Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Procedural Sedation Meds: Ketamine Management of Complications
Uploaded by
Lile Arrisan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views2 pagesOriginal Title
SEDACION
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views2 pagesProcedural Sedation Meds: Ketamine Management of Complications
Uploaded by
Lile ArrisanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
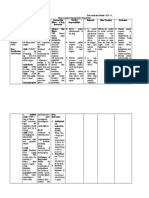
Ketamine Onset:
IV 0.5-1 min Management of Complications
Dissociative analgesic, IM 3-5 min
Laryngospasm
Anxiolytic, Amnestic, Duration: IV 5-15 min
Procedural Sedation Meds Sedative IM 15-30 min
1. Wait: most resolve within 30 seconds
Avoid in: 2. Laryngospasm notch: jaw thrust with inward
Midazolam Onset: IN 1-3 min - ICP with obstruction
Recovery: 60-150 min
thrust towards brainstem
Anxiolytic, Amnestic Oral 15-30 min
- intraocular pressure Dosing Guidelines:
Dosing Guidelines: IV 1-3 min - active resp infxn
IV: Initial 1-2 mg/kg
IN: 0.5 mg/kg Duration: IN 60 min (peak 20 min) - poorly controlled
(max 100mg/dose)
(max 10mg) Oral 60-90 min asthma
* 50mg/dose usually effective
(Conc 5mg/mL) IV 45-60 min (peak 20 min) Repeat 0.5mg/kg (max 50mg/dose ) q5-10min prn
Oral: 0.5 mg/kg (max 20mg) Give over 60 seconds
* less predictable effect IM: 4-5 mg/kg, repeat 2-4 mg/kg after 10-20 min prn 3. Positive pressure
IV: (0.5 - 5 yrs): 0.05-0.1 mg/kg (max 2mg/dose), Adverse events: - Emesis - Laryngospasm 4. Deepen sedation: use midaz or propofol
titrate prn to total max 0.6 mg/kg - Hallucinations - Recovery agitation 5. Low dose succinylcholine: 0.1-0.2 mg/kg IV
(6 - 12 yrs): 0.025-0.05 mg/kg (max 2mg/dose), Comments: - Consider redosing q5min x 2, then prn * preferential vocal cord paralysis without affecting
titrate prn to total max 0.4 mg/kg - Resp complications may increase when total
> 12 yrs: 2 mg, titrate with 1 mg prn
diaphragm
dose >5mg/kg and with IM route 6. Full dose succinylcholine: 1mg/kg IV and intubate
Give over 10-20 seconds - Use higher end of dosing range for toddlers
Adverse events: - Paradoxical reactions - Consider midaz to treat recovery agitation
- Resp depression - mild infusion pain
Nausea/Vomiting (Consider pre-med with h/o motion sickness)
- Consider ondansetron ppx with h/o motion sickness
Comments: - If using with fentanyl, consider ratio of - Vocalizations or myoclonus may occur
Ondansetron: < 10 kg - 0.5 mg IV
2-3 doses of fentanyl for each 1 dose of midaz 10-30kg - 1 mg IV
Propofol Onset: IV < 1 min >30kg - 2 mg IV
Sedative-hypnotic Duration: IV 5-15 min
Reversal: See Management of Complications- Reverse
Benzo
Avoid in Dosing Guidelines:
Oversedation/Respiratory Depression
- egg or soy allergy
IV Induction: (0 - 4 yrs): 2 mg/kg
- hypotension
(5 - 10 yrs): 1.5 mg/kg
Reverse Opioid: Naloxone IV, IN, or IM
Fentanyl Onset: IV 2-3 min
(>10 yrs): 1 mg/kg 0.01 mg/kg - 0.1 mg/kg (max 2 mg/dose)
Analgesic IN 3-5 min Onset: 2 min Duration: IV/IN 20-40 min
Dosing Guidelines: Duration: *May require additional 0.5 mg/kg bolus every 60-90 sec
IV 30 min IM 60-90 min
IV: Initial 1-2 mCg/kg for induction
IN 30 min
(max 100 mCg/dose), - IV Maintenance via pump: 50 - 200 mCg/kg/min start low and titrate q2min to effect
Adverse events: -Bradycardia - Hypotension - Apnea * 0.1 mg/kg will bring about full reversal of depression
titrate with 1 mCg/kg (max 50 mCg/dose) q3min prn,
- Infusion pain AND analgesia
Give over 10-20 seconds
Comments: - Use with fentanyl for analgesia
Suggested total max 5 mCg/kg
- For infusion pain: Apply tourniquet just proximal to IV, Reverse Benzo: Flumazenil IV 0.02 mg/kg
IN: 2 mCg/kg (max 100 mCg/dose)
Lidocaine IV 1mg/kg (max 25mg), remove tourniquette (max 0.2mg/dose, total max 1 mg or 0.05 mg/kg)
(Conc 50 mCg/mL)
after 60 seconds and flush with initial propofol bolus Onset: 1-2 min Duration: 30-60 min
