Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Periodic - 2 Eco Class-11
Periodic - 2 Eco Class-11
Uploaded by
amandeep malikOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Periodic - 2 Eco Class-11
Periodic - 2 Eco Class-11
Uploaded by
amandeep malikCopyright:
Available Formats
BAL VIKAS PROGRESSIVE SCHOOL
22.9.21 PERIODIC TEST - II
WEDNESDAY CLASS XI
TIME: 30 MINUTES ECONOMICS MM: 25
General Instructions.
• All questions are compulsory.
• Each question is of 1 mark.
• There is no negative marking.
1 A characteristics or a phenomenon which is capable of being measured and changes its value overtime is
called
(a)Sample (b) Attribute (c)None (d) Variable
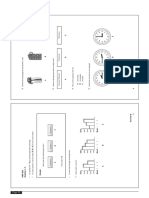
2 Name the type of classification used in the following graph
(a)Quantitative (b) Qualitative (c) Chronological (d) Spatial
3 There are two class interval 0-10 and 10-20 , if a student score 10 marks then he should be included in which
class interval
(a)10-20 (b)Not be included in these intervals (c)Both the 0-10 and 10-20 (d) 0-10
4 Identify the type of variable from the following table
(a) Continuous (b) Discrete (c) Individual (d) None
5Classification like male-female, healthy-unhealthy, educated-uneducated are example of
(a) Dichotomy (b) Manifold (c) Both (d) None
6 From the set of statements given in Column -I and Column II , Choose the correct pair
Column I Column II
a Open end series (i)There is gap between lower limit of a class interval and the upper limit of
the next class interval
b Exclusive series (ii)Upper limit of the class interval is not included
c Frequency Array (iii)upper limit of the last class interval is not given
d Inclusive series (iv)arrangement of discrete variable in ascending order
(a) a-(i) (b) b-(ii) (c) – c (iii) (d)- d(iv)
7 For the mid values given :25,34,43,52,61,70
(a)25-34 (b)24.5-34.5 (c)20-30 (d) 20.5-29.5
8 If Mux of X is 50 and Muy of Y is 40, if the price of Y is RS 8 Then Price of X at equilibrium will be……..
(a) 12 (b) 10 (c) 16 (d) 8
9 A consumer in consumption of two commodities A and B is at equilibrium . The price of A and B are Rs 10
and Rs 20 respectively and Marginal Utility of product A and B is 50 what will be the marginal utility of
Product A
(a)100 (b) 25 (c )250 (d)4
10 Maya derives total utility of 10 utils after having 4 mangoes and total utility on consuming 5 mangoes is 9
what is her marginal utility for the 5th mango
(a) +1 (b) 0 utils (c) -1 (d) 9 utils
11 Given below is the utility schedule of a consumer for commodity X. The price of commodity is Rs 3 per
unit. How many units should the consumer purchase to maximize his satisfaction assuming marginal utility of a
rupee is equal to 2 Units of commodity 1 2 3 4 5 6
Total utility 10 18 25 31 34 34
Marginal utility 10 8 7 6 3 0
(a) 6 (b) 4 (c) 5 (d) 3
12 A consumer consumes only two goods X and Y whose prices are 3Rs and 4 Rs Per unit respectively, if the
consumer chooses a combination of two goods with marginal utility of X equal to 4 and that of Y equal to 3, is
the consumer in equilibrium, then the consumer will
(a) Buy more units of both X and Y (b) Buy more units of Y and less of X
(c ) Buy more units of X and Less of Y (d) Buy less of both X and Y
13 Suppose Mayank consumes Burger and Garlic Bread. Which of the following bundle of Burger and Garlic
Bread will Mayank choose if he has monotonic preferences?
(a)Bundle A(5,7) (b)Bundle B(4,7) (c)Bundle C(5,6) (d) None of these
14 A consumer consumes only two goods if price of one of the good falls the indifference curve :
(a) Shifts upward (b) shifts downward (c) can shift both upwards or downwards (d)does not shift
15 A consumer spends his entire income on consumption of two goods X and Y ,If the price of good X rises
slope of budget line will be
(a)Fall (b)Rise (c)Remains constant (d)None of these
16 What will be the impact on budget line of a consumer , keeping other things constant , if price of good X
falls
(a)Shifts inward (b) Shifts outwards (c ) Rotate inwards on the X axis (d)Rotate outwards on the X axis
17 Indifference set shows different combinations of two goods that give consume the .............level of
satisfaction , the consumer is ...................among all these combinations
(a)Different , different (b)Same , indifferent (c)Indifferent , different (d)None of these
18 TU is derived as …………………
(a)TU=∑MU (b) TU= MU1+MU2+MU+3………MUN (c)Both a and b (d)None of these
19 Marginal utility is always ….
(a)positive (b)negative
(c) can be positive or negative but cannot be zero (d) can be positive or negative or zero
20 Law of diminishing marginal utility states that as more and more units of a commodity is consumed
marginal utility…..
