Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Use Case Diagram: Software Design Methodology
Use Case Diagram: Software Design Methodology
Uploaded by
Sang Vũ MinhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Use Case Diagram: Software Design Methodology
Use Case Diagram: Software Design Methodology
Uploaded by
Sang Vũ MinhCopyright:
Available Formats
Use Case Diagram
Software Design Methodology
Using Use Case Diagrams
Use case diagrams are used to visualize,
specify, construct, and document the (intended)
behavior of the system, during requirements
capture and analysis.
Provide a way for developers, domain experts
and end-users to Communicate.
Serve as basis for testing.
Use case diagrams contain use cases, actors,
and their relationships.
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 2
Use Case name
Use cases specify desired behavior.
A use case is a description of a set of
sequences of actions, including variants, a
system performs to yield an observable
result of value to an actor.
Each sequence represent an interaction of
actors with the system.
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 3
Specifying the Behavior of a Use Case
Describing the flow of events within the use
case.
Can be done in natural language, formal
language or pseudo-code.
Includes: how and when the use case starts and
ends; when the use case interacts with actors
and what objects are exchanged; the basic flow
and alternative flows of the behavior.
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 4
Actors
name
An actor represents a set of roles that
users of use case play when interacting
with these use cases.
Actors can be human or automated
systems.
Actors are entities which require help from
the system to perform their task or are
needed to execute the system’s functions.
Actors are not part of the system.
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 5
Use Cases and Actors
From the perspective of a given actor, a
use case does something that is of value
to the actor, such as calculate a result or
change the state of an object.
The Actors define the environments in
which the system lives
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 6
Example of Use Case Diagram
registration
updating
grades
student faculty
output
generating
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 7
Relationships between Use Cases
1. Generalization - use cases that are
specialized versions of other use cases.
2. Include - use cases that are included as
parts of other use cases. Enable to factor
common behavior.
3. Extend - use cases that extend the
behavior of other core use cases. Enable
to factor variants.
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 8
1. Generalization
The child use case inherits the
behavior and meaning of the parent
parent use case.
The child may add to or
child
override the behavior of its parent.
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 9
More about Generalization
registration
non-graduate graduate
registration registration
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 10
2. Include
<<include>>
base included
The base use case explicitly incorporates
the behavior of another use case at a
location specified in the base.
The included use case never stands
alone. It only occurs as a part of some
larger base that includes it.
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 11
More about Include
Enables to avoid describing the same flow
of events several times by putting the
common behavior in a use case of its own.
updating
grades <<include>>
verifying
student id
output <<include>>
generating
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 12
3. Extend
<<extend>>
base extending
The base use case implicitly incorporates
the behavior of another use case at certain
points called extension points.
The base use case may stand alone, but
under certain conditions its behavior may
be extended by the behavior of another
use case.
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 13
More about Extend
Enables to model optional behavior or
branching under conditions.
<<extend>> Exam-grade
Exam copy
request appeal
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 14
Relationships between Actors
Generalization.
student
graduate non-graduate
student student
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 15
Relationships between Use Cases
and Actors
Actors may be connected to use cases by
associations, indicating that the actor and
the use case communicate with one
another using messages.
updating
grades
faculty
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 16
Example
place
place <<extend>>
conference
phone call
call
cellular
network receive
receive <<extend>>
additional
phone call
call
use
user scheduler
Cellular Telephone
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 17
A More Complicate Example
U p da t e I te m s
B ook s hop
W o rk e r
S h ip O rd e r
U p d a t e S t a ff D e t a ils
C us tom er B ook s hop
1
M anager
R e g is t e r D e t a ils
< < in c lu d e> >
S y s t e m L o g in
< < ex tend>>
H a n d le O rd e r
< < in c lu d e > >
< < in c lu d e> > U p d a t e C u s t o m e r D e t a ils
M a k e O rd e r A d d It e m s t o S h o p p in g C a rt
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 18
os
e
Use Case Description
-
sp
Each use case may includeeci fie
all or part of the following:
Title or Reference Name -smeaningful name of the UC
Author/Date -the
the author and creation date
Modification/Date -go
last modification and its date
Purpose -al
specifies the goal to be achieved
Overview -to
short description of the processes
Cross References -be
requirements references
Actors -ac
agents participating
hie
Pre Conditions - must be true to allow execution
ve
Post Conditions - will be set when completes normally
d
Normal flow of events -by
regular flow of activities
Alternative flow of events -the
other flow of activities
Exceptional flow of events -UC
unusual situations
Implementation issues -Ov
foreseen implementation problems
erv
ie
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 w 19
Example- Money Withdraw
Use Case: Withdraw Money
Author: ZB
Date: 1-OCT-2004
Purpose: To withdraw some cash from user’s bank account
Overview: The use case starts when the customer inserts his credit
card into the system. The system requests the user PIN. The system
validates the PIN. If the validation succeeded, the customer can
choose the withdraw operation else alternative 1 – validation failure
is executed. The customer enters the amount of cash to withdraw.
