Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Single Slider Crank Mechanism Analysis
Uploaded by
sagar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageOriginal Title
Velocity and Acceration dia for Single Slider Crank Chain
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageSingle Slider Crank Mechanism Analysis
Uploaded by
sagarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
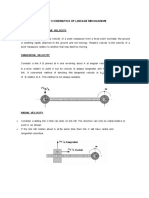
Single Slider Crank Chain: The crank of a slider crank mechanism rotates clockwise at a constant speed of 300 rpm.
The crank is
150 mm and the connecting rod is 600 mm long. Determine: 1 Linear velocity and acceleration of the Slider, 2. Angular velocity
and angular acceleration of the connecting rod, at a crank angle of 45 degree from inner dead centre position.
Step I: Draw the Space diagram as per the given dimensions of a mechanism.
Scale Space diagram: 3 cm = 50 mm
OB = 150 / 50 = 3 cm
BA = 600 / 50 = 12 cm
1. Draw a horizontal chain dotted line represent Inner dead centre line
2. Draw line OB of 3 cm at an angle 45 degree
3. Draw an arc of 12 cm from point B intersecting IDC line
4. Draw the slider at point A
Step II: Draw the Velocity diagram
Angular velocity ꙍBO = 2 π 300 / 60 = 31.4 rad / s
Linear velocity VBO = ꙍBO x BO = 31.4 x 0.15 = 4.71 m/s
Scale Velocity diagram: 4 m/s = 4 cm
1. In Velocity diagram: Point on fixed link is taken as one point
2. Draw vector ob of 4.71 cm perpendicular to OB represents Velocity of B with respect to O
3. Draw perpendicular line to AB from point b
4. Draw parallel line to OA from point o
5. Mark intersection point a and connect ab and oa
6. Calculate Velocity of A with respect to B, VAB = length ab x scale = ____ x 1 = ____ m/s
ꙍAB = VAB / AB = ____ / 0.6 = ____ rad/sec
7. Calculate Velocity of A with respect to O, VAO = length ao x scale = ____ x 1 = ____ m/s
Step III: Draw the Acceleration diagram
Radial component – Perpendicular to the velocity at any given instant i.e. parallel to the given link..
Tangential component – Parallel to the velocity at any given instant i.e. perpendicular to the given link
Draw first Radial component and then Tangential component
If crank rotates at constant speed then there will be no tangential component of the acceleration
If angular acceleration of the crank is not given, therefore there will be no tangential component of the acceleration
arQP = VQP^2 / QP and atQP = αQP x PQ
Total acceleration aQP = arQP + atQP
Link Length (m) Velocity (m/s) ar = V^2 / r (m/s^2) at = α x r
BO 0.15 4.71 4.71^2 / 0.15 = ____ No tangential comp
AB 0.6 3.4 3.4^2 / 0.6 = ____
AO - Its sliding only NA NA
Scale Velocity diagram: 20 m/s^2 = 1 cm
1. In Acceleration diagram: Point on fixed link is taken as one point
2. Draw line o’b’ i.e. radial component of 7.39 cm parallel to OB
3. Draw radial component of A of 0.963 cm with respect to B, parallel to AB
4. Draw Tangential component from x perpendicular to b’x
5. Draw line o’a’ parallel to OA
6. Mark point a’ and connect with o’a’ and b’a’
7. Measure length a’x and Calculate: αAB = atAB / AB = ____ x 20 / 0.6 = ____ rad / s^2
8. Measure length o’a’ and Calculate: αAO = aAO / AO = ____ x 20 = ____ m / s^2
9. Measure length a’b’ and Calculate: αAB = aAB / AB = ____ x 20 = ____ m / s^2
You might also like
- Kinematics of Machines: Velocity and Acceleration AnalysisDocument94 pagesKinematics of Machines: Velocity and Acceleration AnalysisUpender DhullNo ratings yet
- VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION ANALYSISDocument60 pagesVELOCITY AND ACCELERATION ANALYSIStarasasankaNo ratings yet
- Kinematic Analysis of Simple Mechanisms Using Graphical and Analytical MethodsDocument21 pagesKinematic Analysis of Simple Mechanisms Using Graphical and Analytical MethodsRamanathan DuraiNo ratings yet
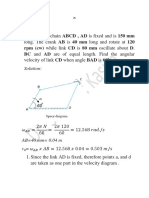
- RPM (CW) While Link CD Is 80 MM Oscillate About D. BC and AD Are of Equal Length. Find The AngularDocument23 pagesRPM (CW) While Link CD Is 80 MM Oscillate About D. BC and AD Are of Equal Length. Find The AngularOm Soliman AlkaberNo ratings yet
