Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Name-Sayantaan Bose College Name - Netaji Subhash Engineering College Dept - Sem - Roll No - 61 UNIVERSITY ROLL NO - 10901621075
Uploaded by
Rohit Kumar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views11 pagesPPT
Original Title
Name-new1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPPT
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views11 pagesName-Sayantaan Bose College Name - Netaji Subhash Engineering College Dept - Sem - Roll No - 61 UNIVERSITY ROLL NO - 10901621075
Uploaded by
Rohit KumarPPT
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
NAME- SAYANTAAN BOSE
COLLEGE NAME- NETAJI SUBHASH ENGINEERING COLLEGE
DEPT-
SEM-
ROLL NO- 61
UNIVERSITY ROLL NO- 10901621075
================
SUBJECT NAME-POWER SYSTEM 1
TOPIC//QUESTION-SHORT-TRANSMISSION LINES
INTRODUCTION
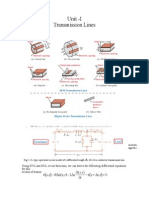
• In AC/DC Power system, Transmission lines are used to transmit the power
from generation station to transmitting station. Transmission lines are pair of
conductor which carry electricity to the consumer’s area. These transmission
lines are classified in to three categories according to the length of the
transmission line. They are, Short transmission line, Medium transmission
line and Long transmission line. In this, we are going to see, the entire study
about short transmission line.
• Short Transmission Line A transmission line having its length less than 80
km is considered as a short transmission line. In short transmission line
capacitance is neglected because of small leakage current and other
parameters (resistance and inductance) are lumped in the transmission line.
SHORT TRANSMISSION LINE DEFINITION:
• The length of the transmission line is less than 50 Mile(80kM) and the
operating voltage is less than 20kV such transmission is called short
transmission line. In short transmission line, the shunt capacitance offers a
very small leakage current due to low voltage, since the shunt capacitance
of the short transmission lines is neglected. Other transmission line
parameters such as resistance and inductance are lumped (Jointly).
• If the overhead transmission line is less than 50km, then this type
of transmission line is referred to as Short Transmission Line.
Generally, the short transmission lines carry operating voltages of
less than 20kV. In these lines, the effect of capacitance is neglected
due to smaller length and low operating voltage.
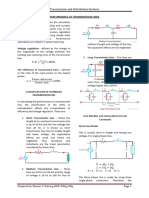
SHORT TRANSMISSION LINE – EQUIVALENT
CIRCUIT AND PHASOR DIAGRAM:
• The short transmission line’s equivalent circuit and phasor diagram
are drawn in the figure given below. Here the lumped parameter R is
considering as line resistance per phase and X is considering as line
inductive reactance per phase of the entire transmission line. As said
earlier the effect of shunt capacitance and conductance is not
considered in the equivalent circuit. The line is shown to have two
ends: sending end (designated by the subscript s) at the generator,
and the receiving end (designated r) at the load. However, consider
• Vr = Receiving end voltage
Vs= Sending End Voltage
Ir = Receiving end Current
Is = Sending end current
cos∅r= power factor of the load
cos∅s = power factor at the sending end
• R1, R2 = Line Resistance…while considering equivalent circuit of short
transmission line, the resistance R1, R2 is considered as R = loop resistance
i.e., resistance of both conductors
• Also the value of resistance R is
• X1, X2 = Line inductive reactance…while considering equivalent circuit of
short transmission line, the reactance X1, X2 is considered as X = loop
reactance i.e., total reactance of both conductors
• The value of the short transmission line’s inductive reactance X is
•
• Here the series impedance is given by Z= R+jX
• In short transmission line, the shunt capacitance and shunt conductance
are neglected, hence sending end current and receiving end current is
same, i.e.
• Voltage Regulation of Short Transmission Line:
• Voltage regulation of the transmission line is the ratio of difference between
sending end voltage and receiving voltage (Vs-Vr) to receiving end voltage
(Vr) is called voltage regulation of the transmission line.
• In short transmission line, as we said above there is no capacitance,
during no load condition the current through the line is considered as
zero, hence at no load condition, receiving end voltage is the same as
sending end voltage.
• Here, vr and vx are the per unit resistance and reactance of the short
transmission line respectively.
WHAT IS TRANSMISSION EFFICIENCY?
