Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vitamin A and D Fat Soluble Vitamin
Uploaded by
Mini BossOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vitamin A and D Fat Soluble Vitamin
Uploaded by
Mini BossCopyright:
Available Formats
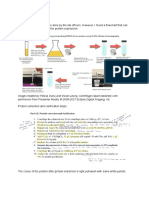
WHAT IS FAT SOLUBLE VITAMINS?
WHAT ARE THE VITAMINS?
-Vitamins are organic compounds that the body and diet both require in trace amounts. Instead
of providing a system of energy, vitamins take part in vital bodily functions. Every vitamin has
important, distinct metabolic roles. As an important nutrient, vitamins are required for supporting
life. To avoid illness and finally death, they must be consumed or acquired in some other way.
There is virtually little chance of having a deficiency in these vitamins or passing away. For the
sake of thoroughness, these vitamins will be covered in the conversation. Vitamin shortages of
all kinds can happen in cases of severe starvation, several disorders that cause poor
absorption, and alcoholism. For completeness' sake and for the benefit of those who are
interested, food sources of vitamins and RDAs are also provided. The two types of vitamins are
fat-soluble (A, D, E, and K) compounds.
EXPLANATION: a vitamin that will disintegrate in fats and oils. The body needs a minimal
amount of vitamins to function properly and remain healthy. The body stores fat-soluble vitamins
in the liver and fatty tissue, where they are absorbed together with dietary fats. Numerous meals
from plants and animals as well as nutritional supplements include them. Fat-soluble vitamins
include A, D, E, and K.
VITAMIN A
- As retinol and retinal, vitamins A contributes to the visual cycle, helps in the eyes' ability
to adapt to variations in light, and preserves the structure of the eye. The synthesis of
compounds in mucus, which is produced by epithelial tissue and maintains the moisture
of the skin, eyes, mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, and respiratory tract, depends
on vitamin A.
-
EX: While vitamin A has a number of purposes in the body, it is particularly crucial for
maintaining healthy mucous membranes, eyes, and skin. It can be found in dietary sources in a
preformed or active state (retinol, retinal, and retinoic acid) or as a precursor in the form of the
plant pigments known as carotenes.
VITAMIN D
- Change to a hormone that enhances calcium and phosphorus absorption,
- Kidney control over phosphorus excretion and mobilization of calcium from bone.
- Vitamin D may also affect how much citric acid is present in tissues and bones as well
as how much amino acid is present in blood.
EX: Chemically, vitamin D is known as cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3). It is essential for the
mineralization of bone and intestinal absorption of calcium and phosphorus. In the absence of
vitamin D, calcium cannot be absorbed. The impact of UV light on cholesterol in the skin can
spontaneously make vitamin D. Humans, with very few exceptions, do not need vitamin D if they
receive 10 to 15 minutes of average daily exposure to sunlight.
You might also like
- Fat-Soluble Vitamins A, D, E & K: Roles, Sources & ImportanceDocument33 pagesFat-Soluble Vitamins A, D, E & K: Roles, Sources & ImportanceDianzerShengNo ratings yet
- The Power of Food: How to Use Nutrition to Transform Your HealthFrom EverandThe Power of Food: How to Use Nutrition to Transform Your HealthNo ratings yet
- Project Report On VitaminsDocument7 pagesProject Report On Vitaminsmonica jain33% (3)
- A Presentation On: Presented byDocument67 pagesA Presentation On: Presented byOlufemi KolawoleNo ratings yet
- Vital Vitamins: Harnessing Nature's Power for Optimal Health and WellbeingFrom EverandVital Vitamins: Harnessing Nature's Power for Optimal Health and WellbeingNo ratings yet
- Fat and Water Soluble VitaminsDocument4 pagesFat and Water Soluble VitaminsAssignmentLab.comNo ratings yet
