Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Single Phase Inverter
Uploaded by
CLAS COACHINGCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Single Phase Inverter
Uploaded by
CLAS COACHINGCopyright:
Available Formats
Single Phase Inverter
The inverter is an electronic circuit that converts fixed DC supply to variable AC
supply. The inverter is used to run the AC loads through a battery or control AC
loads via AC-DC conversion. Inverters are also available as single-phase inverter
and three-phase inverters. Of course, in three-phase inverter more switching
operations are required. Let see the circuit diagram and working principle of
single-phase and three-phase inverters.
Single Phase Inverter
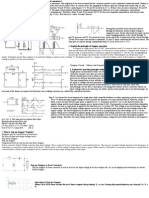
A single-phase inverter or also called as half-bridge inverters, converters DC
supply to single-phase AC supply. For this purpose, two switching devices are
used to convert DC to AC. Diodes, capacitors help the circuit to operate smoothly.
Single-phase Inverter Working Principle
As the name implies, half-bridge inverter, the output varies from +Vs/2 to -Vs/2.
As shown in the circuit, two switching devices are connected in one common
branch or also called a leg. This switching may be SCR, MOSFET, or IGBT.
Generally, we use MOSFET more commonly for high-frequency applications. One
more advantage with MOSFET is it has low switching losses but high conduction
losses.
Single Phase Inverter
As shown in the circuit, we have two switching devices S1 and S2. To obtain one
cycle of Alternating voltage, each device is triggered at one time. The other being
off at the same moment. For example, to obtain the positive cycle of Alternating
supply, device S1 is turned on, while S2 is kept off. Similarly to obtain a negative
cycle of alternating supply, device S2 is turned on while S1 is kept off. The output
wave is shown as below.
Output Voltage Waveform Half Bridge
As shown in the output figure, when S1 is conducting from 0 to T/2 the output
+Vs/2 is obtained. Similarly, when S2 is conducting from T/2 to T, the output -
Vs/2 is obtained. Hence the output alternates between +Vs/2 to -Vs/2, which is
regarded as alternating voltage. T is the total time period of the conduction of two
devices. It can be noted that the output voltage waveform is a stepped square
waveform. In inverters, we never obtain a sinusoidal waveform. The stepped
square waveform alternates between two values, which is considered as alternating
voltage. The same is for three-phase inverter also.
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- DC-AC (Inverters)Document30 pagesDC-AC (Inverters)Joo AdelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 E Learning ELDA Part 4 02052018Document10 pagesChapter 4 E Learning ELDA Part 4 02052018Ade 'aiyie' SasmitaNo ratings yet
- What Is An AutotransformerDocument23 pagesWhat Is An AutotransformerJoseph B Delos Reyes100% (1)
- Power Semiconductor Devices: ON OFFDocument17 pagesPower Semiconductor Devices: ON OFFSaurabhSinghNo ratings yet
- 2 038 PDFDocument11 pages2 038 PDFAmit GauravNo ratings yet
- RectifiersDocument13 pagesRectifiersInfidragon GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Boost Converter - WikipediaDocument13 pagesBoost Converter - WikipediaADITYA PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Converters and Rectifiers (NEW)Document29 pagesConverters and Rectifiers (NEW)I AM NOT CHINESENo ratings yet
- Power Supply: Block DiagramDocument14 pagesPower Supply: Block DiagramVamsi SakhamuriNo ratings yet
- Welcome To All The Teacher's Of: SmitDocument30 pagesWelcome To All The Teacher's Of: Smitsrvdhar100% (2)
- Basic Switching CircuitsDocument19 pagesBasic Switching Circuitsash1968No ratings yet
- Power Electronics L2 ConvertersDocument6 pagesPower Electronics L2 ConvertersBakri BugaNo ratings yet
- 3 Line ConverterDocument10 pages3 Line ConverterJay Romar PabianiaNo ratings yet
- Single Phase InverterDocument8 pagesSingle Phase InverterEasy EducationNo ratings yet
- U21 Assigment 1Document57 pagesU21 Assigment 1Mostafa ElngarNo ratings yet
- Classification of InvertersDocument36 pagesClassification of InvertersMohammad ShoebNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3&4 DC - AC Switched Mode Inverters: ApplicationsDocument37 pagesUNIT 3&4 DC - AC Switched Mode Inverters: Applicationsdivya k sNo ratings yet
- Single Phase InverterDocument7 pagesSingle Phase InverterBHALAJI BIRLANo ratings yet
- Inverters Half and Full BridgeDocument12 pagesInverters Half and Full BridgeSaî CharañNo ratings yet
