Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Structured Questions: CC CC C S S S S CC C
Uploaded by
tjun kit minOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Structured Questions: CC CC C S S S S CC C
Uploaded by
tjun kit minCopyright:
Available Formats
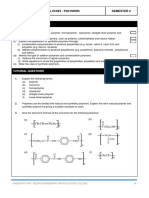
2.
8 A I only C I, II and III only
Oils and Fats B III only D I, II, III and IV
31 Which of the following belong
to the homologous series of 34 The diagram shows the change in structure of natural rubber after process
esters? P.
I Palm oil
c c c c c c
II Margarine s s
process P s s
III Sodium butanoate c
c c c c c c c s c
IV Glycerol s
A I and II only c c c
c c c c
B I and III only
rubber X rubber Y
C III and IV only
D I, II and III only Which of the following statements is true about the change?
A Rubber X is more elastic than rubber Y.
32 Which of the following molecular B Rubber X is stronger than rubberTCY.2/19
formulae of fatty acids is formed C Rubber X is more resistant to heat than rubber Y.
from the hydrolysis of a non- D Rubber X is more easily oxidised than rubber Y.
saturated fat?
A C15H31COOH 35 A rubber tapper faces a problem of transporting latex to a glove-making
B C17H35COOH factory in liquid form. To solve the problem he has to add a substance
C C17H33COOH ’06 into the latex to prevent the coagulation of the latex.
D C23H47COOH Choose the correct substance and the explanation to solve the problem.
2
Substance Explanation
2.9 A Water To make the latex more dilute
Natural Rubber
B Ethanoic acid Contains H+ ions that neutralise the negative
33 Which of the following chemicals charge on the membrane of the rubber particle
can cause latex to coagulate? C Ammonia Contains OH– ions that neutralise the H+ ions
I Methanoic acid solution from the acids produced by bacteria
II Sulphuric acid
III Ethanoic acid D Sodium chloride As a preservative to maintain the original state of
IV Nitric acid solution the latex
Structured Questions
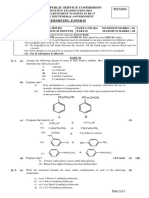
1 Table 1 shows the names, molecular formulae, melting (b) Complete Table 1 by filling in the molecular
points and boiling points of a few straight chain formula of propane and the name of C4H10.
members of a homologous series. [2 marks]
(c) Draw the structural formula of the first member
Molecular Melting Boiling of this homologous series. [1 mark]
Name
formula point (°C) point (°C)
(d) Predict the physical states of
Ethane C2H6 –183 –89 (i) propane [1 mark]
(ii) pentane [1 mark]
Propane –188 –42
(e) Give the name and the molecular formula of the
C4H10 –138 –0.5 member of the same homologous series after
pentane. [2 marks]
Pentane C5H12 –130 36
(f) Write a balanced equation for the complete
Table 1 combustion of ethane. [1 mark]
(a) Give the name and the general formula of this
homologous series. [2 marks]
381 Carbon Compounds
2 Propene is an important hydrocarbon in the petrochemical (b) State the function of concentrated sulphuric acid
industries. Diagram 1 shows the conversion of propene in this reaction. [1 mark]
into other organic compounds. (c) (i) Name the reaction for the preparation of
ethyl ethanoate. [1 mark]
Polypropene (ii) Write the chemical reaction for the reaction
process II in (i). [1 mark]
(d) The experiment is repeated by replacing ethanol
process process with methanol.
Propane Propene Propan-1-ol
I III (i) Name the ester formed. [1 mark]
process IV (ii) Draw the structural formula of the ester
formed. [1 mark]
Compound X (iii) State one physical property of the ester.
[1 mark]
Diagram 1
(e) The flowchart shows the conversion of ethene to
Based on Diagram 1, answer the following questions. ethanol and then to ethanoic acid.
(a) State the homologous series of propene.
[1 mark] process I process II Ethanoic
(b) Name process I. [1 mark]
Ethene Ethanol
acid
(c) Under certain conditions, propene reacts to form
polypropene. Write an equation for the formation Based on the flowchart, write the chemical
of polypropene in process II. [1 mark]
2
equation for
(d) (i) Explain briefly how process III is carried out (i) process I [1 mark]
in industries. [2 marks] (ii) process II [1 mark]
(ii) Draw the structural formula of propan-1-ol. (iii) State a suitable chemical that can be used
[1 mark] to carry out process II. [1 mark]
(e) Acidified potassium manganate(VII) is added to
propene in process IV. 4 Diagram 3 shows conversions I, II and III starting with
(i) Predict the observation that will take place. glucose.