- All Metabolic Reactions That Use Proteins, Fats, and CarbohydratesDocument32 pagesAll Metabolic Reactions That Use Proteins, Fats, and Carbohydratesshannon c. lewisNo ratings yet
- VITAMINS - Essential Nutrients for Growth and DevelopmentDocument28 pagesVITAMINS - Essential Nutrients for Growth and DevelopmentMary Faith MadayagNo ratings yet
- Chapter SixDocument162 pagesChapter SixzyanabdullahNo ratings yet
- Vitamin&minerDocument10 pagesVitamin&minerChandu SekharNo ratings yet
- AkarDocument8 pagesAkarakar.c14936863No ratings yet
- Good Source of NutrientsDocument8 pagesGood Source of NutrientsKaye Angeli TanNo ratings yet
- Fat Soluble VitaminsDocument8 pagesFat Soluble VitaminsmariahNo ratings yet
- Topic 10. Fat-Soluble Vitamins. Antioxidants.Document11 pagesTopic 10. Fat-Soluble Vitamins. Antioxidants.Manar BehiNo ratings yet
- Health EducationDocument23 pagesHealth EducationdinirajNo ratings yet
- 4.1: Vitamins: Vital Dietary ComponentsDocument11 pages4.1: Vitamins: Vital Dietary ComponentsMAZIMA FRANKNo ratings yet
- Essential Nutrients: Types, Roles and Importance of VitaminsDocument17 pagesEssential Nutrients: Types, Roles and Importance of VitaminsSonalee ShahNo ratings yet
- FHN 7 (Fat Soluble Vitamins)Document18 pagesFHN 7 (Fat Soluble Vitamins)SYED ZIYAD FURQANNo ratings yet
- Fat Soluble VitaminsDocument47 pagesFat Soluble Vitaminsmanjunathu731No ratings yet
- Balanced DietDocument10 pagesBalanced DietMsKhan0078100% (1)
- Terjemahan Makalah B Inggris MelvaDocument14 pagesTerjemahan Makalah B Inggris MelvaKeyla AishaNo ratings yet
- Food Chem2 NotesDocument99 pagesFood Chem2 NotesCynthia ngenyNo ratings yet
- Omer Seid, MSC in Human NutritionDocument142 pagesOmer Seid, MSC in Human NutritionruthNo ratings yet
- Balanced DietDocument4 pagesBalanced DietThe CSS PointNo ratings yet
- 1182 Vitamins Elements of Human Nutrition Guide - Copy 2Document22 pages1182 Vitamins Elements of Human Nutrition Guide - Copy 2api-253329505No ratings yet
- Types and Functions of VitaminsDocument15 pagesTypes and Functions of Vitaminsjhashaketh bandiNo ratings yet
- 200l Lasucom Lecture On Vitamins Coenzymes and Cofactors-1Document40 pages200l Lasucom Lecture On Vitamins Coenzymes and Cofactors-1Ewaoluwa AribaNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and minerals essential nutrients Harvard HealthDocument10 pagesVitamins and minerals essential nutrients Harvard HealthVardhan ChittemNo ratings yet
- 5-Vitamin and MineralsDocument61 pages5-Vitamin and MineralsAnonymous 8hcK7j2UNo ratings yet
- Vitaminsfinal 150515162131 Lva1 App6892 PDFDocument52 pagesVitaminsfinal 150515162131 Lva1 App6892 PDFkrishna upadhyayNo ratings yet
- Nutrition QuizDocument32 pagesNutrition QuizAwit100% (1)
- F.sciences AssignmentDocument9 pagesF.sciences AssignmentMuhammad AdnanNo ratings yet
- Fat Soluble Vitamins ReviewedDocument18 pagesFat Soluble Vitamins ReviewedShamim HussenNo ratings yet
- Varanasi-Road, Mirzamurad, Varanasi (U.P.), Ph.0542-2637777, 263768Document19 pagesVaranasi-Road, Mirzamurad, Varanasi (U.P.), Ph.0542-2637777, 263768Vaishali PathakNo ratings yet
- What Are Vitamins and MineralsDocument2 pagesWhat Are Vitamins and MineralsairineNo ratings yet
- Micronutrient Vitamin and Mineral TumbangDocument40 pagesMicronutrient Vitamin and Mineral Tumbangpujipoe85No ratings yet
- Vitamin A: Sources, Functions and Deficiency PreventionDocument7 pagesVitamin A: Sources, Functions and Deficiency PreventionDamani RobertsNo ratings yet
- Characteristics and Functions of Fat-Soluble and Water-Soluble VitaminsDocument44 pagesCharacteristics and Functions of Fat-Soluble and Water-Soluble VitaminsCarl ReyesNo ratings yet
- Aurora Bilingual School: Proyecto: Las VitaminasDocument10 pagesAurora Bilingual School: Proyecto: Las VitaminasVanessa GarciaNo ratings yet
- In The Name of Allah The Most Beneficient & The Most MercifulDocument23 pagesIn The Name of Allah The Most Beneficient & The Most MercifulSyedaFatimaWaqarNo ratings yet
- MSC Chemistry Sem 4th - Lecture 1st VitaminDocument4 pagesMSC Chemistry Sem 4th - Lecture 1st VitaminArpitNo ratings yet
