Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Usually Introduced Say or Tell: Optional
Usually Introduced Say or Tell: Optional
Uploaded by
Thư LêOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Usually Introduced Say or Tell: Optional
Usually Introduced Say or Tell: Optional
Uploaded by
Thư LêCopyright:
Available Formats
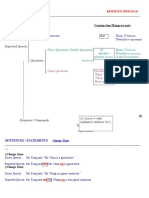
Usually introduced by SAY or TELL
THAT is optional.
Personal pronouns and possessive adjectives changed according to context
Adverbials (of place and time) changed according to context
– Verb forms changed
• This => that
• These => those
Certain words
tonight, today, this that night, that day, that week/month/year week/month/year now
then, at that time, at
once, immediately now that
since yesterday, last night/ the day before, the week/month/year previous night/week/
month/year tomorrow, next week/ the following day/the month/year
day after, the following/
next week/month/year two days/months/years two days/months/years ago
before
• Here => there
• Come => go
Adverbials of time
Past Perfect and Past Perfect Progressive: no change
Reported statements
Past Simple: changed to Past Perfect or remaining the same
Verb forms in time clauses remaining the same
If the reported sentence is out of date, the verb form changes.
If the reported sentence is up to date, the verb form doesn't change. (still true at the
moment of speaking/ writing)
Verb forms in Reported Speech
Reporting verb is in present or future
A style used to report what a speaker actually said
- Definition
Reported Speech
Types
The speaker expresses general truths, permanent states or conditions
• Words changed
• No quotation marks
The reported sentence deals with conditionals type 2 and 3, wishes or unreal past
Verb Forms Not Changing
The speaker is reporting something right after it is said (up to date)
If the speaker reports something which is believed to be untrue, the verb forms
change.
Introduced with ASK, WONDER, INQUIRE, etc.
Statement word order
Reported questions
Wh-questions: ask + wh-word
Yes/No questions: ask + if/whether
To report orders, requests, warnings, advice, and invitations
Used with infinitives or -Ings
• can => could
• may => might
• must => had to-Inf, was/were to-Inf
Reported commands/requests/suggestions
• mustn't => mustn't, was/were not to-Inf, shouldn't
Modals change
• must have p.p. => must have p.p.
• needn't => had to-Inf, didn't have to-Inf, wouldn't have to-Inf
• will => would
A dependent clause which functions as a noun or noun phrase
Definition
Beginning with THAT, a question word, or IF/ WHETHER
Used with embedded Yes/No questions
IF is preferred when the noun clause is the object of the verb.
that-clauses
Derived from statements
Types of nominal clauses
*Talking about choices or alternatives
wh-clauses
Derived from questions
Noun clause as subject
NOUN CLAUSES
Sequence of Tenses
The verb tense in the independent clause determines the verb tense
in the dependent noun clause
After BE (noun clause as subject complement)
WHETHER and IF
After a preposition
Noun clauses as object
After a noun
WHETHER is used in other positions
agree
assume
believe
advise
ask
assure
bet
ask
feel
consider
find
know
convince
inform
Before a to-Infinitive
persuade
notify
remind
mean
point out
realize
say
promise
reassure
show
Immediately before OR NOT
show
see
suggest
teach
write
suppose
tell
warn
Noun clauses after PREPOSITIONS
suspect
think
understand wonder
admit
announce
complain
declare
In different structures
explain
indicate
mention
point out
propose recommend
remark
report
say
suggest
write
You might also like
