Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mathematical English Help Sheet Guide
Uploaded by
nguyễn hoàng anh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesThis document provides a mathematical English help sheet that defines various mathematical symbols, terms, and expressions in written form. It includes Greek letters, functions, limits, derivatives, integrals, and other symbols commonly seen in mathematics. The sheet is intended to help readers understand the pronunciation and meaning of mathematical notation when seen in written English text.
Original Description:
Original Title
Mathematical English Help Sheet 2017
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a mathematical English help sheet that defines various mathematical symbols, terms, and expressions in written form. It includes Greek letters, functions, limits, derivatives, integrals, and other symbols commonly seen in mathematics. The sheet is intended to help readers understand the pronunciation and meaning of mathematical notation when seen in written English text.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesMathematical English Help Sheet Guide
Uploaded by
nguyễn hoàng anhThis document provides a mathematical English help sheet that defines various mathematical symbols, terms, and expressions in written form. It includes Greek letters, functions, limits, derivatives, integrals, and other symbols commonly seen in mathematics. The sheet is intended to help readers understand the pronunciation and meaning of mathematical notation when seen in written English text.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Mathematical English Help Sheet
Written for all
Reading there exist(s)
form
2+2=4 2 plus 2 equals 4 AB A is a subset of B
a–b The union of A and B
A minus B AB
A union B
ab A plus or minus B
The intersect(ion) of A and B
A times B AB
ab A multiplied by B
A intersect B
sin x The sine of X or sine X /sain/
ab A divided by B cos x The cosine of X or cos X /kɒz/
a/b A over B tan x The tangent of X or tan X
½ (a) half sin-1 x The inverse sine of X
⅔ Two thirds sin2 3 Sine squared 3 theta
¾ Three quarters x X prime(d) or X dash(ed)
/3 pi over 3 or pi by 3 x X double prime(d)
X double dash(ed)
f(x) F of X
x̂ X hat
x2 X squared
x X tilde
x3 X cubed
x* X star
xn X to the (power) N
x X bar
(2x + y)7 2 X plus Y all to the (power) 7
x1/n X to the (power) one over N
The square root of X Greek Letters pronunciation
x
Root X
3
Alpha
x The cube root of X Beta /'bi:tǝ/
x
e E to the (power) X , Gamma
e -2x+3 E to the minus 2 X plus 3 , Delta
ln x log X or the natural log of X Epsilon
Zeta /'zi:tǝ/
log x log (to the base 10 of) X
Eta /'i:tǝ/
The absolute value of X
|x| The modulus of X or mod X , Theta /'i:tǝ/
x! X factorial Kappa
Lambda
xn X (sub) N
Mu /mju:/
x x0 X tends to X nought
Nu /nju:/
x>y X is greater than Y Xi /sai/ or /ksai/
xy X is less than or equal to Y Pi /pai/
1 x 2 X is greater than 1 and less than 2 Rho
x y X is much greater than Y , Sigma
Tau /taʊ/ or /tɔ:/
xy X is not equal to Y
, Phi /fai/
xy X is approximately equal to Y
Chi /kai/
xy X is proportional to Y , Psi /sai/ or /psai/
therefore , Omega /'əʊmigə/
implies
if and only if (or means the same as)
Department of Mathematics, International University, VNU-HCMC Page 1 of 2 07/09/2017
Names of Other Symbols
() (round) brackets
[] Square brackets
{} Curly brackets
Nabla
(right) arrow
Written form Reading
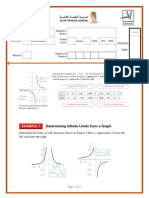
lim f ( x) The limit of F of X as X tends to infinity
x
dy The derivative of Y with respect to X
dx D Y by D X
d2y The second derivative of Y with respect to X
dx 2 D 2 Y by D X squared
y The partial derivative of Y with respect to X
x Partial D Y by D X
y dx The integral of Y with respect to X
b The integral of Y with respect to X between (X equals) A and (X equals) B
a y dx OR The integral of Y with respect to X from (X equals) A to (X equals) B
For all positive , there exists positive such
0, 0, x : 0 x x0 , f ( x) that, for all X satisfying 0 x x0 , the
absolute value of F of X is less than .
Practice
How would you read the following?
3 squared x plus 2 times x times y minus y to the 5
1) 3x2 + 2xy – y5 + 5/13 = (x – 1)3 over 13 equals x minus 1 all to the 3.