- Single Transistor 12v To 230v InverterDocument7 pagesSingle Transistor 12v To 230v Inverteryr48No ratings yet
- Answers of Power Electronics NewDocument9 pagesAnswers of Power Electronics NewSyed ZabiullahNo ratings yet
- Single Transistor 12V To 230V InverterDocument7 pagesSingle Transistor 12V To 230V Inverteryr48No ratings yet
- TransformerDocument11 pagesTransformerahmed saidNo ratings yet
- KMT#4Document5 pagesKMT#4RomanHerreraNo ratings yet
- Various Types of Transformers PDFDocument9 pagesVarious Types of Transformers PDFRajNo ratings yet
- Single-Phase Supply Three-Phase Supply: Half-Wave RectificationDocument7 pagesSingle-Phase Supply Three-Phase Supply: Half-Wave RectificationKhushbakht KhushiNo ratings yet
- Mini Project InverterDocument52 pagesMini Project InverterraycrossharmaNo ratings yet
- What Is An Inverter?Document3 pagesWhat Is An Inverter?Sumon ShariarNo ratings yet
- Report Content - Digital Water MeterDocument44 pagesReport Content - Digital Water MeteramiraNo ratings yet
- Final ReviewDocument19 pagesFinal ReviewSanyam JainNo ratings yet
- EE 241 Experiment 5: Boost ConverterDocument4 pagesEE 241 Experiment 5: Boost ConverterMiguel-Josephine ArmamentoNo ratings yet
- Vishesh TextDocument7 pagesVishesh Textsinghyasharth567No ratings yet
- Seminar Report REVISEDDocument21 pagesSeminar Report REVISEDayash mohantyNo ratings yet
- 505-Lec 02 PDFDocument27 pages505-Lec 02 PDFUdara DissanayakeNo ratings yet
- List of ComponentsDocument13 pagesList of ComponentsBenita AgbagwaraNo ratings yet
- Clap SwitchDocument40 pagesClap SwitchAnand Cool100% (2)
- Unit II Notes I&CDocument65 pagesUnit II Notes I&CShubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Study of AC and-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesStudy of AC and-WPS OfficeBeena PalNo ratings yet
- INVERTERDocument2 pagesINVERTERSuave RevillasNo ratings yet
- Unit-I: 1. What Is An Inverter?Document12 pagesUnit-I: 1. What Is An Inverter?Gnanaseharan ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Unit - 5 - Oscillators & TimersDocument45 pagesUnit - 5 - Oscillators & TimersHarish Kumar K.SNo ratings yet
- Transducers 130331093736 Phpapp01Document21 pagesTransducers 130331093736 Phpapp01Ayush ThakurNo ratings yet
- Background or (Literature Review) : Models of DC/DC Converters DC-DC ConvertersDocument5 pagesBackground or (Literature Review) : Models of DC/DC Converters DC-DC Convertersابو عبدالرحمنNo ratings yet
- Buck ConverterDocument5 pagesBuck ConverterM Zeeshan WazirNo ratings yet
- Boost Converter: The Basic Schematic of A Boost Converter. The Switch Is Typically A MOSFET, IGBT, or BJTDocument7 pagesBoost Converter: The Basic Schematic of A Boost Converter. The Switch Is Typically A MOSFET, IGBT, or BJTSpk SudhinNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines BookDocument222 pagesElectrical Machines BookSUNILNo ratings yet
- CYCLOCONVERTERSDocument8 pagesCYCLOCONVERTERSBabu EvanceNo ratings yet
- Conv DC-DC Paper ENglishDocument5 pagesConv DC-DC Paper ENglishpepe890305No ratings yet
- Clint Inverter PaperDocument13 pagesClint Inverter PaperEngrAneelKumarAkhaniNo ratings yet
- TWO Power Conversion Systems 2.1 Power Electronic ConvertersDocument17 pagesTWO Power Conversion Systems 2.1 Power Electronic ConvertersAlhussain EmbarkNo ratings yet
- Edc Project Report: Prof. Garima SolankiDocument32 pagesEdc Project Report: Prof. Garima SolankiAnime X100% (1)
- Basic Rectifier CircuitsDocument8 pagesBasic Rectifier CircuitssensitivesensesNo ratings yet
- Originalproectphysicsmsword Converted 191225064922Document12 pagesOriginalproectphysicsmsword Converted 191225064922GOKULNo ratings yet
- Eet 06206 HandoutDocument40 pagesEet 06206 HandoutMohammed ShabanNo ratings yet
- Basic of ElectricalDocument10 pagesBasic of ElectricalAbdul RazzakNo ratings yet
- Power Supply Description: Naresh I TechnolgiesDocument14 pagesPower Supply Description: Naresh I Technolgiesreddyece402No ratings yet
- Image 1Document2,174 pagesImage 1CLAS COACHINGNo ratings yet
- Soil Moisture SensorDocument3 pagesSoil Moisture SensorCLAS COACHINGNo ratings yet
- Temperature Sensor General DescriptionDocument2 pagesTemperature Sensor General DescriptionCLAS COACHINGNo ratings yet
- Water Liquid Level Sensor ModuleDocument1 pageWater Liquid Level Sensor ModuleCLAS COACHINGNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic SensorDocument7 pagesUltrasonic SensorCLAS COACHINGNo ratings yet
- Vibration Sensor Working and ApplicationsDocument2 pagesVibration Sensor Working and ApplicationsCLAS COACHINGNo ratings yet