Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adrenal Gland
Uploaded by
Aurelia AlexandraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adrenal Gland
Uploaded by
Aurelia AlexandraCopyright:
Available Formats
01 PHYSIOLOGY
41. Adrenal gland
Questions on the adrenal gland should be relatively straightforward, but you will need a good understanding of
the different endocrine feedback mechanisms that exist. Endocrine-based questions can also easily lead into
clinical issues of under/overactive glands, so for this section we would recommend you familiarise yourself with
hyperaldosteronism (primary and secondary), Addison’s disease, Cushing’s syndrome and phaeochromocytomas.
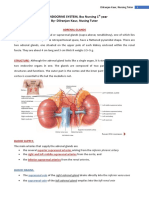
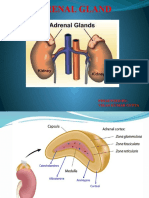
Describe the anatomical The adrenal or suprarenal glands lie on top of the upper poles of the kidneys
organisation of the adrenal and play a key role in the synthesis of corticosteroids and catecholamines.
gland. The adrenal glands are at the level of the twelfth thoracic vertebra.
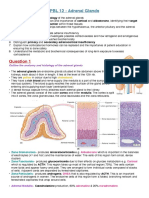
Anatomically, the adrenal gland is divided into two distinct areas: an outer
cortex and inner medulla.
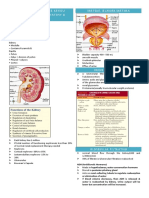
Adrenal cortex:
> Site of synthesis of corticosteroid hormones (glucocorticoids and
mineralocorticoids) and androgens.
> Under neuroendocrine control via the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal
axis.
> Part of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone pathway.
> Divided into three functional zones from outside to inside: zona
glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis (an easy way to
remember this is ‘GFR’).
Adrenal medulla:
> Composed of chromaffin cells.
> Main site of synthesis of adrenaline and noradrenaline.
> Hormone secretion occurs in response to stimulation by pre-ganglionic
(cholinergic) nerve fibres from the sympathetic nervous system (via
splanchnic nerves).
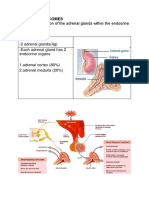
What are the main hormones > Zona glomerulosa: mineralocorticoids (aldosterone).
secreted from each of the three > Zona fasciculata: glucocorticoids (cortisol).
zones of the adrenal cortex?
> Zona reticularis: androgens (dehydroepiandrosterone).
Describe the cortisol negative The hypothalamus secretes corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH), which
feedback pathway. stimulates release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from the anterior
pituitary. ACTH stimulates cortisol secretion from the zona fasciculata of the
adrenal cortex. Cortisol exerts negative feedback on both CRH and ACTH
release.
122
9781785230981_text.indb 122 24/02/16 9:36 pm
ADRENAL GLAND
Describe the control of > Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone (RAA) system: Reduced circulating
aldosterone secretion. volume is detected by the reduction in renal afferent arteriolar pressure
causing renin secretion from the juxtaglomerular cells. Renin cleaves
angiotensinogen to produce angiotensin I, which is then converted to
angiotensin II in the pulmonary vasculature by angiotensin-converting
enzyme (ACE). Angiotensin II promotes aldosterone secretion.
> Fall in plasma sodium concentration: Reduced serum sodium is
detected by the macula densa in the distal convoluted tubule of the
kidney and stimulates the secretion of aldosterone in order to increase
sodium retention.
> Rise in plasma ACTH: Also exerts a direct effect in increasing
aldosterone secretion from the zona glomerulosa.
What are major actions of Cortisol exerts its effects by binding to glucocorticoid receptors and
cortisol? promoting specific enzyme synthesis. The glucocorticoids works in many
ways to provide resistance to 'stress', having effects on metabolism,
immune function and vascular reactivity.
> Metabolism:
• Increased protein catabolism
• Increased hepatic gluconeogenesis and increased plasma glucose
levels
• Increased lipolysis
> Vascular:
• Cortisol is essential in maintaining vascular reactivity to noradrenaline.
> Immune:
• Suppresses the immune system, impairs wound healing and has anti-
inflammatory effects.