2) y e sin x
x
y equals plus or minus the square root of E to the x plus sine x
The absolute value of x minus 1 is greater than 0 is less than or
3) 0 < |x – 1| /2
equal to pi over 2
4) lim f ( x) log 2 7 The limit of F of x as x tends to minus infinity
x
5) an = x! / n! a n equals x factorial over n factorial
dx 13
6) t cos 4t The derivative of x with respect to t equals t to the minus 1 over 3
dt
plus cos 4 times t
7) 2 f ( x) dx The integral of x with respect to between 2 to infinity
Department of Mathematics, International University, VNU-HCMC Page 2 of 2 07/09/2017
You might also like
- X y X y X y X y X X: Mathematical EnglishDocument1 pageX y X y X y X y X X: Mathematical Englishhxx lxxxNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument3 pagesMathsapi-26257902No ratings yet
- Pronunciation of Mathematical ExpressionsDocument3 pagesPronunciation of Mathematical Expressionsbaodepei6034100% (2)
- Université Louis Pasteur - Anglais Scientifique 2006-2007Document3 pagesUniversité Louis Pasteur - Anglais Scientifique 2006-2007thanhbinh12xNo ratings yet
- Mathematic SymbolDocument5 pagesMathematic SymbolphammnguyenhaNo ratings yet
- List of Mathematical Symbols - Simple English Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesList of Mathematical Symbols - Simple English Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRohit RajNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics Symbols GuideDocument3 pagesProbability and Statistics Symbols GuideChindieyciiEy Lebaiey CwekZrdoghNo ratings yet
- List of Probability and Statistics SymbolsDocument6 pagesList of Probability and Statistics SymbolsDave VillarbaNo ratings yet
- Expectation Value: Symbol Symbol Name Meaning / Definition ExampleDocument2 pagesExpectation Value: Symbol Symbol Name Meaning / Definition Examplerijalul fikriNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Polynomial Functions: Digital LessonDocument13 pagesGraphs of Polynomial Functions: Digital LessonAna May BanielNo ratings yet
- Pronunciation of mathematical expressionsDocument3 pagesPronunciation of mathematical expressionsAbu_ONo ratings yet
- Symbol Symbol Name Meaning or Definition ExampleDocument6 pagesSymbol Symbol Name Meaning or Definition Examplessrao2211No ratings yet
- Mathematical Symbols 1Document8 pagesMathematical Symbols 1Arianne Rose FangonNo ratings yet
- Basic Maths Symbols Names With Meaning and ExamplesDocument8 pagesBasic Maths Symbols Names With Meaning and ExamplesArianne Rose FangonNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Limits PDFDocument2 pagesMathematics Limits PDFRahulNo ratings yet
- Calculus and analysis symbol guideDocument3 pagesCalculus and analysis symbol guideAubreyNo ratings yet
- Solutions to Calculus Volume 1 by ApostolDocument236 pagesSolutions to Calculus Volume 1 by ApostolAbdullah CoreNo ratings yet
- R&P TheoryDocument2 pagesR&P Theorywayalpriti100No ratings yet
- MATH 181 1 SEMESTER/AY 2018-2019: Frequently Used Continuous Random VariablesDocument4 pagesMATH 181 1 SEMESTER/AY 2018-2019: Frequently Used Continuous Random VariablesJo Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Probability ReviewDocument9 pagesProbability ReviewDishant JainNo ratings yet
- IMPROPER INTEGRALSDocument39 pagesIMPROPER INTEGRALSJR GinussNo ratings yet
- Equation, Ratio Preparation & Variation: 0 N 1 N 2 N 0 N 1 N 2 N 1/nDocument5 pagesEquation, Ratio Preparation & Variation: 0 N 1 N 2 N 0 N 1 N 2 N 1/nGIRIKNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PolynomialDocument5 pagesChapter 2 PolynomialDøomNo ratings yet
- Maximum Likelihood Estimation: Topic 15Document10 pagesMaximum Likelihood Estimation: Topic 15Sebastian BejaranoNo ratings yet
- Basic Operations and NumbersDocument56 pagesBasic Operations and NumbersDwi LestarinsihNo ratings yet
