Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 67-2
Uploaded by
lelon ongCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 67-2
Uploaded by
lelon ongCopyright:
Available Formats
Set 67 - Page 1 Compiled by Mr.
lelon 012-6556593
6
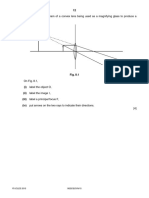
4 (a) Define the specific latent heat of fusion of a substance.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................. [2]
(b) Small pieces of ice at 0 °C are added to 0.35 kg of water. The initial temperature of the water is
24.5 °C. The temperature of the water decreases to 0 °C. The water loses 35 000 J of thermal
energy as it cools. All of the ice added to the water melts.
The specific latent heat of fusion of ice is 3.3 × 105 J / kg.
Calculate:
(i) the specific heat capacity of water
specific heat capacity = ........................................................ [2]
(ii) the mass of ice added to the water.
mass = ........................................................ [3]
[Total: 7]
© UCLES 2020 0625/42/F/M/20
Set 67 - Page 2 Compiled by Mr. lelon 012-6556593
15
10 Fig. 10.1 is a diagram of a soldering iron. Solder is a mixture of metals used to make a permanent
contact between electrical wires.
metal tip
heating element
Fig. 10.1
The heating element raises the temperature of the metal tip. When solder is placed against the tip,
the solder melts over the wires to be joined. When the solder cools, it solidifies and the permanent
connection is made.
The working temperature of the metal tip is 380 °C.
(a) The boxes in Fig. 10.2 show two materials and some different melting points.
material melting point
1000 °C
metal of the
metal tip
380 °C
200 °C
20 °C
solder
0 °C
Fig. 10.2
On Fig. 10.2, draw a line from the metal of the metal tip and a line from the solder to a suitable
melting point for each. [2]
© UCLES 2019 5054/22/M/J/19 [Turn over
Set 67 - Page 3 Compiled by Mr. lelon 012-6556593
16
(b) The heating element is rated at 24 V, 3.3 A.
The heating element is switched on.
The temperature of the metal tip rises from 20 °C to 320 °C in the first 10 s.
(i) Calculate the electrical energy supplied to the heating element in the first 10 s.
energy = ......................................................... [2]
(ii) The metal tip is made of copper and has a mass of 2.3 g. The specific heat capacity of
copper is 0.39 J / (g °C).
Calculate the thermal energy (heat) gained by the metal tip in the first 10 s.
thermal energy = ......................................................... [3]
(c) (i) Describe, in terms of free electrons, the process by which heat transfers through the
metal tip.
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................... [2]
(ii) Heat is lost from the metal tip by convection in the air.
Explain how convection occurs in the air.
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................... [2]
© UCLES 2019 5054/22/M/J/19
Set 67 - Page 4 Compiled by Mr. lelon 012-6556593
17
(d) The temperature of the metal tip is measured with a thermocouple.
(i) In the space below, draw a labelled diagram of a thermocouple. Mark with a letter H the
part of the thermocouple that is placed on the metal tip.
[2]
(ii) State two reasons why a thermocouple thermometer is suitable for measuring how the
temperature of the metal tip varies during the first 10 s.
1. .......................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
2. .......................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
[2]
[Total: 15]
© UCLES 2019 5054/22/M/J/19 [Turn over
Set 67 - Page 5 Compiled by Mr. lelon 012-6556593
7
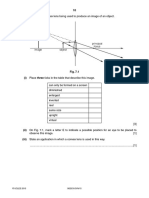
5 (a) Complete the sentences with words that describe the main process of thermal energy transfer
in each case.
A man goes for a walk on a cold day. He touches a metal gate, which removes thermal
energy from his hands by ................................. . He holds the sides of a cup containing a
hot drink. His hands gain thermal energy by ................................. . Some farm workers have
lit a fire. The man warms his hands by the side of the fire. His hands gain thermal energy by
................................. . [3]
(b) Describe in terms of particles the transfer of thermal energy through the metal of the gate
after transfer from the man’s hands.
...................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................. [2]
(c) Fig. 5.1 shows a car on a sunny day in a hot country.
windscreen
object A
Fig. 5.1
The object labelled A is placed inside the windscreen. It is used by the owner of the car to
reduce the temperature rise of the air in the car.
Ring the most suitable material for the outer surface of object A. Explain your choice.
dull black dull white shiny black shiny white
explanation ................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................. [2]
[Total: 7]
© UCLES 2020 0625/42/F/M/20 [Turn over
Set 67 - Page 6 Compiled by Mr. lelon 012-6556593
6
4 (a) State and explain, in terms of molecules, any change in the pressure of a gas when the
volume is reduced at a constant temperature.