- Machine theory tutorial acceleration analysis solutionsDocument11 pagesMachine theory tutorial acceleration analysis solutionskalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Relative Acceleration (1) : From Relative Velocity Circular MotionDocument12 pagesRelative Acceleration (1) : From Relative Velocity Circular Motionkeremmerek1No ratings yet
- MME 2323-Mechanics of Machines April 2019 Marking SchemeDocument18 pagesMME 2323-Mechanics of Machines April 2019 Marking Schemecharles ondiekiNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachineDocument25 pagesKinematics of MachineVidhiNo ratings yet
- Acceleration MechanismsDocument11 pagesAcceleration MechanismsHasan AL-BahraniNo ratings yet
- Lec 7 Velocity and Acceleration Analysis of MechanismsDocument8 pagesLec 7 Velocity and Acceleration Analysis of Mechanismsnegihi2832No ratings yet
- Planar Kinematics of A Rigid Body (V) Impulse and Momentum: by Dr. Toh Hoong ThiamDocument22 pagesPlanar Kinematics of A Rigid Body (V) Impulse and Momentum: by Dr. Toh Hoong Thiamnadia syahiraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document14 pagesChapter 3Jongyoun ChoiNo ratings yet
- Lect Acceleration Analysis - GraphicalDocument63 pagesLect Acceleration Analysis - GraphicalRayan IsranNo ratings yet
- Examples Based On VelocityDocument6 pagesExamples Based On VelocitySalah benhsNo ratings yet
- Linear Velocity, V, of A Point Is The Linear Displacement of That Point Per Unit Time. RecallDocument24 pagesLinear Velocity, V, of A Point Is The Linear Displacement of That Point Per Unit Time. RecallKarthikeyanRamanujamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Solution: Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines (Me 316)Document5 pagesTutorial 2 Solution: Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines (Me 316)Pratik ShirsathNo ratings yet
- 140 Copies - II ME RIT - KOM - U3Document29 pages140 Copies - II ME RIT - KOM - U3Anjanareddy PNo ratings yet
- MECHANISM MOTIONDocument31 pagesMECHANISM MOTIONhamryNo ratings yet
- Assignment 03 AE688Document7 pagesAssignment 03 AE688Mhmoud Al-TamimiNo ratings yet
- Design of Machinery: Chapter 7 - Acceleration AnalysisDocument44 pagesDesign of Machinery: Chapter 7 - Acceleration AnalysisKen Vu100% (1)
- Relative Motion Analysis: Acceleration: Today's ObjectivesDocument28 pagesRelative Motion Analysis: Acceleration: Today's ObjectivesNiki BrincatNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Linkage Mechanisms SolvedDocument16 pagesKinematics of Linkage Mechanisms SolvedEugine BalomagaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 - SolutionsDocument22 pagesTutorial 5 - SolutionsjunedrkaziNo ratings yet
- KOM Unit 2Document29 pagesKOM Unit 2Ahmed Sobhi l أحمد صبحيNo ratings yet
- Mechanism-Relative Velocity Method: V AB V MsDocument10 pagesMechanism-Relative Velocity Method: V AB V MsPravesh ChummunNo ratings yet
- Lec. 2 1Document5 pagesLec. 2 1easesaymichael02No ratings yet
- Radial & Tangential Components of AccelerationDocument20 pagesRadial & Tangential Components of AccelerationdarshanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Dynamics DAM10903/20903/13903: Planar Kinematics of A Rigid BodyDocument8 pagesMechanical Engineering Dynamics DAM10903/20903/13903: Planar Kinematics of A Rigid BodyAbbyNo ratings yet
- ME306-Fall 2013 - Chapter (3) - Velocities Analysis of Mechanisms PDFDocument13 pagesME306-Fall 2013 - Chapter (3) - Velocities Analysis of Mechanisms PDFmurad_ashourNo ratings yet
- Velocity and AccelartionDocument56 pagesVelocity and Accelartionadus lakshmanNo ratings yet
- ME3112 8 Planar Mechanisms - Solved Examples - 16102014133235158Document17 pagesME3112 8 Planar Mechanisms - Solved Examples - 16102014133235158Wai-Yen ChanNo ratings yet
- Lect Acceleration AnalysisDocument107 pagesLect Acceleration AnalysisTalha Khanzada100% (1)
- RELATIVE MOTION ANALYSIS: ACCELERATION COMPONENTSDocument25 pagesRELATIVE MOTION ANALYSIS: ACCELERATION COMPONENTSJoshua D'CruzNo ratings yet
