Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP - Osteoporosis
Uploaded by
Cassey Cureg0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
155 views4 pagesThe nursing care plan outlines interventions to address a 52-year old female patient's impaired mobility due to osteoporosis and lower back pain. Short term goals include the patient verbalizing relief of pain and regaining mobility within 8 hours. Long term goals include maintaining functional mobility for 1-2 weeks. Interventions include monitoring vitals, ensuring safety, range of motion exercises, pain management, nutrition, and collaborating with physical therapy.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe nursing care plan outlines interventions to address a 52-year old female patient's impaired mobility due to osteoporosis and lower back pain. Short term goals include the patient verbalizing relief of pain and regaining mobility within 8 hours. Long term goals include maintaining functional mobility for 1-2 weeks. Interventions include monitoring vitals, ensuring safety, range of motion exercises, pain management, nutrition, and collaborating with physical therapy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
155 views4 pagesNCP - Osteoporosis
Uploaded by
Cassey CuregThe nursing care plan outlines interventions to address a 52-year old female patient's impaired mobility due to osteoporosis and lower back pain. Short term goals include the patient verbalizing relief of pain and regaining mobility within 8 hours. Long term goals include maintaining functional mobility for 1-2 weeks. Interventions include monitoring vitals, ensuring safety, range of motion exercises, pain management, nutrition, and collaborating with physical therapy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
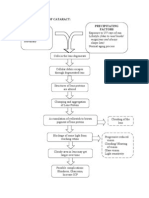
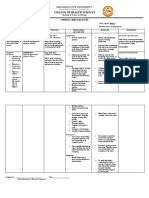
NURSING CARE PLAN
OSTEOPOROSIS
Name: CASSEY MAE M. CUREG Year & Section: BSN 3 – C
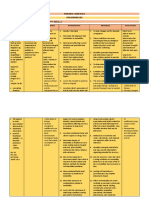
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective: Impaired physical Short Term: 1. Monitor patient’s vital 1. To determine any changes Short Term:
Patient reports mobility related After 8 hours of nursing signs. for baseline comparison. After 8 hours of nursing
difficulty in moving to activity intervention the patient intervention the patient
due to lower back intolerance as will: 2. Ensure patient’s safety. 2. Nurse’s top priority is to was able to:
pain for the last few evidenced by Verbalize relief of provide safety. Verbalize relief of
weeks in the lower pain and limited pain. 3. Note factors affecting pain.
lumbar area. range of motion Display relaxed current situation and 3. Identifies potential Display relaxed
“The pain is (ROM) manner; able to potential time involved. impairments and manner; able to
becoming worse and participate in determines type of participate in
it is keeping me from activities, sleep/rest 4. Assess client’s interventions needed to activities, sleep/rest
doing my daily appropriately developmental level, provide for client’s safety. appropriately
activities.” as stated Compliant with motor skills, ease and Compliant with
by the patient. prescribed capability of movement, 4. This is to determine prescribed
pharmacological posture and gait. presence of pharmacological
Objective: regimen. characteristics of client’s regimen.
Age – 52 y/o Regain or maintain 5. Note older client’s unique impairment and to Regain or maintain
Gender – Female mobility at the general health status. guide choice of mobility at the
highest possible intervention. highest possible
BP – 130/70 level. 6. Evaluate presence and level.
PR – 72 bpm degree of pain, listening 5. While aging, perse, does
RR – 18 cpm Long Term: to client’s description not cause impaired Long Term:
T – 36.5 c* After 1 – 2 weeks of about manner in which mobility, several After 1 – 2 weeks of
nursing intervention, the pain limits mobility. predisposing factors in nursing intervention, the
Facial Grimace patient will maintain addition to age-related patient has maintained
Pain scale 7/10 functional mobility as 7. Ascertain client’s changes can lead to functional mobility as
Limited Range of long as possible and perception of activity immobility. long as possible and
Motion. within limitations. and exercise needs and within limitations.
Verbalization of impact of current 6. To determine if pain
problem and situation. Identify management can improve
request for cultural beliefs and mobility.
information. limitations.
Guarding and 7. Helps to determine
tenderness upon 8. Determine history of client’s expectations and
palpation. falls and relatedness to beliefs related to activity
Pain is fairly current situation. and potential long-term
localized, effect of current
without 9. Asses nutritional status immobility. Also identifies
radiation. and client’s report of barriers that may be
energy level. addressed.
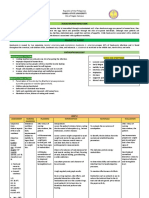
10. Determine presence of 8. Client may be restricting
complications related to activity because of
immobility. weakness or debilitation,
actual injury during a fall,
11. Instruct or assist in the or from psychological
use of siderails, distress that can persist
overhead trapeze, roller after logical distress.
pads walker, and/or
cane. 9. Deficiencies in nutrients
and water, electrolytes,
12. Support affected body and minerals can
parts or joint using negatively affect energy
pillows, rolls, foot and activity tolerance.
supports or shoes, gel
pads, etc. 10. Effects of immobility are
rarely confined to one
13. Provide range of motion body system.
exercises every shift.