Statement .................................................................................................................................
Explanation ...............................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
[3]
(b) Complete Table 4.1 to give the relative order of magnitude of the expansion of gases, liquids
and solids for the same increase of temperature.
Write one of these words in each blank space:
gas liquid solid
Table 4.1
expands most
expands least
[2]
[Total: 5]
© UCLES 2019 0625/42/M/J/19
Set 67 - Page 7 Compiled by Mr. lelon 012-6556593
7
5 (a) (i) A liquid is heated so that bubbles of its vapour rise to the surface and molecules escape
to the atmosphere.
State the name of this process .................................................................................... [1]
(ii) At a lower temperature than in (a)(i), molecules escape from the surface to the
atmosphere.
State the name of this process .................................................................................... [1]
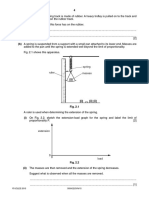
(b) (i) Fig. 5.1 shows apparatus used to determine the power output of a heater.
thermometer
electric heater
metal block
Fig. 5.1
The metal block has a mass of 2.7 kg. The metal of the block has a specific heat capacity
of 900 J / (kg °C).
In 2 min 30 s, the temperature of the block increases from 21 °C to 39 °C.
Calculate the power of the heater.
power = ........................................................ [4]
(ii) State and explain a precaution that can be taken to improve the accuracy of the
experiment.
Statement ..........................................................................................................................
Explanation .......................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
[2]
[Total: 8]
© UCLES 2019 0625/42/M/J/19 [Turn over
Set 67 - Page 8 Compiled by Mr. lelon 012-6556593
5
3 (a) A solar panel receives energy from the Sun at a rate of 5.0 kW.
Thermal energy is transferred from the solar panel to water with an efficiency of 20%.
Cold water of mass 15 kg enters the solar panel every hour.
The specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J / (kg °C).
Calculate the temperature increase of the water.
temperature increase = .....................................................°C [4]
(b) State and explain one advantage and one disadvantage of heating the water in a solar panel
compared with heating the water in a coal-burning boiler.
advantage .................................................................................................................................
explanation ...............................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
disadvantage ............................................................................................................................
explanation ...............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................. [4]
[Total: 8]
© UCLES 2020 0625/42/M/J/20 [Turn over
Set 67 - Page 9 Compiled by Mr. lelon 012-6556593
6
4 Fig. 4.1 shows a liquid-in-glass thermometer without a temperature scale.
The liquid inside the thermometer has a melting point of –39 °C.
Fig. 4.1
(a) Describe simple experiments to mark the positions of the fixed points on this liquid-in-glass
thermometer.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................. [4]
(b) A scientist is measuring temperatures at the South Pole. These temperatures have a minimum
value of –90 °C.
State why the liquid used in the thermometer in Fig. 4.1 would not be suitable for this scientist.
............................................................................................................................................. [1]
(c) State a design change that:
(i) increases the sensitivity of a liquid-in-glass thermometer
..................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) increases the range of a liquid-in-glass thermometer.
..................................................................................................................................... [1]
(d) State the property of the liquid which ensures that the scale on a liquid-in-glass thermometer
is linear.
............................................................................................................................................. [1]
[Total: 8]
© UCLES 2020 0625/42/M/J/20
Set 67 - Page 10 Compiled by Mr. lelon 012-6556593
12
Section B
Answer two questions from this section. Answer in the spaces provided.
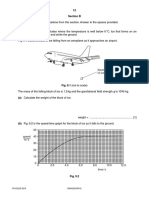
8 Fig. 8.1 shows the circuit diagram of a temperature gauge. It contains an ammeter, a thermistor, a
fixed resistor R and a battery.
thermistor R
Fig. 8.1
The current is measured at different temperatures and a graph of the results is shown in Fig. 8.2.
0.025
0.020
current / A
0.015
0.010
0.005
0
20 40 60 80 100
temperature / °C
Fig. 8.2
(a) (i) State how the resistance of the thermistor changes with temperature and explain how
Fig. 8.2 shows this change.
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................... [2]
© UCLES 2020 5054/22/M/J/20
Set 67 - Page 11 Compiled by Mr. lelon 012-6556593
13
(ii) Resistance and current are used for the measurement of temperature.
State one other physical property that is used for the measurement of temperature.
...........................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................... [1]
(b) A temperature scale involves the use of fixed points.
State what is meant by:
(i) the ice point
...........................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) the steam point.