[1 mark]
(ii) Write a balanced equation for the reaction I Liquid II Liquid
that has occurred. [1 mark] Glucose
yeast A reagent B
(f) Both propene and propane are combustible in
air. Compare and explain the difference in the III concentrated
quantity of soot produced by the two compounds H2SO4 asid
during combustion. [2 marks] Liquid C
3 Diagram 2 shows the set-up of apparatus for the
Diagram 3
preparation of ethyl ethanoate by heating ethanol
and ethanoic acid under reflux. (a) (i) Name conversion I. [1 mark]
(ii) Draw the structural formula of liquid A.
[1 mark]
water out
(b) Liquid B has a vinegary smell.
(i) Name the type of reaction that takes place
in conversion II. [1 mark]
(ii) Write a chemical equation for conversion II.
water in TC 2/20 [1 mark]
(c) Give one chemical test that can be used to
ethanol, ethanoic acid distinguish liquid B from liquid A. [2 marks]
and concentrated
sulphuric acid
(d) (i) Name the homologous series of which
xxxxxxxxxxxxxx liquid C is a member. [1 mark]
(ii) Name liquid C. [1 mark]
heat
(iii) State one use of liquid C. [1 mark]
Diagram 2 (e) Suggest another method to produce liquid A
(a) Why is ethanol and ethanoic acid heated under other than from glucose in conversion I.
reflux? [1 mark] [1 mark]
Carbon Compounds 382
5 Diagram 4 shows the conversion of latex to compound (c) Name compound X. [1 mark]
X. (d) State two differences in physical properties
c c
between natural rubber and compound X.
s s
process I Natural process II s s
[2 marks]
c TC 2/21
Latex c s c
rubber s (e) How is process II carried out in the industry?
c c c [1 mark]
compound X (f) (i) Name a chemical that can be used to retain
latex in the liquid form. [1 mark]
Diagram 4
(ii) Explain the function of the chemical named
(a) Name process I and process II. [2 marks] in (i). [1 mark]
(b) Name a chemical that can be used to carry out (g) Give one use of compound X. [1 mark]
process I. [1 mark]
Essay Questions
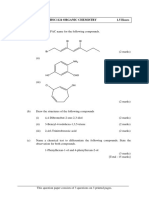
1 (a) Draw the structural formulae of two isomers of 2 (a) Diagram 1 shows the formation of carboxylic acids
but-1-ene and give their IUPAC names. [4 marks] from alcohols.
(b) The information below is referring to carbon
compound X. Alcohols Carboxylic acids
2
Diagram 1
• Carbon 40.0%
• Hydrogen 6.7% Using suitable reagents and with the help of a
• Oxygen 53.3% labelled diagram, describe how you can prepare
• Relative molecular mass = 60 a named carboxylic acid in the laboratory.
• Relative atomic mass of H = 1, C = 12 Include the observation and a test to show that
and O = 16 the product formed is an acid. Write a chemical
equation for the reaction involved.
Based on the information of the carbon compound [10 marks]
X, (b) Many artificial flavours used in the food industry
(i) determine the molecular formula of X. are esters. Various types of esters can be formed
(ii) draw the structural formula of X. from the esterification between an alcohol and a
(iii) name the carbon compound X. carboxylic acid. Name one possible ester that can
(iv) write the general formula for its homologous be formed and describe how you can prepare
series. [8 marks] the named ester in the laboratory. Name the
(c) Margarine can be made from palm oil. Compare alcohol and carboxylic acid that is used and the
and contrast margarine and palm oil in terms of chemical equations involved.
their structures and physical properties. Briefly [10 marks]
describe how palm oil can be converted to
margarine. [8 marks]
Experiment
1 Your planning should include the following:
Hexane is a saturated hydrocarbon whereas hexene
(i) Statement of the problem
is an unsaturated hydrocarbon. Both are colourless
(ii) All the variables
liquids. However they undergo different reactions
(iii) Hypothesis
toward addition reaction.
