Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Introduction To EE
Uploaded by
ganesanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3 Introduction To EE
Uploaded by
ganesanCopyright:
Available Formats
L T P C Hrs
U20EST102 INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
3 0 0 3 45
Course Objectives
To introduce fundamental concepts, various laws and principles associated with electrical circuits and its
analysis.
To provide knowledge about the various factors in AC circuits and resonance condition.
To establish the concepts of three-phase circuits and measuring instruments.
To describe the concept of electrical safety, power system and working of transformers.
To explain the concepts of generators, motors and their applications.
Course Outcomes
On successful completion of the course, students will be able to
CO1 - Interpret the basic concepts, various laws and theorems used in DC circuits.
CO2 - Analyze and solve the AC circuits and develop resonance circuits for transmitter and receiver circuits.
CO3 - Gain knowledge about the three phase circuits and its advantages and working principle of measuring
instruments.
CO4 - Diagnose the concept of power system, importance of electrical safety measures and application of
transformers.
CO5 - Inspect the concept of electromechanical energy conversion and its working principles of generators and
motors.
UNIT I D.C CIRCUIT ANALYSIS AND NETWORK THEOREMS (9 Hrs)
Circuit concepts: Concept of network, Active and passive elements, concept of linear network, unilateral and
bilateral elements, source transformation, ohm‟s law, Kirchhoff‟s current and voltage Law- Series and Parallel
Combination - loop and nodal methods of analysis, star-delta transformation
Network theorems: Superposition Theorem, Thevenin‟s theorem, Norton‟s theorem, maximum power transfer
theorem.
UNIT II STEADY STATE ANALYSIS OF AC CIRCUITS (9 Hrs)
AC fundamentals: Sinusoidal, square and triangular waveforms- Instantaneous, Peak, average and effective
value,formfactor and peak factors, Phasor diagram, phasors representation of sinusoidally varying voltage and
current, analysis of series-parallel RLC circuits. Apparent, active and reactive powers, Impedance diagram,
power triangle, power factor, causes and problems of low power factor, power factor improvement, Resonance
in series and parallel circuits, bandwidth and quality factors.
UNIT III THREE PHASE AC CIRCUITS AND MEASUREMENT INSTRUMENTS (9 Hrs)
Three phase system: Necessity and advantages, phase sequence, star and delta connections, balanced
supply and balanced/unbalanced load, line and phase voltage/current relation, three phase power
measurements-two wattmeter method .
Types of instruments: Construction and working principle of PMMC and MI type instruments, single phase
dynamometer type wattmeter and induction type energy meter, use of multipliers.
UNIT IV INTRODUCTION OF POWER SYSTEM (9 Hrs)
General layout of electrical power system and its functions, Safety measures in electrical system, insulators,
cables, fuse and circuit breakers.
Magnetic Circuit: Concepts, analogy between electric and magnetic circuit, magnetic circuits with DC and AC
excitation, magnetic leakage, BH curve, hysteresis and eddy current losses, mutual coupling-Single/Three
Phase Transformer- construction-Principle of operation, emf equation, load test, OC and SC test, equivalent
circuit, power losses, efficiency, Introduction to auto transformers- copper savings in autotransformers.
UNIT V DC AND AC MACHINES (9 Hrs)
DC Machines: Construction-Principle of operation of DC Motor /Generator-Types, Torque equation of motor
and Emf equation of generator, load test, Torque-Speed characteristics and applications of DC
motors/Generators.
AC Machines: Construction-Principle of operation of single /three phase induction Motors-types- slip-torque
Characteristics-applications-Principle of operation of alternator and synchronous motor, load test -applications.
Text Books
1. D P Kothari and I.J Nagarath, ”Electrical Machines “Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering”, McGraw
Hill Education(India) Private Limited, Third Reprint ,2016
2. Sudhakar.A and ShyamMohan.S.P, “Circuits and Networks Analysis and Synthesis”, Tata McGraw Hill
Publishing Company Ltd., New Delhi, 4th edition, 2010.
3. A.K. Sawhney, „A Course in Electrical & Electronic Measurements &Instrumentation‟ Dhanpat Rai and Co
2004.
