Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Allergic Rhinitis Patho
Uploaded by
Ace Fabrigas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesAllergic rhinitis is caused by an allergic reaction to environmental allergens like pollen, dust, or animal dander. When a sensitized person is exposed to an allergen, it leads to inflammation and increased production of mucus in the nasal passages, causing symptoms like sneezing, nasal congestion, and runny nose. If left untreated, allergic rhinitis can lead to complications like asthma, sinusitis, and ear infections. Treatment involves avoidance of allergens when possible and medications like antihistamines, decongestants, nasal corticosteroids, and immunotherapy to reduce symptoms. Nursing care focuses on proper use of medications, monitoring for complications, educating patients on
Original Description:
Original Title
Allergic-Rhinitis-Patho
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAllergic rhinitis is caused by an allergic reaction to environmental allergens like pollen, dust, or animal dander. When a sensitized person is exposed to an allergen, it leads to inflammation and increased production of mucus in the nasal passages, causing symptoms like sneezing, nasal congestion, and runny nose. If left untreated, allergic rhinitis can lead to complications like asthma, sinusitis, and ear infections. Treatment involves avoidance of allergens when possible and medications like antihistamines, decongestants, nasal corticosteroids, and immunotherapy to reduce symptoms. Nursing care focuses on proper use of medications, monitoring for complications, educating patients on
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesAllergic Rhinitis Patho
Uploaded by
Ace FabrigasAllergic rhinitis is caused by an allergic reaction to environmental allergens like pollen, dust, or animal dander. When a sensitized person is exposed to an allergen, it leads to inflammation and increased production of mucus in the nasal passages, causing symptoms like sneezing, nasal congestion, and runny nose. If left untreated, allergic rhinitis can lead to complications like asthma, sinusitis, and ear infections. Treatment involves avoidance of allergens when possible and medications like antihistamines, decongestants, nasal corticosteroids, and immunotherapy to reduce symptoms. Nursing care focuses on proper use of medications, monitoring for complications, educating patients on
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
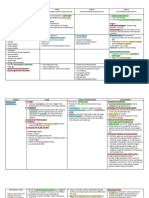
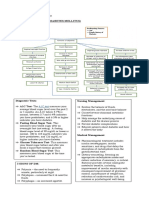
Allergic Rhinitis
Etiology: Disease Process: Signs and Symptoms:
Predisposing factors
Allergen Exposure
• Red itchy swollen eyes
• Genetics ↓
• Sneezing
• Age
• Runny nose
• Sex Allergy Sensitization
• Nasal congestion
• Female Gender ↓
• Family History
Increase IgE
• Birth during the pollen Allergic rhinitis can affect
season ↓ quality of life by also
Mast Cells producing fatigue, loss of
↓ sleep, and poor concentration.
Precipitating factors
• Exposure to Inflammatory
environmental Mediators Laboratory/
allergen Diagnostics:
(pollen,dust,animal
hair, molds spores) • Nasal smears,
Local Increase
• Presence of allergens
Trigeminal
of mucous • RAST
Inflammation Nerve
IgE glands (Radioallergo
• Exposure to smoking secretion sorbent test)
• Bacterial or viral • peripheral
infection blood counts,
• Food allergy If not treated: If treated: • total serum
IgE,
• epicutaneous
Prognosis: Nursing Management: and
intradermal
If left untreated, many • Improving breathing testing,
complications may result, such pattern • food
as allergic asthma, chronic nasal • Promoting elimination
obstruction, chronic otitis media understanding of allergy and
with hearing loss, anosmia and allergy control challenge,
(absence of the sense of smell), • Coping with a chronic • and nasal
and, in children, orofacial dental disorder provocation
deformities. Early diagnosis and • Monitoring and tests.
adequate treatment are essential managing potential
to reduce complications and complications
relieve symptoms. • Promoting home and
community based care
• Identify the patient’s
known allergens (eg,
medications,foods,
insects, environmental
allergens).
• • Describe the patient’s
typical allergic reaction
and its severity.