- 6 Acceleration PolygonDocument10 pages6 Acceleration Polygonalibaba011No ratings yet
- Velocity and Accelerations in Planar Mechanisms, Coriolis Component of AccelerationDocument63 pagesVelocity and Accelerations in Planar Mechanisms, Coriolis Component of AccelerationMPee Finance SumerpurNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Acceleration Analysis - Relative Velocity MethodDocument9 pagesUnit 2 Acceleration Analysis - Relative Velocity MethodkargoNo ratings yet
- Mechanism PPT Chapt 6 From Gemechu Group-1Document53 pagesMechanism PPT Chapt 6 From Gemechu Group-1zazenaw46zazuNo ratings yet
- HMWK 21Document1 pageHMWK 21capturemrahNo ratings yet
- D Dynamics: Lecture Notes 05: Kinematics of The Rigid Body Rigid BodyDocument15 pagesD Dynamics: Lecture Notes 05: Kinematics of The Rigid Body Rigid BodyKish ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Analysis MethodDocument12 pagesAcceleration Analysis MethodKlucifer XinNo ratings yet
- 5 Velocity GraphicalDocument22 pages5 Velocity GraphicalRaj GururajNo ratings yet
- TVKBPDocument13 pagesTVKBPTommyVercettiNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Analysis Mechanisms Compute ComponentsDocument29 pagesAcceleration Analysis Mechanisms Compute ComponentsGloria Trigoso LeónNo ratings yet
- Sample Exams - Mechanics DynamicsDocument22 pagesSample Exams - Mechanics DynamicsrahulNo ratings yet
- Planar Kinematics of A Rigid Body (III) Impulse and MomentumDocument22 pagesPlanar Kinematics of A Rigid Body (III) Impulse and Momentumnadia syahiraNo ratings yet
- 16 Planar Kinematics of Rigid BodyDocument47 pages16 Planar Kinematics of Rigid BodyzackziffiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-MechanismDocument28 pagesChapter 5-MechanismDanielRaoNo ratings yet
- Ch5 - 2 Relative VelocityDocument22 pagesCh5 - 2 Relative Velocitym_er100No ratings yet
- EMM 301: Kinematics of Mechanisms Using Velocity and Acceleration DiagramsDocument11 pagesEMM 301: Kinematics of Mechanisms Using Velocity and Acceleration DiagramsJohn KimaniNo ratings yet
- Four Bar Linkage AnalysisDocument10 pagesFour Bar Linkage Analysissach30131No ratings yet
- Acceleration in Slider Crank MechanismDocument8 pagesAcceleration in Slider Crank MechanismSalah benhsNo ratings yet
- Chap2 Kinematics Analysis - ProblemsDocument4 pagesChap2 Kinematics Analysis - ProblemsHưng Vương QuangNo ratings yet
- Velocity - Acceleration DiagramDocument9 pagesVelocity - Acceleration DiagramvisheshNo ratings yet
- MECH 314 Dynamics of Mechanisms: 1 Problem SpecificationDocument6 pagesMECH 314 Dynamics of Mechanisms: 1 Problem SpecificationLarbi ElbakkaliNo ratings yet
- MECH1230 Dynamics Unit 2 - Rigid Body KinematicsDocument48 pagesMECH1230 Dynamics Unit 2 - Rigid Body KinematicsJamie ThomsonNo ratings yet
- KOM Lect13Document24 pagesKOM Lect13Pranav C PNo ratings yet
- Graphical position analysis continuationDocument12 pagesGraphical position analysis continuationJosline MuriikiNo ratings yet
- lect6Document33 pageslect6hamock.dir1No ratings yet
- ME/AE 160 - ADAMS Assignment Three Motion AnalysisDocument2 pagesME/AE 160 - ADAMS Assignment Three Motion AnalysisAamir AliNo ratings yet
- Velocity and Acceration Dia For Four Bar ChainDocument1 pageVelocity and Acceration Dia For Four Bar ChainsagarNo ratings yet
- The Guide For Writing Word Documents in o Ease The Lives of Authors, Editors, ADocument6 pagesThe Guide For Writing Word Documents in o Ease The Lives of Authors, Editors, AsagarNo ratings yet
- ImfDocument1 pageImfsagarNo ratings yet
- ImfDocument1 pageImfsagarNo ratings yet
- ImfDocument1 pageImfsagarNo ratings yet
- ImfDocument1 pageImfsagarNo ratings yet
- The Guide For Writing Word Documents in o Ease The Lives of Authors, Editors, ADocument6 pagesThe Guide For Writing Word Documents in o Ease The Lives of Authors, Editors, AsagarNo ratings yet
- The Guide For Writing Word Documents in o Ease The Lives of Authors, Editors, ADocument11 pagesThe Guide For Writing Word Documents in o Ease The Lives of Authors, Editors, AsagarNo ratings yet