The system checks the amount of cash in the user account, its credit
limit. If the withdraw amount in the range between the current
amount + credit limit the system dispense the cash and prints a
withdraw receipt, else alternative 2 – amount exceeded is executed.
Cross References: R1.1, R1.2, R7
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 20
Example- Money Withdraw (cont.)
Actors: Customer
Pre Condition:
The ATM must be in a state ready to accept transactions
The ATM must have at least some cash on hand that it can
dispense
The ATM must have enough paper to print a receipt for at least
one transaction
Post Condition:
The current amount of cash in the user account is the amount
before the withdraw minus the withdraw amount
A receipt was printed on the withdraw amount
The withdraw transaction was audit in the System log file
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 21
Example- Money Withdraw (cont.)
Typical Course of events:
Actor Actions System Actions
1. Begins when a Customer arrives at ATM
2. Customer inserts a Credit card into ATM 3. System verifies the customer ID and
status
5. Customer chooses “Withdraw” operation 4. System asks for an operation type
7. Customer enters the cash amount 6. System asks for the withdraw amount
8. System checks if withdraw amount is
legal
9. System dispenses the cash
10. System deduces the withdraw amount
from account
11. System prints a receipt
13. Customer takes the cash and the receipt 12. System ejects the cash card
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 22
Example- Money Withdraw (cont.)
Alternative flow of events:
Step 3: Customer authorization failed. Display an
error message, cancel the transaction and eject the
card.
Step 8: Customer has insufficient funds in its account.
Display an error message, and go to step 6.
Step 8: Customer exceeds its legal amount. Display
an error message, and go to step 6.
Exceptional flow of events:
Power failure in the process of the transaction before
step 9, cancel the transaction and eject the card
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 23
Example- Money Withdraw (cont.)
One method to identify use cases is actor-based:
- Identify the actors related to a system or organization.
- For each actor, identify the processes they initiate or participate in.
A second method to identify use cases is event-based:
- Identify the external events that a system must respond to.
- Relate the events to actors and use cases.
The following questions may be used to help identify the
use cases for a system:
- What are tasks of each actor ?
- Will any actor create, store, change, remove, or read information in the
system ?
- What use cases will create, store, change, remove, or read this
information ?
- Will any actor need to inform the system about sudden, external
changes ?
- Does any actor need to be informed about certain occurrences in the
system ?
- Can all functional requirements be performed by the use cases ?
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 24
Moving on
The “things” that “live” inside the system
are responsible for carrying out the
behavior the actors on the outside expect
the system to provide.
To implement a use case, we create a
society of classes that work together to
carry out the behavior of the use case.
@by Pham Ngoc Hung, Coltech, VNU, 2010 25
You might also like
- Involute Splines: According To DIN 5482Document2 pagesInvolute Splines: According To DIN 5482ehtisham khanNo ratings yet
- Software ArchitectureDocument23 pagesSoftware Architecturezainvi.sf6018No ratings yet
- Double SwitchingDocument4 pagesDouble SwitchingAru GuptaNo ratings yet
- Uml Diagram For Hospital Management SystemDocument34 pagesUml Diagram For Hospital Management SystemVani Garikipati100% (1)
- Glucose Meter Oxidase Arduino UnoDocument7 pagesGlucose Meter Oxidase Arduino Unologix50% (2)
- Use Case Diagrams: Introduction To Software EngineeringDocument31 pagesUse Case Diagrams: Introduction To Software EngineeringHữu NghĩaNo ratings yet