- TOEFL Grammar Guide (Advanced) - 15 Advanced Grammar Rules You Must Know To Achieve A 100+ Score On The TOEFL Exam!From EverandTOEFL Grammar Guide (Advanced) - 15 Advanced Grammar Rules You Must Know To Achieve A 100+ Score On The TOEFL Exam!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- B1 Irregular Verbs T033: Fill in The Missing Forms of The Irregular VerbsDocument2 pagesB1 Irregular Verbs T033: Fill in The Missing Forms of The Irregular VerbsAyesha50% (2)
- Comparison (FCE Infographics)Document4 pagesComparison (FCE Infographics)Gemma HSNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeechPetra BajacNo ratings yet
- Direct & Indirect SpeechDocument18 pagesDirect & Indirect Speechadindanur302No ratings yet
- Presentation 24Document14 pagesPresentation 24Thurein Lin ThantNo ratings yet
- Class 8B Reported Speech-Jan11,2023Document7 pagesClass 8B Reported Speech-Jan11,2023Dhruv RawatNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech PDFDocument14 pagesReported Speech PDFMarcoOn75hzNo ratings yet
- English 111 ReviewerDocument7 pagesEnglish 111 ReviewerCharles IldefonsoNo ratings yet
- VERB TENSES - WILL X GOING TO - GERUND X INFINITIVE - MODAL VERBSDocument5 pagesVERB TENSES - WILL X GOING TO - GERUND X INFINITIVE - MODAL VERBSMike NunesNo ratings yet
- Eight Parts of SpeechDocument173 pagesEight Parts of SpeechJan Kenrick SagumNo ratings yet
- Indirect Speech PrezentacijaDocument13 pagesIndirect Speech PrezentacijaVilaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Reported SpeechDocument12 pagesUnit 1 Reported SpeechMarina Bagan MoltoNo ratings yet
- CEF LevelsDocument2 pagesCEF LevelsAmy LéaNo ratings yet
- SC Revise1Document6 pagesSC Revise1tanmoyr2001No ratings yet
- Grammar Points For Each CEF LevelDocument2 pagesGrammar Points For Each CEF LevelBotella DeaguaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Table of Contents in EnglishDocument4 pagesGrammar Table of Contents in EnglishNani KishoreNo ratings yet
- Guía de Estudio InglésDocument8 pagesGuía de Estudio Ingléspauc27mNo ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument10 pagesPresent Continuousluz elaine gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Types Conjunctionthings To NoteDocument9 pagesTypes Conjunctionthings To NoteZone ZeeNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument9 pagesReported SpeechlexnxrreisNo ratings yet
- The Reported SpeechDocument9 pagesThe Reported Speechapi-19975062No ratings yet
- Grammar Study:: Reported SpeechDocument10 pagesGrammar Study:: Reported SpeechLeticia González ChimenoNo ratings yet
- All TensesDocument74 pagesAll TensesimamNo ratings yet
- Exploring Inversion and FrontingDocument32 pagesExploring Inversion and FrontingTrần Thái Đình KhươngNo ratings yet
- Direct SpeechDocument15 pagesDirect SpeechMuhammad DaniyalNo ratings yet
- Sentences: Subject, Predicates, Modifiers, and ObjectsDocument18 pagesSentences: Subject, Predicates, Modifiers, and ObjectsGabriela SiandaNo ratings yet
- Booklet B2Document8 pagesBooklet B2ninacalle0782No ratings yet
- Reported Speech: A Short GuideDocument10 pagesReported Speech: A Short GuideShreya ANo ratings yet
- Grammar Per Level: BASIC I (Fundamentals)Document6 pagesGrammar Per Level: BASIC I (Fundamentals)Mario GomezNo ratings yet
- Narration RulesDocument2 pagesNarration RulesRajesh Kumar Duggal69% (26)
- Reported Statements & QuestionsDocument10 pagesReported Statements & QuestionsSofia SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Full)Document6 pagesReported Speech (Full)kaustubhchoudhary2005No ratings yet
- Inversion and FrontingDocument50 pagesInversion and FrontingPilar Sánchez LozanoNo ratings yet
- CEFR Grammar LevelsDocument4 pagesCEFR Grammar LevelsnuongtranNo ratings yet