- General Characteristics of Vitamins and MineralsDocument2 pagesGeneral Characteristics of Vitamins and MineralsSophia RamiroNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: Pharmaceutical Chemistry - II (Biochemistry)Document30 pagesVitamins: Pharmaceutical Chemistry - II (Biochemistry)AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Function of FatsDocument14 pagesFunction of FatsPrincess CudalNo ratings yet
- VitaminesDocument32 pagesVitamineskaranpandey5645No ratings yet
- F&N AssignmentDocument8 pagesF&N AssignmentRicardo JohnNo ratings yet
- Essential nutrients for a healthy bodyDocument10 pagesEssential nutrients for a healthy bodyRachit VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Requirements of a Balanced DietDocument8 pagesRequirements of a Balanced DietAbdullah SaleemNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and minerals: essential nutrients for healthDocument14 pagesVitamins and minerals: essential nutrients for healthAlejandraNo ratings yet
- Article Vitamin and MineralDocument9 pagesArticle Vitamin and MineralSyahirah Sinta NurfalishaNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument6 pagesVitaminsGalina MiriutaNo ratings yet
- Fat Soluble VitaminDocument41 pagesFat Soluble VitaminHusna AmalanaNo ratings yet
- PPT on Pharmacology of VitaminsDocument59 pagesPPT on Pharmacology of VitaminsabenezergebrekirstosNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Minerals: Essential Micronutrients for HealthDocument4 pagesVitamins and Minerals: Essential Micronutrients for HealthFaisal IzharNo ratings yet
- FotDocument14 pagesFotHimanshu Garg100% (1)
- VITAMINSDocument25 pagesVITAMINSSalimaThasneem75% (4)
- Project Report On VitaminsDocument3 pagesProject Report On Vitaminsmonica jainNo ratings yet
- Vitamin E: A Presentation byDocument13 pagesVitamin E: A Presentation byArkaprava BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: CO + H O C H O + ODocument10 pagesCarbohydrates: CO + H O C H O + OMini BossNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol Ors 1Document3 pagesParacetamol Ors 1Mini BossNo ratings yet
- Digestion: By: Roselita O. Natividad and Teresita G Montaño, PHD Nat. Science - Ateneo de Zamboanga UniversityDocument5 pagesDigestion: By: Roselita O. Natividad and Teresita G Montaño, PHD Nat. Science - Ateneo de Zamboanga UniversityMini BossNo ratings yet
- V. Integration (Independent Practice) A. Morals: First Argument Counter-Argument Reaction: Undeserved Success Provides NoDocument3 pagesV. Integration (Independent Practice) A. Morals: First Argument Counter-Argument Reaction: Undeserved Success Provides NoMini BossNo ratings yet
- TOPIC - Insulin Hormone Organ AnaPhy (Parenteralmed)Document9 pagesTOPIC - Insulin Hormone Organ AnaPhy (Parenteralmed)Mini BossNo ratings yet
- PERTUSSISDocument2 pagesPERTUSSISMini BossNo ratings yet
- Ateneo de Zamboanga University: Worksheet 1Document2 pagesAteneo de Zamboanga University: Worksheet 1Mini BossNo ratings yet
- Notes About BiologyDocument81 pagesNotes About BiologyRichard Coffey100% (1)
- Biochemistry of GlycoproteinDocument6 pagesBiochemistry of GlycoproteinMahathir Mohmed100% (7)
- BiochemistryDocument7 pagesBiochemistryAbdelwahab AliNo ratings yet
- Oligo ExtraDocument2 pagesOligo ExtraGabriela Zaldivar MendozaNo ratings yet
- Transcription: From DNA To RNADocument74 pagesTranscription: From DNA To RNAmd habibur rahmanNo ratings yet
- LaudabletasksDocument25 pagesLaudabletasksiremsenakNo ratings yet
- 1.molecules of Life PDFDocument47 pages1.molecules of Life PDFaeylynnNo ratings yet
- DNA, RNA & Proteins True or FalseDocument3 pagesDNA, RNA & Proteins True or Falsejefferson.baldoquinNo ratings yet
- Bi Substrate Reaction PDFDocument25 pagesBi Substrate Reaction PDFKiran DalalNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology Topic 1 AssessmentDocument15 pagesA Level Biology Topic 1 AssessmentgsapkaiteNo ratings yet
- Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th Ed Booksmedicos - Org (1) (0685-0755)Document71 pagesLehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th Ed Booksmedicos - Org (1) (0685-0755)Ricky HerreraNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Properties & Protein Structure QuestionsDocument7 pagesAmino Acid Properties & Protein Structure QuestionsJeevikaGoyalNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Structure Functions Biological MoleculesDocument26 pagesCarbohydrates Structure Functions Biological Moleculesbuena carillaNo ratings yet
- Babcock Institute Dairy Feed EssentialsDocument4 pagesBabcock Institute Dairy Feed Essentialsimran LarNo ratings yet
- Molecular Structure of Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesMolecular Structure of Nucleic AcidsdedexNo ratings yet
- Enzymes MCQ Topic Quiz Lesson ElementDocument19 pagesEnzymes MCQ Topic Quiz Lesson ElementArvin DiNozzoNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument10 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceSneha HipparkarNo ratings yet
- Apotekarske Laboratorije Naziv Dokumenta Obuhvaćen Dokumnetom Datum Pripreme/ Datum Posljednjeg AžuriranjaDocument2 pagesApotekarske Laboratorije Naziv Dokumenta Obuhvaćen Dokumnetom Datum Pripreme/ Datum Posljednjeg AžuriranjajalijaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology 2013 Scoring Guidelines: © 2013 The College BoardDocument5 pagesAP Biology 2013 Scoring Guidelines: © 2013 The College BoardALLAN ELIEZER BORGES RAMOSNo ratings yet
- Main Functions of ProteinDocument3 pagesMain Functions of ProteinsweetwaffleNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week 3 - 4Document13 pagesQ4 Week 3 - 4MARILES PRUDENCIANO0% (1)
- Buckingham - Molecular Diagnostics-Fundamentals Methods and Clinical ApplicationsDocument479 pagesBuckingham - Molecular Diagnostics-Fundamentals Methods and Clinical Applicationsfakefacebook75891% (11)
- Technique Lab ReportDocument3 pagesTechnique Lab Reportlightning proNo ratings yet
- 1989 - Gierasch - Signal SequencesDocument8 pages1989 - Gierasch - Signal Sequencespond_1993No ratings yet
- Eukaryotic DNA Replication Blok9Document15 pagesEukaryotic DNA Replication Blok9'Alivia Nabdakh ClocheNo ratings yet
- NutraHacker Complete SASDocument9 pagesNutraHacker Complete SASJustin KellyNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Molecular Biology of The Cell Sixth EditionDocument30 pagesTest Bank For Molecular Biology of The Cell Sixth EditionglendavictoriabbkNo ratings yet
- QC CERTIFICATE TITLEDocument1 pageQC CERTIFICATE TITLEnaeem186No ratings yet
- SAMBA (J&K) (NAAC Accredited B) Recognized by J&K Govt. and Affiliated to the University of JammuDocument11 pagesSAMBA (J&K) (NAAC Accredited B) Recognized by J&K Govt. and Affiliated to the University of JammuajaysmbNo ratings yet
- Watermelon 2Document2 pagesWatermelon 2Wania ShahidNo ratings yet
- Instant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookFrom EverandInstant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Body Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomFrom EverandBody Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Summary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- The Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyFrom EverandThe Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Allen Carr's Easy Way for Women to Lose Weight: The original Easyway methodFrom EverandAllen Carr's Easy Way for Women to Lose Weight: The original Easyway methodRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Glucose Goddess Method: A 4-Week Guide to Cutting Cravings, Getting Your Energy Back, and Feeling AmazingFrom EverandGlucose Goddess Method: A 4-Week Guide to Cutting Cravings, Getting Your Energy Back, and Feeling AmazingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (59)
- Glucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarFrom EverandGlucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (349)
