Professional Documents
Culture Documents
04 Aldehydes & Ketones Set Test Final E
Uploaded by
Bad boy boyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
04 Aldehydes & Ketones Set Test Final E
Uploaded by
Bad boy boyCopyright:
Available Formats
Aldehydes and Ketones 1303
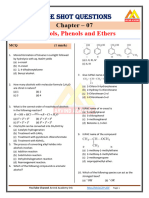
1. Benzophenone can be converted into benzene using O
||
[Tamil Nadu CET 2001]
(c) CH 3 C CH 3 (d) C 2 H 5 OH
(a) Fused alkali
8. The product of following reaction
(b) Anhydrous AlCl3
O 2
is
H / Pt
[Kerala CET 2000]
(c) Sodium amalgam in water
CH OH
(d) Acidified dichromate 3
(a) (b)
2. The reagent(s) which can be used to distinguish acetophenone from CH 3
benzophenone is (are) OH
[CBSE PMT 1990]
(c) H (d)
(a) 2, 4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine
(b) Aqueous solution of NaHSO 3 9. OH
Which of the following aldehydes is most reactive towards
(c) Benedict reagent nucleophilic addition reactions
[Roorkee 1992; RPMT 1997]
(d) I 2 and Na 2 CO 3
(a) HCHO (b) CH 3 CHO
3. When acetaldehyde is heated with Fehling solution, it gives a red
precipitate of [MP PET 1989, 93; (c) C2 H 5 CHO (d) CH 3 COCH 3
IIT 1982; MP PET/PMT 1998; RPMT 2002]
10. Which one of the following gives iodoform test
(a) Cu (b) CuO [AIIMS 1996]
(c) Cu 2 O (d) Cu (OH ) 2 (a) Formaldehyde
4. The general order of reactivity of carbonyl compounds for (b) Ethyl alcohol
nucleophilic addition reactions is [CBSE PMT 1995] (c) Benzyl alcohol
(a) H 2 C O RCHO ArCHO R 2 C O Ar2 C O (d) Benzaldehyde
11. The active ion in Tollen's reagent is
(b) ArCHO Ar2 C O RCHO R 2 C O H 2 C O
(a) Cu (b) Cu (NH 3 )2
(c) Ar2 C O R 2 C O ArCHO RCHO H 2 C O
(d) H 2 C O R 2 C O Ar2 C O RCHO ArCHO (c) Ag (d) Ag(NH 3 )2
5. Which of the following gives an alcohol and salt of carboxylic acid 12. Among the following compounds, which will react with acetone to
when reacted with conc. NaOH give a product containing C N
[MP PMT 1999] [IIT 1998]
(a) CH 3 CHO (a) C 6 H 5 NH 2
(b) C 6 H 5 CHO (b) (CH 3 )3 N
(c) CH 3 COCH 3 (c) C 6 H 5 NHC 6 H 5
(d) C 6 H 5 COCH 3 (d) C 6 H 5 NHNH 2
6. Which of the following compounds would undergo Cannizzaro's 13. Which of the following does not give yellow precipitate with I 2
reaction and NaOH [MP PET 1996]
[CPMT 1989; AFMC 1991; MNR 1995]
