Stageryandelrosario9yahooNo ratings yet
- PEDIA Review TransesDocument12 pagesPEDIA Review TransesJennie KimNo ratings yet
- 3) Bacterial Skin Infections Semi NotesDocument2 pages3) Bacterial Skin Infections Semi NotesIssa MoodNo ratings yet
- PATHO - Last Lesson Part1Document2 pagesPATHO - Last Lesson Part1KHEAHNA FAITH PORRAS BARROANo ratings yet
- Capacio Case#5&6Document7 pagesCapacio Case#5&6Lorenz CapacioNo ratings yet
- Amirah Maisarah Binti Azarman - Group BDocument7 pagesAmirah Maisarah Binti Azarman - Group BMOHD MU'IZZ BIN MOHD SHUKRINo ratings yet
- Ncp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasDocument4 pagesNcp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasFran LanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Disease Prevention and Control (Communicable) : Health 8Document4 pagesLesson 1 - Disease Prevention and Control (Communicable) : Health 8Ashleigh ReignNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics Absorption: Distribution: Metabolism: EliminationDocument2 pagesPharmacokinetics Absorption: Distribution: Metabolism: EliminationChrislyn LangegNo ratings yet
- Document From BenjaminfjodDocument21 pagesDocument From BenjaminfjodBenjamin VanlaltlansangaNo ratings yet
- Contact Dermatitis Fact SheetsDocument1 pageContact Dermatitis Fact SheetsJoe Aire SalvediaNo ratings yet
- Course Task 7 Dengue Fever, Filariasis, Malaria and EncephalitisDocument4 pagesCourse Task 7 Dengue Fever, Filariasis, Malaria and EncephalitisBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- Insect Bites StingsDocument1 pageInsect Bites StingsnamibadiNo ratings yet
- Presentasi ScabiesDocument21 pagesPresentasi ScabiesMunawwar AwaNo ratings yet
- DermatologyDocument19 pagesDermatologypkpmmc1957No ratings yet
- Rectal SuppositoriesDocument2 pagesRectal SuppositoriesAngel Leo M. ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument3 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameFrancis Xavier S. MendezNo ratings yet
- Biosecurity SOPDocument26 pagesBiosecurity SOPIsam SalehNo ratings yet
- Notes on Diseases of Cattle: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentFrom EverandNotes on Diseases of Cattle: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentNo ratings yet
- Pigmentation DisordersDocument5 pagesPigmentation DisordersWoo Rin ParkNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Neuro ExamDocument13 pagesNeonatal Neuro ExamLisa SariNo ratings yet
- Ramachandran Medical Application FormDocument3 pagesRamachandran Medical Application FormRuban JebaduraiNo ratings yet
- Case Study CholecystitisDocument27 pagesCase Study CholecystitisBandana RajpootNo ratings yet
- The Aim of Ear, Nose and ThroatDocument32 pagesThe Aim of Ear, Nose and ThroatabdulNo ratings yet
- Heller Bergman 1953Document11 pagesHeller Bergman 1953Sirine AjourNo ratings yet
- 2020 Article 363Document8 pages2020 Article 363RIAN NUGRAHANo ratings yet
- Ward Quiz 1 Musculoskeletal PDFDocument3 pagesWard Quiz 1 Musculoskeletal PDFPNo ratings yet
- DescargarDocument7 pagesDescargarJonathan NaulaNo ratings yet
- Vestibular NeuronitisDocument3 pagesVestibular NeuronitisAnish RajNo ratings yet
- An Environmental Scientific Report Into The Crude Oil Spillage Incidence in Tein Community Biseni Bayelsa State NigeriaDocument6 pagesAn Environmental Scientific Report Into The Crude Oil Spillage Incidence in Tein Community Biseni Bayelsa State NigeriaOlumide AjayiNo ratings yet
- International Ayurvedic Medical JournalDocument7 pagesInternational Ayurvedic Medical JournalChandu PanditNo ratings yet
- Asthalin InhalerDocument7 pagesAsthalin InhalerINDAH WIDYANING TYASNo ratings yet
- Ati 3Document17 pagesAti 3academicexcellence21No ratings yet
- Elliot. Colin-The Antonine Plague, Climate Change and Local Violence in Roman EgyptDocument29 pagesElliot. Colin-The Antonine Plague, Climate Change and Local Violence in Roman EgyptJuan Andrés SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document27 pagesChapter 15Jessica nonyeNo ratings yet
- Chang Sepsis and Septic ShockDocument19 pagesChang Sepsis and Septic ShockPediatria UDec 2020No ratings yet
- OrthoDocument148 pagesOrthoCess KimNo ratings yet
- Coliform Bacteria in Drinking Water PDFDocument2 pagesColiform Bacteria in Drinking Water PDFaldoNo ratings yet
- SinusitisDocument14 pagesSinusitisdr Rizaldi AbesyNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Seizure and Prescribing Patterns of Aed in Patients With NeuroDocument120 pagesPrevalence of Seizure and Prescribing Patterns of Aed in Patients With NeurosnigdhaNo ratings yet
- Seram Anguillae (Eel Serum)Document2 pagesSeram Anguillae (Eel Serum)Shah FaisalNo ratings yet
- Meningitis JournalDocument6 pagesMeningitis JournalMaylinda VebriantiNo ratings yet
- Bahan Paparan Prof. Ratu Ayu - Guest Lecture OH 27 Agustus 2021 Rev3 VfinalDocument23 pagesBahan Paparan Prof. Ratu Ayu - Guest Lecture OH 27 Agustus 2021 Rev3 VfinalZulkarnaenUchihaNo ratings yet
- Condyloma Acuminata (JURNAL)Document8 pagesCondyloma Acuminata (JURNAL)Renaldi RNo ratings yet