- Grammar MattersDocument18 pagesGrammar MattersNatalia SantosNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument9 pagesReported SpeechRahamath razhul Faculty of AHSNo ratings yet
- Tommy BoyDocument8 pagesTommy BoyawaiskhattakNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: Theory With ExamplesDocument5 pagesReported Speech: Theory With ExamplesMacarena GalvariniNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech RulesDocument4 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech RulesEisha SabilaNo ratings yet
- Direct To Indirect SpeechDocument3 pagesDirect To Indirect SpeechNeenaNo ratings yet
- Phrases: Andi Darmawan 4114110020Document22 pagesPhrases: Andi Darmawan 4114110020Zulfida Fahmi AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: Grammar FocusDocument2 pagesReported Speech: Grammar FocusViktorija AtanasovskaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeechisiturmomNo ratings yet
- Reported - Speech PERT 6-7Document12 pagesReported - Speech PERT 6-7HRD RSIA ZAINABNo ratings yet
- Quoted and Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesQuoted and Reported SpeechPRECIOUS KAYE MARIE BANTIGUENo ratings yet
- Pearson Readers Grammar Contents WebDocument1 pagePearson Readers Grammar Contents WebPrzemysław KapuścińskiNo ratings yet
- Pearson Readers Grammar Contents WebDocument1 pagePearson Readers Grammar Contents WebGinanaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech and Phrasal VerbsDocument11 pagesReported Speech and Phrasal VerbsTarik AattaNo ratings yet
- Ingles Instrumental IV - Clase 6Document46 pagesIngles Instrumental IV - Clase 6Nicolás LaraNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech PDFDocument10 pagesReported Speech PDFTiago SousaNo ratings yet
- 5 Syntactic StructuresDocument16 pages5 Syntactic StructuresVldz MrlyNo ratings yet
- Noun Clauses/Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) : Quoted Speech Later ReportingDocument3 pagesNoun Clauses/Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) : Quoted Speech Later ReportingTuyen TonyNo ratings yet
- SC Cheat SheetDocument1 pageSC Cheat SheetSaurabh JainNo ratings yet
- Weekdays Touchstone: Level Cycle Unit 1Document36 pagesWeekdays Touchstone: Level Cycle Unit 1Erika JohanaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument16 pagesReported SpeechLarbi NadiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1, 6 Lessons - EnglishDocument5 pagesChapter 1, 6 Lessons - EnglishTannieNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechNiranjan SNo ratings yet
- Grammar Study:: Reported SpeechDocument10 pagesGrammar Study:: Reported SpeechEsteban VélihNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech EditedDocument4 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech EditedAri ZahNo ratings yet
- Clause TypesDocument2 pagesClause TypesPham Ngoc Phuoc AnNo ratings yet
- De Thi Hoc Ki 1 Tieng Anh 10 Ilearn Smart World de So 1 1668067080Document11 pagesDe Thi Hoc Ki 1 Tieng Anh 10 Ilearn Smart World de So 1 1668067080Thư LêNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Listening (10 phút - 4 điểm) …… Question 1 Nghe và viết số. (1 điểm)Document5 pagesPart 1 Listening (10 phút - 4 điểm) …… Question 1 Nghe và viết số. (1 điểm)Thư LêNo ratings yet
- De Thi Hoc Ki 1 Tieng Anh 10 Ilearn Smart World de So 1 1668067080Document11 pagesDe Thi Hoc Ki 1 Tieng Anh 10 Ilearn Smart World de So 1 1668067080Thư LêNo ratings yet
- ReadingDocument15 pagesReadingThư LêNo ratings yet
- CYLET Flyers Unit 9 A Good Year! (Continued) Reading & WritingDocument22 pagesCYLET Flyers Unit 9 A Good Year! (Continued) Reading & WritingThư LêNo ratings yet