(a) C 2 H 5 OH (b) CH 3 CHO
(a) Propionaldehyde
(b) Benzaldehyde (c) CH 3 COCH 3 (d) HCHO
(c) Bromobenzene 14. In this reaction
(d) Acetaldehyde CH 3 CHO HCN
7. NaOH / H reacts with [BHU 2003] H /OH
CH 3 CH (OH )CN CH 3 CH (OH )COOH
(a) C 6 H 5 OCH 3 (b) CH 3 OH
an asymmetric centre is generated. The acid obtained would be
(a) 20% D + 80% L-isomer
1304 Aldehydes and Ketones
(b) D-isomer (a) Friedel-Craft's alkylation
(c) L-isomer (b) Friedel-Craft's acylation
(d) 50% D + 50% L-isomer (c) Cannizzaro reaction
15. Aldehydes are produced in atmosphere by [NCERT 1982]
(d) Claisen condensation
(a) Oxidation of secondary alcohols
18. Which of the following fails to answer the iodoform test.
(b) Reduction of alkenes [CBSE PMT 1989]
(c) Reaction of oxygen atoms with hydrocarbons (a) Pentanone–1
(d) Reaction of oxygen atoms with ozone (b) Pentanone–2
16. Which of the following compounds will give positive test with (c) Propanone–2
Tollen's reagent
(d) Ethanol
[CBSE PMT 1994; Kurukshetra CEE 1998; AFMC 2002]
19. The reagent used for the separation of acetaldehyde from
(a) Acetamide
acetophenone is [AIIMS 2004]
(b) Acetaldehyde
(a) NaHSO 4
(c) Acetic acid
(d) Acetone (b) C 6 H 5 NHNH 2
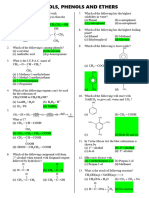
O O (c) NH 2 OH
|| ||
17. ArH R C Cl
Ar C R HCl is an example
Lewis acid
(d) NaOH I 2
of
(SET -27)
C 6 H 5 COC 6 H 5 KOH C6 H 6 C6 H 5 COOK
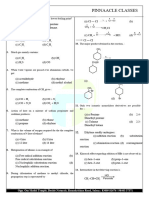
Fusion 2. (d) Acetophenone gives iodoform reaction while benzophenone does
1. (a)
Benzopheno ne Benzene Pot. benzoate
give this.
2
3. (c) CH 3 CHO 2Cu CH 3 COO Cu 2 O 3 H 2 O
5 OH
C 6 H 5 COOK KO H K 2 CO 3 C 6 H 6 Fehling solution Red ppt.
Benzene
Aldehydes and Ketones 1305
4. (a) The size of the alkyle group. Causes hindrance to attacking This reaction is Friedel–Craft’s acylation.
group. As the number and size of the alkyl groups incirease the
18. (a) 1-pentanone is an impossible compound does not have
hindrance to the attack of nucleophile also increases.
Thus the reactivity follows the order O
||
H 2 C O RCHO ArCHO R 2 C O Ar2 C O . CH 3 C group.
5. (b) Benzaldehyde does not have the -hydrogen so it will
undergoes cannizzaro’s reaction. 19. (a) NaHSO 3 gives the addition reaction with Aldehyde and only
2C 6 H 5 CHO
C 6 H 5 CH 2 OH C 6 H 5 COONa
NaOH aliphatic ketone. Acetophenone is the aromatic ketone so it
6. (b) C 6 H 5 CHO Aldehydes – Those aldehyde in which H does not give the addition product with NaHSO 3 aldehyde
atom is absent can participate in Cannizzaro’s reaction. from the addition product with NaHSO 3 which on treatment
7. (c) 2CH 3 CO CH 3
dil NaOH with acid or base give again aldehyde.
OH O OH
| || |
CH 3 C CH 2 C CH 3 RCHO HSO 3 Na R C H R CHO
H or
(Diacetone alcohol)
| OH
| SO 3 Na
CH 3
H C6 H 5 COCH 3 NaHSO 3 No reaction
8. (c) O
H 2 / Pt
OH
9. (a) Because alkyl group is absent and they have +ve inductive effect
and increases the electron density on the carbonyl group.
10. (b) The compound having -hydrogen will give iodoform test.
Ethyl alcohol and secondary alcohols also give positive iodoform
test because by the action of halogens in alkaline medium, they
are oxidesed to acetaldehyde and methyl ketones respectively.
CH 3 CH 2 OH I2
CH 3 CHO I2
CI 3 CHO
NaOH NaOH
CHI 3 HCOONa
H 2O
NaOH
***
11. (d) During reaction Ag gets reduced Ag metal and forms silver
mirror.