- Mass TransportationDocument20 pagesMass Transportationyoyo_8998No ratings yet
- EDCO - Catalog - 8 - 2017 - Floor GrindingDocument64 pagesEDCO - Catalog - 8 - 2017 - Floor GrindinghrithikvNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM 7 - CDDocument4 pagesPROBLEM 7 - CDRavidya ShripatNo ratings yet
- Trends and Fads in Business SVDocument2 pagesTrends and Fads in Business SVMarie-Anne DentzerNo ratings yet
- Autodesk Revit 2014 ContentDocument6 pagesAutodesk Revit 2014 ContentGatot HardiyantoNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Noise-Cancelling CMOS Active Inductor and Its Application in RF Band-Pass Filter DesignDocument8 pagesResearch Article: Noise-Cancelling CMOS Active Inductor and Its Application in RF Band-Pass Filter DesignAbhay S KochharNo ratings yet
- Einstein and Oppenheimer's Real Relationship Was Cordial and Complicated Vanity FairDocument1 pageEinstein and Oppenheimer's Real Relationship Was Cordial and Complicated Vanity FairrkwpytdntjNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal ADS Bab 14-16Document1 pageLatihan Soal ADS Bab 14-16nadea06_20679973No ratings yet
- Pragmatics: The Study of Its Historical Overview, Meanings, Scope and The Context in Language UseDocument7 pagesPragmatics: The Study of Its Historical Overview, Meanings, Scope and The Context in Language UseIHINOSEN IYOHANo ratings yet
- Netprobe 2000Document351 pagesNetprobe 2000Jordon CampbellNo ratings yet
- DLL in Science 5 Q1 W1Document3 pagesDLL in Science 5 Q1 W1Rhinalyn Andaya Barberan100% (2)
- Atma Bodha of Shri SankaracharyaDocument1 pageAtma Bodha of Shri SankaracharyaMerike TazaNo ratings yet
- Simha Lagna: First House Ruled by The Planet Sun (LEO) : The 1st House Known As The Ascendant orDocument3 pagesSimha Lagna: First House Ruled by The Planet Sun (LEO) : The 1st House Known As The Ascendant orRahulshah1984No ratings yet
- AR Ageing FinalDocument13 pagesAR Ageing FinalHAbbunoNo ratings yet
- Quick Guide in The Preparation of Purchase Request (PR), Purchase Order (PO) and Other Related DocumentsDocument26 pagesQuick Guide in The Preparation of Purchase Request (PR), Purchase Order (PO) and Other Related DocumentsMiguel VasquezNo ratings yet
- Nikon SMZ 10A DatasheetDocument3 pagesNikon SMZ 10A DatasheetNicholai HelNo ratings yet
- RCC Chimneys - CICIND Code PDFDocument23 pagesRCC Chimneys - CICIND Code PDFVasanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Exam SchedDocument16 pagesComprehensive Exam SchedMark ErvinNo ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hours Total Marks: 100: Printed Page 1 of 2 Sub Code: KEE302Document2 pagesTime: 3 Hours Total Marks: 100: Printed Page 1 of 2 Sub Code: KEE302AvinäshShärmaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Sir MarcosDocument7 pagesLesson Plan Sir MarcosJhon AgustinNo ratings yet
- OPM - Assignment 2Document12 pagesOPM - Assignment 2Nima IraniNo ratings yet
- Basic Instructions: A Load (Contact) SymbolDocument3 pagesBasic Instructions: A Load (Contact) SymbolBaijayanti DasNo ratings yet
- Testing Methods for Selectivity Bias in Panel Data ModelsDocument24 pagesTesting Methods for Selectivity Bias in Panel Data Modelsstehta16529No ratings yet
- REHAU 20UFH InstallationDocument84 pagesREHAU 20UFH InstallationngrigoreNo ratings yet
- Solid Solution For Catalytic Ammonia Synthesis FromDocument8 pagesSolid Solution For Catalytic Ammonia Synthesis FromAhmad AlShahrourNo ratings yet
- Informatica Mapping ScenariosDocument81 pagesInformatica Mapping ScenariosSri Kanth SriNo ratings yet
- SIKA Concrete Repair Site HandbookDocument24 pagesSIKA Concrete Repair Site HandbookkeesinvongNo ratings yet
- Hot and Cold CorrosionDocument6 pagesHot and Cold CorrosioniceburnerNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Power PlantDocument158 pagesModule 1 Power PlantEzhilarasi NagarjanNo ratings yet
- Drone Hexacopter IjisrtDocument4 pagesDrone Hexacopter IjisrtDEPARTEMEN RUDALNo ratings yet