Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Appendixyyy
Uploaded by
Albert CorderoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Appendixyyy
Uploaded by
Albert CorderoCopyright:
Available Formats
Appendix – Doc Trespeces Ruptured
o Localized
Judeilan A. Macahilo
o Generalized
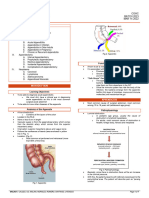
Appendix
Congestive – obstruction, dilatation, hyperemic; CBC:
- Immunologic organ that actively participates in 10-12
secretion of IgA
Suppurative – purulent exudate is still inside the lumen
- Appendectomy may protect against subsequent
of appendix
development of inflammatory bowel disease
Gangrenous – infarct, ischemia
Pathophysiology:
Ruptured – microperforation
Proximal obstruction luminal distension replication
of resident bacteria increased luminal pressure Generalized – pain in >1 quadrant
(venous pressure exceeded) mucosal ischemia
bacterial invasion infarction appendiceal rupture Diagnosis:
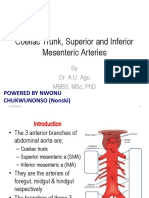
Midgut – superior mesenteric artery Hx and PE
o Direct tenderness on RLQ
Hindgut – inferior mesenteric artery Bacteriology
o E. coli and B. fragilis
*obstruction anywhere in the appendix
Diagnostic and ancillary procedures:
*normal flora – Gram (-) and some Gram (+) o CBC and urinalysis
o Ultrasound – “target” sign
Symptomatology: o CT scan
Vague, dull, diffuse, mid-abdomen pain o Diagnostic laparoscopy
Crampy abdominal pain Urinalysis – rule out UTI, pyelonephritis
Anorexia, nausea&vomiting
Differentials:
Localization to RLQ
Generalized abdominal pain Acute gastroenteritis
- Visceral pain Peptic ulcer disease
- Parietal pain Meckel’s diverticulitis
- Localized pain due to distension of the appendix Acute mesenteric adenitis
Urinary problems
Tip of the appendix – mostly located at the retrocecal
Gynecologic disorder
area; changes in location
o PID
Direct tenderness – most definitive sign of appendicitis o Ectopic pregnancy
Rectal Exam – right anterior pain if tip of appendix is at Treatment:
the retrocecal area
Hydration
- If appendix is antececal?, there will be no pain Antibiotic regimen:
- If appendix is ruptured, pain on all quadrants o Prophylactic Tx
Emergency appendectomy
Stages:
Incidental Appendectomy:
Congestive
Suppurative early stage - Children about to undergo chemotherapy
Gangrenous - Disabled
- With Crohn’s Interval appendectomy
- About to travel to remote area
* do the incision right in the mass
Clean, contaminated – early stages of appendicitis
*put a drain – if you can’t find the appendix
- Prophylactic antibiotic
- Broad-spectrum antibiotic 1 hour prior to
surgery Chronic Appendicitis
Contaminated – ruptured - Appendicitis in the young
- Appendicitis in the elderly
- Therapeutic antibiotic
- Gram (+), (-), anaerobes - Appendicitis with HIV infection
- Metronidazole, 2nd generation cephalosporin In young and elderly – do not expect the classic signs
- Emergency appendectomy and symptoms
Pain reliever – if already diagnosed with appendicitis With HIV – same Tx
- NO if still observing Acute Appendicitis during pregnancy
20-45 y.o – appendicitis is common Surgical risk: 10-15%
Early appendicitis – Mc Burney’s incision Fetal mortality in ruptured cases: 20%
Location of appendiceal tip varies
Generalized – midline incision Any suspicion of appendicitis during pregnancy,
prompt surgery is indicated
Gangrenous – therapeutic antibiotic
Carcinoid of the appendix
Ruptured – use of a monofilament thread, with a drain
Incidental finding
Management:
Periappendiceal Abscess o Appendectomy
<1cm
With a Hx of symptoms of appendicitis No metastases
Presence of an ill-defined mass o Right hemicolectomy - >1.5 cm
May be tender or non-tender Involvement of meso-appendix
+/- of systemic symptoms
Mucocele