- Use Case & Use Case Diagram: © PKD, Asst. Professor, CIT Dept at UPES - Sept 2013Document27 pagesUse Case & Use Case Diagram: © PKD, Asst. Professor, CIT Dept at UPES - Sept 2013praba karanNo ratings yet
- Immersive Robotic Telepresence For Remote Educational ScenariosDocument21 pagesImmersive Robotic Telepresence For Remote Educational ScenariosbscnioewnfwoeiNo ratings yet
- Object-Oriented Modeling: Use Case DiagramDocument28 pagesObject-Oriented Modeling: Use Case DiagramZelph AgrestNo ratings yet
- Introduction To UML: Jayant Shrivastava, TCSDocument35 pagesIntroduction To UML: Jayant Shrivastava, TCSmadeiniitNo ratings yet
- Experience ClipDocument10 pagesExperience Clipmatija.prskaloNo ratings yet
- Metaphors To Drive By: Exploring New Ways To Guide Human - Robot InteractionDocument8 pagesMetaphors To Drive By: Exploring New Ways To Guide Human - Robot InteractionHazu WanNo ratings yet
- A Computer Remote Control System Based On Speech RDocument17 pagesA Computer Remote Control System Based On Speech RShalini KumaranNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (LeungChiHei)Document7 pagesAssignment 1 (LeungChiHei)Lee Tin YanNo ratings yet
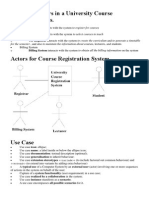
- Example: Actors in A University Course Registration SysDocument10 pagesExample: Actors in A University Course Registration Sysgoingforward77No ratings yet
- J170 A Novel Context-Aware Recommender Systems Based On A J166 Deep Sequential Learning Approach (CReS)Document12 pagesJ170 A Novel Context-Aware Recommender Systems Based On A J166 Deep Sequential Learning Approach (CReS)Timothy K ShihNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document24 pagesTutorial 2thunderstorm123No ratings yet
- The Recurrent Reinforcement Learning Crypto Agent: Gabriel Borrageiro Nick Firoozye Paolo BaruccaDocument16 pagesThe Recurrent Reinforcement Learning Crypto Agent: Gabriel Borrageiro Nick Firoozye Paolo Baruccaicosahedron_manNo ratings yet
- Review 1 - Use CaseDocument22 pagesReview 1 - Use Case19021210 Lý Hoàng AnhNo ratings yet
- TMEC: A Trust Management Based On Evidence Combination On Attack-Resistant and Collaborative Internet of VehiclesDocument10 pagesTMEC: A Trust Management Based On Evidence Combination On Attack-Resistant and Collaborative Internet of Vehiclesparameshwari pNo ratings yet
- Experimenting Through The Web A Linear Variable Differential TransformerDocument7 pagesExperimenting Through The Web A Linear Variable Differential Transformerkhalil alhatabNo ratings yet
- Find You - Multi-View-Based Location Inference For Twitter UsersDocument15 pagesFind You - Multi-View-Based Location Inference For Twitter Userseric.lealNo ratings yet
- Chapter Exercise:: Week Assignments 5-3Document6 pagesChapter Exercise:: Week Assignments 5-3Hermawan Dwi WijayaNo ratings yet
- BPEL4Chor: Extending BPEL For Modeling Choreographies: Gero Decker, Oliver Kopp, Frank Leymann, Mathias WeskeDocument9 pagesBPEL4Chor: Extending BPEL For Modeling Choreographies: Gero Decker, Oliver Kopp, Frank Leymann, Mathias WeskeRaluca TudorieNo ratings yet
- Mobile Phones: Positive and Negative Effects On The Academic Performance of Academic Strand Students in HNHSDocument6 pagesMobile Phones: Positive and Negative Effects On The Academic Performance of Academic Strand Students in HNHSVenz AndreiNo ratings yet
- Rumour Detection Based On Graph Convolutional NeuronDocument8 pagesRumour Detection Based On Graph Convolutional NeuronSanthosh SNo ratings yet
- Virtual Telepresence and Gesture Controlled RobotDocument7 pagesVirtual Telepresence and Gesture Controlled RobotsridharparthipanNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument80 pagesThesisAnkurBalarNo ratings yet
- Guangyong 2019Document4 pagesGuangyong 2019Hacker ShotsNo ratings yet
- Adversarial Training For Fake News ClassificationDocument10 pagesAdversarial Training For Fake News ClassificationKarthik YogeshNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework of Mobile LearningDocument4 pagesConceptual Framework of Mobile Learningneildump12No ratings yet