What are the main actions of Aldosterone increases the reabsorption of sodium from the distal convoluted
aldosterone? tubules of the kidney, resulting in sodium retention and plasma expansion. It
also increases urinary potassium excretion.
Describe how catecholamines Catecholamines are synthesised in the chromaffin cells of the adrenal
are synthesised. medulla:
L-TYROSINE
↓ Tyrosine hydroxylase
L-DOPA
↓ Dopa decarboxylase
DOPAMINE
↓ Dopamine hydroxylase
NORADRENALINE
↓ Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase
ADRENALINE
123
9781785230981_text.indb 123 24/02/16 9:36 pm
You might also like
- Adrenal Gland: Dr. Fatimah Eliana, SPPD, KemdDocument46 pagesAdrenal Gland: Dr. Fatimah Eliana, SPPD, KemdZahra AstriantaniNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-04-26 at 12.52.44 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2023-04-26 at 12.52.44 PMRenadNo ratings yet
- Adrenocortical Hormones: Learning ObjectivesDocument3 pagesAdrenocortical Hormones: Learning ObjectivesMarlin Berliannanda TawayNo ratings yet
- Endo Adrenal ElhDocument26 pagesEndo Adrenal Elhodiodi57No ratings yet
- Adrnl StressDocument43 pagesAdrnl StressPraveen ChowdharyNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Cortex DR - GomezDocument13 pagesAdrenal Cortex DR - Gomezvicbart11No ratings yet
- Adrenal Cortex Disorders NotesDocument3 pagesAdrenal Cortex Disorders NotesGwendareign ElizanNo ratings yet
- ADRENALSDocument60 pagesADRENALSJyoti ChadhaNo ratings yet
- LO Tutuor 13 Sken 3 Blok4Document33 pagesLO Tutuor 13 Sken 3 Blok4Nadiaa RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland DisordersDocument3 pagesAdrenal Gland DisordersJem Fabico Dee-AhrNo ratings yet
- Adrenal GlandDocument36 pagesAdrenal Glandpranutan739No ratings yet
- Endocrine System Part 3Document55 pagesEndocrine System Part 3Cristina RocheNo ratings yet
- Week 11. Endocrinology 3Document17 pagesWeek 11. Endocrinology 3MACOB, ETHELHYN JHANENo ratings yet
- Endo 3 Notes PDFDocument9 pagesEndo 3 Notes PDFDilNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Glands Clinical Chemistry (Laboratory) : Lesson 7Document5 pagesAdrenal Glands Clinical Chemistry (Laboratory) : Lesson 7Cherry Ann ColechaNo ratings yet
- Urinary System: Quick Review Review of Urinary Anatomy & Physiology Ureters, Bladder, UrethraDocument6 pagesUrinary System: Quick Review Review of Urinary Anatomy & Physiology Ureters, Bladder, UrethraLongyapon Sheena StephanieNo ratings yet
- Chem+Path +adrenal+2021 H+VreedeDocument39 pagesChem+Path +adrenal+2021 H+VreedeKamogelo AlbertNo ratings yet
- PBL 12 - Adrenal GlandsDocument7 pagesPBL 12 - Adrenal GlandsKrishna OochitNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland: Presented By:-Vikas Kumar GuptaDocument17 pagesAdrenal Gland: Presented By:-Vikas Kumar GuptaPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Adrenal GlandDocument49 pagesAdrenal GlandRaphael AnajeNo ratings yet
- Adrenocortical HormonesDocument46 pagesAdrenocortical HormoneschayChay gapolNo ratings yet
- (MS II Lec) Endocrine System2Document8 pages(MS II Lec) Endocrine System2IlawNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: THE Adrenal GlandsDocument50 pagesEndocrine System: THE Adrenal GlandsAbdel Aziz NazihNo ratings yet
- (GROUP 01) Med Chem REPORTING: ANS, CNS, AUTACOIDS - PKZBDocument301 pages(GROUP 01) Med Chem REPORTING: ANS, CNS, AUTACOIDS - PKZBPrincess Krenzelle BañagaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Smijal PG Its Year Department of PeriodonticsDocument98 pagesDr. Smijal PG Its Year Department of PeriodonticsMax FaxNo ratings yet
- Effects Adrenal Hormones RegebDocument7 pagesEffects Adrenal Hormones RegebPraveena MoganNo ratings yet