Encourage active range 11. For position changes,
of motion exercises. transfers and to facilitate
safe ambulation.
14. Encourage participation
in diversional or 12. To maintain position of
recreational activities. function and reduce risk
Maintain a stimulating of pressure ulcers.
environment (radio, TV,
newspapers, personal 13. Helps to prevent joint
possessions, pictures, contractures and muscle
clock, calendar, visits atrophy.
from family and friends).
14. Provides an opportunity
15. Instruct patient or assist for release of energy,
with active and passive refocuses attention,
ROM exercises of enhances patient’s sense
affected and unaffected of self-control and self-
extremities. worth, and aids in
reducing social isolation.
16. Administer medications
prior to activity as 15. Increases blood flow to
needed for pain relief. muscles and bone to
improve muscle tone,
17. Provide client with maintain joint mobility;
ample time to perform prevent contractures or
mobility-related tasks. atrophy and calcium
resorption from disuse.
18. Instruct family regarding
ROM exercises, 16. To permit maximal effort
methods of transferring and involvement in
patients from bed to activity.
wheelchair, and turning
at routine intervals. 17. --
18. Prevents complications of
19. Collaborate with immobility and knowledge
physical medicine assists family members to
specialist and be better prepared for
occupational or physical home care.
therapists in providing
range-of-motion 19. To develop individual
exercise (active or exercise mobility
passive), isotonic muscle program, to identify
contractions, assistive appropriate mobility
devices and activities. devices, and to limit or
reduce effects and
20. Discuss safe ways that complications of
client can exercise. immobility.
21. Encourage 20. Multiple options proved
client’s/significant client choices and variety.
other’s (SO’s)
involvement in decision- 21. Enhances commitment to
making as much as plan, optimizes outcome.
possible.
22. …
22. Review importance and
purpose of regular 23. Multiple options provide
exercise client choices and variety.
23. Discuss safe ways that
client can exercise.
You might also like
- A Simple Guide to Pseudohypoparathyroidism, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Pseudohypoparathyroidism, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Geria NCP, Dela CruzDocument7 pagesGeria NCP, Dela CruzStephany Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Drug Study: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Drug Study: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationteejay andradaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For CamoxDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For CamoxRolena Johnette B. Piñero100% (2)
- Psych NCPDocument4 pagesPsych NCPnoman-053No ratings yet
- NCP Drug Study Final Paranoid SchizophreniaDocument11 pagesNCP Drug Study Final Paranoid SchizophreniaCherubim Lei DC FloresNo ratings yet
- Psych NCP SchizopreniaDocument5 pagesPsych NCP SchizopreniaPatricia Lae Retonda DeLazoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanCaracel Cabrera SobionoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For A Person With SchizophreniaDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For A Person With SchizophreniaDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Nursing Prioritization and NCP (Bataan)Document7 pagesNursing Prioritization and NCP (Bataan)Rudy Mark ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Planrexale riaNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Comprehensive Case Study 1Document11 pagesRunning Head: Comprehensive Case Study 1api-546355462No ratings yet
- HemodialysisDocument2 pagesHemodialysisjustin_saneNo ratings yet
- A Beautiful Mind FinalDocument5 pagesA Beautiful Mind FinalSimar Sahni100% (1)
- Psychia Ncp-MetchelDocument9 pagesPsychia Ncp-MetchelCarmelita SaltNo ratings yet
- Rle Module Rle Unit Week: Bachelor of Science in Nursing: Rle NCM 105 - Psychiatric NursingDocument6 pagesRle Module Rle Unit Week: Bachelor of Science in Nursing: Rle NCM 105 - Psychiatric NursingAllisson BeckersNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Nursingintervention Rationale Evaluation Discharge PlanningDocument5 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Nursingintervention Rationale Evaluation Discharge PlanningBSN 3B-Bulatao,Goergie Ann L. CPUSNNo ratings yet
- NCP Psyche 1Document7 pagesNCP Psyche 1Pete SkullNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LithiumDocument3 pagesDrug Study - LithiumPRINCESS KOBAYASHINo ratings yet
- Patho NCP DrugsDocument8 pagesPatho NCP DrugsMyco Reyes GarcesNo ratings yet
- X. Nursing Care Plan: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesX. Nursing Care Plan: ObjectiveRenea Joy ArruejoNo ratings yet