Treatment:
- Due to: retention cysts, mucosal hyperplasia,
o Percutaneous aspiration cystadenoma, cystadenocarcinoma
o Observation - Surgery: appendectomy with wide resection of
o Surgery mesoappendix
o Interval appendectomy - Right hemicolectomy for (+) margins at the base
or (+) periappendiceal lymph node
No symptoms, just a mass: diagnostic, barium,
observation
Percutaneous aspiration if:
Cannot tolerated surgery
Antibiotic
You might also like
- Endoscopic Ultrasound Management of Pancreatic Lesions: From Diagnosis to TherapyFrom EverandEndoscopic Ultrasound Management of Pancreatic Lesions: From Diagnosis to TherapyAntonio FacciorussoNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis Signs, Stages, and TreatmentDocument2 pagesAcute Appendicitis Signs, Stages, and TreatmentMikhail BrionesNo ratings yet
- Appendic It eDocument58 pagesAppendic It eZayneb ZeroualNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument3 pagesAcute Appendicitis Diagnosis and TreatmentMavi HayalNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Rectum and Anal CanalDocument68 pagesDiseases of Rectum and Anal CanalKoridor Falua Sakti Halawa 21000063No ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis and Peritonitis: RLQ, To The Pelvis, Right FlankDocument4 pagesAcute Appendicitis and Peritonitis: RLQ, To The Pelvis, Right FlankIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Appendix: Acute Appendicitis, Its Complications, NeoplasmsDocument70 pagesAppendix: Acute Appendicitis, Its Complications, NeoplasmsDr-Mohammad Ali-Fayiz Al TamimiNo ratings yet
- Acute Abdominal Pain GuideDocument19 pagesAcute Abdominal Pain GuideAudricNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis: Basic Information DiagnosisDocument5 pagesAppendicitis: Basic Information DiagnosisCarlos Meza HernandezNo ratings yet
- Etiology: Acute AppendicitisDocument3 pagesEtiology: Acute AppendicitisWenna Grace OdtujanNo ratings yet
- DIAGNOSING ACUTE APPENDICITISDocument27 pagesDIAGNOSING ACUTE APPENDICITISogespaikiNo ratings yet
- By Col - Abrar Hussain ZaidiDocument47 pagesBy Col - Abrar Hussain ZaidiSilvanaPutriNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis in a 15-Year-Old FemaleDocument48 pagesAcute Appendicitis in a 15-Year-Old FemaleSimon Peter MollanedaNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document5 pagesWeek 2Maica LectanaNo ratings yet
- Diverticular DiseaseDocument8 pagesDiverticular DiseaseaizatamlikhaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Abdomen 1Document23 pages1 - Abdomen 1noushad aminNo ratings yet
- Intussusception 161007042729 PDFDocument44 pagesIntussusception 161007042729 PDFDina MarselinaNo ratings yet
- Colon Anatomy and Appendicitis GuideDocument30 pagesColon Anatomy and Appendicitis GuideKiara GovenderNo ratings yet
- Causes of Acute PeritonitisDocument6 pagesCauses of Acute PeritonitisYalin AbouhassiraNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis in ChildrenDocument71 pagesAcute Appendicitis in ChildrenMohamed KamaraNo ratings yet
- K-25 Acute AppendicitisDocument23 pagesK-25 Acute AppendicitiscarinasheliapNo ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument19 pagesAppendicitisSagar ShahNo ratings yet
- 161004acuteaof Gi - MadridDocument73 pages161004acuteaof Gi - MadridMAPACHE 91No ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument17 pagesAppendicitisalwinNo ratings yet
- GastroDocument6 pagesGastroKathleen PabalanNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis: Statement of The ProblemDocument4 pagesAcute Appendicitis: Statement of The ProblemGianne Cacerez PahilaNo ratings yet
- Angel Problem 4a GITDocument48 pagesAngel Problem 4a GITMaxend Arselino SilooyNo ratings yet