(a)Begins to increase (b) remains constant (c) begins to decrease d) none of these
21 If MUX is Graeter than MUY then consumption of ……………
Px PY
(a)X will fall and Y will increase (b)X will rise and Y will fall
(c)X and Y both will fall (d)X and Y both will rise
22 From the following data how much percent of persons are earning more than Rs 1499
Income in Rs No of persons
500-999 15
1000-1499 28
1500-1999 36
2000-2499 7
(a) 50% (b)45% (c) 40% (d) 60%
23 Find the number of observations between 250-300 from the following data:
Value No of observations
more than 200 56
more than 250 38
more than 300 15
more than 350 0
(a) 56 (b)23 (c) 15 (d) 8
24 Read the following statements: Assertion and Reason. Choose one of the correct alternatives given below:
Assertion(A)Marginal utility can never be negative
Reason (R) Total utility is maximum when marginal utility is zero
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are True and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are True and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is True but Reason (R) is False.
(d) Assertion (A) is False but Reason (R) is True.
25 Read the following statements: Assertion and Reason. Choose one of the correct alternatives given below:
Assertion(A)An indifference curve is always convex to the origin
Reason (R) MRS is always diminishing because of law od diminishing marginal utility
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are True and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are True and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is True but Reason (R) is False.
(d) Assertion (A) is False but Reason (R) is True.
You might also like
- Multiple Choice Test Bank Questions No Feedback - Chapter 1Document47 pagesMultiple Choice Test Bank Questions No Feedback - Chapter 1Đức NghĩaNo ratings yet
- Ubc 1973Document700 pagesUbc 1973adfadNo ratings yet
- Intraday Trading Techniques, Formula & Tricks - 100% ProfitableDocument9 pagesIntraday Trading Techniques, Formula & Tricks - 100% Profitableharishvasanth198278% (9)
- Practice Midterm 2Document12 pagesPractice Midterm 2Marcia Sharpe WilsonNo ratings yet
- 11 Economics, (English Medium), QPDocument11 pages11 Economics, (English Medium), QPNandiniNo ratings yet
- Xi Eco Comprehensive Assignment 2024Document5 pagesXi Eco Comprehensive Assignment 2024navnoorsingh582No ratings yet
- Xi Eco 2023Document4 pagesXi Eco 2023sindhuNo ratings yet
- Economics Sample Papers IVDocument5 pagesEconomics Sample Papers IVMaithri MurthyNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Consumer's Equilibrium and Demand Multiple Choice Questions: Choose The Correct AnswerDocument37 pagesQuestion Bank Consumer's Equilibrium and Demand Multiple Choice Questions: Choose The Correct AnswerJayant VijanNo ratings yet
- Paper:4 Mock Test-5 MARKS:100Document16 pagesPaper:4 Mock Test-5 MARKS:100Ayathii EducareNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Grade 11Document9 pagesSample Paper Grade 11Varshni ShreeNo ratings yet
- Only Microeconomics Question Bank-FinalDocument39 pagesOnly Microeconomics Question Bank-Finalanugya jainNo ratings yet
- ! - Statistics Test PYQs 2 SolutionDocument50 pages! - Statistics Test PYQs 2 Solutionvishmon09041104No ratings yet
- Eco Annual Revision Worksheet 2023-24Document6 pagesEco Annual Revision Worksheet 2023-24Reuel MathewsNo ratings yet
- Economics-XI-Set ADocument15 pagesEconomics-XI-Set AAkshad AroraNo ratings yet
- PB Paper DoneDocument8 pagesPB Paper Donepriyanshi.bansal25No ratings yet
- Eco Test SamplePaperDocument6 pagesEco Test SamplePaperSadaf TalmizNo ratings yet
- 11std Economics QPDocument8 pages11std Economics QPpatel13005No ratings yet
- Economics Sample Papers IIIDocument5 pagesEconomics Sample Papers IIIMaithri MurthyNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Sample Papers Economics 2023 1 PDFDocument5 pagesClass 11 Sample Papers Economics 2023 1 PDFMaithri MurthyNo ratings yet
- 11th Final Exam 2023 Set 3Document3 pages11th Final Exam 2023 Set 3Yash NagpureNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Ashoka University Ma Economics Entrance ExaminationDocument10 pagesInstructions: Ashoka University Ma Economics Entrance ExaminationJayesh RaghuwanshiNo ratings yet
