Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 1 - Microscope
Uploaded by
Huỳnh Như Đặng Thụy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesLesson 1 - Microscope
Uploaded by
Huỳnh Như Đặng ThụyCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
LESSON 1: MICROSCOPE
I. INTRODUCTION
"Micro" refers to tiny, "scope" refers to view or look at. Microscopes are used to make
more detailed observations and measurements of objects too small for the naked eye.
(Total magnification of any image you see through the ocular lens is the product of
the objective and ocular lens magnifications)
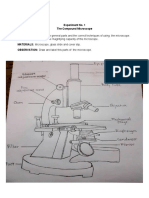
1. Microscope structures
1.1. The optical elements include:
OCULAR LENS (EYEPIECE); OBJECTIVE LENS; LAMP
- OCULAR LENS (eyepiece) – The microscope will have either one
(monocular) or two (binocular) ocular lenses. These are the lenses you will look
through when examining a specimen with the microscope.
- OBJECTIVE LENSES –These lenses allow you to change the degree of
magnification. The degree of magnification for each objective lens is indicated on its
side.
4X – This objective magnifies the image by a factor of 4.
10X – This objective magnifies the image by a factor of 10
40X – This objective magnifies the image by a factor of 40
100X – This objective magnifies the image by a factor of 100. It is referred to as the
“oil immersion objective” since it requires a drop of immersion oil on the slide to
provide good resolution.
1.2. Mechanical parts:
COARSE FOCUS; FINE FOCUS KNOBS ; MECHANICAL STAGE KNOBS ;
STAGE; STAGE CLIP; BASE; ARM ; DIAPHRAGM ; CONDENSER LENS
2. Proper Use of Microscope
To protect the microscope and the specimen, be careful when using glass, screw
must slowly, slightly, gentle and proceed in the following order:
water or oil on TOP OF COVERSLIP
est to longest
objective lenses
Requirements: Students need patience during the time using microsope!
3. Preparing slide
1) Collect all your apparatus (carrying the microscope carefully).
2) Lay the sample on the microscope slide in a single flat layer.
3) Place a very small drop of water/iodine/ lugol/... on to the sample.
4) Carefully lower a cover slip on top of the sample (make sure there are no air
bubbles).
5) Place the slide on the stage of the microscope.
6) Make sure the lowest objective lens is over the specimen.
7) Carefully use the course focusing knob to lower the objective lens to just above
the slide
8) Look through the eye piece and carefully use the fine focusing knob to focus the
image.
9) Draw what you see through the microscope.
II. EXPERIMENTS
1. Plant cells
- Use a blade to cut off outer cells (few pieces) of an onion bulb and submerge in water
(about 1 min).
- Put each onion piece onto a water drop on a lame, then cover a lamelle on the sample
and observe via microscope with objective lenses of 10x and 40x.
- Remove gently water on the lame using paper tissue. Put 2 drops of NaCl 8% on the
sample. After 5-10 mins, repeat the observation and take note the change.
2. Yeast cells
Put one drop of baker yeast culture on a lame. Cover a lamelle on the sample and
observe via microscope with objective lenses of 10x and 40x.
3. Animal cells
- Obtain mucous membrane cells in human mouth via a clean toothpick and put the
sample on a drop of Lugol solution on a lame. Cover a lamelle on the sample and
observe via microscope with objective lenses of 10x and 40x.