• Efficiency is nothing but a ratio between receiving end power to
sending end power and the transmission efficiency is expressed in
percentage. The transmission efficiency says about the transmission
line how much power successfully delivered to receiving end from
sending end.
THE EFFICIENCY OF THE TRANSMISSION LINE:
• In that, You never get 100% of efficiency from short transmission line
since the remaining (100 – η)% of input power consider as losses.
Actually, short transmission line has its own line resistance. So, there
will be an ohmic loss in the resistance of line. If Ps is the input power
at sending end, then only (Ps – Loss) will be available at the receiving
end. Therefore (100 -η)% is the loss in transmission line resistance.
Let see the new method to calculate transmission efficiency. Here loss
of the transmission line will be Loss= I2*R. Therefore, resistance of the
short transmission line will be
CONCLUSION
• A transmission line having its length less than 80 km is considered as a
short transmission line. In short transmission line capacitance is neglected
because of small leakage current and other parameters (resistance and
inductance) are lumped in the transmission line.
• Line voltage drop, voltage regulation, and short-transmission efficiency are
important factors that govern the performance of the short-transmission lines.
• The voltage regulation of a short-transmission line varies with the effect of the line
parameters R, L, and C on the line length.
• In a short transmission line, the voltage regulation depends on the line current,
load power factor, and line parameters R and L.
You might also like
- Short Transmission LineDocument39 pagesShort Transmission LineSudip MondalNo ratings yet
- Module 3.2Document42 pagesModule 3.2JASPER PAYAPAYA100% (1)
- Mod 2Document130 pagesMod 2JUHI SINGHNo ratings yet
- Int To Power - Lecture 8 - Transmission Line Models and PerformanceDocument41 pagesInt To Power - Lecture 8 - Transmission Line Models and PerformanceYoussef Hossam100% (1)
- PS II Before T1Document77 pagesPS II Before T1venkat rajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document62 pagesChapter 5qalbeessaashiboNo ratings yet
- Transmission LinesDocument25 pagesTransmission LinesKhadija AminNo ratings yet
- Performance of Line (Power System)Document12 pagesPerformance of Line (Power System)EE-053-Nirmal TuduNo ratings yet
- TRANSMISSION LINES-libre PDFDocument32 pagesTRANSMISSION LINES-libre PDFJuan Pablo Ossa YepesNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Performance Analysis (Modeling)Document40 pagesTransmission Line Performance Analysis (Modeling)Elias BeyeneNo ratings yet
- Transmission LinesDocument7 pagesTransmission LinesSunil ParikhNo ratings yet
- Types of Transmission WiresDocument15 pagesTypes of Transmission WiresGamal AymanNo ratings yet
- Transmission Lines and CapacityDocument32 pagesTransmission Lines and Capacitysatish reddyNo ratings yet
- Performance of Transmission LinesDocument10 pagesPerformance of Transmission LinesMizanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulation, Line Loss and Efficiency: Experiment No. 10Document4 pagesVoltage Regulation, Line Loss and Efficiency: Experiment No. 10Faiza IqbalNo ratings yet
- Transmission Lines: T C NjendaDocument39 pagesTransmission Lines: T C NjendaTakawiraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 (Chaptr 5)Document31 pagesLecture 7 (Chaptr 5)Eti'el Films / ኢትኤል ፊልሞችNo ratings yet
- EE 741-Primary & Secondary SystemsDocument39 pagesEE 741-Primary & Secondary SystemsΔημητρηςΣαρακυρουNo ratings yet
- Unit-Ii Performance of Transmission LinesDocument38 pagesUnit-Ii Performance of Transmission Linesirshad224No ratings yet
- Power Systems - I - UNIT - IVDocument38 pagesPower Systems - I - UNIT - IVManish MadhuNo ratings yet
- PSA Unit 1Document26 pagesPSA Unit 1sravanNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line,: ASCR (Aluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced) Are Used in This Type of Transmission LineDocument5 pagesTransmission Line,: ASCR (Aluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced) Are Used in This Type of Transmission Linemana danaNo ratings yet