- Intussusception TransDocument4 pagesIntussusception TransJames Maravillas100% (1)
- Surgery NotesDocument200 pagesSurgery NotesJasneet SinghNo ratings yet
- PancreasDocument7 pagesPancreasMiguel Cuevas DolotNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Acute Abdomen. 7th YrDocument54 pagesNeonatal Acute Abdomen. 7th YrFreeburn SimunchembuNo ratings yet
- OSCE Gynae-OSCE-MMSSDocument24 pagesOSCE Gynae-OSCE-MMSSMohammad Saifullah100% (1)
- Appendix 2Document30 pagesAppendix 2SilvanaPutriNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis Slide ShowDocument13 pagesAcute Appendicitis Slide Showsharifah shyrannieNo ratings yet
- L09 - Diseases of The PeritoneumDocument13 pagesL09 - Diseases of The PeritoneumS sNo ratings yet
- Score: 7: High Likelihood of AppendicitisDocument2 pagesScore: 7: High Likelihood of AppendicitisMichelle Vera GabunNo ratings yet
- Session 6Document72 pagesSession 6Alliah Marie CababarosNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis - ClinicalKeyDocument38 pagesAppendicitis - ClinicalKeyjpma2197No ratings yet
- (Surg2-Trans) 4.01 AppendixDocument7 pages(Surg2-Trans) 4.01 AppendixJake Brandon M. Andal, RNDNo ratings yet
- Small Intestine and ColonDocument9 pagesSmall Intestine and Colonlentini@maltanet.netNo ratings yet
- Acute AppendicitisDocument5 pagesAcute AppendicitisSHINMEN TAKEZONo ratings yet
- Acute Abdomen Causes, Symptoms, and TreatmentDocument4 pagesAcute Abdomen Causes, Symptoms, and TreatmentLenard BangugNo ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument4 pagesAppendicitisRonaldoNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis: Anetha Jodhan Ravindra SinghDocument34 pagesAppendicitis: Anetha Jodhan Ravindra SinghMarlon GeorgeNo ratings yet
- SGD AppendicitisDocument11 pagesSGD Appendicitisนีล ไบรอันNo ratings yet
- Functions and anatomy of the small intestineDocument8 pagesFunctions and anatomy of the small intestineErald PaderangaNo ratings yet
- Concept Map On AppendicitisDocument6 pagesConcept Map On Appendicitisitalisayan_rondario80% (5)
- Surgery ExamDocument82 pagesSurgery Examrajarajachozhan139No ratings yet
- 10 StomachDocument10 pages10 StomachApabrita KarmakarNo ratings yet
- K.26 Acute AbdomenDocument45 pagesK.26 Acute Abdomenlidz_margaretNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis 1 CDocument30 pagesOsteomyelitis 1 CMohammad Shahnewaz Hossain KhanNo ratings yet
- AppendicitiesDocument58 pagesAppendicitiesGAURAV50% (2)
- Acute AbdomenDocument46 pagesAcute AbdomenErwin Siregar100% (2)
- Appendicitis HasanDocument6 pagesAppendicitis HasanHasan MohammedNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis in Children: Common and Often UrgentDocument6 pagesAppendicitis in Children: Common and Often UrgentHasan MohammedNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis: View ChapterDocument6 pagesAppendicitis: View ChapterHookrz HookNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis Diagnosis and Treatment in 40 CharactersDocument5 pagesAppendicitis Diagnosis and Treatment in 40 CharactersHookrz HookNo ratings yet
- Surgery: The Appendix ExplainedDocument5 pagesSurgery: The Appendix ExplainedJoseph De JoyaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Franklin - Acute Appendicitis - FDRDocument31 pagesDr. Franklin - Acute Appendicitis - FDRAbel MncaNo ratings yet