• Document the patient’s
Management: allergies (eg, medications,
Medical Management foods, insects, environmental
allergens) in the patient’s
The goal of therapy is to medical record.
provide relief of symptoms.
Therapy may include one or all • Post allergy alerts
of the following interventions: appropriately.
Avoidance therapy use of air • Encourage the patient to wear
conditioners, air cleaners, a medical alert band and to
humidifiers, removal of dust carry information about
catching furnishings, carpets allergies at all times.
and window coverings, removal • Monitor the patient closely
of pets from the home or after administration of new
bedroom use of pillow and medications and exposure to
mattress covers that are new foods, contrast agents,
impermeable to dust mites and a latex, and other allergens.
smoke free environment
• Investigate potential for
Pharmacotherapy: allergic reactions with all new
Antihistamines are the major medications through
class of medications prescribed consultation with the
for the symptomatic relief of pharmacist.
allergic rhinitis.
• Instruct the patient to question
Adrenergic agents: all medications and new foods.
Adrenergic agents, • Identify early manifestations
vasoconstrictors of mucosal of allergic reactions.
vessels, are used topically (nasal
and ophthalmic formulations) in • Administer emergency
addition to the oral route. treatment for allergic reactions.
Mast cell stabilizers: • Monitor the patient’s response
and status for
Intranasal cromolyn sodium
(NasalCrom) is a spray that acts 12–14 hours after a severe
by stabilizing the mast cell allergic reaction.
membrane, thus reducing the • Instruct the patient and family
release of histamine and other about emergency home
mediators of the allergic management of allergic
response. reaction.
Corticosteroids: • Instruct the patient and family
Intranasal corticosteroids are about avoidance measures to
indicated in more severe cases reduce risk of exposure to
of allergic and perennial rhinitis allergens.
that cannot be controlled by
more conventional medications
such as decongestants,
antihistamines, and intranasal
cromolyn.
Leukotriene Modifiers: Prioritized Problem/Nursing
Diagnosis:
As previously discussed,
leukotrienes have many effects Ineffective breathing pattern
on the inflammatory cycle. related to allergic reaction
Leukotriene modifiers, such as
zileuton
(Zyflo), zafirlukast (Accolate),
and montelukast (Singulair),
block the synthesis or action of
leukotrienes and prevent the
signs and symptoms associated
with asthma
And Immunotherapy:
Allergen desensitization
(allergen immunotherapy,
hyposensitization) is primarily
used to treat IgE-mediated
diseases by injections of
allergen extracts.
Immunotherapy,also referred to
as allergy vaccine therapy,
involves the administration of
gradually increasing quantities
of specific allergens to the
patient until a dose is reached
that is effectivein reducing
disease severity from natural
exposure
You might also like
- Nursing Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument14 pagesNursing Fluids and Electrolytesaga1028100% (18)
- Psychiatric Nursing Ebook 8th Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Ebook 8th Edition Ebook PDFcarey.sowder235100% (39)
- Acute and Chronic SinusitisDocument39 pagesAcute and Chronic SinusitissuciNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Crisis PathoDocument4 pagesHypertensive Crisis PathoJanelle Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Treatment Dysarthria EfficacyDocument12 pagesTreatment Dysarthria EfficacySwathi GeethaNo ratings yet
- Coovadias Paediatrics and Child Health 7eDocument1,170 pagesCoovadias Paediatrics and Child Health 7eCuthbert Tinotenda Musarurwa90% (10)
- NUTRITIONAL NEEDS OF CRITICALLY ILL CHILD SanthoshDocument21 pagesNUTRITIONAL NEEDS OF CRITICALLY ILL CHILD SanthoshSanthosh.S.U100% (1)