Adverse events: - Resp depression
Comments: - If using with midaz, consider ratio of start low and titrate q1min to effect
2-3 doses of fentanyl for each 1 dose of midaz
Pentobarbital Onset: IV 3-5 min
Hypnotic, Amnestic Duration: IV 15-45 min * Avoid in patients with seizure d/o
Dosing Guidelines:
Reversal: See Management of Complications - Reverse IV: Initial 2 mg/kg (max 100mg/dose) **Monitor for return of sedation as reversal agent wanes
Opioid titrate with 1-2mg/kg q5 min prn (total max 6mg/kg) ***May require redosing for longer acting agents
Give over 30 seconds
NOTE: The medication dosing contained within these guidelines is provided for Adverse events: - Paradoxical reaction
reference only. Please refer to your institutional formulary or ordering guidelines Note: Patients who receive any reversal agents must be
when placing orders for clinical care of patients. - resp depression - Hypotension - Prolonged recovery monitored for 2 hours after the last dose of the reversal
Comments: - Lowers ICP
Created in 2015 by Windsor RB, Johnson K, Fleegler E, Krauss B, Dwyer D,
Manzi S
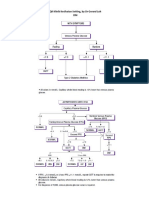
NPO Guidelines Sedation Teams
Procedural Sedation 2 hrs: Clear liquids DOM Sedation:
Quick Reference 4 hrs: unfortified breast milk
6 hrs: nonhuman milk, formula, fortified breastmilk
- Page “Sedation MD on Call” from 7a - 6p Mon-Fri
- Candidates: ASA I or II
ASA Physical Status Classification 8 hrs: solid food - Non-OR based sedations
ASA I: Healthy patient, no organic or psychiatric dz * Risk of aspiration in procedural sedation (not general - Exclusions: age < 3 mo, O2 requirement, difficult airway,
ASA II: Mild systemic dz with no impact on daily fxn anesthesia) is low regardless of NPO status HCT < 20, active URI or asthma, prior adverse reaction to
ASA III: Significant or severe systemic dz that limits fxn ** No formal NPO criteria for ED sedations sedation, OSA, active emesis, DNI
ASA IV: Severe dz that is constant threat to life
ASA V: Moribound pt likely to die within 24hrs Preparation and Setup Anesthesia: 5-9111 (Attending to Attending)
ASA VI: Brain dead organ donor - Responsible for all sedations in OR
“SOAP-ME”
Suction: Suction cannister, tubing, and Yankauer tip Capnography
Red Flags for Sedation Noninvasive ventilation monitoring
- Craniofacial abnormalities / high risk airway on exam
- h/o difficult airway and/or difficult sedation Oxygen: Preoxygenate with simple facemask or non-
- active vomiting or severe, uncontrolled GERD rebreather with 12-15 L/min for 3 min prior to induction
- active URI * Nasal cannulas do not provide preoxygenation
- OSA ** Continue facemask over capnography through case
- Symptomatic asthma FiO2: Room Air - 21%
Simple facemask (12-15L) - 50-60%
Nonrebreather (12-15L) - 90-100%
Levels of Sedation Resucitation bag (Anesthesia or self-inflating bag)
Appropriately sized mask
Minimal/ Airway: ETTs (uncuffed) = age (yrs) + 16
Anxiolysis Moderate Deep * Down 1/2 size for cuffed tubes 4
Capnography pearls:
Set up with appropriately sized ETT and one size smaller
Response Nml with Purposeful Purposeful - Cessation of airflow (flat waveform) - Central apnea or
verbal stim with verbal with repeat complete airway onstruction (ie laryngospasm)
Laryngoscope: < 2 yrs Miller 1
or tactile or painful - Detects cessation of ventilation immediately - pulse ox
* Estimates 2-12 yrs Miller 2/Mac 2
stim stim detects desaturations 1-5 minutes (depending on age,
>12 yrs Mac 3
preoxygenation, and comorbidities)
Adult/large adolescent Mac 4
Airway Unaffected No May require Oral Airway/Nasal airway
intervention intervention Age, Apnea duration, and desats (with preoxygenation)
required Pharmaceuticals: See Medication guidelines Age time (mean) -90% O2 sat time (range)- 90% O2 sat
(sec) (sec)