12. (ad) C 6 H 5 NH 2 and C 6 H 5 NH .NH 2 will give the compounds
containing C N -group.
13. (d) HCHO No reaction
I2 / NaOH
14. (d) CH 3CHO HCN CH 3 CHOHCN
hydrolysis
CH 3 CHOHCOOH
D L isomer of lacticacid
15. (c) Aldehydes are compounds containing C, H and O . So
hydrocarbons react with atmospheric oxygen to give aldehydes.
16. (b) Tollen’s reagent is ammonical silver nitrate solution. Its
reacting species is Ag . It oxidises aliphatic as well as
aromatic aldehydes.
R CHO Ag RCOOH Ag
Redox
reaction
anhyd. AlCl
17. (b) ArH R CO Cl
3
Ar CO R HCl
You might also like
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument22 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsBhavesh K100% (1)
- ISO-4063-List of Welding ProcessesDocument7 pagesISO-4063-List of Welding ProcessesGM100% (1)
- Aldehydes & Ketones (Booklet-2Document15 pagesAldehydes & Ketones (Booklet-2kraken monsterNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Level I KVPYDocument2 pagesHydrocarbon Level I KVPYRAGHUL MNo ratings yet
- 4 - Carboxylic Acids and Its Derivatives (Booklet-1)Document16 pages4 - Carboxylic Acids and Its Derivatives (Booklet-1)kraken monsterNo ratings yet
- Types of Pipe Joints in PlumbingDocument6 pagesTypes of Pipe Joints in PlumbingRoi KimssiNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual for The Elements of Polymer Science and EngineeringFrom EverandSolution Manual for The Elements of Polymer Science and EngineeringRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Organic Chemistry Basic Principles NEET PaperDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry Basic Principles NEET PaperApex InstituteNo ratings yet
- 02 Aldehydes & Ketones Que. Final EDocument14 pages02 Aldehydes & Ketones Que. Final EJagdish SinghNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids PDFDocument5 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids PDFmadhurima maityNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Biology Lab ManualDocument55 pagesUnit 2 Biology Lab ManualLeeana60% (5)
- MAGNETOM - Free-Max - Special-Issue - Short RSNA Edition 2020Document49 pagesMAGNETOM - Free-Max - Special-Issue - Short RSNA Edition 2020Leonardo Beltran GalvisNo ratings yet
- Active Food Packaging. M. L. RooneyDocument293 pagesActive Food Packaging. M. L. RooneyUriel Peña100% (2)
- Research PaperDocument32 pagesResearch Papershehryaralishah970No ratings yet
- P Block 6Document5 pagesP Block 6fakefake8006No ratings yet
- 04 Hydrocarbon Set Test Final EDocument3 pages04 Hydrocarbon Set Test Final EΒίητ ε ΗάωωάNo ratings yet
- Chem AlcoholsDocument2 pagesChem Alcoholspinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- Backup of 02-Halogen Containing Compounds-QueDocument13 pagesBackup of 02-Halogen Containing Compounds-QueChandrapal RathoreNo ratings yet
- Acid, Derivatives, Amines AssignmentDocument14 pagesAcid, Derivatives, Amines AssignmentNISHAANT SOUNDARARAJANNo ratings yet
- 02-Halogen Containing compounds-Que.-Final-EDocument14 pages02-Halogen Containing compounds-Que.-Final-EShreenithiNo ratings yet
- Xi CheDocument2 pagesXi Chepinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- 02 Halogen Containing Compounds Que. Final EDocument10 pages02 Halogen Containing Compounds Que. Final Esri anjaneyaNo ratings yet
- PAPER 1Document9 pagesPAPER 1Vector AcademyNo ratings yet
