Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 2-2 (The Smith Chart) Materials Needed
Module 2-2 (The Smith Chart) Materials Needed
Uploaded by
jones semi mediumOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 2-2 (The Smith Chart) Materials Needed
Module 2-2 (The Smith Chart) Materials Needed
Uploaded by
jones semi mediumCopyright:
Available Formats
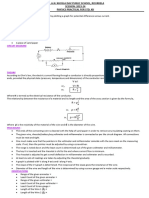
Module 2-2 (The Smith Chart)
Materials needed:
Pencil
Smith Chart (hard copy at least 5)
Compass
Ruler
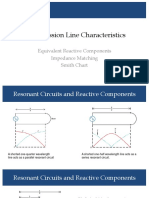
Smith Chart
The Smith chart is a special kind of impedance
coordinate system that portrays the relationship of
impedance at any point along a uniform transmission
line to the impedance at any other point on the line.
The Smith chart was developed by Philip H. Smith at Bell
Telephone Laboratories. The chart is based on two sets
of orthogonal circles. One set represents the ratio of the
resistive component of the line impedance (R) to the Called impedance circle
characteristic impedance of the line (Zo). The second
*1 cycle is λ/2
set of circles represents the ratio of the reactive
component of the line impedance (±jX) to the *Clockwise from the load going towards the source
characteristic impedance of the line (Zo). Parameters
plotted on the Smith chart include the following:
1. Impedance (or admittance (reciprocal of impedance))
at any point along a transmission line
2. Reactance (or susceptance(reciprocal of reactance))
at any point along a transmission line
3. Reflection coefficient magnitude (|Γ|) and angle in
degrees (θ Γ )
4. Length of transmission line between any two points
in wavelengths
5. Standing wave ratio (SWR)
*Yellow is the normalized rmax
*Yellow is purely resistance meaning no reactance
Normalized value are always small letters
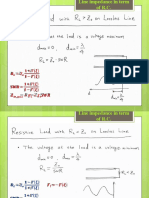
*blue is the admittance Steps in using smith chart for quarter wavelength
matching
Steps in using smith chart for stub matching with
quarter wavelength transformer
Steps in using smith chart for stub matching
*after reading SWR on the circle, put a point of the SWR
below the graph and draw a straight line, then put a half
or diagonal to half the circle to read the angle of
reflection coefficient
You might also like
- Smith ChartDocument11 pagesSmith ChartBill WhiteNo ratings yet
- Basic Meter in Ac MeasurementsDocument69 pagesBasic Meter in Ac MeasurementsWatashiNoNo ratings yet
- Microwave Engineering Lecture No: 7-10 Unit No: 1: Smith ChartDocument12 pagesMicrowave Engineering Lecture No: 7-10 Unit No: 1: Smith ChartAshutosh PattanayakNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Characteristics: Equivalent Reactive Components Impedance Matching Smith ChartDocument18 pagesTransmission Line Characteristics: Equivalent Reactive Components Impedance Matching Smith ChartMarie Claire Leonor GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electronic Communication Systems: Fourth EditionDocument22 pagesPrinciples of Electronic Communication Systems: Fourth EditionRenz EbenNo ratings yet
- L9. The Smith Chart: Theoretical NotionsDocument5 pagesL9. The Smith Chart: Theoretical NotionsCristina SchusterNo ratings yet
- Applied EM7 e CH 02Document81 pagesApplied EM7 e CH 02محمد عبد الوهابNo ratings yet
- 7 e Applied EMCh 2Document82 pages7 e Applied EMCh 2Dr. Mohammad ZunoubiNo ratings yet
- Smith ChartDocument12 pagesSmith ChartHammna AshrafNo ratings yet
- Transmission Lines Course - 2Document54 pagesTransmission Lines Course - 2daekmmmmNo ratings yet
- Transmission LinesDocument5 pagesTransmission LinesEchizen KinichiNo ratings yet
- 519 - Transmission Line Theory by VishnuDocument24 pages519 - Transmission Line Theory by VishnuSairam SairamNo ratings yet
- 3 Transmission LinesDocument19 pages3 Transmission Linesfathin noorshafirahNo ratings yet
- Practicals - Class XiiDocument38 pagesPracticals - Class XiiTITAN KALOS100% (1)
- Transmission Lines Notes FMDocument12 pagesTransmission Lines Notes FMlamontfreemannNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document82 pagesCH 2100475175No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Direct Current MetersDocument42 pagesChapter 2 - Direct Current MetersANDREW LEONG CHUN TATT STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Physics PracticalDocument24 pagesPhysics PracticalPeddini Pradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- By Prof. Dr. R.K.DashDocument25 pagesBy Prof. Dr. R.K.Dashabdul jawadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document71 pagesLecture 3MONEER THAMEERNo ratings yet
- CP 13Document43 pagesCP 13M Alwan Nur AjieNo ratings yet
- Physics Practicals 1Document8 pagesPhysics Practicals 1AnantNo ratings yet
- EXP2-SURFACE ROUGHNESS MEASUREMENT-non GuidedDocument3 pagesEXP2-SURFACE ROUGHNESS MEASUREMENT-non GuidedRyan LauNo ratings yet
