Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earthquakes
Uploaded by
Swiftie0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesEarthquakes
Uploaded by
SwiftieCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Earthquakes
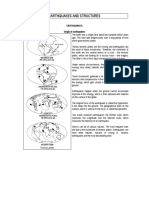
An earthquake is the vibrations of the earth’s surface that follow a release of
energy in the earth’s crust.
An earthquake occurs when the stresses/pressure caused by plate movements are
released.
Most earthquakes occur at the circum-pacific plate boundary.
The point at which 2 plates meet is called a focus. When they meet they release
energy that comes in the form of vibrations known as seismic waves. The point
directly above the focus is called the epicenter.
The Richter scale is how earthquakes are measured. It is a scale of 0-10 with 10 being the
highest, causing absolute destruction with 0 chances of survival.
Dealing with earthquakes:
● Better forecasting and monitoring of crustal movements
● Earthquake proof building designs
● Emergency procedures
Impact of earthquakes depends on:
● Strength of earthquake
● Number of aftershocks
● Population density
● Type of building (eg hut vs. skyscraper)
● Time of day (night has less people, day has more)
● Types of rock + sediments
● Distance from epicenter
● Secondary hazards (landslides, tsunamis)
Earthquake-proof building designs (single storey house):
● Hollow, concrete brick (prevents damage)
● Roof built with concrete cement
● House is slightly elevated (foundations are slightly above the ground to prevent
contact with vibrating surface)
● Foundation is made from stone
● Foundations are multiple (vibrations are divided amongst the foundations, absorb
shock waves and less vibrations reach the house)
● Steel reinforcements in foundations (allows flexibility so that the steel vibrates
with the ground and no cracks appear)
Earthquake-proof building designs (tall building):
● Cross-bracing (reinforce walls using two steel beams)
● Shock absorbers/base isolators (absorb tremors and vibrations of earthquakes)
● Shear walls (concrete walls with steel bars in them to reduce rocking movements)
● Hollow bricks (if the walls fall the hollow bricks will not cause as much damage)
You might also like
- Seismic Design PrinciplesDocument21 pagesSeismic Design PrinciplesmaheshNo ratings yet
- Design of Earthquake Resistant StructuresDocument25 pagesDesign of Earthquake Resistant StructuresVinod Kumar A100% (2)
- Earthquake Resistant Building StructuresDocument6 pagesEarthquake Resistant Building StructuresShubhayu DuttaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistance StructuresDocument17 pagesEarthquake Resistance StructuresphanikanthreddyNo ratings yet
- A Project Report OnDocument35 pagesA Project Report OnAshokupadhye1955No ratings yet
- Unit II: Earthquake Disaster MitigationDocument106 pagesUnit II: Earthquake Disaster Mitigationgdevi80No ratings yet
- Presentation ON EarthquakeDocument39 pagesPresentation ON EarthquakeRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- EARTHQUAKE - NotesDocument11 pagesEARTHQUAKE - NotesSrushti NaikNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant StructuresDocument19 pagesEarthquake Resistant StructuresBharath Kumar H RNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant StructuresDocument35 pagesEarthquake Resistant StructuresRon Vora0% (1)
- Seminar Project 2nd Part Earthquake Resisting BuildingDocument31 pagesSeminar Project 2nd Part Earthquake Resisting BuildinganimeshranjandhnNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Design CoceptsfinalDocument102 pagesEarthquake Design CoceptsfinalrenukaNo ratings yet
- Mamush Chapter2Document74 pagesMamush Chapter2ebirahimmusanNo ratings yet
- Disaster Resistant ArchitectureDocument78 pagesDisaster Resistant ArchitectureSurbahon Rajkumar100% (1)
- Repair Rehabilitation and RetrofittingDocument151 pagesRepair Rehabilitation and RetrofittingvempadareddyNo ratings yet
- Tips To Design Earthquake Resistant Building - Jean-Rayner KuswadiDocument40 pagesTips To Design Earthquake Resistant Building - Jean-Rayner KuswadiMae Lingan-LasqueroNo ratings yet
- Lesson Notes EarthquakesDocument2 pagesLesson Notes EarthquakesmttaibNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistent Building ConstructionDocument10 pagesEarthquake Resistent Building ConstructionSrinivas Gowda MNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Lecture 3Document10 pagesEarthquake Lecture 3Abdullah ZubairNo ratings yet
- KS2 MVE EarthquakesFactsheetforteachers-6Document4 pagesKS2 MVE EarthquakesFactsheetforteachers-6hamid hussainNo ratings yet
- Ground ShakingDocument2 pagesGround ShakingjarveyjamespiamonteNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING PDFDocument9 pagesLecture 1 INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING PDFowaisNo ratings yet
- Geography PDFDocument8 pagesGeography PDFmugdha raiNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes: Earthquake HazardDocument30 pagesEarthquakes: Earthquake HazardMuhammad Moaz ArshadNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument3 pagesEarthquakeMuhammad ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Earth Quake Resistant Design and Disaster Management: Class 1Document20 pagesEarth Quake Resistant Design and Disaster Management: Class 1Linas FathimaNo ratings yet