- Premenstrual Dysphoric DisorderDocument11 pagesPremenstrual Dysphoric Disorderapi-3764215No ratings yet
- NCP 1 Nursing DiagnosisDocument6 pagesNCP 1 Nursing DiagnosisJosh BlasNo ratings yet
- Beautiful MindDocument6 pagesBeautiful Mindapi-285003633No ratings yet
- Jose Rizal Memorial State University: CommentsDocument4 pagesJose Rizal Memorial State University: CommentsJustine CagatanNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPJoseph Dableo ParreñoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study East AveDocument15 pagesDrug Study East AveSean Philippe CabralNo ratings yet
- Nursing Prioritization (Schizophrenia)Document6 pagesNursing Prioritization (Schizophrenia)Elaine Dionisio TanNo ratings yet
- GORDONSDocument3 pagesGORDONSnikki cullenNo ratings yet
- Drugs and NCPDocument4 pagesDrugs and NCPApril Anne CostalesNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument9 pagesCase StudyPalwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System Disorders NCLEX Practice - Quiz #2 - 50 Questions - NurseslabsDocument52 pagesGastrointestinal System Disorders NCLEX Practice - Quiz #2 - 50 Questions - NurseslabsGypsy Joan TranceNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan Deviced For Teenage Mother and NewbornDocument34 pagesTeaching Plan Deviced For Teenage Mother and NewbornYzel Vasquez AdavanNo ratings yet
- NCP Case PresDocument5 pagesNCP Case Pressyd19No ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Active Fluid Volume LossDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Active Fluid Volume LossMelDred Cajes BolandoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HaldolDocument2 pagesDrug Study HaldolGracia EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis For CholecystectomyDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis For CholecystectomyMiguel VillacarlosNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FluphenazineDocument4 pagesDrug Study FluphenazineaolbinarNo ratings yet
- Olanzapine Drug StudyDocument5 pagesOlanzapine Drug Studyjohnlester_jlfNo ratings yet
- Resource Unit. AdwcwdDocument6 pagesResource Unit. AdwcwdGreg Martin OrbegosoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPmsinsanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationLi Luren Raphaelle TanNo ratings yet
- College of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDocument2 pagesCollege of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: - DateDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: - DateSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- Case File GERDDocument9 pagesCase File GERDMutiara Shifa100% (1)
- NCP UreteroDocument1 pageNCP UreteroCerie Anne OlayNo ratings yet
- Cholecystectomy (: Laparoscopic GallstonesDocument4 pagesCholecystectomy (: Laparoscopic GallstonesAlexia BatungbacalNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Coping NCPDocument4 pagesIneffective Coping NCPFrancis Alfred EscaranNo ratings yet
- MastitisDocument13 pagesMastitisapi-232713902No ratings yet
- NCPDocument18 pagesNCPStephanie Villanueva AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Fluoracil Drug StudyDocument3 pagesFluoracil Drug StudyNicole Louize CaloraNo ratings yet
- Solutions: 1 US A Te CareDocument2 pagesSolutions: 1 US A Te CareelonaNo ratings yet
- Risk For SuicideDocument3 pagesRisk For SuicidepamfiestaNo ratings yet
- Chlorpromazine Drug StudyDocument10 pagesChlorpromazine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Potential Nursing Care Plan SchizopremiaDocument1 pagePotential Nursing Care Plan SchizopremiaopxNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication: Department of Health, PhilippinesDocument35 pagesTherapeutic Communication: Department of Health, PhilippinesKeith Clarence BunaganNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDocument9 pagesNCP Impaired Physical MobilityChristian Apelo SerquillosNo ratings yet
- NCP - PoliomyelitisDocument4 pagesNCP - PoliomyelitisCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- NCP - Hip DysplasiaDocument4 pagesNCP - Hip DysplasiaCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- NCP - PoliomyelitisDocument4 pagesNCP - PoliomyelitisCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- "My Neck Feels Stiff and There's Pain Coming From It. Every Time I Move It, It Only Gets Worse." As Stated by TheDocument4 pages"My Neck Feels Stiff and There's Pain Coming From It. Every Time I Move It, It Only Gets Worse." As Stated by TheCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Jkms 36 E227 s001Document3 pagesJkms 36 E227 s001Cassey CuregNo ratings yet