- Use of ModalsDocument5 pagesUse of ModalsThư LêNo ratings yet
- Grammar Review Test 4: AnswersDocument5 pagesGrammar Review Test 4: AnswersThư LêNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Unit10Document18 pagesGrade 5 Unit10Thư LêNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 StarterDocument12 pagesGrade 5 StarterThư LêNo ratings yet
- Countable and Uncountable NounsDocument13 pagesCountable and Uncountable NounsAndresinho SievchenkoNo ratings yet
- Grammar - File12 C ROMERO VIDALDocument3 pagesGrammar - File12 C ROMERO VIDALYuy Oré Pianto50% (2)
- Practice Sheet 8.1 Memorizing The Pael Aphel Ethpeel and Ethpaal Perfect - Ok PDFDocument4 pagesPractice Sheet 8.1 Memorizing The Pael Aphel Ethpeel and Ethpaal Perfect - Ok PDFCibbbsNo ratings yet
- Aswika Pestiana Translation 2Document9 pagesAswika Pestiana Translation 2Imam ShofwaNo ratings yet
- EJ1216998Document8 pagesEJ1216998Suhaib FadelNo ratings yet
- GERUNDDocument14 pagesGERUNDDwiprasastiNo ratings yet
- Prefix Dan SuffixDocument10 pagesPrefix Dan SuffixEdy YantoNo ratings yet
- Telegram Channel Telegram GroupDocument188 pagesTelegram Channel Telegram GroupSapna RaiNo ratings yet
- Here You Will Get Following Materials:-: All Study Materials in Free of CostDocument12 pagesHere You Will Get Following Materials:-: All Study Materials in Free of Costvvs .b.s1453No ratings yet
- P5eng04 2Document32 pagesP5eng04 2C LMNo ratings yet
- Week 4-English 4Document71 pagesWeek 4-English 4Fatima ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Contents Serbo-Croatian GrammarDocument2 pagesContents Serbo-Croatian GrammarLeo VasilaNo ratings yet
- When To Use ApostrophesDocument4 pagesWhen To Use ApostrophesAlberto CarranzaNo ratings yet
- Linkers and Connectors InglesDocument5 pagesLinkers and Connectors InglesjumencruNo ratings yet
- Тема 1. Systemic character of language 1.1. The notion of grammarDocument12 pagesТема 1. Systemic character of language 1.1. The notion of grammarВалерия БеркутNo ratings yet
- Present Simple and Continuous Future MeaningDocument14 pagesPresent Simple and Continuous Future MeaningRaluca MorariuNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Past Continuous: The Past Continuous Means That at A Time in The Past We Were in The Middle of An ActionDocument2 pagesPast Simple Past Continuous: The Past Continuous Means That at A Time in The Past We Were in The Middle of An ActionКсения Скрыль100% (1)
- First Certificate in English: Examination Report Syllabuses 0100 and 0102 JUNE 2000Document31 pagesFirst Certificate in English: Examination Report Syllabuses 0100 and 0102 JUNE 2000Curtis GautschiNo ratings yet
- TN 15 Little Ducks WalkDocument2 pagesTN 15 Little Ducks Walkmarz sidNo ratings yet
- Mimi Kara Oboeru N3-ChoukaiDocument169 pagesMimi Kara Oboeru N3-Choukainguyen minh duc100% (1)
- 10 Put The Words in The Correct Order To Make SentencesDocument3 pages10 Put The Words in The Correct Order To Make Sentenceskatherin guamanNo ratings yet
- 11 Writing Your First DraftDocument20 pages11 Writing Your First DraftAL ' ARISNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument12 pagesTensesRitaLucasNo ratings yet
- English Worksheet Part2Document2 pagesEnglish Worksheet Part2Deivi GaniNo ratings yet
- Interactive English Program PDFDocument2 pagesInteractive English Program PDFFaizaNo ratings yet
- Cefr Grammar Levels - 1425642569 PDFDocument6 pagesCefr Grammar Levels - 1425642569 PDFkhaledhnNo ratings yet
- Kingsland Intermediate (1) BookDocument123 pagesKingsland Intermediate (1) Bookcarlos mejiaNo ratings yet
- Act. 7: Final ExamDocument2 pagesAct. 7: Final ExamRaul Andres Portela Moreno86% (7)