- Basic Math Symbols: Valentine Kindangen 16811015Document3 pagesBasic Math Symbols: Valentine Kindangen 16811015Hiskia MumuNo ratings yet
- SymbolsDocument1 pageSymbolsjovan avery dalluayNo ratings yet
- Continuous RV-handout 2Document6 pagesContinuous RV-handout 2Jo Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Algebra Symbols ListDocument2 pagesAlgebra Symbols ListJohn BondNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Infinite LimitsDocument7 pagesMathematics: Infinite LimitsAisha AlshmsiNo ratings yet
- Limits at Infinity & Horizontal AsymptotesDocument13 pagesLimits at Infinity & Horizontal AsymptotesThanh TiếnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 LimitsDocument19 pagesChapter 1 LimitsIrsyadNo ratings yet
- Greek Letters Common Usages: X X y y X yDocument3 pagesGreek Letters Common Usages: X X y y X yClydeLisboaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Curve SketchingDocument7 pagesSummary of Curve SketchingOsman JallohNo ratings yet
- SAT Math To Know in One Page PDFDocument3 pagesSAT Math To Know in One Page PDFhaya khaledNo ratings yet
- Example 8: Solution:: Z X Xy yDocument8 pagesExample 8: Solution:: Z X Xy yTayyab HusaainNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1B: For F Cosh, F (2) Cosh 2, A Horizontal Sketch of Scale FactorDocument5 pagesExercise 1B: For F Cosh, F (2) Cosh 2, A Horizontal Sketch of Scale FactorChuanjue LeeNo ratings yet
- Math Analysis Semester 1 Final ReviewDocument10 pagesMath Analysis Semester 1 Final ReviewmayanbNo ratings yet
- 3.2 the Exponential, Gamma, And Chi-Square Distributions 習題Document7 pages3.2 the Exponential, Gamma, And Chi-Square Distributions 習題sandywu930510No ratings yet
- Chapter-4 combinedDocument79 pagesChapter-4 combinedhayatasil19No ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesLecture NotesJustin Paul TumaliuanNo ratings yet
- MATH 101 Calculus I Midterm Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesMATH 101 Calculus I Midterm Exam QuestionsQasim FarooqNo ratings yet
- 11 Normal DistributionDocument48 pages11 Normal DistributionHemanthNo ratings yet
- U1L3 - Key Features of Parent FunctionsDocument2 pagesU1L3 - Key Features of Parent FunctionsAubrey MillsideNo ratings yet
- 2 8Document38 pages2 8georgNo ratings yet
- Lgebraic AND Ranscendental Quations: Chapt ErDocument18 pagesLgebraic AND Ranscendental Quations: Chapt ErAyush BhadauriaNo ratings yet
- How To Pronounce Mathematical Formulae in English: Last Up-Dated Feb 2016, by Dr. Pho Duc TaiDocument2 pagesHow To Pronounce Mathematical Formulae in English: Last Up-Dated Feb 2016, by Dr. Pho Duc TaiTrọng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- FormelsammhgcsaDocument2 pagesFormelsammhgcsaJANNo ratings yet
- Random Variables: Distributions, Expectations and PropertiesDocument74 pagesRandom Variables: Distributions, Expectations and PropertiesAshwani SharmaNo ratings yet
- Practice Calculus Test With Trig: An F Anx G An F G X F F X GDocument11 pagesPractice Calculus Test With Trig: An F Anx G An F G X F F X GphrqdurhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Limit and Continuity: by Solomon Bati Mathematics Dept Jimma University 2010Document87 pagesChapter 1: Limit and Continuity: by Solomon Bati Mathematics Dept Jimma University 2010Usmaan GammachuuNo ratings yet
- Abel-Jacobi Theorem: To Cite This VersionDocument13 pagesAbel-Jacobi Theorem: To Cite This VersionvahidNo ratings yet
- Calculus SymbolsDocument1 pageCalculus Symbolspcr123No ratings yet
- Mathematical SymbolsDocument2 pagesMathematical SymbolsNathan LakaNo ratings yet
- Graphical Models: Worksheet 1 MT 2020: A: Warm-UpDocument3 pagesGraphical Models: Worksheet 1 MT 2020: A: Warm-Upscribdaccount314159No ratings yet
- MATH 101 - Understanding Left, Right Handed Limits and Squeeze TheoremDocument45 pagesMATH 101 - Understanding Left, Right Handed Limits and Squeeze TheoremHasan AsharNo ratings yet