- Bharat Ratna Dr. B.R. Ambedkar University, Delhi School of Liberal Studies Entrance Test 2015-16 MA EconomicsDocument18 pagesBharat Ratna Dr. B.R. Ambedkar University, Delhi School of Liberal Studies Entrance Test 2015-16 MA EconomicsBidishaNo ratings yet
- Practice Problem Set 2 With AnswersDocument12 pagesPractice Problem Set 2 With AnswersJoy colabNo ratings yet
- Economics XiDocument10 pagesEconomics XiAllwin GanaduraiNo ratings yet
- Part A - Statistics For Economics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument8 pagesPart A - Statistics For Economics Multiple Choice QuestionsNimay KumarNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Sample Papers Economics 2023 3Document4 pagesClass 11 Sample Papers Economics 2023 3NeerajNo ratings yet
- Economics Sample Papers IDocument4 pagesEconomics Sample Papers IPARI BHADHAURIANo ratings yet
- MA - Economics - 2014Document20 pagesMA - Economics - 2014Yasoda KumariNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics 1 Final ReviewDocument12 pagesMicroeconomics 1 Final ReviewCảnh Dương100% (1)
- Ca Foundation Question Paper May 2019 PDFDocument9 pagesCa Foundation Question Paper May 2019 PDFaslam firdosNo ratings yet
- IEO Samplepaper Second Year All-StreamsDocument6 pagesIEO Samplepaper Second Year All-StreamssusheelgadaleyNo ratings yet
- Test Series: October, 2018 Foundation Course Mock Test Paper - 2 Paper - 4: Business Economics and Business and Commercial Knowledge Part I: Business Economics Max. Marks: 60 QuestionsDocument16 pagesTest Series: October, 2018 Foundation Course Mock Test Paper - 2 Paper - 4: Business Economics and Business and Commercial Knowledge Part I: Business Economics Max. Marks: 60 QuestionsKolkataKnightNo ratings yet
- 9-7-23 f130 cf-3630 Stats QueDocument6 pages9-7-23 f130 cf-3630 Stats Queindian kingNo ratings yet
- Ca Foundation Business Economics Additional Question PaperDocument9 pagesCa Foundation Business Economics Additional Question PaperSushant TaleNo ratings yet
- Cpet21 Economics Set1Document14 pagesCpet21 Economics Set1Yashodharma SinghNo ratings yet
- Econ, Sample Exam 270Document8 pagesEcon, Sample Exam 270VivienNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument4 pagesEconomicsFukra GamerNo ratings yet
- 8sec IDocument11 pages8sec IMonaliMadhulitaNo ratings yet
- Tancet (Mca) : Mock Test - IiDocument10 pagesTancet (Mca) : Mock Test - IiKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Business LawDocument9 pagesBusiness Lawj.nikhiltrader01No ratings yet
- Test Series: June, 2022 Mock Test Paper 2 Foundation Course Paper 4: Business Economics and Business and Commercial Knowledge Part-I: Business Economics QuestionsDocument15 pagesTest Series: June, 2022 Mock Test Paper 2 Foundation Course Paper 4: Business Economics and Business and Commercial Knowledge Part-I: Business Economics QuestionsShrwan SinghNo ratings yet
- 5B. Problems in PrelimnariesDocument6 pages5B. Problems in PrelimnariesANANTHARAJ BNo ratings yet
- State Level Statistics Revision TestDocument15 pagesState Level Statistics Revision TesttafcentralstudentsNo ratings yet
- Maths 1,2,3,9,13Document3 pagesMaths 1,2,3,9,13Ankit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- TSS - Grade11 - Economics Term-2 (2023-24) Revision SheetDocument5 pagesTSS - Grade11 - Economics Term-2 (2023-24) Revision Sheetastro gamerNo ratings yet
- Statistics - 10 Yr Pyq'sDocument137 pagesStatistics - 10 Yr Pyq'sVinayakNo ratings yet
- Maths Stats EM Question 08.11.23Document16 pagesMaths Stats EM Question 08.11.23Ravi BhanuNo ratings yet
- Eco. & BCK QP (23.5.23)Document10 pagesEco. & BCK QP (23.5.23)ajanushkajain1234No ratings yet
- STA2023 Exam ReviewDocument19 pagesSTA2023 Exam ReviewdhfbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Part 2Document17 pagesChapter 4 - Part 2dylanNo ratings yet
- M. Com Admission Test QP (Marketing)Document7 pagesM. Com Admission Test QP (Marketing)Sattick AdhikaryNo ratings yet
- CFN 9256 Maths, Logical Reasoning & Stats QUESTION PAPERDocument5 pagesCFN 9256 Maths, Logical Reasoning & Stats QUESTION PAPERvishwasiddharthan04No ratings yet