(iv) List of materials and apparatus
You are required to plan an experiment to differentiate (v) Procedure
the two compounds. (vi) Tabulation of data [17 marks]
383 Carbon Compounds
You might also like
- Fossil Hydrocarbons: Chemistry and TechnologyFrom EverandFossil Hydrocarbons: Chemistry and TechnologyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Chemistry A Modern View: Exercise Book 3 Suggested AnswersDocument39 pagesChemistry A Modern View: Exercise Book 3 Suggested Answersapi-3826695No ratings yet
- Carbon Compound p2 - AnswerDocument8 pagesCarbon Compound p2 - AnswerzarifNo ratings yet
- Single Science End of Topic Assessment With MarkschemeDocument18 pagesSingle Science End of Topic Assessment With Markschemeerin mooreNo ratings yet
- Fuels (Multiple Choice) QPDocument11 pagesFuels (Multiple Choice) QPGreesha Parag DamaniaNo ratings yet
- (Iii) What Is The Chemical Name For Slaked Lime?Document16 pages(Iii) What Is The Chemical Name For Slaked Lime?Fatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgDg EqbLe8xpbdb48m1x1aXZd5w3B7LLPytxgxTOMB61trQBdGUtI-ncGQuIhaPDtK GN-49AuqkGbD-8eBYkZICQdBufIU3TGWgFrCIhZsNOVV6CjrZ9SnnoVc S5iULRlRt0y4bUjqhroDocument27 pagesACFrOgDg EqbLe8xpbdb48m1x1aXZd5w3B7LLPytxgxTOMB61trQBdGUtI-ncGQuIhaPDtK GN-49AuqkGbD-8eBYkZICQdBufIU3TGWgFrCIhZsNOVV6CjrZ9SnnoVc S5iULRlRt0y4bUjqhroAFNo ratings yet
- Formula and EquationsDocument28 pagesFormula and EquationsFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Paper 2 TESDocument34 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Paper 2 TESYotos XdNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry - Test 8Document2 pages12 Chemistry - Test 8Khan HaeeNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Fossil Fuels 1985Document6 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Fossil Fuels 1985api-3826629No ratings yet
- Xi CheDocument2 pagesXi Chepinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- Polymers K-CET Crash: Homework QuestionsDocument3 pagesPolymers K-CET Crash: Homework QuestionsCHIRAG GOWDANo ratings yet
- Alkane Alkene QuestionsDocument10 pagesAlkane Alkene QuestionsormattNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - 1669679477-CHEM EASE-2 2022-2023 - Grade 12 (Sample)Document9 pagesKami Export - 1669679477-CHEM EASE-2 2022-2023 - Grade 12 (Sample)Dava RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Petroleum Products 1985Document13 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Petroleum Products 1985api-3826629No ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in This Section. Indicate The Correct Answer On The Space Provided in Page 2Document5 pagesAnswer All Questions in This Section. Indicate The Correct Answer On The Space Provided in Page 2seanNo ratings yet
- 2022 Alcohol and Phenol Tutorial QPDocument11 pages2022 Alcohol and Phenol Tutorial QPHANNAH GOH (TJC)No ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry End Semester ExaminationDocument4 pagesEngineering Chemistry End Semester ExaminationShivam SinghNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Q&A - 1Document4 pagesOrganic Chemistry Q&A - 1Abaring KathrynaNo ratings yet
- Goc - PDF QuestionsDocument4 pagesGoc - PDF QuestionsPoorvi MathurNo ratings yet
- B. Tech - 6 Semester Semester End Regular Examination: Course code:19CH009Document3 pagesB. Tech - 6 Semester Semester End Regular Examination: Course code:19CH009sivakrosuriNo ratings yet
- Butane SynthesisDocument13 pagesButane SynthesisAbdulhamid AliNo ratings yet
- PR PyqDocument23 pagesPR PyqAVERAGENo ratings yet
- CH 17Document14 pagesCH 17Al-ameen G. TaludjogNo ratings yet
- 9.chem G.test 4 (15-18)Document3 pages9.chem G.test 4 (15-18)Tanveer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry II (Alkanoic Acids and Alkanols)Document8 pagesOrganic Chemistry II (Alkanoic Acids and Alkanols)alexogbisaouNo ratings yet
- Alcohols & Carboxylic Acids 4 QPDocument11 pagesAlcohols & Carboxylic Acids 4 QPkrishav shuklaNo ratings yet