REPORT
1. Draw a microscope and explain functions of its main parts.
2. Describe each type of cell and phenomenon observed during the experiments.
You might also like
- Microscope SHĐCDocument3 pagesMicroscope SHĐCthien.ttrleNo ratings yet
- Using the Compound MicroscopeDocument5 pagesUsing the Compound MicroscopeEarl JohnNo ratings yet
- Exp 3 Group 4 Ent1243Document18 pagesExp 3 Group 4 Ent1243alipokada99No ratings yet
- 2 Microscopy LabDocument18 pages2 Microscopy Lablux0008No ratings yet
- 2 Micros PDFDocument18 pages2 Micros PDFKenny JosefNo ratings yet
- BNWL7-SCI TB C06 QR11 Laboratory-ActivitiesDocument26 pagesBNWL7-SCI TB C06 QR11 Laboratory-ActivitiesTricia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No. 1Document6 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 1jasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Practical HandbookDocument41 pagesParasitology Practical Handbookmaximazarov100% (1)
- The Microscope: Summary of ExerciseDocument18 pagesThe Microscope: Summary of Exerciserashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Mic461Document6 pagesLab Report Mic461Puteri NursyafiqahNo ratings yet
- Operation of the MicroscopeDocument6 pagesOperation of the MicroscopeAntonio Charisma100% (1)
- Lab 1: The Microscope (10 Points) : Exercise 1.1: Microscope Structure and FunctionDocument12 pagesLab 1: The Microscope (10 Points) : Exercise 1.1: Microscope Structure and Functionrashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- Biology-Lab Manual Jun2014 - VersionDocument34 pagesBiology-Lab Manual Jun2014 - VersionLe Phuong LyNo ratings yet
- 4 Micros PDFDocument6 pages4 Micros PDFNuraini OchadahNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Farmasi 3 PDFDocument7 pagesLab Manual Farmasi 3 PDFamirulNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 The Use and Care of The MicroscopeDocument7 pagesActivity No. 1 The Use and Care of The MicroscopeRheal P EsmailNo ratings yet
- 1 MicroDocument4 pages1 MicroPauline MaryNo ratings yet
- MIBO-111 PracticalDocument55 pagesMIBO-111 PracticalShinchan DoremonNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 2 Microscope Anph111Document5 pagesLab Exercise 2 Microscope Anph111Jhon Leonard FatalloNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 1 MICROSDocument9 pagesLab Exercise 1 MICROSCrizzajen IsipNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Objectives: LAB EXERCISE: Microscopy and The CellDocument17 pagesLaboratory Objectives: LAB EXERCISE: Microscopy and The CellJasper LeysonNo ratings yet
- How to Use a Compound MicroscopeDocument5 pagesHow to Use a Compound MicroscopeSilpa JenaNo ratings yet
- 1 Mic125Document8 pages1 Mic125nadiazkiNo ratings yet
- Mic125 Lab ManualDocument35 pagesMic125 Lab ManualAqilah NajwaNo ratings yet
- Exploring Microscopes and Measuring SpecimensDocument14 pagesExploring Microscopes and Measuring SpecimensAqilah Azman100% (1)
- Lab 1 - MicrosDocument8 pagesLab 1 - MicrosQuino AmarelaNo ratings yet
- 01 Intro To MicroscopesDocument7 pages01 Intro To MicroscopesKarunakarNo ratings yet
- Lab 1. Understanding The Work of Microscopes: Campbell Biology, Reece Et Al, 2016) )Document7 pagesLab 1. Understanding The Work of Microscopes: Campbell Biology, Reece Et Al, 2016) )Ade Rizky FajrullohNo ratings yet
- Act 1 Microscope As A Biological ToolDocument14 pagesAct 1 Microscope As A Biological ToolSidNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 2 MicroscopeDocument7 pagesLab Exercise 2 MicroscopeChristopher GalivoNo ratings yet
- BIO210 Lab Report 2Document6 pagesBIO210 Lab Report 2Isra MallaNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument27 pagesLab ManualaswzNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 1 MICROSDocument9 pagesLab Exercise 1 MICROSCrizzajen IsipNo ratings yet
- Microscope Usage and Handling ProceduresDocument5 pagesMicroscope Usage and Handling Proceduresgrafei pennaNo ratings yet