- Draw up initial dose and bolus doses before case
2 day - 6 mo 96.5 sec 77 - 118 sec
Unaffected Adequate May be - Keep saline flushes separate from medications
Spont. 7 mo - 23 mo 118.5 sec 79 - 163 sec
inadequate - Locate and have immediate access to reversal and 2 yr - 5 yr 160 sec 114 - 205 sec
ventilation
emergency drugs 6 yr - 10 yr 215 sec 165 - 274 sec
11 yr - 18 yr 382 sec 185 - 490 sec
CV fxn Unaffected Usually Usually Monitors:
Patel. Age and onset of desaturations in apnoeic children. Can J Anesth. 1994
unaffected unaffected - Cardiorespiratory (EKG) monitoring
Documenting levels of sedation: - Blood pressure monitoring
- Rising etCO2 or low etCO2 can reflect
- Continuous pulse oximetry
1 - Anxious, agitated, restless hypoventilation
- Continuous capnography
2 - Cooperative, oriented, or tranquil - Rising CO2: low RR, nml Vt (hypopnea)
3 - Asleep, brisk response to light stroke to cheek Extra: - Low etCO2: shallow respirations leading to
4 - Asleep, sluggish response to light stroke to cheek Ensure all procedural equipment and staff are in room dilution of alveolar gas by dead space
5 - No response to light stroke to cheek (US, fluoro, etc)
You might also like
- Pharmacology of Sedative DrugsDocument55 pagesPharmacology of Sedative DrugswgalalNo ratings yet
- Sedation, Analgesics, and Paralysis For MV Patients: Sedatives Promote Sleep, Reduce Anxiety and AgitationDocument3 pagesSedation, Analgesics, and Paralysis For MV Patients: Sedatives Promote Sleep, Reduce Anxiety and Agitationفاطِمه سيد ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- CMR SedationDocument2 pagesCMR SedationYong Wai100% (1)
- TABLE 2. Anticonvulsant Drug Therapies For Convulsive Status Epilepticus (CSE)Document2 pagesTABLE 2. Anticonvulsant Drug Therapies For Convulsive Status Epilepticus (CSE)nasibdinNo ratings yet
- Induction Agents MOA Onset, Duration Special Uses / Notes PropofolDocument3 pagesInduction Agents MOA Onset, Duration Special Uses / Notes PropofolpaveethrahNo ratings yet
- NaloxoneDocument3 pagesNaloxoneTracyNo ratings yet
- Pasion, James Nicole R. BSN - 2 NCM 101 Lec Assignment: 1 ML, 0.2 MGDocument4 pagesPasion, James Nicole R. BSN - 2 NCM 101 Lec Assignment: 1 ML, 0.2 MGۦۦ JamesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyJam CorrosNo ratings yet
- Analgesics and SedativesDocument2 pagesAnalgesics and SedativesdrchiNo ratings yet
- Opioid Equianalgesic ChartDocument1 pageOpioid Equianalgesic Chartdamondouglas100% (7)
- ACLS Algorithm GuideDocument1 pageACLS Algorithm GuideAhmed AlkhaqaniNo ratings yet
- kineme case studyDocument8 pageskineme case studyislafab25No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument14 pagesAssignmentKimberly Claire DegalaNo ratings yet
- Kartu Kode ObatDocument2 pagesKartu Kode ObatHerdaru DyahNo ratings yet
- Recommended Anesthetic Agents for RabbitsDocument1 pageRecommended Anesthetic Agents for RabbitsRais RyuzakiNo ratings yet
- ACLS Simulation ScriptDocument4 pagesACLS Simulation ScriptLeslee Amor EspirituNo ratings yet
- Checklist & Algoritma ACLSDocument16 pagesChecklist & Algoritma ACLSNadhif JovaldyNo ratings yet
- Checklist & Algoritma ACLSDocument16 pagesChecklist & Algoritma ACLSNadhif JovaldyNo ratings yet
- Procedural Sedation GuideDocument9 pagesProcedural Sedation GuideZayar SweNo ratings yet
- Most Common Medication - in Emergency RoomDocument24 pagesMost Common Medication - in Emergency RoomFerdos AdemNo ratings yet
- Algoritma EklampsiaDocument1 pageAlgoritma EklampsiaTheresia ChesarNo ratings yet
- StatusEpilepticus Pocket CardDocument2 pagesStatusEpilepticus Pocket CardDiana MihaiNo ratings yet
- CHEST Seizure Status Epilepticus InfographicDocument1 pageCHEST Seizure Status Epilepticus InfographicDRCRISTOBALTENIZANo ratings yet