- Du Ca Tio N: Chate Group of EducationDocument3 pagesDu Ca Tio N: Chate Group of EducationNUCLEAR GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Test 42 - Polymer - Middle of PyramidDocument5 pagesTest 42 - Polymer - Middle of PyramidJay PatelNo ratings yet
- 04 Hydrocarbon Set Test Final EDocument3 pages04 Hydrocarbon Set Test Final EΒίητ ε ΗάωωάNo ratings yet
- CAPE Chemistry 2010 U1 P2Document10 pagesCAPE Chemistry 2010 U1 P2SadharshanSinghNo ratings yet
- 'Test' On Oil, Alkanes, Alkenes and AlcoholsDocument3 pages'Test' On Oil, Alkanes, Alkenes and AlcoholsDaniella FreemanNo ratings yet
- Model Paper Engg - Chemistry 1 1 r16Document1 pageModel Paper Engg - Chemistry 1 1 r16vrkoradaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem Chemistry Assignment-2-2022-BatchDocument2 pages2nd Sem Chemistry Assignment-2-2022-Batchshrabani.mahataNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Allen QuestionsDocument20 pagesOrganic Chemistry Allen Questionstiruvalarnayatty100% (1)
- Research PaperDocument32 pagesResearch Papershehryaralishah970No ratings yet
- 25 Jan 23 Evening English 1Document18 pages25 Jan 23 Evening English 1DEPRESSED GAMERNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20.0-Polymer Soalan (74-76)Document5 pagesChapter 20.0-Polymer Soalan (74-76)ChemMatrikNo ratings yet
- CH 11. Hydrocarbons (Chem +1)Document44 pagesCH 11. Hydrocarbons (Chem +1)Sajag GargNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Symposium Questions 2023Document17 pagesChemistry Symposium Questions 2023Doris KinyuaNo ratings yet
- FHSC1124 Test 2 RevisionDocument5 pagesFHSC1124 Test 2 RevisiontravisthenNo ratings yet
- Chem II - Test 2 Exam Questions - Jan2010Qs-IDocument8 pagesChem II - Test 2 Exam Questions - Jan2010Qs-IutpNo ratings yet
- Isomerism Level Wise Practice Sheet by Mr. Dhirendra Kumar For Class 11th ChemistryDocument7 pagesIsomerism Level Wise Practice Sheet by Mr. Dhirendra Kumar For Class 11th ChemistryManoj SisodiaNo ratings yet
- 04 Aldehydes & Ketones Set Test Final EDocument3 pages04 Aldehydes & Ketones Set Test Final EBad boy boyNo ratings yet
- Css Chemistry2 2023Document3 pagesCss Chemistry2 2023Shoukat hussain PirzadaNo ratings yet
- Impure Water inDocument17 pagesImpure Water inFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry Paper 2 Exam 17Document4 pagesA Level Chemistry Paper 2 Exam 17Anthony AndyNo ratings yet
- CAPE Chemistry 2011 U2 P2Document11 pagesCAPE Chemistry 2011 U2 P2hahaNo ratings yet
- Wa0011.Document9 pagesWa0011.gauravsalunkhe367No ratings yet
- Practice Questions 2014Document5 pagesPractice Questions 2014Ruqiyya IsrafilovaNo ratings yet
- 02 Aldehydes & Ketones Que. Final EDocument14 pages02 Aldehydes & Ketones Que. Final EJagdish SinghNo ratings yet
- 2023 ChemistryDocument6 pages2023 Chemistrysumitali7638No ratings yet
- 02-Carboxylic Acids and Their derivatives-Que.-Final-EDocument13 pages02-Carboxylic Acids and Their derivatives-Que.-Final-EAbhishek RavirajNo ratings yet
- CAPE Chemistry 2006 U1 P2Document14 pagesCAPE Chemistry 2006 U1 P2Lilian RegeNo ratings yet
- Chem Papr Aldehyde Ketone and Carboxylic AcidDocument3 pagesChem Papr Aldehyde Ketone and Carboxylic AciduvsNo ratings yet
- Urs Fjs Fjs Fjs Fjs SFJDocument16 pagesUrs Fjs Fjs Fjs Fjs SFJFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Carbon Compounds As Fuels & Feedstock 2 QPDocument15 pagesCarbon Compounds As Fuels & Feedstock 2 QPmariamNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice Questions: XO X. (Relative Atomic Mass: O, 16Document5 pagesMultiple-Choice Questions: XO X. (Relative Atomic Mass: O, 16tjun kit minNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument21 pagesAnswer All Questions in This Sectiontjun kit minNo ratings yet
- Born-Haber EntropyDocument3 pagesBorn-Haber Entropytjun kit minNo ratings yet
- Guan Chong: MalaysiaDocument6 pagesGuan Chong: Malaysiatjun kit minNo ratings yet
- Singlet OxygenDocument62 pagesSinglet Oxygenhamid_hinnaNo ratings yet