...........................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................... [1]
(c) At 80 °C, the potential difference (p.d.) across the thermistor is 3.6 V.
(i) State what is meant by potential difference.
...........................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Calculate the resistance of the thermistor when the temperature is 80 °C.
resistance = ......................................................... [3]
(iii) The electromotive force (e.m.f.) of the battery is 25 V.
Calculate the resistance of the resistor R.
resistance = ......................................................... [2]
© UCLES 2020 5054/22/M/J/20 [Turn over
Set 67 - Page 12 Compiled by Mr. lelon 012-6556593
14
(d) The current scale on the ammeter is linear.
Using values from Fig. 8.2, a student marks the scale on the ammeter with temperature
values that correspond to the values of the current.
The temperature is then read directly from the temperature scale on the ammeter.
(i) State what is meant by a sensitive thermometer.
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) State and explain at which temperatures this thermometer is most sensitive.
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................... [2]
(e) The temperature gauge is used to measure the temperature of a room.
Suggest why the temperature obtained using the gauge is slightly higher than the actual
temperature of the room.
...................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................. [1]
[Total: 15]
© UCLES 2020 5054/22/M/J/20
You might also like
- Mission Magnum I ManualDocument41 pagesMission Magnum I Manualwatt_hr100% (2)
- Heat Treatment of Welded JointsDocument11 pagesHeat Treatment of Welded JointsMuhammed SulfeekNo ratings yet
- 2600, 2400, 2300 FOGGERS: User'S ManualDocument2 pages2600, 2400, 2300 FOGGERS: User'S Manualver_at_work100% (1)
- Cessna Citation XLS+ ReviewerDocument14 pagesCessna Citation XLS+ ReviewerMK Lariosa100% (2)
- Fundamentals of Water System Design - SIDocument281 pagesFundamentals of Water System Design - SItran duy100% (2)
- Flender Manual GeneralDocument42 pagesFlender Manual GeneralYenny LaraNo ratings yet
- WS 7 IG I Chemistry ELLECTRICITYAND CHEMICALCHDocument4 pagesWS 7 IG I Chemistry ELLECTRICITYAND CHEMICALCHRaj MalkanNo ratings yet
- 4 Ideal Gas0001Document18 pages4 Ideal Gas0001Pooja MehraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument20 pagesChapter 4 PDFSiti Arbaiyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Toddle MytestDocument11 pagesToddle MytestashwithanumandlaNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Reactivity of Metals 3 QPDocument16 pages4.1 Reactivity of Metals 3 QPDumpsterFireGamingNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/23Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/23jamalNo ratings yet
- Chem 4Document33 pagesChem 4S 9K32No ratings yet
- Thermal Properties & Temperature 6 QPDocument9 pagesThermal Properties & Temperature 6 QPJeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- Bonding Question.Document5 pagesBonding Question.hui sin limNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/41Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/41Mahir VasoyaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structuure and BondingDocument6 pagesAtomic Structuure and BondingHarshika Prasanganie Abeydeera100% (1)
- Experimental Particulate Nature F5Document25 pagesExperimental Particulate Nature F5Shepherd W NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- Liquid Out, Temperature 25.5 °C Tube: M/gs P / WDocument7 pagesLiquid Out, Temperature 25.5 °C Tube: M/gs P / WGianra RadityaNo ratings yet
- Igcse Electrochemistry Review PDFDocument7 pagesIgcse Electrochemistry Review PDFbilly ogadaNo ratings yet
- Black Body Radiation 2 QPDocument16 pagesBlack Body Radiation 2 QPNaeemNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemistry QuestionsDocument24 pagesElectricity & Chemistry QuestionsIsaa gabNo ratings yet
- Electrical Quantities WorksheetDocument10 pagesElectrical Quantities WorksheetMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Add MathsDocument20 pagesAdd MathsTS ShongNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Pre-U: CHEMISTRY 9791/02Document20 pagesCambridge Pre-U: CHEMISTRY 9791/02laksh bissoondialNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atoms (With Answer)Document6 pagesStructure of Atoms (With Answer)Hui ShuenNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Magnetism FDocument17 pagesTopic 7 Magnetism FsaadNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelCallie Jia LiNo ratings yet
- 9701/23/M/J/20 © Ucles 2020Document10 pages9701/23/M/J/20 © Ucles 2020Fire stormNo ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry AQA Topic 2 Inorganic I Year 1 Periodicity - QP PDFDocument38 pagesA Level Chemistry AQA Topic 2 Inorganic I Year 1 Periodicity - QP PDFTanika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemistry 2 QPDocument10 pagesElectricity & Chemistry 2 QPValerine VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Set 62 - Chapter 2Document12 pagesSet 62 - Chapter 2lelon81No ratings yet