- Single Correct: Class: Adv - CC Time: 45 Min Class Test-3: OzonolysisDocument4 pagesSingle Correct: Class: Adv - CC Time: 45 Min Class Test-3: Ozonolysisbruh pogNo ratings yet
- 02 Chemical Analysis Que. Final EDocument14 pages02 Chemical Analysis Que. Final ErwfiuNo ratings yet
- 17-8-23 Q XI prep.Document1 page17-8-23 Q XI prep.tomod26971No ratings yet
- ND SPL Test Xii Che Neet 15-12-23Document7 pagesND SPL Test Xii Che Neet 15-12-23Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2nd Year Eamcet Named Reaction Identification of Functional Group-1Document7 pagesChemistry 2nd Year Eamcet Named Reaction Identification of Functional Group-1Surya Charan Reddy100% (1)
- 24 Hydrocarbon Set Test Final EDocument3 pages24 Hydrocarbon Set Test Final EKumar kartikeyNo ratings yet
- 13DPP18DAMINEEXCELDocument9 pages13DPP18DAMINEEXCELarryan keshanNo ratings yet
- Chem Sci Paper IIDocument7 pagesChem Sci Paper IIprivateinfNo ratings yet
- Time: 1 Hrs Max. Marks: 87 Single Correct: OH OH OH OHDocument5 pagesTime: 1 Hrs Max. Marks: 87 Single Correct: OH OH OH OHlakshmi.vedanarayanan7785No ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds SheetDocument6 pagesCarbonyl Compounds SheetRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: CHO H CH CH C CHDocument8 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: CHO H CH CH C CHUjjwal TomarNo ratings yet
- Bottom of Pyramid - Test # 15 - Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDocument7 pagesBottom of Pyramid - Test # 15 - Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsJay PatelNo ratings yet
- Du Ca Tio N: Chate Group of EducationDocument3 pagesDu Ca Tio N: Chate Group of EducationNUCLEAR GAMINGNo ratings yet
- 09-S and P Block Elements - Set-Test-Final-EDocument3 pages09-S and P Block Elements - Set-Test-Final-EAbhishek RavirajNo ratings yet
- Anjaam Practice Sheet-3 PDFDocument4 pagesAnjaam Practice Sheet-3 PDFtemp93630No ratings yet
- Ah 5 ArchivesDocument4 pagesAh 5 ArchivesAbhishek UttamNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic acidPYQsJEEMainsDocument45 pagesAldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic acidPYQsJEEMainsmjonfire3023No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Single Correct QuestionsDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry Single Correct Questionslakshmi.vedanarayanan7785No ratings yet
- Question Chap 7 Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument9 pagesQuestion Chap 7 Alcohols, Phenols and EthersakshayorbgkapapaNo ratings yet
- Topic: Organic Compounds Containing HalogensDocument5 pagesTopic: Organic Compounds Containing Halogensvictoria schoolNo ratings yet
- Aep - CPP - 1Document9 pagesAep - CPP - 1ayesha sheikhNo ratings yet
- Waghs Chemistry: Chapter-Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic AcidsDocument3 pagesWaghs Chemistry: Chapter-Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic AcidsRiddhesh100% (1)
- Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids YuvabrigadeDocument4 pagesAldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids YuvabrigadeRavishankar H SNo ratings yet
- ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS Paper PDF Ans KeyDocument4 pagesALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS Paper PDF Ans KeyRISHIKESH SHIRSATHNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids PDFDocument5 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids PDFmadhurima maityNo ratings yet
- Organic QuestionsDocument51 pagesOrganic Questionshemab30851No ratings yet