- "She Can't Breathe Well Especially During Episodes of Spasms" As Verbalized byDocument2 pages"She Can't Breathe Well Especially During Episodes of Spasms" As Verbalized byCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Gec 8 - Activity 1Document9 pagesGec 8 - Activity 1Cassey CuregNo ratings yet
- NCP - Hip DysplasiaDocument4 pagesNCP - Hip DysplasiaCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Community-Health-Survey-11aDocument8 pages2.0 Community-Health-Survey-11aCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting COVID 19 Vaccine Acceptance Among Public Market VendorsDocument57 pagesFactors Affecting COVID 19 Vaccine Acceptance Among Public Market VendorsCassey Cureg100% (1)
- Final - CholeraDocument12 pagesFinal - CholeraCassey Cureg100% (1)
- Final - Food PoisoningDocument10 pagesFinal - Food PoisoningCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Final - TYPHOID FEVERDocument13 pagesFinal - TYPHOID FEVERCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Poliomyelitis: Isabela State UniversityDocument14 pagesPoliomyelitis: Isabela State UniversityCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Hook Worm Infection: Republic of The Philippines City of Ilagan CampusDocument10 pagesHook Worm Infection: Republic of The Philippines City of Ilagan CampusCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Hepatits: Isabela State UniversityDocument11 pagesHepatits: Isabela State UniversityCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Exam Year Questions and AnswersDocument8 pagesExam Year Questions and AnswersArdianto SuhendarNo ratings yet
- Inside: FOR Those WHO ThinkDocument24 pagesInside: FOR Those WHO ThinkJurdiney JuniorNo ratings yet
- Ati AtihanDocument13 pagesAti AtihanMary grace S. MuyonNo ratings yet
- Basic First Aid 0808Document72 pagesBasic First Aid 0808BS AnilKumarNo ratings yet
- Renovation Guidelines Urban Deca Homes Ortigas: I-Millenia Building Solutions IncDocument12 pagesRenovation Guidelines Urban Deca Homes Ortigas: I-Millenia Building Solutions IncCharlton CabagingNo ratings yet
- Penicillin ActDocument5 pagesPenicillin Actcecile towerNo ratings yet
- Research For A Same Sex Marriage DebateDocument11 pagesResearch For A Same Sex Marriage DebateJanna Marzo100% (1)
- The Darwinian Concept of EvolutionDocument6 pagesThe Darwinian Concept of EvolutionAlfredo VergaraNo ratings yet
- Catalytic Converter Using Nano TechnologyDocument4 pagesCatalytic Converter Using Nano TechnologySwathi PadalaNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of BioconDocument12 pagesFinancial Analysis of BioconNipun KothariNo ratings yet
- Drooling PDFDocument2 pagesDrooling PDFSuprit SnNo ratings yet
- 6.625 X 2.875 DLH PACKER (17-24) 935-6625-103 Rev BDocument7 pages6.625 X 2.875 DLH PACKER (17-24) 935-6625-103 Rev BDEATH ASSASSIN GAMERNo ratings yet
- TriconexDocument38 pagesTriconexajmalahmed82No ratings yet
- VMA 1615 ControllerDocument14 pagesVMA 1615 ControllerStephen LimNo ratings yet
- LVTSL004 Grundfos - Peerless VT Pump BrochureDocument5 pagesLVTSL004 Grundfos - Peerless VT Pump BrochuredanilobossuNo ratings yet
- Bustamante - NSTP100 Essay #9Document1 pageBustamante - NSTP100 Essay #9Jimin ParkNo ratings yet
- Pathoma CH 1 NotesDocument2 pagesPathoma CH 1 NotesjdNo ratings yet
- Post-Op Instructions For Immediate DenturesDocument1 pagePost-Op Instructions For Immediate DenturesMrunal DoiphodeNo ratings yet
- Discover Biology The Core 6th Edition Singh Test BankDocument16 pagesDiscover Biology The Core 6th Edition Singh Test Bankkylebrownorjxwgecbq100% (16)
- Probenecid Drug StudyDocument1 pageProbenecid Drug StudykyawNo ratings yet
- CV GULFAM (Safety Trainer)Document3 pagesCV GULFAM (Safety Trainer)Gulfam ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Actus ReusDocument7 pagesActus ReusSaffah Mohamed0% (1)
- Farenhiet 451 - EssayDocument5 pagesFarenhiet 451 - Essayapi-275502795No ratings yet
- Lesson 3 The Ideal Gasq PDFDocument4 pagesLesson 3 The Ideal Gasq PDFireneNo ratings yet
- List of CarcinogensDocument3 pagesList of CarcinogensDisha TNo ratings yet
- Important Monthly Current Affairs Capsule - October 2022Document382 pagesImportant Monthly Current Affairs Capsule - October 2022FebzNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Drain Pan Treatments: DescriptionDocument3 pagesAir Conditioning Drain Pan Treatments: DescriptionCrescent MoonNo ratings yet
- Love Is More Powerful Than HateDocument4 pagesLove Is More Powerful Than Hatepachichoy100% (3)
- (Answer: τ (y = 1 mm) = 1.49 Pa) : MEE20003 Fluid Mechanics 1 Tutorial 1Document2 pages(Answer: τ (y = 1 mm) = 1.49 Pa) : MEE20003 Fluid Mechanics 1 Tutorial 1Afwan IrfanNo ratings yet
- How To Test An RF Coaxial Cable Using A VNADocument5 pagesHow To Test An RF Coaxial Cable Using A VNAStefanvnvNo ratings yet