- PART TEST-1 (Ogranic Chemistry) PDFDocument6 pagesPART TEST-1 (Ogranic Chemistry) PDFKinshuk RastogiNo ratings yet
- Hammett Correlations and Their Applications in Elucidating Reaction MechanismDocument14 pagesHammett Correlations and Their Applications in Elucidating Reaction MechanismdyaharifNo ratings yet
- Nomanclature Type 1Document20 pagesNomanclature Type 1Vinod Kumar100% (1)
- Naming Ethers - Chemistry Steps - 1660645071113Document7 pagesNaming Ethers - Chemistry Steps - 1660645071113Hakeem AdekunleNo ratings yet
- P (N (i-Bu) CH CH) N: Nonionic Lewis Base for Promoting the Room-Temperature Synthesis of r,β-Unsaturated Esters, Fluorides, Ketones, and Nitriles Using Wadsworth -Emmons PhosphonatesDocument9 pagesP (N (i-Bu) CH CH) N: Nonionic Lewis Base for Promoting the Room-Temperature Synthesis of r,β-Unsaturated Esters, Fluorides, Ketones, and Nitriles Using Wadsworth -Emmons PhosphonatesDiogomussumNo ratings yet
- 2-Organometallic ChemistryDocument37 pages2-Organometallic ChemistryAbhisar UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Chapters 1, 2 and 3 Study Guide Organic ChemisryDocument34 pagesChapters 1, 2 and 3 Study Guide Organic ChemisryNeedBooksDontSueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Chemical Composition of CellDocument16 pagesChapter 4: Chemical Composition of CellHema LataNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Aldehydes and KetonesDocument9 pagesModule 8 Aldehydes and KetonesMaxine AquinoNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules 2Document9 pagesBiological Molecules 2Feranmi AkinboboyeNo ratings yet
- SSC Chemistry - Chap 11Document12 pagesSSC Chemistry - Chap 11Shohag RaihanNo ratings yet
- Notes Chapter 04Document23 pagesNotes Chapter 04Rachelle Donnie Ellicott-ChathamNo ratings yet
- Alkenes and Alkynes CHM456Document93 pagesAlkenes and Alkynes CHM456nanaNo ratings yet
- Essential Chemistry SPM Question Bank Chapter 11 2010Document8 pagesEssential Chemistry SPM Question Bank Chapter 11 2010Thilagavathy MuruganNo ratings yet
- Kalsi P S Organic Reactions and Their Mechanisms New Age ScienceDocument716 pagesKalsi P S Organic Reactions and Their Mechanisms New Age ScienceVineet Jhamb100% (1)
- Alcohols Phenols PDFDocument88 pagesAlcohols Phenols PDFAnanda VijayasarathyNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Exercise - I Exercise - Ii Exercise-Iii Exercise Iv Answer KeyDocument39 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Exercise - I Exercise - Ii Exercise-Iii Exercise Iv Answer KeyRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Ch. 13: Conjugation and AromaticityDocument5 pagesCh. 13: Conjugation and Aromaticityjhbk31No ratings yet
- PROBLEM - SET - 6 - AnswerDocument4 pagesPROBLEM - SET - 6 - AnswerDylan BobNo ratings yet
- A New Synthesis of Lysergic AcidDocument3 pagesA New Synthesis of Lysergic AcidOscar ArzuaNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument7 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsMoomin Ahmad DarNo ratings yet
- AIATS-2022 (CF+OYM) Test-08 - Code-A - Solutions - 20.03.2022Document21 pagesAIATS-2022 (CF+OYM) Test-08 - Code-A - Solutions - 20.03.2022SRIJANo ratings yet
- Krebs (Citric Acid) Cycle Steps by Steps ExplanatDocument2 pagesKrebs (Citric Acid) Cycle Steps by Steps ExplanatDesiree Marila Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- SN2 RXDocument25 pagesSN2 RXGebby FebriliaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Phenol Ether (1) 6Document9 pagesAlcohol Phenol Ether (1) 6sdnishacNo ratings yet
- Aid For Ferrocene AssignDocument32 pagesAid For Ferrocene AssignGuangyu XuNo ratings yet
- Expt 7 Classification Tests For HydrocarbonsDocument7 pagesExpt 7 Classification Tests For HydrocarbonsRizzalaine Caringal87% (30)
- Synthesis of 1-Phenylazo 'Sudan 1'Document5 pagesSynthesis of 1-Phenylazo 'Sudan 1'seryuyuyu100% (2)
- CHEM05 LectureDocument62 pagesCHEM05 LecturegirlonfireNo ratings yet