- Midazolam IM drug tabulationDocument6 pagesMidazolam IM drug tabulationAdiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- Rapid Sequence Intubation Medications: Sedation For Rapid Sequence Intubation Agent/Class Dose Onset Duration Key NotesDocument1 pageRapid Sequence Intubation Medications: Sedation For Rapid Sequence Intubation Agent/Class Dose Onset Duration Key NotessafasayedNo ratings yet
- Acls Patient Algorithms: Greg Cook's Version of A Phoenix Fire DPT ClasicDocument4 pagesAcls Patient Algorithms: Greg Cook's Version of A Phoenix Fire DPT ClasicDouglas Greg CookNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug Studyjoaqiun100% (1)
- Drug Study Case AnalysisDocument7 pagesDrug Study Case AnalysisNine SaguiboNo ratings yet
- Life Saving DrugsDocument7 pagesLife Saving DrugsJozel Cuanico100% (3)
- Paramedic Drugs: Drug Class Indications Dosage NameDocument14 pagesParamedic Drugs: Drug Class Indications Dosage NameIbrahem Al100% (6)
- Adenosine: Rapid IV PushDocument4 pagesAdenosine: Rapid IV PushsabboNo ratings yet
- Algorithm-ACLS CA 200731Document1 pageAlgorithm-ACLS CA 200731Hyunsoo EllisNo ratings yet
- Drug Infusions in ICU Made Simple 2016 by MansdocsDocument28 pagesDrug Infusions in ICU Made Simple 2016 by Mansdocsabdullah almatary0% (1)
- 4 SeizuresDocument11 pages4 SeizuresApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: ContraindicationsDocument1 pageDrug Study: ContraindicationsMenly SusadaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Epinephrine: RecommendedDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Epinephrine: RecommendedShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- Intubation Pharmacology GuideDocument19 pagesIntubation Pharmacology GuideFANI RUDIYANTI 1No ratings yet
- Dilution Protocol For AdultsDocument23 pagesDilution Protocol For AdultsSharumathi ChandraNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Drugs 1Document21 pagesCritical Care Drugs 1Asri ErnadiNo ratings yet
- Salazar Medsurg Drug StudyDocument2 pagesSalazar Medsurg Drug StudyAlyssa Marie PepitoNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument3 pagesDiazepamGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- General AnestheticDocument2 pagesGeneral AnestheticKirby AcobaNo ratings yet
- Short acting sedative and hypnotic drug indications, doses and side effectsDocument2 pagesShort acting sedative and hypnotic drug indications, doses and side effectsJulene WoodNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action: After An Oral Administration Pen G Is Absorbed in GI Widely Distributed MostDocument3 pagesMechanism of Action: After An Oral Administration Pen G Is Absorbed in GI Widely Distributed MostJR BetonioNo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide for Nausea, GERD and GastroparesisDocument2 pagesMetoclopramide for Nausea, GERD and GastroparesisBeatrizz P GellaNo ratings yet
- Any Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently ReceivingDocument1 pageAny Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently Receivinggeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- NHP - Analgesia Primatas Não HumanosDocument4 pagesNHP - Analgesia Primatas Não HumanosMalu Verruck TortolaNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Intravenous Medications ChartDocument2 pagesCritical Care Intravenous Medications ChartMichelle Danielle MolinaNo ratings yet
- Ccu Guideline Nicvd-1Document9 pagesCcu Guideline Nicvd-1Farhan AnikNo ratings yet
- QR Klinik Kesihatan Setting, by DR Gerard Loh DMDocument34 pagesQR Klinik Kesihatan Setting, by DR Gerard Loh DMlailatul husnaNo ratings yet
- CNS Depressants - Anxiolytics & Sedative HypnoticsDocument4 pagesCNS Depressants - Anxiolytics & Sedative HypnoticsJustin HulinNo ratings yet
- Medication Administration PolicyDocument76 pagesMedication Administration PolicyJully GaciasNo ratings yet
- Magnesium SulfateDocument1 pageMagnesium SulfateIvanne Hisoler67% (3)