- Secrets From the Eating Lab: The Science of Weight Loss, the Myth of Willpower, and Why You Should Never Diet AgainFrom EverandSecrets From the Eating Lab: The Science of Weight Loss, the Myth of Willpower, and Why You Should Never Diet AgainRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- The Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingFrom EverandThe Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Find Your Path: Honor Your Body, Fuel Your Soul, and Get Strong with the Fit52 LifeFrom EverandFind Your Path: Honor Your Body, Fuel Your Soul, and Get Strong with the Fit52 LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Keto Friendly Recipes: Easy Keto For Busy PeopleFrom EverandKeto Friendly Recipes: Easy Keto For Busy PeopleRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Sugar Crush: How to Reduce Inflammation, Reverse Nerve Damage, and Reclaim Good HealthFrom EverandSugar Crush: How to Reduce Inflammation, Reverse Nerve Damage, and Reclaim Good HealthRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Forever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellFrom EverandForever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellNo ratings yet
- Metabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeFrom EverandMetabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeNo ratings yet
- Proteinaholic: How Our Obsession with Meat Is Killing Us and What We Can Do About ItFrom EverandProteinaholic: How Our Obsession with Meat Is Killing Us and What We Can Do About ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- Happy Gut: The Cleansing Program to Help You Lose Weight, Gain Energy, and Eliminate PainFrom EverandHappy Gut: The Cleansing Program to Help You Lose Weight, Gain Energy, and Eliminate PainRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- The Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsFrom EverandThe Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (49)
- Foods That Cause You to Lose Weight: The Negative Calorie EffectFrom EverandFoods That Cause You to Lose Weight: The Negative Calorie EffectRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- The Beck Diet Solution Weight Loss Workbook: The 6-Week Plan to Train Your Brain to Think Like a Thin PersonFrom EverandThe Beck Diet Solution Weight Loss Workbook: The 6-Week Plan to Train Your Brain to Think Like a Thin PersonRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- The Complete Beck Diet for Life: The 5-Stage Program for Permanent Weight LossFrom EverandThe Complete Beck Diet for Life: The 5-Stage Program for Permanent Weight LossRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- The Fast800 Diet: Discover the Ideal Fasting Formula to Shed Pounds, Fight Disease, and Boost Your Overall HealthFrom EverandThe Fast800 Diet: Discover the Ideal Fasting Formula to Shed Pounds, Fight Disease, and Boost Your Overall HealthRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (37)
- How to Be Well: The 6 Keys to a Happy and Healthy LifeFrom EverandHow to Be Well: The 6 Keys to a Happy and Healthy LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Volumetrics Eating Plan: Techniques and Recipes for Feeling Full on Fewer CaloriesFrom EverandThe Volumetrics Eating Plan: Techniques and Recipes for Feeling Full on Fewer CaloriesNo ratings yet
- The Candida Cure: The 90-Day Program to Balance Your Gut, Beat Candida, and Restore Vibrant HealthFrom EverandThe Candida Cure: The 90-Day Program to Balance Your Gut, Beat Candida, and Restore Vibrant HealthNo ratings yet
- Hungry for Change: Ditch the Diets, Conquer the Cravings, and Eat Your Way to Lifelong HealthFrom EverandHungry for Change: Ditch the Diets, Conquer the Cravings, and Eat Your Way to Lifelong HealthRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- Eat to Lose, Eat to Win: Your Grab-n-Go Action Plan for a Slimmer, Healthier YouFrom EverandEat to Lose, Eat to Win: Your Grab-n-Go Action Plan for a Slimmer, Healthier YouNo ratings yet
- Summary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietFrom EverandSummary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)