- Performance of Transmission LinesDocument3 pagesPerformance of Transmission LinesJeremy DeleonNo ratings yet
- 23-07-07 2-NOTES Lesson-03Document11 pages23-07-07 2-NOTES Lesson-03Jomel CamanianNo ratings yet
- Current & Voltage Relations LectureDocument10 pagesCurrent & Voltage Relations LectureJunied TazrianNo ratings yet
- Chapter-Three: Performance of Transmission LinesDocument29 pagesChapter-Three: Performance of Transmission LinesGetahun shankoNo ratings yet
- EE 14 - FinalsDocument2 pagesEE 14 - FinalsSantos, Jewella C.No ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Line Model and Performance: RegulationDocument23 pagesChapter 5: Line Model and Performance: RegulationFatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 TL Modelling and PerformanceDocument9 pagesLecture 2 TL Modelling and PerformanceJustine ReyesNo ratings yet
- TL Modelling and PerformanceDocument9 pagesTL Modelling and PerformanceApril BalceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-2-3Document170 pagesChapter 1-2-3Nitish Nageshwara RaoNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Modelling and PerformanceDocument8 pagesTransmission Line Modelling and PerformanceAlexis AguillonNo ratings yet
- Performance of Transmission LinesDocument24 pagesPerformance of Transmission LinesOmkar SheteNo ratings yet
- Name: Kaustubh Deepak Urade REG NO: 2017BEL018Document5 pagesName: Kaustubh Deepak Urade REG NO: 2017BEL018Kaustubh UradeNo ratings yet
- R. Krishnan - Electric Motor Drives - Modeling, Analysis, and Control (2001)Document52 pagesR. Krishnan - Electric Motor Drives - Modeling, Analysis, and Control (2001)Tarushree SabarwalNo ratings yet
- PT Cep Hardware 3Document8 pagesPT Cep Hardware 3Memer XYZNo ratings yet
- Distribution Netwok Design FinalDocument44 pagesDistribution Netwok Design FinalEzana EzanaNo ratings yet
- CP 13Document43 pagesCP 13M Alwan Nur AjieNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 Performance of TXN LineDocument25 pagesChapter - 4 Performance of TXN LinemarNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Transmission Line PerformanceDocument48 pagesCH 3 Transmission Line PerformanceZerihun PaulosNo ratings yet
- Power SystemDocument364 pagesPower SystemDevil YADAVNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 Transmission Lines AdditionalDocument55 pagesChapter2 Transmission Lines AdditionalHussna AlhinaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4a.transmission Line Parameters and EffectsDocument19 pagesLecture 4a.transmission Line Parameters and Effectswakolesha TadeoNo ratings yet
- 2 - Transmission Line ParametersDocument83 pages2 - Transmission Line ParametersEshet ShumetNo ratings yet
- 17-Ee-117, 102 CepDocument14 pages17-Ee-117, 102 CepMoattar MalikNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument5 pagesUnit InitinmgNo ratings yet
- Reactive and Active Power Transfer Experiment - Additional NotesDocument51 pagesReactive and Active Power Transfer Experiment - Additional NotesOmkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Transmission Lines New1Document52 pagesChapter 2 Transmission Lines New1abdul hadi ps100% (1)
- Current and Voltage RelationshipDocument4 pagesCurrent and Voltage RelationshipMike AndayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Transmission Line ParametersDocument83 pagesChapter 2 - Transmission Line Parametersfiraol temesgenNo ratings yet
- Short and Medium Transmisssion LineDocument11 pagesShort and Medium Transmisssion LineCHARLES KENT DOLOTINANo ratings yet
- Transmission LineDocument6 pagesTransmission LineNirmal UndugodaNo ratings yet
- Medium Transmission Line DefDocument2 pagesMedium Transmission Line DefAnonymous r0DuMhsARINo ratings yet
- Unit - I Transmission Line Theory 1.1 General Theory of Transmission LinesDocument21 pagesUnit - I Transmission Line Theory 1.1 General Theory of Transmission LinesSiva KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit III-reactive Powerûvoltage ControlDocument58 pagesUnit III-reactive Powerûvoltage ControlLalith Krishnan100% (2)