- Biology GK Questions Answers MCQDocument18 pagesBiology GK Questions Answers MCQAmy Lalringhluani100% (1)
- Case (Rhinitis Alergi) 2Document38 pagesCase (Rhinitis Alergi) 2christopherNo ratings yet
- OB MustKnowsDocument90 pagesOB MustKnowsHarlyn MagsinoNo ratings yet
- System Disorder: Dermatitis and Acne: Atopic Dermatitis 57Document1 pageSystem Disorder: Dermatitis and Acne: Atopic Dermatitis 57Kassandra MerrillNo ratings yet
- Urticaria AngioedemaDocument19 pagesUrticaria AngioedemaIvan VeriswanNo ratings yet
- Immunology TA v.01 Paramita Mycomments v.01Document80 pagesImmunology TA v.01 Paramita Mycomments v.01Miral Sandipbhai MehtaNo ratings yet
- Food Allergy Concept MapDocument4 pagesFood Allergy Concept MapIzhra MargateNo ratings yet
- Hypersensitivity and Autoimmune DiseasesDocument5 pagesHypersensitivity and Autoimmune DiseasesJulia LipanaNo ratings yet
- 0 HypersenstivityDocument1 page0 HypersenstivityAshok KarvNo ratings yet
- Atopic Dermatitis, Allergic Rhinits, and Asthma: Tracie Kirkland, DNP, RN, ANP-BC, CPNPDocument19 pagesAtopic Dermatitis, Allergic Rhinits, and Asthma: Tracie Kirkland, DNP, RN, ANP-BC, CPNPNick flemmingNo ratings yet
- Allergic Rhinitis & Vasomotor Rhinitis: Dr. Ritesh Mahajan ENT Consultant GMC, KathuaDocument70 pagesAllergic Rhinitis & Vasomotor Rhinitis: Dr. Ritesh Mahajan ENT Consultant GMC, Kathuamanoj kumarNo ratings yet
- Etiology and Pathogenesis of Urticaria and AngioedemaDocument34 pagesEtiology and Pathogenesis of Urticaria and AngioedemaNUR NATHANIANo ratings yet
- Web 24 - Teti Madiadipoera - Treatment and Management of Rhinitis AllergyDocument38 pagesWeb 24 - Teti Madiadipoera - Treatment and Management of Rhinitis AllergyEdzhar HasiholanNo ratings yet
- Dr. Khairiyadi, M.Kes., Sp.A Departemen Ilmu Kesehatan Anak RSUD Ulin BanjarmasinDocument78 pagesDr. Khairiyadi, M.Kes., Sp.A Departemen Ilmu Kesehatan Anak RSUD Ulin BanjarmasinEldhaNo ratings yet
- Health7 Q4 W1-4-FinalDocument11 pagesHealth7 Q4 W1-4-FinalLouren Joy StylesNo ratings yet
- Allergology and ImmunologyDocument14 pagesAllergology and ImmunologyRea Dominique CabanillaNo ratings yet
- RhinitisDocument22 pagesRhinitisJo CanensNo ratings yet
- Allergy Diagnostics and Treatment 2022Document44 pagesAllergy Diagnostics and Treatment 2022Rohan TejaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Classification Mechanisms of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument9 pagesDrug Study: Classification Mechanisms of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesLloyd GalindoNo ratings yet
- Tata Laksana Rinitis Alergi Pada Dewasa FINALDocument27 pagesTata Laksana Rinitis Alergi Pada Dewasa FINALNikko Khairul DafaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7-Non Infection Rhino Disorder-Dr. Kartono Sudarman, SP - THT-KL (K) (2021)Document31 pagesLecture 7-Non Infection Rhino Disorder-Dr. Kartono Sudarman, SP - THT-KL (K) (2021)PutriNo ratings yet
- v13n3 CPG UpdateDocument7 pagesv13n3 CPG UpdateedfZSEADFsfsafafNo ratings yet
- Allergy Overview: - Nomenclature - Pathophysiology - Diagnosis - ManagementDocument96 pagesAllergy Overview: - Nomenclature - Pathophysiology - Diagnosis - ManagementPhaimNo ratings yet
- Allergic RhinitisDocument96 pagesAllergic Rhinitisnaveen05051996No ratings yet
- Angioedema Pod CastDocument10 pagesAngioedema Pod CastCritical Care 360No ratings yet
- Bactericidal Inhibits Cell Wall Mucopeptide Synthesis: CeftriaxonDocument4 pagesBactericidal Inhibits Cell Wall Mucopeptide Synthesis: Ceftriaxonzesty-merr-l-akut-9424No ratings yet
- CLIN-PHARM-LEC-Allergic-Rhinitis-transes_2Document5 pagesCLIN-PHARM-LEC-Allergic-Rhinitis-transes_2Yssah Moira HamacNo ratings yet
- Allergic Rhinitis: Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument59 pagesAllergic Rhinitis: Diagnosis and TreatmentYibeltalNo ratings yet