- 1.thermal Properties QuestionsDocument10 pages1.thermal Properties QuestionsGaspard Bouchard secondaryNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties - Temperature 1 QPDocument10 pagesThermal Properties - Temperature 1 QPAnanya GSNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Thermal Properties of MatterDocument32 pages3.2 Thermal Properties of MatterMartinNo ratings yet
- Test On Group II ElementsDocument5 pagesTest On Group II ElementsKoo Keung EngNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Manya PunjabiNo ratings yet
- Redox HLDocument19 pagesRedox HLmikeasmith404No ratings yet
- Electricity Questions PDFDocument33 pagesElectricity Questions PDFShrinay Chandra0% (1)
- P1 - Heat TransferDocument16 pagesP1 - Heat TransferredaNo ratings yet
- Sem 3 Nov 2020 Paper 2 HLDocument20 pagesSem 3 Nov 2020 Paper 2 HLFARRIS ATHMAR BIN SHAHRULNIZANo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument3 pagesChemistrysalmanismart123No ratings yet
- Thermal Physics Extension QsDocument5 pagesThermal Physics Extension QsRamesh ShresthaNo ratings yet
- 14 ElectricityDocument8 pages14 Electricityspiritarts690No ratings yet
- 16+ Chemistry Nov 2019Document18 pages16+ Chemistry Nov 2019Kitty chenNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Homework PupilDocument8 pagesElectrolysis Homework Pupilnicole.fiorentini.almeidaNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemistry 1 QPDocument11 pagesElectricity & Chemistry 1 QPValerine VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and Reduction mj2020Document2 pagesOxidation and Reduction mj2020FenNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education Practice QuestionsDocument11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education Practice QuestionslNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/41Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/41Govind ShankarNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument12 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelCody MYNo ratings yet
- Mock PaperDocument9 pagesMock PaperjunetaskinNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table 5 QPDocument11 pagesPeriodic Table 5 QPYabhijit DuttaNo ratings yet
- Efficiency 1 QP (1) 222222222222Document12 pagesEfficiency 1 QP (1) 222222222222DumpsterFireGamingNo ratings yet
- 1.4 TestDocument5 pages1.4 TestdfghjNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/22Document12 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/22Putu SeptianNo ratings yet
- Mock 1 Paper 2 Code 200112Document14 pagesMock 1 Paper 2 Code 200112Quazi Sahil HossainNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties & Temperature 2 QPDocument9 pagesThermal Properties & Temperature 2 QPJinYoongLimNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure QuestionsDocument7 pagesAtomic Structure QuestionsSophiaNo ratings yet
- 9701 - s17 - QP - 42 CharlesDocument30 pages9701 - s17 - QP - 42 Charlescharlesma123No ratings yet
- 0620/32/F/M/16 © Ucles 2016Document7 pages0620/32/F/M/16 © Ucles 2016aaryavaminNo ratings yet
- Scholastica: Mock 1Document11 pagesScholastica: Mock 1Fatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Extra Sheet 2 (Sent Online)Document13 pagesExtra Sheet 2 (Sent Online)Mona Abd-ElazizNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Electricity Revision BookletDocument46 pagesUnit 2 Electricity Revision BookletaffordabalzNo ratings yet
- My TestDocument10 pagesMy TestMarin PesicNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-09Document1 pagePages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-09lelon ongNo ratings yet
- Omoda 5 BrochureDocument4 pagesOmoda 5 Brochurelelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 32-10Document2 pagesPages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 32-10lelon ong0% (1)
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-10Document2 pagesPages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-10lelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-08 PDFDocument1 pagePages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-08 PDFlelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-10Document2 pagesPages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-10lelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 33-06Document2 pagesPages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 33-06lelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-6 - Gas PressureDocument1 pagePages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-6 - Gas Pressurelelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 32-06Document1 pagePages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 32-06lelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 32-08Document2 pagesPages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 32-08lelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-06 PDFDocument1 pagePages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-06 PDFlelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-5 - ThermometerDocument1 pagePages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-5 - Thermometerlelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-07Document2 pagesPages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-07lelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 32-07Document2 pagesPages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 32-07lelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-9 - Chapter Kinematic and ThermalDocument3 pagesPages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-9 - Chapter Kinematic and Thermallelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 33-05Document1 pagePages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 33-05lelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-4 - Thermal TransferDocument1 pagePages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-4 - Thermal Transferlelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-5 - ThermometerDocument1 pagePages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-5 - Thermometerlelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-6 - Gas PressureDocument1 pagePages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-6 - Gas Pressurelelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-05Document1 pagePages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-05lelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 33-05Document1 pagePages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 33-05lelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-4 - Thermal TransferDocument1 pagePages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-4 - Thermal Transferlelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 32-05Document1 pagePages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 32-05lelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 21-9 - Chapter Kinematic and Vector DiagramDocument2 pagesPages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 21-9 - Chapter Kinematic and Vector Diagramlelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 21-9 - Chapter Kinematic and Vector DiagramDocument2 pagesPages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 21-9 - Chapter Kinematic and Vector Diagramlelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-04Document1 pagePages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-04lelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-3 - PressureDocument2 pagesPages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-3 - Pressurelelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-2 - Hookes LawDocument1 pagePages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-2 - Hookes Lawlelon ongNo ratings yet
- Pages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 21-4 - MomentDocument1 pagePages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 21-4 - Momentlelon ongNo ratings yet
- Numesh Engineered Wire Mesh Design TablesDocument20 pagesNumesh Engineered Wire Mesh Design TablesYakhoob KhanNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Heavy-Duty MAG WeldingDocument9 pagesAdvantages of Heavy-Duty MAG WeldingNaksalitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 and 8 Work Inside 6Document11 pagesChapter 7 and 8 Work Inside 6lozzzzzNo ratings yet
- BR BoilerHouseComponents enDocument28 pagesBR BoilerHouseComponents enJosé Pedro MagalhãesNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Practices - IIDocument27 pagesMaintenance Practices - IIrashmiameNo ratings yet
- Stulz Cyberair DX Iom Ocs0135Document56 pagesStulz Cyberair DX Iom Ocs0135skrajnishNo ratings yet
- Design and Configure SAG Mill Liners For Maximum Tonnage PerformanceDocument12 pagesDesign and Configure SAG Mill Liners For Maximum Tonnage PerformanceDiegoAlvarezHuguezNo ratings yet
- TP6551 MobileOperationDocument48 pagesTP6551 MobileOperationAnonymous M0OEZEKoGiNo ratings yet
- Technical Documentation Engine Spare Parts Catalogue: MAN Diesel & TurboDocument450 pagesTechnical Documentation Engine Spare Parts Catalogue: MAN Diesel & TurboMrberkNo ratings yet
- Máy SliceDocument15 pagesMáy SliceHoang NguyenNo ratings yet
- The Marinov Generator1Document7 pagesThe Marinov Generator1Ioan CozmaNo ratings yet
- Bucket ElevatorDocument18 pagesBucket Elevatorlhmamda ismailNo ratings yet
- ch13 Solution Manual Soil Mechanics and Foundations PDFDocument32 pagesch13 Solution Manual Soil Mechanics and Foundations PDFArnel Suarez100% (1)
- A Mini Project On Design of Flexible PavementDocument94 pagesA Mini Project On Design of Flexible Pavementsohail irfanNo ratings yet
- MWWSSB 11 Sewer TesRTRting and InpectionDocument5 pagesMWWSSB 11 Sewer TesRTRting and InpectionZeeshan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Vibration Control in Washing Machine With The Help of Suspension SystemDocument14 pagesVibration Control in Washing Machine With The Help of Suspension Systempradeep eliNo ratings yet
- MDDocument15 pagesMDRakesh Kumar Singh (Phase 1B)No ratings yet
- Kirloskar Brothers Limited: A Kirloskar Group Company Established 1888Document2 pagesKirloskar Brothers Limited: A Kirloskar Group Company Established 1888Mohan CharanchathNo ratings yet
- Series 560 & 570: Pressure Safety Valves ASME Section I (560) & VIII (570) NB Certified For Air, Gas and SteamDocument4 pagesSeries 560 & 570: Pressure Safety Valves ASME Section I (560) & VIII (570) NB Certified For Air, Gas and SteamEdbaac BANo ratings yet
- 950H - Sebp3866-24 - K5K - Vol 1Document898 pages950H - Sebp3866-24 - K5K - Vol 1pikinhos100% (6)
- Halton TsaDocument9 pagesHalton TsaNetri KrisztiánNo ratings yet
- Nasa TM-106943Document29 pagesNasa TM-106943LizardladNo ratings yet
- Summtive Sci 6 WK3Document2 pagesSummtive Sci 6 WK3Maria Roxanne Martinez100% (1)