- Micrbio Lect - Nematodes 2 - Dr. SombillaDocument5 pagesMicrbio Lect - Nematodes 2 - Dr. SombillaAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Read MeDocument1 pageRead MeAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy-Esophagus & StomachDocument5 pagesAnatomy-Esophagus & StomachAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Books Recommended for Second Year Medical StudentsDocument2 pagesBooks Recommended for Second Year Medical StudentsAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Don't QuitDocument2 pagesDon't QuitAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Articular and Musculoskeletal DisordersDocument6 pagesArticular and Musculoskeletal DisordersAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Renal Drugs - Dr. UretaDocument4 pagesRenal Drugs - Dr. UretaAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Conditions Ankle Et FootDocument3 pagesConditions Ankle Et FootAlbert Cordero0% (1)
- Data Sheet: Talipariti Tiliaceum Cocos NuciferaDocument1 pageData Sheet: Talipariti Tiliaceum Cocos NuciferaAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Invitation (Judge)Document1 pageInvitation (Judge)Albert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Www.i Ex TV - ComDocument1 pageWww.i Ex TV - ComAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- BFS Form 2 Data SheetDocument2 pagesBFS Form 2 Data SheetAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- TEX2 - UE Management v.1Document7 pagesTEX2 - UE Management v.1Albert Cordero100% (1)
- Yellow Wizards Audit SheetDocument1 pageYellow Wizards Audit SheetAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Health Literacy of Primary Care Givers of Young Children Common To All To Be InterviewedDocument2 pagesHealth Literacy of Primary Care Givers of Young Children Common To All To Be InterviewedAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Schengen Visa Application FormDocument4 pagesSchengen Visa Application Formmbmazari33No ratings yet
- A Dre No CorticoidsDocument2 pagesA Dre No CorticoidsAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System HistoDocument4 pagesGastrointestinal System HistoAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Dr. Aguirre Pancreas: ND RDDocument3 pagesAnatomy Dr. Aguirre Pancreas: ND RDAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- 2 AcknowledgementsDocument1 page2 AcknowledgementsAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy-Esophagus & StomachDocument5 pagesAnatomy-Esophagus & StomachAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Biologic Response ModifiersDocument1 pageBiologic Response ModifiersAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Adverse EffectsDocument1 pageAdverse EffectsAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Aug 2016Document4 pagesAug 2016Albert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Feb 2016Document4 pagesFeb 2016Albert CorderoNo ratings yet
- April 2016Document4 pagesApril 2016Albert CorderoNo ratings yet
- DODOTDocument1 pageDODOTAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- April 2016Document4 pagesApril 2016Albert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Arthropod Characteristics: Hemocoel, Metamorphosis, TrilobitomorphaDocument3 pagesArthropod Characteristics: Hemocoel, Metamorphosis, TrilobitomorphaAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Anus Chapter Sabiston SurgeryDocument16 pagesAnus Chapter Sabiston SurgeryJanny2009No ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms: GastritisDocument2 pagesSigns and Symptoms: GastritisMohamed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument6 pagesPeptic Ulcer DiseaseBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Necrotizing EnterocolitisDocument24 pagesNecrotizing Enterocolitisfadhila khairunnisaNo ratings yet
- BPSU Case Study on CholedocholithiasisDocument8 pagesBPSU Case Study on CholedocholithiasisYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- Short Bowel Syndrome Management in ChildrenDocument7 pagesShort Bowel Syndrome Management in ChildrenrodyNo ratings yet