- TrigDocument33 pagesTrigHappybabyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6Document3 pagesAssignment 6VISHVENDRA CHAUHANNo ratings yet
- I. Graphs of Sin X, Cos X, and Tan X Practice ProblemsDocument15 pagesI. Graphs of Sin X, Cos X, and Tan X Practice ProblemsStevenNo ratings yet
- 03nicole de GuzmanDocument13 pages03nicole de GuzmanEden AniversarioNo ratings yet
- Linear Functions Linear FunctionsDocument8 pagesLinear Functions Linear FunctionsNerinel CoronadoNo ratings yet
- 95 To 06 Ext 2 Complex Numbers PDFDocument8 pages95 To 06 Ext 2 Complex Numbers PDFhsathasivanNo ratings yet
- Unit CircleDocument7 pagesUnit CircleAileen OrbinaNo ratings yet
- Law of SineDocument2 pagesLaw of Sineglenn maltoNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodical Exam in Basic Calculus ReviewerDocument10 pages1st Periodical Exam in Basic Calculus ReviewerralphNo ratings yet
- Differentiating Trigonometric Functions PDFDocument4 pagesDifferentiating Trigonometric Functions PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Complex Analysis: George VoutsadakisDocument83 pagesIntroduction To Complex Analysis: George VoutsadakisJohn Michael Ochea NatadNo ratings yet
- William Rowan Hamilton - On Conjugate Functions, or Algebraic Couples-P.D. Hardy (2000)Document5 pagesWilliam Rowan Hamilton - On Conjugate Functions, or Algebraic Couples-P.D. Hardy (2000)lk;kdNo ratings yet
- TrigDocument38 pagesTrigmksayshiNo ratings yet
- FHMM1014 Topic 1 Numbers and Sets StudentDocument125 pagesFHMM1014 Topic 1 Numbers and Sets StudentPok Zheng HanNo ratings yet
- 1013L1 Chapter3Document43 pages1013L1 Chapter3Sheet HappyNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 Elementary FunctionsDocument17 pagesChapter3 Elementary FunctionsEric RodriguezNo ratings yet
- E. T. Whittaker, G. N. Watson - A Course of Modern Analysis-Cambridge University Press (2021)Document721 pagesE. T. Whittaker, G. N. Watson - A Course of Modern Analysis-Cambridge University Press (2021)Rafe BelmontNo ratings yet
- Notations DLMF (NIST) PDFDocument4 pagesNotations DLMF (NIST) PDFQuantDev-MNo ratings yet
- Logarithm equations and calculationsDocument2 pagesLogarithm equations and calculationsAbi DanielDinaNo ratings yet
- InterpolationDocument37 pagesInterpolationMyWBUT - Home for Engineers100% (2)
- Sin5Ocos3O-Cos5Osin2: 4coosyoDocument202 pagesSin5Ocos3O-Cos5Osin2: 4coosyoRaghvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Mat3003 Complex-Variables-And-partial-differential-equations TH 1.1 47 Mat3003Document2 pagesMat3003 Complex-Variables-And-partial-differential-equations TH 1.1 47 Mat3003MagnetoSamparkaNo ratings yet
- XII Maths DPP (06) - Prev Chaps + Functions - ITF + Limits, Continuity + MODDocument14 pagesXII Maths DPP (06) - Prev Chaps + Functions - ITF + Limits, Continuity + MODAjiteshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 I Trigonometry II StudentDocument41 pagesChapter 15 I Trigonometry II StudentAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Laurent Series AnalysisDocument9 pagesLaurent Series AnalysisBindeshwar YadavNo ratings yet
- H2 Chapter 15 Complex Number 1 Tutorial Student Copy 2023Document3 pagesH2 Chapter 15 Complex Number 1 Tutorial Student Copy 2023JiahengNo ratings yet
- Complex Analysis, Probability and Statistical MethodsDocument2 pagesComplex Analysis, Probability and Statistical MethodsRaj0% (2)
- BITS Pilani Math Assignment 1Document2 pagesBITS Pilani Math Assignment 1aryan pancholiNo ratings yet
- Maths Trigonometry Worked ExamplesDocument37 pagesMaths Trigonometry Worked ExamplesSANTHOSH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Fórmulas de Cálculo Diferencial e Integral: Jesús Rubí Miranda (Document3 pagesFórmulas de Cálculo Diferencial e Integral: Jesús Rubí Miranda (Yahel VazquezNo ratings yet