4. V. K. Metha&RohitMetha,”Principles of Power System”, S.Chand, 2005
Reference Books
1. V.Deltoro, “Principle of Electrical Engg.” PHI.
2. M.A Mallick, Dr. I. Ashraf, “Fundamental of Electrical Engg,” Word Press, Lucknow.
3. A. Hussain, “Basic Electrical Engg” DhanpatRai& sons.
Web References
1. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vd2UJiIPbag
2. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GHrHRBMjno0
3. https://nptel.ac.in/courses/108/108/108108076/
4. https://nptel.ac.in/courses/108/105/108105112/
5. https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/video-lectures/
COs/POs/PSOs Mapping
Program Specific
Program Outcomes (POs)
COs Outcomes (PSOs)
PO1 PO2 PO3 PO4 PO5 PO6 PO7 PO8 PO9 PO10 PO11 PO12 PSO1 PSO2 PSO3
1 3 2 1 2 3 - - - - - - 3 3 3 2
2 3 3 2 1 3 - - - - - - 3 3 3 2
3 3 3 2 1 3 - - - - - - 3 3 3 2
4 3 3 2 1 3 - - - - - - 3 3 3 2
5 3 3 2 1 3 - - - - - - 3 3 3 2
You might also like
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- UNIT - I:Polyphase Induction Motor:: Electrical Machine-IIDocument10 pagesUNIT - I:Polyphase Induction Motor:: Electrical Machine-IIRam DinNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 1: Synthetic Methodology to Converters and Components TechnologyFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 1: Synthetic Methodology to Converters and Components TechnologyNo ratings yet
- CT SyllabusDocument2 pagesCT SyllabusramNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Electrical Power: Lecture Notes of Distribution of Electrical Power CourseFrom EverandDistribution of Electrical Power: Lecture Notes of Distribution of Electrical Power CourseNo ratings yet
- COURSE STRUCTURE AND SUBJECT DETAILS FOR SECOND YEAR B.TECH PROGRAMME IN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGYDocument45 pagesCOURSE STRUCTURE AND SUBJECT DETAILS FOR SECOND YEAR B.TECH PROGRAMME IN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGYSankarsan SahooNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseFrom EverandElectrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseNo ratings yet
- Analyze The Various Electrical NetworksDocument2 pagesAnalyze The Various Electrical Networksi sai ramNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics and Energy Conversion Systems, Fundamentals and Hard-switching ConvertersFrom EverandPower Electronics and Energy Conversion Systems, Fundamentals and Hard-switching ConvertersNo ratings yet
- VSSUT (EEE) SyllabusDocument47 pagesVSSUT (EEE) SyllabusAshutosh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Electrical Power: Lecture Notes of Distribution of Electric Power CourseFrom EverandDistribution of Electrical Power: Lecture Notes of Distribution of Electric Power CourseNo ratings yet
- AKU Patna Syllabus 3rd YearDocument20 pagesAKU Patna Syllabus 3rd Yearडाँ सूर्यदेव चौधरीNo ratings yet
- Relevant Characteristics of Power Lines Passing through Urban AreasFrom EverandRelevant Characteristics of Power Lines Passing through Urban AreasNo ratings yet
- Consolidated 4th Sem Scheme and Syllabus Updated0Document15 pagesConsolidated 4th Sem Scheme and Syllabus Updated0pranavrajrkmvNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electrical Engineering Lab (ECE)Document3 pagesPrinciples of Electrical Engineering Lab (ECE)jagadeeshNo ratings yet
- Course 2. Basic Electrical Technology (Video Course) Faculty Coordinator(s) : 1Document32 pagesCourse 2. Basic Electrical Technology (Video Course) Faculty Coordinator(s) : 1Ursap BuddyNo ratings yet
- EE Power Generation Systems DesignDocument32 pagesEE Power Generation Systems DesignPARTH DAVENo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Theory Lectures & LabsDocument2 pagesBasic Electrical Theory Lectures & LabsCSD04No ratings yet
- Bee IliyasDocument3 pagesBee Iliyassr2846877No ratings yet
- Syllabus BeeDocument2 pagesSyllabus BeeMahender NavapetaNo ratings yet
- 5th SEMDocument10 pages5th SEMChandra SekaranNo ratings yet
- EE1101Document2 pagesEE1101balajiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus VI-EEDocument6 pagesSyllabus VI-EERam DinNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines OBE, Clo Plo.Document4 pagesElectrical Machines OBE, Clo Plo.Awais KhanNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies - APDocument5 pagesRajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies - APNamagundla Ravines ReddyNo ratings yet
- Electrical SyllabusDocument2 pagesElectrical Syllabusharsh dubeyNo ratings yet