- ALD and AMineDocument3 pagesALD and AMineAnubrata SarkarNo ratings yet
- Sheet-3-Hydro CarbonDocument8 pagesSheet-3-Hydro CarbonZooper lNo ratings yet
- Aep - CPP - 2Document11 pagesAep - CPP - 2ayesha sheikhNo ratings yet
- AlkanesDocument6 pagesAlkanesQwertyNo ratings yet
- 07 Addition and Condensation of Enols and Enolate Ions (1) .PDF - 1Document15 pages07 Addition and Condensation of Enols and Enolate Ions (1) .PDF - 1JeetNo ratings yet
- Chem CGRDocument5 pagesChem CGRpinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- CET Org Chem HydrocarbonsDocument9 pagesCET Org Chem HydrocarbonsSourabh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- AT JE E: PhenolDocument12 pagesAT JE E: PhenolAnshu BhawsarNo ratings yet
- Black Board Problems For JEE Advanced Set-7Document8 pagesBlack Board Problems For JEE Advanced Set-7DikshantNo ratings yet
- TPJC H2 Chem 08prelim Ans AllDocument10 pagesTPJC H2 Chem 08prelim Ans AllRonald McdonaldNo ratings yet
- VHVKJKJDocument26 pagesVHVKJKJArsinno Azain LeoninnNo ratings yet
- CU-2020 B.Sc. (Honours) Chemistry Semester-III Paper-CC-7 QPDocument4 pagesCU-2020 B.Sc. (Honours) Chemistry Semester-III Paper-CC-7 QPbuntyckbtNo ratings yet
- Amines - PYQ Practice SheetDocument9 pagesAmines - PYQ Practice Sheetindiamumbai1234567No ratings yet
- Alkane Neet DPPDocument2 pagesAlkane Neet DPPYogita GNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Test 3 (20 Marks)Document7 pagesAlcohol Test 3 (20 Marks)savita patilNo ratings yet
- Sandip Sir Thermorg Chem QNDocument1 pageSandip Sir Thermorg Chem QNBad boy boyNo ratings yet
- Solid State MCQDocument6 pagesSolid State MCQBad boy boyNo ratings yet
- Astm Thermorg Chem QNDocument1 pageAstm Thermorg Chem QNBad boy boyNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Mcqs x1 11Document1 pageThermodynamics Mcqs x1 11Bad boy boyNo ratings yet
- Class XII Org Chem QNDocument1 pageClass XII Org Chem QNBad boy boyNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Ans KeyDocument1 pageThermodynamics Ans KeyBad boy boyNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics McqsDocument1 pageThermodynamics McqsBad boy boyNo ratings yet
- THERMO and Stat Mcqs x1 11Document1 pageTHERMO and Stat Mcqs x1 11Bad boy boyNo ratings yet
- 04ionic Equilibrium Set Test Final EDocument5 pages04ionic Equilibrium Set Test Final EBad boy boyNo ratings yet
- THERMODYNAMICS Ans KeyDocument1 pageTHERMODYNAMICS Ans KeyBad boy boyNo ratings yet
- 04ionic Equilibrium Set Test Final EDocument5 pages04ionic Equilibrium Set Test Final EBad boy boyNo ratings yet
- Class XI Org Chem QNDocument5 pagesClass XI Org Chem QNBad boy boyNo ratings yet
- 03 Aldehydes & Ketones Sol. Final EDocument10 pages03 Aldehydes & Ketones Sol. Final EBad boy boyNo ratings yet
- 01 Aldehydes & Ketones Theory Final EDocument22 pages01 Aldehydes & Ketones Theory Final EBad boy boyNo ratings yet
- Economic Competitiveness of Compact Steam Methane Reforming Technology For On-Site Hydrogen Supply A Foshan Case StudyDocument13 pagesEconomic Competitiveness of Compact Steam Methane Reforming Technology For On-Site Hydrogen Supply A Foshan Case Study吳浩宇No ratings yet
- Laboratory Chemical Testing Services ISO 17025 AccreditationDocument3 pagesLaboratory Chemical Testing Services ISO 17025 AccreditationWasimMogalNo ratings yet
- Acrylamide Formation in Plantain (Musa Paradisiaca) ChipsDocument8 pagesAcrylamide Formation in Plantain (Musa Paradisiaca) ChipsLuisaGordonNo ratings yet