- Rhinitis Alergi DR - NikenDocument21 pagesRhinitis Alergi DR - NikenDayita ApritutiNo ratings yet
- Allergy: Presented By: Group 3Document22 pagesAllergy: Presented By: Group 3Ralp ManglicmotNo ratings yet
- Acneiform Rash PDFDocument5 pagesAcneiform Rash PDFDevana MaelissaNo ratings yet
- A Complete Ear, Nose and Throat (ENT) Examination Must Be Performed On All Patients With ARDocument2 pagesA Complete Ear, Nose and Throat (ENT) Examination Must Be Performed On All Patients With ARNoemiPelilaLay-osBetatNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Allergic RhinitisDocument11 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Allergic RhinitisJustineValJadeLacabaNo ratings yet
- 2-Viral GatroenteritisDocument16 pages2-Viral Gatroenteritisademabdella38No ratings yet
- Journal Reading Allergic RhinitisDocument39 pagesJournal Reading Allergic RhinitisBimaKharismaNo ratings yet
- AR IR by NRDocument96 pagesAR IR by NRnaveen05051996No ratings yet
- Type I HypersensitivityDocument4 pagesType I HypersensitivityFavour chinomsoNo ratings yet
- Coass II-Allergy RhinitisDocument77 pagesCoass II-Allergy RhinitisdnnivNo ratings yet
- Appropriate Allergic Testing and InterpretationDocument40 pagesAppropriate Allergic Testing and InterpretationEllenNo ratings yet
- AIDS - LifletsDocument2 pagesAIDS - LifletsJOki EstebanNo ratings yet
- Atopic Dermatitis and Allergies: Pediatric & Gastrointestinal PerspectiveDocument25 pagesAtopic Dermatitis and Allergies: Pediatric & Gastrointestinal PerspectiveHeni PurwaningsihNo ratings yet
- Allergic Rhinitis: Ahmed Shahab M08082Document23 pagesAllergic Rhinitis: Ahmed Shahab M08082Ahmed ShahabNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Allergy For Primary Care Clinicians: March 17, 2021Document58 pagesPaediatric Allergy For Primary Care Clinicians: March 17, 2021Naomi SargeantNo ratings yet
- pet-owner-parasite-screening-brochure-en-caDocument3 pagespet-owner-parasite-screening-brochure-en-capotatoonion1902No ratings yet
- The Basic Reaction of Hypersensitivity in Allergic DiseasesDocument51 pagesThe Basic Reaction of Hypersensitivity in Allergic DiseasesSherly Gunawan ZhangNo ratings yet
- Answered: Your Most Burning Questions About Eczema: BIO222: Immunology Maya Ballout ID: 20188034Document38 pagesAnswered: Your Most Burning Questions About Eczema: BIO222: Immunology Maya Ballout ID: 20188034Maya BalloutNo ratings yet
- bpj24 Hayfever Pages14-23Document10 pagesbpj24 Hayfever Pages14-23gaspe1999No ratings yet
- Food Allergy Manifestations and Atopic DermatitisDocument32 pagesFood Allergy Manifestations and Atopic DermatitisernitaNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Sir FedsDocument19 pagesCommunicable Disease Sir FedsHarold LinNo ratings yet
- Comorbidities and The Impact of Atopic Dermatitis: Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PHD, MPHDocument8 pagesComorbidities and The Impact of Atopic Dermatitis: Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PHD, MPHNabila MomorNo ratings yet
- Classifying Adverse Drug ReactionsDocument3 pagesClassifying Adverse Drug ReactionsVincent Joshua TriboNo ratings yet
- Metro Allergy Collateral LBLDocument2 pagesMetro Allergy Collateral LBLSnig KavNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Emmanual Pious 59 120 BATCHDocument12 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosus: Emmanual Pious 59 120 BATCHTobias AlanNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: M@Bile ScanneDocument1 pageGeneric Name:: M@Bile ScanneWinnie AriolaNo ratings yet
- Allergic Rhinitis: Yucheng YangDocument22 pagesAllergic Rhinitis: Yucheng YangNidya PutrijNo ratings yet
- Allergic RhinitisDocument22 pagesAllergic RhinitissuciNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument10 pagesConcept MapStephen Yor100% (1)