- Faculty Name: P.SELVAKUMAR Designation: LECTURER: Department: Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument27 pagesFaculty Name: P.SELVAKUMAR Designation: LECTURER: Department: Electrical and Electronics EngineeringSOWKATHKUTHBUDEEN_J14No ratings yet
- Final Year BTech Electronics Syllabus 2022-23Document48 pagesFinal Year BTech Electronics Syllabus 2022-23SiddhantNo ratings yet
- S5 SylabusDocument24 pagesS5 SylabuspaajiNo ratings yet
- B. Tech Electrical Engineering 5th Sem CurriculumDocument19 pagesB. Tech Electrical Engineering 5th Sem CurriculumBijayKumarDasNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines-II LabDocument43 pagesElectrical Machines-II Labmat labNo ratings yet
- 19ee306 - Basic Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation EngineeringDocument6 pages19ee306 - Basic Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation EngineeringhariNo ratings yet
- Ece 131 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering SyllabusDocument2 pagesEce 131 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Syllabustukutanigel423No ratings yet
- EE Curriculum & Evaluation SchemeDocument35 pagesEE Curriculum & Evaluation Schemerudraee41No ratings yet
- T2F50C1 Type of Course: Core: Teaching Scheme (L-T-P: 3-0-2) Credits 04 Marks: 150 Theory: 100 Practical: 50Document6 pagesT2F50C1 Type of Course: Core: Teaching Scheme (L-T-P: 3-0-2) Credits 04 Marks: 150 Theory: 100 Practical: 50sunilNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Analysis of Electrical MachinesDocument3 pagesModeling and Analysis of Electrical MachinesPrabhu MoorthyNo ratings yet
- Fo - QR Fohkkx: V.Meku RFKK Fudksckj Iz'Kklu Vèkh (KD VFHK Ark DK DK Kzy Iksvz Cys J & 744 101Document7 pagesFo - QR Fohkkx: V.Meku RFKK Fudksckj Iz'Kklu Vèkh (KD VFHK Ark DK DK Kzy Iksvz Cys J & 744 101Ranjit RajendranNo ratings yet
- Department: Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Subject Name CodeDocument27 pagesDepartment: Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Subject Name CodeBala SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods and AC MachinesDocument8 pagesNumerical Methods and AC MachinesVIGNESH L RNo ratings yet
- M tech-PEDDocument27 pagesM tech-PEDvvps777No ratings yet
- EEE1001 Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument2 pagesEEE1001 Basic Electrical EngineeringboomaNo ratings yet
- Be EeeDocument38 pagesBe EeeGopinathblNo ratings yet
- PedDocument32 pagesPedPartha SarathyNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUSDocument2 pagesSYLLABUSNithin KumarNo ratings yet
- EeeDocument268 pagesEeeNajiruddin ShaikNo ratings yet
- EeeDocument391 pagesEeeGhulam AbbasNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument119 pagesBasic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringNlrNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Basic Electrical 2018-19Document2 pagesSyllabus For Basic Electrical 2018-19iamrichtraderNo ratings yet
- ECE131Document2 pagesECE131sohamNo ratings yet
- UNIT - I:Basic Concepts of Electric Drives:: Motor Mechanism DynamicsDocument6 pagesUNIT - I:Basic Concepts of Electric Drives:: Motor Mechanism DynamicsRam DinNo ratings yet
- Eee 8th Sem r2008Document18 pagesEee 8th Sem r2008Ashok VannanNo ratings yet
- JNTUA B. Tech Syllabus R15 Regulation II Year I Semester 2 1 Electrical Electronics Engineering EEEDocument16 pagesJNTUA B. Tech Syllabus R15 Regulation II Year I Semester 2 1 Electrical Electronics Engineering EEEThulasi PrasadNo ratings yet
- 21 Ele 13Document3 pages21 Ele 13c rajNo ratings yet
- Ma205 Transforms and Partial Differential Equations: L T P CDocument8 pagesMa205 Transforms and Partial Differential Equations: L T P CArjun PrasadNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument1 pageSyllabussraavanamNo ratings yet
- ES103Document3 pagesES103Sualé SualéNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Syllabus 2018 19Document89 pages1st Year Syllabus 2018 19Abhishek GargNo ratings yet
- EE001 SyllabusDocument2 pagesEE001 SyllabusAditya YadavNo ratings yet
- FRM Course Syllabus IPDownloadDocument1 pageFRM Course Syllabus IPDownloadMovie ClipsNo ratings yet
- B. E. Sem Vi (Electrical) E-601: Electrical Machines - IiiDocument10 pagesB. E. Sem Vi (Electrical) E-601: Electrical Machines - IiibaruaeeeNo ratings yet
- MOE Lecture Module Verification Report - FinalDocument2 pagesMOE Lecture Module Verification Report - FinalganesanNo ratings yet
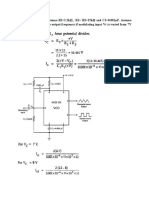