- Reagent Immuno-Trol Low Cells: For in Vitro Diagnostic Use RX Only in The U.S.ADocument2 pagesReagent Immuno-Trol Low Cells: For in Vitro Diagnostic Use RX Only in The U.S.AHưng HoàngNo ratings yet
- ChE 134 Attrition Mill - GuanlaoDocument1 pageChE 134 Attrition Mill - GuanlaoJelor Gallego100% (1)
- Antifouling Seaforce 200 Av: Technical Data SheetDocument4 pagesAntifouling Seaforce 200 Av: Technical Data SheetLinnie McleodNo ratings yet
- Upaya Meminimalisir Dampak Lingkungan Dari Penggunaan Pestisida Dalam Pertanian (Dampak Lingkungan Dan Penanggulangannya)Document9 pagesUpaya Meminimalisir Dampak Lingkungan Dari Penggunaan Pestisida Dalam Pertanian (Dampak Lingkungan Dan Penanggulangannya)HafizNo ratings yet
- Phyto NanotechnologyDocument3 pagesPhyto NanotechnologyKrishnendu PramanikNo ratings yet
- CRP-turbilatex: Quantitative Determination of C-Reactive Protein (CRP)Document3 pagesCRP-turbilatex: Quantitative Determination of C-Reactive Protein (CRP)Assane SenghorNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Texture Development in A Deep Drawing ProcessDocument11 pagesSimulation of Texture Development in A Deep Drawing ProcessAnya CooperNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Enzymatic Reaction RatesDocument5 pagesFactors Affecting Enzymatic Reaction RatesJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Aaaa-A (Aaa) - NNNNNN (A) : Piping ClassDocument1 pageAaaa-A (Aaa) - NNNNNN (A) : Piping Classsanjay masoodNo ratings yet
- 104755-Beef Rations Cereal StrawDocument8 pages104755-Beef Rations Cereal StrawJUAN MANUEL CABRALESNo ratings yet
- O Level Chemistry Topics GuideDocument304 pagesO Level Chemistry Topics GuideIrtiza FarooqNo ratings yet
- Rack PDFDocument8 pagesRack PDFWan Norain Awang LongNo ratings yet
- Low Corrosion Fine Point Paint Marker: Safety Data SheetDocument8 pagesLow Corrosion Fine Point Paint Marker: Safety Data SheetRonald MesinaNo ratings yet
- Concentration of SolutionsDocument15 pagesConcentration of Solutionsriska raharjoNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Grade 9 10Document14 pagesQuestion Paper Grade 9 10Inspire BoosterNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere: Reduction of NO Emission From The Cement Industry in South Korea: A ReviewDocument15 pagesAtmosphere: Reduction of NO Emission From The Cement Industry in South Korea: A ReviewAmit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ssab Astm A537 C2Document2 pagesSsab Astm A537 C2vasotermiNo ratings yet
- Safeguarding Us and The Environment: Flame Retardant High Insulation Resistance Rohs & Reach ComplaintDocument4 pagesSafeguarding Us and The Environment: Flame Retardant High Insulation Resistance Rohs & Reach ComplaintAnkanPattanayakNo ratings yet
- Water Proofing Damp Proofing AND Thermal InsulationDocument19 pagesWater Proofing Damp Proofing AND Thermal InsulationgauriNo ratings yet
- MTC Review ChecklistDocument5 pagesMTC Review ChecklistShaheen Andre ChikkuNo ratings yet
- IsoCore Flange Isolation Gaskets and Kits Provide Cost Effective Alternative to PhenolicDocument4 pagesIsoCore Flange Isolation Gaskets and Kits Provide Cost Effective Alternative to PhenolicShenhua Kronen SohneNo ratings yet
- A Textbook of Electrical Technology Vol. 2 - Theraja-P1Document29 pagesA Textbook of Electrical Technology Vol. 2 - Theraja-P1Muhammad TaimoorNo ratings yet