- Gesture Based UIDocument14 pagesGesture Based UIV MERIN SHOBINo ratings yet
- An Experiment in Feature Engineering: Pamela ZaveDocument25 pagesAn Experiment in Feature Engineering: Pamela ZaveP6E7P7No ratings yet
- The Use of Mobile Applications in HigherDocument15 pagesThe Use of Mobile Applications in HigherNaveed AnvarNo ratings yet
- Behaviour & Information TechnologyDocument13 pagesBehaviour & Information TechnologyMary Louise TomaquinNo ratings yet
- Ifugao State University: Appendix ADocument15 pagesIfugao State University: Appendix ALeah BobisNo ratings yet
- MSC Thesis LseDocument4 pagesMSC Thesis Lsesashajoneskansascity100% (2)
- SE Lecture 06 - Use Case Modeling 27042021 121950pmDocument45 pagesSE Lecture 06 - Use Case Modeling 27042021 121950pmMohammad TaimurNo ratings yet
- Use Case Diagrams-IDocument39 pagesUse Case Diagrams-IRahul LokeshNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id4367406 PDFDocument19 pagesSSRN Id4367406 PDFCha KimNo ratings yet
- Final Thesis CompilationDocument45 pagesFinal Thesis CompilationqueenNo ratings yet
- Basic Use CasesDocument20 pagesBasic Use CasesbelisaNo ratings yet
- Use Case Diagram-1Document42 pagesUse Case Diagram-1shubham tiwariNo ratings yet
- LectureNotes03 SlidesDocument22 pagesLectureNotes03 SlidesmaryamNo ratings yet
- IROS2021 - Deep Learning Using GazeboDocument9 pagesIROS2021 - Deep Learning Using Gazeboroykaushik4uNo ratings yet
- Use Cases DiagramDocument25 pagesUse Cases DiagramKiên LêNo ratings yet
- Free Open Source Software - ICTDocument12 pagesFree Open Source Software - ICTlunarlunaNo ratings yet
- Dimensions of Project Complexity and Their Impact On Cost EstimationDocument10 pagesDimensions of Project Complexity and Their Impact On Cost EstimationEduardo MenaNo ratings yet
- Java Programming MicroprojectDocument16 pagesJava Programming MicroprojectYashvardhan VibhuteNo ratings yet
- A Survey of Artificial Intelligence For Cognitive Radios-xAc PDFDocument16 pagesA Survey of Artificial Intelligence For Cognitive Radios-xAc PDFHasan AljabaliNo ratings yet
- A Skeleton-Based Approach For The Design and Implementation of Distributed Virtual EnvironmentsDocument8 pagesA Skeleton-Based Approach For The Design and Implementation of Distributed Virtual Environmentsdlcmsm1626No ratings yet
- Cooperation Observation The Framework and Basic Task PatternsDocument8 pagesCooperation Observation The Framework and Basic Task PatternsMarinelNo ratings yet
- 2001 AEHedonicspecificationand NNDocument15 pages2001 AEHedonicspecificationand NNIustina HorgaNo ratings yet
- Jeductechsoci 13 3 3Document10 pagesJeductechsoci 13 3 3mohammedNo ratings yet
- Mobile Context-Awareness: Capabilities, Challenges and ApplicationsDocument3 pagesMobile Context-Awareness: Capabilities, Challenges and ApplicationsSurentharNo ratings yet
- Computer Science EducationDocument20 pagesComputer Science EducationMohammad LorgatNo ratings yet
- CSE 311 - Web Services: Chapter 1 - Concept of A ServiceDocument12 pagesCSE 311 - Web Services: Chapter 1 - Concept of A ServiceHarsha Vardhan GorantlaNo ratings yet
- Reuse in Use-Case Models:, , and InheritanceDocument6 pagesReuse in Use-Case Models:, , and InheritanceAfiq AmeeraNo ratings yet
- Flow Coupling Between Active and Passive Fluids Across Interfaces of Compressed Active DropletsDocument2 pagesFlow Coupling Between Active and Passive Fluids Across Interfaces of Compressed Active DropletsWarit Abi NurazaqNo ratings yet
- 2015-Heterogeneous Multi-Task Assignment in Mobile Crowdsensing Using Spatiotemporal Correlation PDFDocument15 pages2015-Heterogeneous Multi-Task Assignment in Mobile Crowdsensing Using Spatiotemporal Correlation PDFqilongwuNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Mobile Phones On StudentsDocument35 pagesThe Effect of Mobile Phones On Studentsgbengadaniel1963No ratings yet