- Small Bowel Obstruction Concept MapDocument1 pageSmall Bowel Obstruction Concept MapTessa Claire JaranowskiNo ratings yet
- Perkembangan Baru Resusitasi Jantung ParuDocument27 pagesPerkembangan Baru Resusitasi Jantung ParuMarcelina Aprisia PrimadiNo ratings yet
- Complementary therapy for reducing pain in gastritis patientsDocument28 pagesComplementary therapy for reducing pain in gastritis patientsYendy AftirandiNo ratings yet
- Sjögren's SyndromeDocument18 pagesSjögren's Syndromezakaria dbanNo ratings yet
- World Alzheimer Report 2022Document416 pagesWorld Alzheimer Report 2022bowman1977No ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus in PediatricsDocument22 pagesDiabetes Mellitus in PediatricsKermaigne MirandaNo ratings yet
- Chest Tube, Urinary Catheter, Ryles Tube InsertionDocument60 pagesChest Tube, Urinary Catheter, Ryles Tube InsertionMohd Johari Mohd ShafuwanNo ratings yet
- Holistic Diabetes ReportDocument26 pagesHolistic Diabetes ReporttittaniaNo ratings yet
- Nejmoa 1805374Document10 pagesNejmoa 1805374Lia Diana RaileanuNo ratings yet
- Donating Blood Saves LivesDocument4 pagesDonating Blood Saves LivesGigi2000100% (2)
- Astrazeneca Case StudyDocument8 pagesAstrazeneca Case StudyViren SharmaNo ratings yet
- 82-Arshad Original Article PDFDocument34 pages82-Arshad Original Article PDFmakram_0451No ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrhythmias Guide - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment OptionsDocument5 pagesCardiac Arrhythmias Guide - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment OptionsaksinuNo ratings yet
- ASCO 2017 Edbook PDFDocument871 pagesASCO 2017 Edbook PDFf2ko4100% (2)
- The Seton Fund - Spring 2015Document11 pagesThe Seton Fund - Spring 2015kelly_dodsonNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Liver CirrhosisDocument3 pagesCase Study of Liver Cirrhosisbuzz Q100% (1)
- Graham - A Prospective Study of Physiotherapist Prescribed Community Based Exercise in Inflammatory Peripheral NeuropathyDocument8 pagesGraham - A Prospective Study of Physiotherapist Prescribed Community Based Exercise in Inflammatory Peripheral NeuropathykarinaNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedures HospitalDocument5 pagesStandard Operating Procedures HospitalCesar Francisco95% (37)
- Neuro ImagingDocument41 pagesNeuro ImagingRuchiyyihNo ratings yet
- Reflective Essay For CSDocument2 pagesReflective Essay For CScammel ramosNo ratings yet
- NP Facts: The Voice of The Nurse Practitioner®Document1 pageNP Facts: The Voice of The Nurse Practitioner®giuzolinNo ratings yet
- Clinical Massage Therapy: Assessment and Treatment of Orthopedic MassageDocument35 pagesClinical Massage Therapy: Assessment and Treatment of Orthopedic MassagemassagekevinNo ratings yet
- TelemedicineDocument23 pagesTelemedicineNedhi Singh100% (2)
- Anorectal MalformationDocument17 pagesAnorectal MalformationSilvester SikoraNo ratings yet
- DCR 's-4 AprilDocument33 pagesDCR 's-4 AprilVidya BudihalNo ratings yet
- Six Tiered HMDocument21 pagesSix Tiered HMDoctors NewsNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Plan Protect StaffDocument5 pagesCOVID-19 Plan Protect StaffArgie Corbo BrigolaNo ratings yet
- Toxic Anterior Segment Syndrome-An Updated ReviewDocument9 pagesToxic Anterior Segment Syndrome-An Updated ReviewAri Setiyawan NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Work Comp C4Document5 pagesWork Comp C4ijustwanawriteNo ratings yet
- Distal Tibial Fractures Intramedullary NailingDocument8 pagesDistal Tibial Fractures Intramedullary NailingasdaadNo ratings yet
- Challenges Faced by Australian RadiologistsDocument12 pagesChallenges Faced by Australian RadiologistsVijay RajNo ratings yet
- Hand Sanitizer Factsheet PDFDocument2 pagesHand Sanitizer Factsheet PDFIlmu PengetahuanNo ratings yet