- Transmision of Electric PowerDocument110 pagesTransmision of Electric PowerQadeer ZahidNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- BRENTON TarrantDocument4 pagesBRENTON TarrantSayyidNo ratings yet
- Sample Valuation ReportDocument15 pagesSample Valuation Reportayush singlaNo ratings yet
- A Vision System For Surface Roughness Characterization Using The Gray Level Co-Occurrence MatrixDocument12 pagesA Vision System For Surface Roughness Characterization Using The Gray Level Co-Occurrence MatrixPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- USA Nozzle 01Document2 pagesUSA Nozzle 01Justin MercadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and The Other Terrestrial WorldsDocument27 pagesChapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and The Other Terrestrial WorldsEdwin ChuenNo ratings yet
- GT I9100g Service SchematicsDocument8 pagesGT I9100g Service SchematicsMassolo RoyNo ratings yet
- COMMISSIONING COUPLE Aafidavit SANKET DOCTORDocument2 pagesCOMMISSIONING COUPLE Aafidavit SANKET DOCTORYogesh ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Matokeo CBDocument4 pagesMatokeo CBHubert MubofuNo ratings yet
- Automated Facilities Layout Past Present and FutureDocument19 pagesAutomated Facilities Layout Past Present and FutureJose Luis Diaz BetancourtNo ratings yet
- Book Review Fiction New HereDocument7 pagesBook Review Fiction New HereFILZAH SYAUQINA BINTI SUBLY Pelajar KPTM IpohNo ratings yet
- Credit Risk ManagementDocument64 pagesCredit Risk Managementcherry_nu100% (12)
- The Function and Importance of TransitionsDocument4 pagesThe Function and Importance of TransitionsMarc Jalen ReladorNo ratings yet
- Final Notice To Global Girls Degree CollgeDocument2 pagesFinal Notice To Global Girls Degree CollgeIbn E AdamNo ratings yet
- License Fee PaidDocument1 pageLicense Fee Paidmy nNo ratings yet
- Basler Electric TCCDocument7 pagesBasler Electric TCCGalih Trisna NugrahaNo ratings yet
- CLASS XI (COMPUTER SCIENCE) HALF YEARLY QP Bhopal Region Set-IIDocument4 pagesCLASS XI (COMPUTER SCIENCE) HALF YEARLY QP Bhopal Region Set-IIDeepika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Travelstart Ticket (ZA10477979) PDFDocument2 pagesTravelstart Ticket (ZA10477979) PDFMatthew PretoriusNo ratings yet
- The Dust Bunnies COL FKBDocument36 pagesThe Dust Bunnies COL FKBPradeep ManralNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Mechanical Properties of Steel Using Artificial Neural NetworkDocument7 pagesPrediction of Mechanical Properties of Steel Using Artificial Neural NetworkInternational Association of Scientific Innovations and Research (IASIR)No ratings yet
- Merchant Shipping MINIMUM SAFE MANNING Regulations 2016Document14 pagesMerchant Shipping MINIMUM SAFE MANNING Regulations 2016Arthur SchoutNo ratings yet
- Lit 30Document2 pagesLit 30ReemAlashhab81No ratings yet
- Computerized Flat Knitting Machine Computerized Flat Knitting Machine Computerized Flat Knitting Machine Computerized Flat Knitting MachineDocument61 pagesComputerized Flat Knitting Machine Computerized Flat Knitting Machine Computerized Flat Knitting Machine Computerized Flat Knitting MachineAmira's ClothesNo ratings yet
- Elerick Ron Cynthia 1983 SouthAfricaDocument4 pagesElerick Ron Cynthia 1983 SouthAfricathe missions networkNo ratings yet
- Rule 7bDocument38 pagesRule 7bKurt ReoterasNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument18 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisAbdul MajeedNo ratings yet
- AYUSH Warli Art 100628Document10 pagesAYUSH Warli Art 100628adivasi yuva shakti0% (1)
- STRUNK V THE STATE OF CALIFORNIA Etal. NYND 16-cv-1496 (BKS / DJS) OSC WITH TRO Filed 12-15-2016 For 3 Judge Court Electoral College ChallengeDocument1,683 pagesSTRUNK V THE STATE OF CALIFORNIA Etal. NYND 16-cv-1496 (BKS / DJS) OSC WITH TRO Filed 12-15-2016 For 3 Judge Court Electoral College ChallengeChristopher Earl Strunk100% (1)
- Model Contract FreelanceDocument3 pagesModel Contract FreelancemarcosfreyervinnorskNo ratings yet
- Haymne Uka@yahoo - Co.ukDocument1 pageHaymne Uka@yahoo - Co.ukhaymne ukaNo ratings yet
- Things You Can Do at Burnham ParkDocument2 pagesThings You Can Do at Burnham ParkBcpo TeuNo ratings yet