- DeBoer Bucharest Individual PatientDocument4 pagesDeBoer Bucharest Individual PatientGeorgianaGabrielaNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosage in Children 2Document12 pagesDrug Dosage in Children 2851BaEcoEve3 SxcNo ratings yet
- Allergic Rhinitis and RhinosinusitisDocument53 pagesAllergic Rhinitis and RhinosinusitisSinta FiraniNo ratings yet
- Treat Your Allergies NaturallyDocument18 pagesTreat Your Allergies NaturallyMiruna RomanNo ratings yet
- DeclarationDocument1 pageDeclarationAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Volunteer ConsentDocument1 pageVolunteer ConsentAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Volunteer ConsentDocument1 pageVolunteer ConsentAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Epi ReportDocument5 pagesEpi ReportAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Inp LasDocument3 pagesInp LasAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Medward Pe Sle Post Debridement of Fourniers GangreneDocument46 pagesMedward Pe Sle Post Debridement of Fourniers GangreneAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- NCM 118acase Analysis IV B2Document26 pagesNCM 118acase Analysis IV B2Ace FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Time FrameDocument1 pageTime FrameAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis & DiptheriaDocument20 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis & DiptheriaAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- FDAR Eclarinal 4 B5Document4 pagesFDAR Eclarinal 4 B5Ace FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Understand Dengue: Causes, Symptoms & PreventionDocument4 pagesUnderstand Dengue: Causes, Symptoms & PreventionAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ParacetamolDocument2 pagesDrug Study ParacetamolAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- NCP and Drug Study For Ob WardDocument7 pagesNCP and Drug Study For Ob WardAce Fabrigas100% (1)
- Prevent Bacterial Meningitis With VaccinesDocument9 pagesPrevent Bacterial Meningitis With VaccinesAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Diseases Causative Agent Signs and Symptoms (3) Mode of Transmission Incubation Period Nursing Intervention With Rationale (2) Preventive MeasuresDocument5 pagesDiseases Causative Agent Signs and Symptoms (3) Mode of Transmission Incubation Period Nursing Intervention With Rationale (2) Preventive MeasuresAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Risk For IneffectiveDocument6 pagesRisk For IneffectiveAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Gordon College: College of Allied Health StudiesDocument2 pagesGordon College: College of Allied Health StudiesAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ParacetamolDocument2 pagesDrug Study ParacetamolAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Endocrine: (Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus) : A1C TestDocument8 pagesEndocrine: (Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus) : A1C TestAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Risk Control Measures for Facility HazardsDocument2 pagesRisk Control Measures for Facility HazardsAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Allergic Rhinitis 1Document5 pagesAllergic Rhinitis 1Ace FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Table 2. Nurses' Preparedness For Disaster N % Organizations Considered Most Involved in Disastrous SituationsDocument6 pagesTable 2. Nurses' Preparedness For Disaster N % Organizations Considered Most Involved in Disastrous SituationsAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Onco, Endocrine, Gastrointestinal, Hepatobiliary, Immunologic DisordersDocument2 pagesOnco, Endocrine, Gastrointestinal, Hepatobiliary, Immunologic DisordersAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Good Foods For DiabeticsDocument1 pageGood Foods For DiabeticsAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Based on the description of the habitat containing coniferous trees, moss, lichen and cold climate location, the biome that a Hawk Owl lives in is the Tundra biomeDocument21 pagesBased on the description of the habitat containing coniferous trees, moss, lichen and cold climate location, the biome that a Hawk Owl lives in is the Tundra biomeAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- By Dr. B. Williams, Media SpecialistDocument27 pagesBy Dr. B. Williams, Media SpecialistAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Appendicitis: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Appendicitis: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Imaging Features of Pediatric Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictorial EssayDocument15 pagesImaging Features of Pediatric Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictorial EssayMarwin JouleNo ratings yet
- Perceived Awareness of Clozapine Associated With Socio - Demographic Status, Clinical, and Side Effect Profile Among Patients From Mental Health Hospital, Taif, Saudi ArabiaDocument8 pagesPerceived Awareness of Clozapine Associated With Socio - Demographic Status, Clinical, and Side Effect Profile Among Patients From Mental Health Hospital, Taif, Saudi ArabiaJAVED ATHER SIDDIQUINo ratings yet
- SCH - HLTH 6002 Rehabilitation Assessment 1 Case StudyDocument17 pagesSCH - HLTH 6002 Rehabilitation Assessment 1 Case StudyHimanshu Sappal100% (2)
- Nursing Assessment Template 01Document20 pagesNursing Assessment Template 01Endla SriniNo ratings yet
- A. Antineoplastic DrugsDocument48 pagesA. Antineoplastic DrugsKim Shyen BontuyanNo ratings yet
- Emotional DisturbanceDocument37 pagesEmotional DisturbanceAngelo MirabelNo ratings yet
- Ecg For The Exam-Score 2020Document17 pagesEcg For The Exam-Score 2020prasannasimhaNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors For Surgical Site InfectionDocument5 pagesRisk Factors For Surgical Site InfectionElizabeth Mautino CaceresNo ratings yet
- Three Men in A Boat AnswersDocument3 pagesThree Men in A Boat Answersmuneersn100% (3)
- Primary Level Care of MalariaDocument26 pagesPrimary Level Care of Malariaokwadha simionNo ratings yet
- 3.the Immune ResponseDocument135 pages3.the Immune ResponsebekaluNo ratings yet
- A4 Size MC3 Midterms ReviewerDocument9 pagesA4 Size MC3 Midterms ReviewerEl Grace EligedoNo ratings yet
- A. Complete Blood Count (CBC)Document6 pagesA. Complete Blood Count (CBC)raul nino MoranNo ratings yet
- 4 - PASTEST 2019 For MRCP2-Dr - Hisham Alshamekh - EndocrineDocument763 pages4 - PASTEST 2019 For MRCP2-Dr - Hisham Alshamekh - EndocrineYS NateNo ratings yet
- PPE-Conducted Partnership Appreciation and Other School Based Initiatives NarrativeDocument2 pagesPPE-Conducted Partnership Appreciation and Other School Based Initiatives NarrativeCarlz BrianNo ratings yet
- Sources of Epidemiological Data BoazDocument4 pagesSources of Epidemiological Data Boazgeorgeloto1288% (8)
- Classi Fications of Adverse Drug Reactions: 1. EidosDocument6 pagesClassi Fications of Adverse Drug Reactions: 1. Eidosdolemite4No ratings yet
- Tumor Flash Cards - Osteochondroma and Multiple Hereditary ExostosisDocument23 pagesTumor Flash Cards - Osteochondroma and Multiple Hereditary Exostosislaxge54No ratings yet
- Para Lab ReportDocument20 pagesPara Lab ReportSagayduro Xyrille Angel N.No ratings yet
- Soal Dan Jawaban Uas English For NurseDocument4 pagesSoal Dan Jawaban Uas English For Nurseahsan fillahNo ratings yet
- Bibliografia 2222Document28 pagesBibliografia 2222francivan111No ratings yet
- Oral Exam NotesDocument3 pagesOral Exam NotesDrumz StaffNo ratings yet