- Adrenaline & Noradrenaline: DR Nida Fatima Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Amu AligarhDocument46 pagesAdrenaline & Noradrenaline: DR Nida Fatima Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Amu AligarhDivya Rekha KolliNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument54 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemEzio SartoraNo ratings yet
- Cholinoceptor - Activating (Cholinergic Agonist) and Cholinesterase - Inhibiting DrugsDocument53 pagesCholinoceptor - Activating (Cholinergic Agonist) and Cholinesterase - Inhibiting DrugsDan FabrosNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Metabolism: Adrenal GlandsDocument2 pagesEndocrine Metabolism: Adrenal GlandsEcaterina Borovic-PavlovschiNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of The Adrenal GlandDocument9 pagesFunctional Anatomy of The Adrenal GlandPaula SchaeferNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Cortex HormonesDocument21 pagesAdrenal Cortex HormonesAaa JjjjNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland Final 2Document8 pagesAdrenal Gland Final 2Std DlshsiNo ratings yet
- 17 Adrenal GlandDocument33 pages17 Adrenal GlandPande Indra PremanaNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland: Structure, Hormones and Clinical Disorders-: Professor Dr. Najat A. HasanDocument18 pagesAdrenal Gland: Structure, Hormones and Clinical Disorders-: Professor Dr. Najat A. HasanDrFarah Emad Ali100% (1)
- Adrenal Gland by DR Rajnee Ist PartDocument29 pagesAdrenal Gland by DR Rajnee Ist Part9460106212No ratings yet
- Dr. Dwi Indria Anggraini, MSC., Spkk. Faculty of Medicine Lampung UniversityDocument36 pagesDr. Dwi Indria Anggraini, MSC., Spkk. Faculty of Medicine Lampung UniversityAnfasha_26No ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland: by M. Jyotirmayee Sister Tutor, N.T.IDocument23 pagesAdrenal Gland: by M. Jyotirmayee Sister Tutor, N.T.IlindaNo ratings yet
- Mineralocorticoid - AldosteoneDocument17 pagesMineralocorticoid - AldosteoneExplore Life ScienceNo ratings yet
- 8 Hormones of Adrenal GlandDocument27 pages8 Hormones of Adrenal GlandRana AbdullahNo ratings yet
- B.SC - Hons. Biotechnology 4th Sem Dr. Arvind ShuklaDocument7 pagesB.SC - Hons. Biotechnology 4th Sem Dr. Arvind Shuklamain.manishapatelNo ratings yet
- UW Notes - 8 - Endocrine ArrangeddDocument40 pagesUW Notes - 8 - Endocrine Arrangeddmind blocNo ratings yet
- 2021 COMET Krisis Adrenal (Compatibility Mode) (1) - Pages-1-27Document27 pages2021 COMET Krisis Adrenal (Compatibility Mode) (1) - Pages-1-27Octo IndradjajaNo ratings yet
- Omar THE ADRENAL GLANdDocument4 pagesOmar THE ADRENAL GLANdRenien Khim BahayaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15 - Adrenal Gland BNS KUMDocument17 pagesLecture 15 - Adrenal Gland BNS KUMabdulsaboor30No ratings yet
- Chap3 The Adrenal GlandDocument20 pagesChap3 The Adrenal GlandSharon GabrielNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland - DR CokerDocument59 pagesAdrenal Gland - DR CokerIshaqNo ratings yet
- Insufisiensi Adrenal (Dr. Makbul)Document52 pagesInsufisiensi Adrenal (Dr. Makbul)Rahmat AzimiNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Glands DiseasesDocument17 pagesAdrenal Glands DiseasesDr-Dalya ShakirNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Adrenal GlandDocument26 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Adrenal GlandYAMINIPRIYANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 79. Adrenal GlandsDocument42 pagesChapter 79. Adrenal GlandsJeremy IrvanNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Glands 2018 - 2019Document32 pagesAdrenal Glands 2018 - 2019Bianca BiaNo ratings yet
- 19 SYNTHESIS OF ADRENALINEADRENERGIC RECEPTORS by COL AZMAT ALIDocument53 pages19 SYNTHESIS OF ADRENALINEADRENERGIC RECEPTORS by COL AZMAT ALIAhmed YTNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument8 pagesAdrenal Gland: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadujana rastanawiNo ratings yet