- LessonsDocument16 pagesLessonsThư TrầnNo ratings yet
- General Bio PT#2Document3 pagesGeneral Bio PT#2Annissa PacaldoNo ratings yet
- General Bio PT#2Document3 pagesGeneral Bio PT#2Annissa PacaldoNo ratings yet
- Lab Act 1Document6 pagesLab Act 1Marwin Rivarez Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Module in ScienceDocument6 pagesModule in Sciencenasser pazaulan12No ratings yet
- Biology Practical 2Document8 pagesBiology Practical 2N.THEVANo ratings yet
- Compound Microscope Parts and UseDocument4 pagesCompound Microscope Parts and UseGis ELNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 - The Microscope (BIO11A) - 1Document9 pagesExercise 1 - The Microscope (BIO11A) - 1EMNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document4 pagesModule 1Kathy Mae Morales Forcadilla - DaclanNo ratings yet
- Mic461 Lab Manual Oct2023Document17 pagesMic461 Lab Manual Oct2023Nur Syakirah Abd NasirNo ratings yet
- MICROPARA Activity-13 PDFDocument7 pagesMICROPARA Activity-13 PDFLorenz Jude CańeteNo ratings yet
- Microlab Activity 2 The Microscopes - DHAWELL ANN F. CARPIODocument6 pagesMicrolab Activity 2 The Microscopes - DHAWELL ANN F. CARPIODhawell AnnNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Microscopy: I. PurposeDocument17 pagesLab 2 Microscopy: I. PurposeJOHA CORNEJONo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument42 pagesMicroscopemichameilromero13No ratings yet
- Bio083 Practical 1Document7 pagesBio083 Practical 12023499618No ratings yet
- Pusat Pengajian Pendidikan Jarak Jauh Universiti Sains MalaysiaDocument9 pagesPusat Pengajian Pendidikan Jarak Jauh Universiti Sains MalaysiaBaby girlNo ratings yet
- Compund MicroscopeDocument6 pagesCompund MicroscopebellarosyNo ratings yet
- Using The Microscope: Introductory PracticalDocument11 pagesUsing The Microscope: Introductory Practicalalex zhangNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cell Biology: Senior High School DepartmentDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Cell Biology: Senior High School DepartmentJericho LindoNo ratings yet
- B.Sc.I Journal 23.7.15Document128 pagesB.Sc.I Journal 23.7.15Sarvesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Lab 1: Learn Microscope Use and CareDocument8 pagesLab 1: Learn Microscope Use and Carerashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab ManualDocument32 pagesBiology Lab ManualDũng Nguyễn100% (1)
- Virtual Lab 1. Introduction To The Microscope: Senior High School DepartmentDocument5 pagesVirtual Lab 1. Introduction To The Microscope: Senior High School Departmentbabalo loNo ratings yet
- De Guzman, M.J., ACTIVITY PAPER #2 Microscopy Asynchronous ActivityDocument4 pagesDe Guzman, M.J., ACTIVITY PAPER #2 Microscopy Asynchronous ActivityMaui Vecinal de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Understanding MicroscopesDocument5 pagesUnderstanding MicroscopesJana Ysabela PaquibotNo ratings yet
- Breaking Down Energy Consumption in Industrial Grinding MillsDocument12 pagesBreaking Down Energy Consumption in Industrial Grinding Millsrolandoh1No ratings yet
- Apjmr-2015-3 4 5 05Document7 pagesApjmr-2015-3 4 5 05Rani RubiyantiNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Processing Equipment Saravacos2016Document781 pagesHandbook of Processing Equipment Saravacos2016Sang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chitosan Coating Extends Shelf Life of Ready-to-Cook Meat ProductsDocument6 pagesChitosan Coating Extends Shelf Life of Ready-to-Cook Meat ProductsHuỳnh Như Đặng ThụyNo ratings yet
- Exercise Physical and Colloid ChemistryDocument2 pagesExercise Physical and Colloid ChemistryHuỳnh Như Đặng ThụyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesLesson 4 - PhotosynthesisHuỳnh Như Đặng ThụyNo ratings yet