- Business Statistics Question Bank Send Up (2022-23)Document8 pagesBusiness Statistics Question Bank Send Up (2022-23)Stephen JonesNo ratings yet
- Eco - BCK Prelim Solution 5-12-23Document9 pagesEco - BCK Prelim Solution 5-12-23roshanchoudhary4350No ratings yet
- Eco2003f - Supp Exam - 2010 PDFDocument12 pagesEco2003f - Supp Exam - 2010 PDFSiphoNo ratings yet
- JNU MA ECO PYQ 2014-21 by NviNomicsDocument147 pagesJNU MA ECO PYQ 2014-21 by NviNomicsniharikayadav1102No ratings yet
- Economics MCQ'SDocument9 pagesEconomics MCQ'Sgpatil1356No ratings yet
- MCQs CH 15 MicroDocument6 pagesMCQs CH 15 MicroishtiaqlodhranNo ratings yet
- Xi - Economics - Model PaperDocument6 pagesXi - Economics - Model Papermitrasupratik42No ratings yet
- dPP1 1Document12 pagesdPP1 1akshitwalia209No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument13 pagesAssignmentabdur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Mudra: Amity Business SchoolDocument4 pagesMudra: Amity Business SchoolShubhangi RaiNo ratings yet
- HR MaltaDocument3 pagesHR MaltaHittMan BajgainNo ratings yet
- Yadadri Bhuvanagiri - Bommalaramaram - MPPS Thimmapuram - 36200700102 - P200700102 - 20231109 - 000006 - Green Chalk BoardsDocument2 pagesYadadri Bhuvanagiri - Bommalaramaram - MPPS Thimmapuram - 36200700102 - P200700102 - 20231109 - 000006 - Green Chalk BoardsdurgaprasadNo ratings yet
- Bank Ganesha TBKDocument3 pagesBank Ganesha TBKTam sneakersNo ratings yet
- Real-Estate Transactions in Knox County: February 28, 2021Document1 pageReal-Estate Transactions in Knox County: February 28, 2021register-mailNo ratings yet
- ALE Sample Paper Listening BEC para RotarDocument7 pagesALE Sample Paper Listening BEC para RotarmariainesboniverNo ratings yet
- Advanced - L6 SsDocument5 pagesAdvanced - L6 SsXuan HoangNo ratings yet
- On Tap - KTQT 2-2023Document47 pagesOn Tap - KTQT 2-2023TRINH BÙI THỊ TUYẾTNo ratings yet
- Trade CycleDocument4 pagesTrade CycleRashi BishtNo ratings yet
- NSTP Proj. ProposalDocument3 pagesNSTP Proj. Proposalalegarbes PatNo ratings yet
- 0.50mm, 0.60mm, 0.69mm and 0.86mm: Technical DatasheetDocument1 page0.50mm, 0.60mm, 0.69mm and 0.86mm: Technical Datasheetxiping dingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3, Cost AllocationDocument9 pagesChapter 3, Cost AllocationDEREJENo ratings yet
- ACE Agreement 3: Design and ConstructDocument31 pagesACE Agreement 3: Design and Constructmohamed_gameel_3No ratings yet
- Forecastingch3-1921 FallDocument70 pagesForecastingch3-1921 FallDizzycheese2234No ratings yet
- Scrubmaster B70CL Instruction ManualDocument42 pagesScrubmaster B70CL Instruction Manualabdelkader namaniNo ratings yet
- Engagement Letter - TRANSFER OF TITLEDocument1 pageEngagement Letter - TRANSFER OF TITLEAinah Rae Labanta-BanzonNo ratings yet
- Analyzing The Balance of Payment Position of India: June 2017Document15 pagesAnalyzing The Balance of Payment Position of India: June 2017Veer KohliNo ratings yet
- Insulating Floors With StyrofoamDocument23 pagesInsulating Floors With StyrofoamSteven SebastianNo ratings yet
- European Spot Gas Markets-05-Jan-2021Document18 pagesEuropean Spot Gas Markets-05-Jan-2021Tihomir RoščićNo ratings yet
- CI Signed JP54 ROI-LFDocument3 pagesCI Signed JP54 ROI-LFPT. Inti Maritim SekawanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Influence of Knowledge Management and Lean Management On The Performance of Construction ProjectsDocument8 pagesAnalysis of The Influence of Knowledge Management and Lean Management On The Performance of Construction ProjectsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- SSC Filters o & M ManualDocument25 pagesSSC Filters o & M ManualRamesh arumugamNo ratings yet
- Report ElectrodesDocument12 pagesReport Electrodesrian1099No ratings yet
- Project Report ON MR - Shamiulla Kalander: Purchase of MachineryDocument12 pagesProject Report ON MR - Shamiulla Kalander: Purchase of MachineryGangadhara PVNo ratings yet
- C. Castro Company-Cdc 2018Document42 pagesC. Castro Company-Cdc 2018Gennelyn Lairise Rivera100% (1)
- Dusty EconomicDocument13 pagesDusty EconomicInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- ARC8421 260 LMoran - FoundationDocument1 pageARC8421 260 LMoran - FoundationLeyla MoranNo ratings yet