- M Tech Presentation 2Document17 pagesM Tech Presentation 2dheerajbhawar786No ratings yet
- Assignment - 4 Sakshi SharmaDocument5 pagesAssignment - 4 Sakshi SharmaSakshi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Construction Techniques: Submitted To:-Submitted By: - Manjeet Singh 17020100005Document34 pagesEarthquake Construction Techniques: Submitted To:-Submitted By: - Manjeet Singh 17020100005Manjeet CinghNo ratings yet
- GeologyDocument1 pageGeologyduguiesjNo ratings yet
- Chapter #15: Seismic Proof ConstructionDocument17 pagesChapter #15: Seismic Proof ConstructionM.IDREES KhanNo ratings yet
- S.L.Kunalan V.Manivannan: (Ii - Year / Iv Semester) Department of Civil EngineeringDocument11 pagesS.L.Kunalan V.Manivannan: (Ii - Year / Iv Semester) Department of Civil Engineeringgsudhanta1604No ratings yet
- Lecture 02 EarthqaukesDocument72 pagesLecture 02 Earthqaukesahmad hassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Earth QuakeDocument37 pagesChapter Four: Earth QuakeYomif BokuNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design PrinciplesDocument10 pagesSeismic Design PrinciplesVenkata Raju KalidindiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document43 pagesChapter 3Sintayehu DemekeNo ratings yet
- Effect of Earth Quake On RCC Buildings in Seismic ZonesDocument13 pagesEffect of Earth Quake On RCC Buildings in Seismic Zonesfaisal saifNo ratings yet
- How Earthquake-Resistant Buildings WorkDocument2 pagesHow Earthquake-Resistant Buildings WorkAlista Yuchun AbrianiNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document26 pagesPart 1hsnaterNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant BuildingDocument36 pagesEarthquake Resistant Buildingsai projectNo ratings yet
- Earthquake-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesEarthquake-WPS OfficeveroncardodelvalleNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes: Bio 1 - Lesson 6 Earth ScienceDocument8 pagesEarthquakes: Bio 1 - Lesson 6 Earth SciencePaul Omar PastranoNo ratings yet
- What Is Earthquake?: Why Do Earthquakes Happen?Document7 pagesWhat Is Earthquake?: Why Do Earthquakes Happen?Derick DelacruzNo ratings yet
- 02 Earthquakes and StructuresDocument7 pages02 Earthquakes and StructuresVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- What Is An Earthquake?Document6 pagesWhat Is An Earthquake?Shardul JoshiNo ratings yet
- 11-28-12 Earthquakes and StructuresDocument2 pages11-28-12 Earthquakes and StructuresasdNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument10 pagesEarthquakeBakhtyir muhamadNo ratings yet
- Seminar On "Earthquake Resistant Building Construction": Submitted By:-Amir HussainDocument26 pagesSeminar On "Earthquake Resistant Building Construction": Submitted By:-Amir Hussainwajid ahmadNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Power PointDocument25 pagesPlate Tectonics Power PointLory Grace TorresNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes & SocietyDocument29 pagesEarthquakes & SocietyGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Pandit Lakhmi Chand State University of Performing and Visual Arts, Rohtak Faculty of Urban Planning and ArchitectureDocument38 pagesPandit Lakhmi Chand State University of Performing and Visual Arts, Rohtak Faculty of Urban Planning and ArchitectureShubham Singh BishtNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument32 pagesEarthquakeRica Jewel VistaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant BuildimgsDocument16 pagesEarthquake Resistant Buildimgsharish guptaNo ratings yet
- ERD Lecture 2 Measurement of Earthquake.Document27 pagesERD Lecture 2 Measurement of Earthquake.sujan pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Analysis LectureDocument56 pagesEarthquake Analysis LecturehsnaterNo ratings yet
- Dynamic EarthDocument56 pagesDynamic EarthRavindr KumarNo ratings yet
- FAILURE OF FOUNDATION Presentation1Document13 pagesFAILURE OF FOUNDATION Presentation1Ma sajidNo ratings yet
- Farewell PilgrimageDocument3 pagesFarewell PilgrimageSwiftieNo ratings yet
- Mid Point WSDocument2 pagesMid Point WSSwiftieNo ratings yet
- Holy Prophet's Sickness and DemiseDocument2 pagesHoly Prophet's Sickness and DemiseSwiftieNo ratings yet
- Khyber ExpeditionDocument2 pagesKhyber ExpeditionSwiftieNo ratings yet
- Tabuk ExpeditionDocument2 pagesTabuk ExpeditionSwiftieNo ratings yet
- Battle of HunainDocument3 pagesBattle of HunainSwiftieNo ratings yet
- Battle of UhudDocument4 pagesBattle of UhudSwiftieNo ratings yet
- Tawhid AssignmentDocument2 pagesTawhid AssignmentSwiftie100% (1)
- Treaty of HudaibiyahDocument3 pagesTreaty of HudaibiyahSwiftieNo ratings yet
- Islamiat HZ Abu Bakr, Umar, UthmanDocument2 pagesIslamiat HZ Abu Bakr, Umar, UthmanSwiftieNo ratings yet
- Comma Splice and Fused Sentences WRKSHT 1Document5 pagesComma Splice and Fused Sentences WRKSHT 1SwiftieNo ratings yet
- Percentage (Chapter 8) Book 1 Reverse Percentages (Ref. Ex. 8B) Worksheet 4 Class VIIIDocument3 pagesPercentage (Chapter 8) Book 1 Reverse Percentages (Ref. Ex. 8B) Worksheet 4 Class VIIISwiftieNo ratings yet
- Comma Splice and Fused Sentences WRKSHT 2Document4 pagesComma Splice and Fused Sentences WRKSHT 2SwiftieNo ratings yet