- Robust Processing of Spoken Situated Dialogue: A Study in Human-Robot InteractionFrom EverandRobust Processing of Spoken Situated Dialogue: A Study in Human-Robot InteractionNo ratings yet
- Case Studies in GOF Behavioural Patterns: Case Studies in Software Architecture & Design, #4From EverandCase Studies in GOF Behavioural Patterns: Case Studies in Software Architecture & Design, #4No ratings yet
- Trust between Cooperating Technical Systems: With an Application on Cognitive VehiclesFrom EverandTrust between Cooperating Technical Systems: With an Application on Cognitive VehiclesNo ratings yet
- Obsolete: Low Cost Accelerometers With Digital Output ADXL202/ADXL210Document11 pagesObsolete: Low Cost Accelerometers With Digital Output ADXL202/ADXL210adfumegaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Arduino: Spoken Tutorial Project National Mission On Education Through ICTDocument55 pagesOverview of Arduino: Spoken Tutorial Project National Mission On Education Through ICTSibin SibinNo ratings yet
- TIA Selection ToolDocument12 pagesTIA Selection ToolTarakPanchalNo ratings yet
- CHS320 Three Phase Smart Meter v1.0 (Without Keypad)Document2 pagesCHS320 Three Phase Smart Meter v1.0 (Without Keypad)Alaim AlvesNo ratings yet
- Super Uno r3 Starter Kit Ae108Document155 pagesSuper Uno r3 Starter Kit Ae108ErmalNo ratings yet
- ISPTools enDocument3 pagesISPTools ensoyenak879No ratings yet
- CV Gabriel Oscar Reyes SeverianoDocument2 pagesCV Gabriel Oscar Reyes SeverianoKira TNo ratings yet
- Error Detection and CorrectionDocument37 pagesError Detection and CorrectionMikiyas AbebeNo ratings yet
- ASD-231i NTSC/PAL To 4:2:2 Adaptive Decoder With TBC: Guide To Installation and OperationDocument28 pagesASD-231i NTSC/PAL To 4:2:2 Adaptive Decoder With TBC: Guide To Installation and OperationdarwinNo ratings yet
- M Bus Documentation AnnotationsDocument80 pagesM Bus Documentation AnnotationsmcmayerNo ratings yet
- TCS Topics PatternDocument4 pagesTCS Topics PatternAkshay KayapakNo ratings yet
- Midterm Solutions Mar 30Document6 pagesMidterm Solutions Mar 30Sahil SethNo ratings yet
- MPMC MCQDocument9 pagesMPMC MCQDhivyaManian83% (6)
- Google Protocol Buffers For Embedded Iot: Integration in A Medical Device ProjectDocument32 pagesGoogle Protocol Buffers For Embedded Iot: Integration in A Medical Device ProjectNhân Nhậu NhẹtNo ratings yet
- JVM JRE JDK Program Exe FlowDocument6 pagesJVM JRE JDK Program Exe Flowshubham gajbhiyeNo ratings yet
- Test Driven Lasse Koskela Chapter 1: The Big Picture: Paul AmmannDocument14 pagesTest Driven Lasse Koskela Chapter 1: The Big Picture: Paul AmmannAminaHodžićNo ratings yet
- An Internal Error Has Occurred. (Code - 0x8003001D, Could Not Access File For Write Operation) - When Saving A Change in SmartConsoleDocument3 pagesAn Internal Error Has Occurred. (Code - 0x8003001D, Could Not Access File For Write Operation) - When Saving A Change in SmartConsolewedex56106No ratings yet
- Graphical Input DevicesDocument7 pagesGraphical Input Devices3dkeynit_11igoldNo ratings yet
- Shell Scripting Tutorial: How To Create Shell Script in Linux/UnixDocument6 pagesShell Scripting Tutorial: How To Create Shell Script in Linux/UnixFayum BirajdarNo ratings yet
- Clownfish Voice ChangerDocument6 pagesClownfish Voice Changerkeoka1623No ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument54 pagesProject Report138 GowriNo ratings yet
- CC2530ZDK Sensor Demo Users GuideDocument18 pagesCC2530ZDK Sensor Demo Users GuideJeff LuoNo ratings yet
- Galinina Et Al. - 2015 - 5G multi-RAT LTE-WiFi Ultra-Dense Small Cells Performance Dynamics, Architecture, and TrendsDocument17 pagesGalinina Et Al. - 2015 - 5G multi-RAT LTE-WiFi Ultra-Dense Small Cells Performance Dynamics, Architecture, and Trendskabi6713No ratings yet
- Lab 10 SolutionDocument4 pagesLab 10 SolutionJyz1No ratings yet
- JetsonTX1 Developer Kit Carrier Board SpecDocument32 pagesJetsonTX1 Developer Kit Carrier Board SpecShivram TabibuNo ratings yet
- ThinkPad E580 20KS003NCADocument3 pagesThinkPad E580 20KS003NCAdmembrenoNo ratings yet