- Temperature Compensation Arrangement: Pointer PointerDocument16 pagesTemperature Compensation Arrangement: Pointer PointerAbhinav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Drawing VSWR Circle On Smith ChartDocument19 pagesDrawing VSWR Circle On Smith ChartGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Standing Wave Ratio: Relationship To The Reflection CoefficientDocument5 pagesStanding Wave Ratio: Relationship To The Reflection Coefficientpreethy.wilsNo ratings yet
- Smith ChartsDocument5 pagesSmith Chartsskrishna261No ratings yet
- AC CIRCUITS ReviewerDocument7 pagesAC CIRCUITS ReviewerKyle Joshua BunhanNo ratings yet
- AntennaDocument340 pagesAntennadeepa reddyNo ratings yet
- Working Formulae - Xii - 2022-23Document2 pagesWorking Formulae - Xii - 2022-23manavNo ratings yet
- Compact Ranges: Microwave Antennas Need - U.P.W For Illumination - Far Field Distances in The SetupDocument49 pagesCompact Ranges: Microwave Antennas Need - U.P.W For Illumination - Far Field Distances in The SetupSyed MuzzuNo ratings yet
- Standing Wave RatioDocument6 pagesStanding Wave RatioGen RabliNo ratings yet
- Lucrare 11 - DobraDocument10 pagesLucrare 11 - DobraShantul KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Inf2 2Document9 pagesInf2 2Nixon RamonNo ratings yet
- High Frequency Transformer Modeling: Janzisz Biernacki and Darizisz CzarkowskiDocument4 pagesHigh Frequency Transformer Modeling: Janzisz Biernacki and Darizisz CzarkowskiAntônio Kaminski JúniorNo ratings yet
- Biconical AntennaDocument68 pagesBiconical AntennaJULIETHERESE MNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical'sDocument43 pagesPhysics Practical'sTvara PatelNo ratings yet
- Physics Experiment 01 (Ohm's Law) - 2Document2 pagesPhysics Experiment 01 (Ohm's Law) - 2yubraj sethNo ratings yet
- The Smith Chart: Introduction and BasicsDocument9 pagesThe Smith Chart: Introduction and BasicsMuhammad Umair Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- PSA Notes Full - PPT (Compatibility Mode)Document48 pagesPSA Notes Full - PPT (Compatibility Mode)Moavia HassanNo ratings yet
- Notes 20 DC 20 MetersDocument15 pagesNotes 20 DC 20 MetersAnonymous NFTqyEfoPNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical For Class 12Document33 pagesPhysics Practical For Class 12SanjuNo ratings yet
- Smith ChartDocument6 pagesSmith ChartStephen Dunifer100% (2)
- NOTES (2023-2024) Subject: PHYSICS Class: XII Experiment No.1: Ohm'S LawDocument5 pagesNOTES (2023-2024) Subject: PHYSICS Class: XII Experiment No.1: Ohm'S LawMichael IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line RepresentationDocument9 pagesTransmission Line Representationvictorkaranjamwangi7015No ratings yet
- Fault Analysis in A Three-Phase SystemDocument10 pagesFault Analysis in A Three-Phase SystemKarushan R.MNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits 2 EE 003 (TIP Reviewer)Document28 pagesElectrical Circuits 2 EE 003 (TIP Reviewer)James LindoNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media Lab ManualDocument21 pagesTransmission Media Lab ManualMohamed EidNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 Transmission Line PerformanceDocument39 pagesChapter - 4 Transmission Line Performancealemaklil21No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Sinusoidal Alternating Waveforms: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadDocument31 pagesChapter 13 - Sinusoidal Alternating Waveforms: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadSajjad Hossain ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Example DeviceDocument21 pagesExample Devicealiffshaari.workNo ratings yet
- Micrsotrip Antenna-2 PDFDocument8 pagesMicrsotrip Antenna-2 PDFVIBHISHAN KUMARNo ratings yet
- F) Superimposed On The Reflected Wave (With Amplitude R)Document5 pagesF) Superimposed On The Reflected Wave (With Amplitude R)mosizaza100% (1)
- XII Practical Lab Manual (2022 - 2023)Document29 pagesXII Practical Lab Manual (2022 - 2023)Kanishk KrishnanNo ratings yet
- 3 Microwave MeasurementsDocument70 pages3 Microwave Measurementsbiotech_vidhyaNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Impedance Matching: 1. Quarter-Wave Transformer MatchingDocument28 pagesTransmission Line Impedance Matching: 1. Quarter-Wave Transformer MatchingEm ReyesNo ratings yet
- G12 Physics Experiment 23-24Document43 pagesG12 Physics Experiment 23-24anonymous3256tNo ratings yet
- CarsonDocument6 pagesCarsonSubas Ratna TuladharNo ratings yet
- Linear Network Theory: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionFrom EverandLinear Network Theory: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionNo ratings yet
- Review (3221)Document9 pagesReview (3221)jones semi mediumNo ratings yet
- Table of ComparisonDocument3 pagesTable of Comparisonjones semi mediumNo ratings yet
- Module 3 ReviewDocument7 pagesModule 3 Reviewjones semi mediumNo ratings yet
- Table of ComparisonDocument3 pagesTable of Comparisonjones semi mediumNo ratings yet
- ECE 3221 (Module 1)Document10 pagesECE 3221 (Module 1)jones semi mediumNo ratings yet