- For The VCO Circuit, Assume R2 2.2k VCC 12V. Determine The Output Frequency If Modulating Input VC Is Varied From 7V To 8VDocument1 pageFor The VCO Circuit, Assume R2 2.2k VCC 12V. Determine The Output Frequency If Modulating Input VC Is Varied From 7V To 8VganesanNo ratings yet
- Address of CollegeDocument34 pagesAddress of CollegeganesanNo ratings yet
- MTech Courses offered at top Anna University affiliated collegesDocument9 pagesMTech Courses offered at top Anna University affiliated collegesganesanNo ratings yet
- Address For PrintDocument4 pagesAddress For PrintganesanNo ratings yet
- Study of Pavement Condition Index (PCI) Relationship With International Roughness Index (IRI) On Flexible PavementDocument6 pagesStudy of Pavement Condition Index (PCI) Relationship With International Roughness Index (IRI) On Flexible Pavementsazwan2No ratings yet
- Dynamics of Cage Floating Breakwater: K. MuraliDocument9 pagesDynamics of Cage Floating Breakwater: K. MuraliSuman.SNo ratings yet
- Test results and costs for disease diagnosisDocument3 pagesTest results and costs for disease diagnosisWathek Al Zuaiby67% (6)
- Aristotle's Biology and MetaphysicsDocument7 pagesAristotle's Biology and MetaphysicsVuk SuboticNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Control System of ATDocument4 pagesHydraulic Control System of ATAsmaa EidNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Overview for Green BeltsDocument31 pagesSix Sigma Overview for Green BeltsAnkitNo ratings yet
- Electric Field Mapping: Experiment 1Document5 pagesElectric Field Mapping: Experiment 1Pi PoliNo ratings yet
- State Transition Diagram To PLC Ladder Logic Translation Whitepaper PDFDocument15 pagesState Transition Diagram To PLC Ladder Logic Translation Whitepaper PDFMihaiBarbuNo ratings yet
- Current Pillar DesignDocument24 pagesCurrent Pillar DesignjmgumbwaNo ratings yet
- DOP-C02demo Exam Practice QuestionsDocument7 pagesDOP-C02demo Exam Practice Questionslovegeorge393No ratings yet
- Psd4135G2: Flash In-System-Programmable Peripherals For 16-Bit McusDocument94 pagesPsd4135G2: Flash In-System-Programmable Peripherals For 16-Bit McusSiva Manohar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Devialet Phantom English PDFDocument11 pagesDevialet Phantom English PDFSATYAM NAIDUNo ratings yet
- BS Iso 12817-2013Document28 pagesBS Iso 12817-2013Ігор БадюкевичNo ratings yet
- Dcma 14-Point Assessment For Project ScheduleDocument5 pagesDcma 14-Point Assessment For Project ScheduleEngr. Mahbub HimelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology: Joher B. Mendez, JR., R.N., M.DDocument65 pagesIntroduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology: Joher B. Mendez, JR., R.N., M.DJoherNo ratings yet
- Central Corneal Thickness: Ultrasound Pachymetry Verus Anterior Segment Optical Coherence TomographyDocument5 pagesCentral Corneal Thickness: Ultrasound Pachymetry Verus Anterior Segment Optical Coherence TomographybasharatNo ratings yet
- Analysis of tapping process in three types of cast iron focusing on torque, axial force and tool wearDocument8 pagesAnalysis of tapping process in three types of cast iron focusing on torque, axial force and tool wearFlorin MilasNo ratings yet
- JAVA AND JAVAUI HANDSON - Hackerrank Assessments-1 PDFDocument15 pagesJAVA AND JAVAUI HANDSON - Hackerrank Assessments-1 PDFtkkhhaarree0% (1)
- Mini ProjectDocument45 pagesMini Projectmanohar manuNo ratings yet
- Sky TowerDocument19 pagesSky TowerAlcohol You LaterNo ratings yet
- ICAO Annex 14 Vol II - Heliports Update - Workshop #2 2012 PDFDocument167 pagesICAO Annex 14 Vol II - Heliports Update - Workshop #2 2012 PDFMário Mineiro100% (1)
- Identity MineralDocument5 pagesIdentity MineralOl SreylinNo ratings yet
- Spark Training in BangaloreDocument36 pagesSpark Training in BangalorekellytechnologiesNo ratings yet
- PLC SCADA Based Temperature Control SystemDocument5 pagesPLC SCADA Based Temperature Control SystemSaurav TiwariNo ratings yet
- Lab Report KmiaDocument6 pagesLab Report KmiaAfifi TahirNo ratings yet
- Micron NAND Flash MLC 16-32-64 - 128GbDocument115 pagesMicron NAND Flash MLC 16-32-64 - 128GbSatya NarayanaNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet 2Document2 pagesProblem Sheet 2em mNo ratings yet
- IUAT v1.13 Engineering-3 User Manual For IndiaDocument24 pagesIUAT v1.13 Engineering-3 User Manual For IndiamgrfanNo ratings yet
- Fish RespirationDocument4 pagesFish Respirationmekala17181705No ratings yet
- Pelton Turbine ReportDocument10 pagesPelton Turbine ReportShea Cheng Kuang100% (2)