- 8 Synthesis of AspirinDocument6 pages8 Synthesis of AspirinChelsea Reyna TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration and EnzymesDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration and EnzymesHuỳnh Như Đặng ThụyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Macromolecules of CellsDocument2 pagesLesson 2 - Macromolecules of CellsHuỳnh Như Đặng ThụyNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of A MicroscopeDocument1 pageParts and Functions of A MicroscopeDivine Josol CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Lab Equipments ReviewerDocument8 pagesLab Equipments ReviewerCherish Faith TubigNo ratings yet
- METTIGOFO sm4 50hzDocument15 pagesMETTIGOFO sm4 50hzFabio Emanuele BrandaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Camera and LensesDocument24 pagesParts of Camera and LensesKhushi JaiswalNo ratings yet
- NVLS Extreme Vision PNVG 20200528Document2 pagesNVLS Extreme Vision PNVG 20200528lfx160219No ratings yet
- Optical Instruments ModuleDocument6 pagesOptical Instruments ModulejaspherNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Introduction To MicroscopesDocument26 pagesLecture 2-Introduction To MicroscopesThuto SmithNo ratings yet
- As 128694 VHX-7000 C 601376 WW GB 2092 5Document40 pagesAs 128694 VHX-7000 C 601376 WW GB 2092 5Khairul AzharNo ratings yet
- Application For Vacuum Pumps 2005Document9 pagesApplication For Vacuum Pumps 2005jogik123456No ratings yet
- Indoor/Outdoor 2012 Tarifa Price ListDocument244 pagesIndoor/Outdoor 2012 Tarifa Price ListLaura LizanzuNo ratings yet
- Lista Almacen Proway 2022 - Imp. JulDocument5 pagesLista Almacen Proway 2022 - Imp. JulFermin Tafur LliuyaNo ratings yet
- Bunsen BurnerDocument17 pagesBunsen BurnerMaiza TiborNo ratings yet
- Washing Machine Service ManualDocument37 pagesWashing Machine Service ManualJoaquin VidalNo ratings yet
- History of The MicroscopeDocument12 pagesHistory of The MicroscopeJhing Nuer DomingoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No. 1 - Common Laboratory ApparatusesDocument11 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 1 - Common Laboratory ApparatusesJuliane JaynNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Single Mode Laser-External Modulation-Temperature Effort.Document7 pages3.5 Single Mode Laser-External Modulation-Temperature Effort.DEEPAK SNo ratings yet
- Pentax SpotmaticDocument24 pagesPentax SpotmaticAndrea LamacchiaNo ratings yet
- Lenses Guide to Types and Optical CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesLenses Guide to Types and Optical CharacteristicsStephanieNo ratings yet
- Anamorphic Lenses and Format Compression Ratios for 8mm FilmmakingDocument11 pagesAnamorphic Lenses and Format Compression Ratios for 8mm FilmmakingAleksandar SaricNo ratings yet
- Microscope Parts and FunctionsDocument30 pagesMicroscope Parts and Functionssudirman0103651972No ratings yet
- Ricoh KR-5Document24 pagesRicoh KR-5Luis Monteiro MeloNo ratings yet
- Entretien Machines 2021Document20 pagesEntretien Machines 2021kabambaNo ratings yet
- Microscope Parts and Functions GuideDocument3 pagesMicroscope Parts and Functions GuideJhonLloyd DomingoNo ratings yet
- Identify Lab EquipmentDocument3 pagesIdentify Lab EquipmentKemoy FrancisNo ratings yet
- Parts List for Filters and ElementsDocument36 pagesParts List for Filters and ElementsYemane BekruNo ratings yet
- Gambar - Single Line Diagram Internal Treatment Unit 1-4: Steam Drum WaterDocument2 pagesGambar - Single Line Diagram Internal Treatment Unit 1-4: Steam Drum WaterMuhammad Syarif HidayatullahNo ratings yet
- GLASSWAREDocument23 pagesGLASSWAREFrestiskaNo ratings yet
- MQ13 02 DR 3310 In5911 - 0Document2 pagesMQ13 02 DR 3310 In5911 - 0Luis MantillaNo ratings yet
- Canon - MT 24-Ex - ManualDocument90 pagesCanon - MT 24-Ex - ManualCrina BuragaNo ratings yet
- Eyepiece Objective Lenses Head Nosepiece: Proper Care and HandlingDocument1 pageEyepiece Objective Lenses Head Nosepiece: Proper Care and HandlingRafael SaldivarNo ratings yet