- Dental Management of Diseases of The Gastrointestinal SystemDocument61 pagesDental Management of Diseases of The Gastrointestinal SystemkomalgorayaNo ratings yet
- All About GIT PhysiologyDocument79 pagesAll About GIT PhysiologySherwan R Shal91% (23)
- Colonic Interposition For Benign DiseaseDocument18 pagesColonic Interposition For Benign DiseaseOhana S.No ratings yet
- Coeliac Trunk, Superior and Inferior Mesenteric ArteriesDocument24 pagesCoeliac Trunk, Superior and Inferior Mesenteric ArteriesKosisochukwu sixtus Ugwunnaji100% (1)
- Coloproctology: Incidence of Fistula After Management of Perianal AbscessDocument4 pagesColoproctology: Incidence of Fistula After Management of Perianal AbscessHafiidz Fatich RosihanNo ratings yet
- Emergency Surgery Section ECTES 2018 ValenciaDocument5 pagesEmergency Surgery Section ECTES 2018 Valenciagarbass1905No ratings yet
- Accessory Organ of The AbdomenDocument58 pagesAccessory Organ of The AbdomenOgundipe olorunfemiNo ratings yet
- DYSPHAGIADocument35 pagesDYSPHAGIAChristopher Yeoh100% (2)
- JaundiceDocument75 pagesJaundiceangel_sagun_1No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Hiatal Hernia ReliefDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Hiatal Hernia ReliefLalaine Nadulpit100% (2)
- 1.CBE CME Obstructive JaundiceDocument39 pages1.CBE CME Obstructive JaundicedeepikaNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Costs and Short-Term Clinical Outcomes of Per-Oral Endoscopic Myotomy and Laparoscopic Heller MyotomyDocument6 pagesComparison of Costs and Short-Term Clinical Outcomes of Per-Oral Endoscopic Myotomy and Laparoscopic Heller MyotomyDavids MarinNo ratings yet
- Esophageal Diverticula - AMBOSSDocument1 pageEsophageal Diverticula - AMBOSSRazan Al-ZataryNo ratings yet
- Zoology AscriseDocument12 pagesZoology AscrisepappunaagraajNo ratings yet
- Drenajul Biliar Percutan in Icterul Obstructiv NeoDocument10 pagesDrenajul Biliar Percutan in Icterul Obstructiv Neociuca bogdanNo ratings yet
- Portal HypertensionDocument13 pagesPortal HypertensionCiprian BoesanNo ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis and Enterocolitis PBL ObjectivesDocument5 pagesGastroenteritis and Enterocolitis PBL ObjectivesPaul A IBattledaily ScavellaNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Drugs and Pharmcotherapy - DrdhritiDocument60 pagesPeptic Ulcer Drugs and Pharmcotherapy - Drdhritidbrahma100% (2)
- Emilok 2011 MKT Plan TOTAL2Document19 pagesEmilok 2011 MKT Plan TOTAL2maawi2002yahoocomNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Concet of EliminationDocument32 pagesUnit 6 Concet of EliminationAbdur Rehman100% (1)
- Drug Cards Milk of MagnesiaDocument1 pageDrug Cards Milk of MagnesiaAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Subtotal Cholecystectomy-''Fenestrating'' Vs ''Reconstituting'' Subtypes and The Prevention of Bile Duct Injury - Definition of The Optimal Procedure In  Difficult Operative ConditionsDocument8 pagesSubtotal Cholecystectomy-''Fenestrating'' Vs ''Reconstituting'' Subtypes and The Prevention of Bile Duct Injury - Definition of The Optimal Procedure In  Difficult Operative ConditionsBolivar Isea100% (1)
- Self Hypnosis May Reduce Nausea & Vomiting in Early PregnancyDocument4 pagesSelf Hypnosis May Reduce Nausea & Vomiting in Early PregnancyMelda Sri WahyuNingsihNo ratings yet
- Digestive System GuideDocument6 pagesDigestive System GuideQueencess Ara TorresNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (327)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- Daniel Kahneman's "Thinking Fast and Slow": A Macat AnalysisFrom EverandDaniel Kahneman's "Thinking Fast and Slow": A Macat AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (130)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)