- Summary & Mcqs of Adrenal Gland: Done byDocument7 pagesSummary & Mcqs of Adrenal Gland: Done byHabib Ullah100% (1)
- CUSHINGSDocument205 pagesCUSHINGSDaroo D.TNo ratings yet
- 5adrenal GlandDocument6 pages5adrenal GlandZiedTrikiNo ratings yet
- Adrenal & KortisolDocument47 pagesAdrenal & KortisolPrisca AngelinaNo ratings yet
- Anti Fribrinolitic DrugsDocument15 pagesAnti Fribrinolitic DrugsAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Pulse OximetryDocument3 pagesPulse OximetryAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- ADâncimea de Anestezie MOnITORINGDocument3 pagesADâncimea de Anestezie MOnITORINGAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- The Primary FRCA Structured Oral Examination: Study Guide 1Document13 pagesThe Primary FRCA Structured Oral Examination: Study Guide 1Aurelia Alexandra0% (1)
- Ultrasound Și DopplerDocument3 pagesUltrasound Și DopplerAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Airway Management - Supraglottic Airway PDFDocument4 pagesAirway Management - Supraglottic Airway PDFPiet Pogen PoelNo ratings yet
- Hypotermia and HipertermiaDocument9 pagesHypotermia and HipertermiaAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- 22 The Application of Farmacodynamics in The Optimization of Antibiotic Therapy PDFDocument2 pages22 The Application of Farmacodynamics in The Optimization of Antibiotic Therapy PDFAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- CT Și RMNDocument3 pagesCT Și RMNAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Monitori de DiscnecțieDocument2 pagesMonitori de DiscnecțieAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Vaporisers: Classify The Types of Vaporiser in UseDocument7 pagesVaporisers: Classify The Types of Vaporiser in UseAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Poluare Și ScavengingDocument3 pagesPoluare Și ScavengingAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Sisteme de BreathingDocument5 pagesSisteme de BreathingAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Cursuri de Revisitare Și ValveDocument4 pagesCursuri de Revisitare Și ValveAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- venTILATORIDocument3 pagesvenTILATORIAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Blockade MonitoringDocument7 pagesNeuromuscular Blockade MonitoringAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Presiune de Sânge MeasurementDocument3 pagesPresiune de Sânge MeasurementAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Temperature MeasurementDocument4 pagesTemperature MeasurementAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Oxygen MeasurementDocument4 pagesOxygen MeasurementAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Presiune Arterială WaveformDocument3 pagesPresiune Arterială WaveformAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Lasers: What Do You Understand by The Term Laser'?Document3 pagesLasers: What Do You Understand by The Term Laser'?Aurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- PH MeasurementDocument2 pagesPH MeasurementAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Featuri de Siguranță A Machinelor AnesteziceDocument3 pagesFeaturi de Siguranță A Machinelor AnesteziceAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- SIGURANȚĂ eLeCTRICĂDocument3 pagesSIGURANȚĂ eLeCTRICĂAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Adaptarea Gazelor MediceDocument4 pagesAdaptarea Gazelor MediceAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- States of Matter, Heat Capacity and Latent Heat: PhysicsDocument7 pagesStates of Matter, Heat Capacity and Latent Heat: PhysicsAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Utput MonitoringDocument7 pagesCardiac Utput MonitoringAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide MeasurementDocument2 pagesCarbon Dioxide MeasurementAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- ReFLexeSDocument2 pagesReFLexeSAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- COMPONENTE eLeCTRICEDocument3 pagesCOMPONENTE eLeCTRICEAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- The Role of Emotions in Marketing: Richard P. BagozziDocument23 pagesThe Role of Emotions in Marketing: Richard P. BagozziEngin OzsahinNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and Heredity NotesDocument63 pagesReproduction and Heredity NotesmceldowneaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 OPERANT LEARNING FinalDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 5 OPERANT LEARNING FinalWeyvin Maury Onde100% (1)
- DAVIS MedSurg Notes Nurse S Clinical Pocket Guide FA Davis 2007Document242 pagesDAVIS MedSurg Notes Nurse S Clinical Pocket Guide FA Davis 2007amaliea234100% (1)
- ACS Parotidectomy PDFDocument10 pagesACS Parotidectomy PDFadel santosNo ratings yet
- Master Techniques in Orthopaedic Surgery Soft Tissue SurgeryDocument944 pagesMaster Techniques in Orthopaedic Surgery Soft Tissue SurgeryAbotaleb Mohd100% (15)
- Dna StructureDocument23 pagesDna Structureapi-315792432No ratings yet
- P.E Training Program NotesDocument4 pagesP.E Training Program Notesjohn smithNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology: Chapter 3 .3 HomeostasisDocument12 pagesForm 5 Biology: Chapter 3 .3 HomeostasisZifan NafriNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Smell and Taste-MyDocument46 pagesPhysiology of Smell and Taste-MyHamid Hussain HamidNo ratings yet
- Clinical - Bilirubin TestDocument9 pagesClinical - Bilirubin Testbarbie.monster89100% (3)
- F&E ExamDocument3 pagesF&E ExamDino PringNo ratings yet
- J. Nutr.-1963-Consolazio-407-15Document9 pagesJ. Nutr.-1963-Consolazio-407-15azuredreamNo ratings yet
- PT - SCIENCE 6 - Q2 - FinalDocument5 pagesPT - SCIENCE 6 - Q2 - FinalIrine BrionesNo ratings yet
- Common Sense Cardio Training by Nick Mitchell - UP FitnessDocument13 pagesCommon Sense Cardio Training by Nick Mitchell - UP FitnessSean DrewNo ratings yet
- Fluids Foods Did You Urinate?: Bladder DiaryDocument1 pageFluids Foods Did You Urinate?: Bladder DiaryAnika TasnimNo ratings yet
- By: Abduljabbar Hamid Jabbar: University of Baghdad-College of Medicine M. B. Ch. BDocument14 pagesBy: Abduljabbar Hamid Jabbar: University of Baghdad-College of Medicine M. B. Ch. BXena XenaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Heston Standing Orders LandscapeDocument3 pagesDr. Heston Standing Orders LandscapeJosh Heston100% (1)
- Ectopia Lentis PDFDocument7 pagesEctopia Lentis PDFBeerappaJanpetNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Quarter 4 Module 2 Week 2 Cell Division Let's UnderstandDocument4 pagesScience 8 Quarter 4 Module 2 Week 2 Cell Division Let's Understandabadloraine0331No ratings yet
- Aferisis Transfuncional Teromuco BCTDocument310 pagesAferisis Transfuncional Teromuco BCTNorma RamosNo ratings yet
- Crossword BLANKDocument2 pagesCrossword BLANKJessamie Pigte AbsueloNo ratings yet
- Wear It Right (3M)Document2 pagesWear It Right (3M)wfng77No ratings yet
- UG022524 International GCSE in Human Biology 4HB0 For PrintDocument42 pagesUG022524 International GCSE in Human Biology 4HB0 For PrintHosni ShowikeNo ratings yet
- Mak 008 BulDocument4 pagesMak 008 BulAngga Witra NandaNo ratings yet
- Catalase TestDocument29 pagesCatalase TestmaleehaNo ratings yet
- Thirty Day CleanseDocument2 pagesThirty Day CleanseChelaru AlinaNo ratings yet
- Waec 2021 Biology Practical: BOTH HAVE: I. Large Neural Canal Ii. Transverse Process Iii. Neural SpinesDocument8 pagesWaec 2021 Biology Practical: BOTH HAVE: I. Large Neural Canal Ii. Transverse Process Iii. Neural SpinesJacob Spiritual100% (2)
- ProbDocument5 pagesProbMa Christina Miravalles SergioNo ratings yet
- Transitional EpitheliumDocument7 pagesTransitional EpitheliumsakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet