Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Skema
Uploaded by
Myyna kloverCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Skema
Uploaded by
Myyna kloverCopyright:
Available Formats
J1
PEPERIKSAAN PERCUBAAN SIJIL PELAJARAN MALAYSIA
KERTAS 1
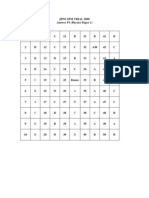
1 D 2 B 3 A 4 B 5 B 6 B 7 D 8 C 9 C 10 B
11 C 12 B 13 D 14 B 15 A 16 B 17 D 18 B 19 A 20 D
21 B 22 D 23 C 24 C 25 C 26 B 27 A 28 B 29 B 30 A
31 D 32 D 33 A 34 D 35 A 36 A 37 D 38 C 39 A 40 B
KERTAS 2
BAHAGIAN A
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
1 (a) Pembiasan cahaya 1 1
Refraction of light
(b) Laju cahaya 1 1
Speed of light
(c)
Rajah mestilah dilukis berdasarkan:
Diagram should be drawn based on:
M1 Garis lurus dilukis dari hujung objek ke garis normal 1
Straight line which is draw from the end of object to the
normal line
M2 Garis lurus dilukis dari hujung imej ke garis normal 1 2
dan segaris dengan garis cahaya memasuki mata
Straight line which is draw from the end of image to the
normal line and inline to the line of light enters the eye
Jumlah 4
2 (a) Pancaran// Pembebasan elektron daripada permukaan 1 1
logam yang disinari cahaya dengan frekuensi tertentu.
Emission// Release of electron from metal surface illuminated
by a beam of light at a certain frequency.
(b) M1 Penukaran unit/ Conversion of unit
560 × 10–9 1
M2 Penggantian nilai/ Substitution of value
EK = 6.63 × 10–34 3 × 10 –9 – 5.16 × 1014
8
(
560 × 10 ) 1
M3 Jawapan akhir/ Final answer
– EK= 6.63 × 10–34 J atau/ or EK = 0.0815 eV 1 3
(c) Tidak/ No 1 1
Jumlah 5
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 1 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J2
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
3 (a) Diod/ Diode 1 1
(b) (i) Diod disambung dalam pincang songsang// Lapisan 1 1
susutan lebar
Diode connected in reverse biased// Depletion layer wider
(ii) Songsangkan sambungan diod// terminal bateri 1 1
Reverse the connection of diode// terminal of batteries
(c) (i) 2 betul:
1 markah
Atau
Or
4 betul:
2 markah 2
(ii) 1 1
Jumlah 6
4 (a) Tindak balas berantai// Pembelahan nukleus 1 1
Chain reaction// Nucleus fission
(b) 235
92
U + 10n = 140
54
Xe + 94
38
Sr + 210n 1 1
(c) (i) Cacat jisim/ Mass defect
= (235.04395 + 1.00867) – (139.9216 + 93.9154 + 1
1.00867 + 1.008867)
= 0.19828 u 1
= 0.19828 × 1.66 × 10–27
= 3.291448 × 10–28 kg 1 3
(ii) Tenaga/ Energy
= 3.291448 × 10–28 × (3 × 108)2 1
= 2.9623 × 10–11 J 1 2
(d) Rod pengawal menyerap neutron 1
Control rod absorbs the neutron
Moderator memperlahan neutron 1 2
Moderator slow down the neutron
Jumlah 9
5 (a) sama dengan/ equals to 1 1
(b) (i) Frekuensi alat kawalan jauh A lebih kecil daripada 1 1
frekuensi alat kawalan jauh B// Frekuensi alat kawalan
jauh dalam Rajah 5.1 lebih kecil daripada frekuensi alat
kawalan dalam Rajah 5.2
The frequency of the controller A is smaller than the controller
B// The frequency of the controller in Diagram 5.1 is smaller
than the controller in Diagram 5.2
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 2 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J3
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(ii) Kereta mainan B masih boleh dikawal walaupun berada 1 1
pada jarak 80 m daripada alat kawalan.
Toy car B can be still controlled even though its distance is
80 m from the controller.
(c) M1 Penggantian nilai/ Substitution of value
Kereta mainan A/ Toy car A
v 3 × 108 1
λ= =
f 2.7 × 107
= 11.11 m 1
Kereta mainan B/ Toy car B
3 × 108
λ=
4.9 × 107
1 3
= 6.12 m
(d) Panjang gelombang radio alat kawalan A lebih besar 1 1
daripada B
Wavelength of radio wave of controller A is larger than B
(e) (i) Frekuensi, f bertambah, jarak maksimum antara 1 1
pemancar dan antena, x bertambah// Frekuensi, f
berkadar terus dengan jarak maksimum maksimum
antara pemancar dan antena, x
Frequency, f increases, the maximum distance between the
transmitter and the antenna, x increases// Frequency, f directly
proportional to the maximum distance between the transmitter
and the antenna, x
(ii) Frekuensi, f bertambah, panjang gelombang berkurang// 1 1
Frekuensi, f berkadar songsang dengan panjang
gelombang
Frequency, f increases, the wavelength decreases// Frequency, f
inversely proportional to the wavelength
Jumlah 9
6 (a) Transformer injak turun 1 1
Step-down transformer
(b) Vp Vs
=
Np Ns
240 = 60 1
1000 Ns
Ns = 250
NEF = 250 – 200 = 50 1
VEF = 60 – 48 = 12 V 1 3
(c) (i) Np> NDE > NEF 1 1
(ii) Sama 1 1
Same// Equals
(iii) Vp > VDE > VEF 1 1
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 3 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
MODEL ZON UTARA FIZIK TKT 4 - POTENSI aw by mzaidee
J4
10
0
55 55
0
5
5
50 10
50 45
40
15 10
20
15
35 25
30
45 15
G4-2
Sub Markah
40 20
35 25
Soalan Jawapan
30
G4-1
markah penuh
(d) Bilangan lilitan gegelung bertambah, nilai voltan 1 1
bertambah
Numbers of turns of coil increases, the value of voltage
increases
(e) Sifar// 0 A 1 1
G4-3
Zero
Jumlah 9
7 (a) Daya yang membolehkan sesuatu objek bergerak 1 1
mengikut laluan membulat
G4-4dan arahnya sentiasa menuju
ke pusat bulatan
A force that makes an object to follow a circular path with
direction always toward the centre of curvature
(b) F 1 1
G4-5
G4-6
(c) 4 × (25)2 1
F=
1.6
= 1562.5 N 1 2
(d) (i) Pendek 1
Short
Sebab: Daya memusat tinggi// Daya memusat berkadar 1 2
songsang dengan jejari tali, r
Reason: High centripetal force// Centripetal force inversely
proportional to radius of string, r
(ii) Besar// Tinggi 1
Big// High
Sebab: Daya memusat tinggi// Daya memusat berkadar 1 2
terus dengan laju linear// Pecutan memusat tinggi
Reason: High centripetal force// Centripetal force directly
proportional to linear speed// Centripetal acceleration high
(e) H 1 1
Jumlah 9
8 (a) Tekanan yang disebabkan oleh berat lapisan udara yang 1 1
bertindak ke atas permukaan Bumi
The pressure due to the weight of the layer of air acting on the
surface of the Earth
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 4 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J5
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(b) Bertambah 1
Increase
Pada altitud tinggi, udara yang tipis menyebabkan 1 2
tekanan atmosfera menjadi rendah// peratusan oksigen di
udara berkurang.
At high altitude, thin of air causes the atmospheric pressure to
become low// the percentage of oxygen in the air reduces.
(c) (i) Meningkatkan kadar penyedutan udara masuk melalui 1
enjin
To increasing the rate of air absorption through the engine
Sebab: Menyalurkan lebih udara ke dalam kabin kapal 1 2
terbang
Reason: To provide more air into the airplane cabin
(ii) Menggunakan topeng oksigen 1
Use the oxygen mask
Sebab: Untuk membekalkan oksigen yang mencukupi 1 2
Reason: To supply enough oxygen
(iii) 1
Ia dapat menahan daripada perubahan bentuk yang 1 2
disebabkan oleh perbezaan tekanan yang menghasilkan
daya dari dalam kapal terbang yang lebih besar daripada
daya dari luar.
The design of the window resists deformation caused by the
extreme differences in pressure, that producing greater force
acting from inside on the airplane compared to the force from
outside.
Jumlah 9
BAHAGIAN B
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
9 (a) Kuantiti haba, Q yang diserap semasa peleburan atau 1 1
dibebaskan semasa pembekuan bagi 1 kg bahan itu tanpa
perubahan suhu.
Quantity of heat, Q that is absorbed during melting or released
during freezing of 1 kg of the substance without any change in
temperature.
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 5 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J6
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(b) Dari Q ke R: Gas terkondensasi menjadi cecair. 1
From Q to R: Gas is condensing into liquids.
Haba pendam dibebaskan supaya molekul membentuk 1
semula ikatan.
The latent heat is released so that the molecular bond form.
Molekul bergerak di antara satu sama lain. 1
Molecules are moving on each other.
Tenaga kinetik molekul tidak berkurang. 1
Kinetic energy of molecules does not decrease.
[Mana-mana dua/ Any two]
Dari R ke S: Cecair menyejuk sehingga takat beku.
1
From R to S: Liquid cools to freezing point.
1
Haba dibebaskan dan suhu berkurang.
Heat is released and temperature decreases.
Tenaga kinetik molekul berkurang. 1 4
Kinetic energy of molecules decreases.
[Mana-mana dua/ Any two]
(c) Tenaga diserap untuk menukar 0.5 kg daripada gas
120°C kepada cecair 120°C
Energy absorbed to convert 0.5 kg from gas 120°C to liquid
120°C
Q1 = mlv
= (0.5)(480 000)
= 240 000 J 1
Tenaga diserap untuk menukar 0.5 kg daripada cecair
120°C kepada cecair 100°C
Energy absorbed to convert 0.5 kg from liquid 120°C to liquid
100°C
Q2 = mcθ
= (0.5)(1720)(120 – 100)
= 17 200 J 1
Jumlah tenaga diperlukan
Total energy required
Q = Q1 + Q2
= 240 000 + 17 200 1
= 257 200 J 1 4
[Jawapan akhir dengan unit yang betul]
[Final answer with the correct unit]
(d) Tiada haba yang hilang ke persekitaran. 1 1
No heat is lost to the surrounding.
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 6 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J7
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(e) Penerangan
Ciri-ciri
Characteristics Explanation
Bilangan tingkap: – Membenarkan lebih
Banyak banyak pengaliran udara 1+1
Number of windows: Allow more air flow
Many – Jimat tenaga elektrik
yang digunakan
Save electrical energy used
Jarak dari lantai ke Peredaran udara di dalam
siling: Tinggi rumah lebih baik 1+1
Distance from floor to Better air ventilation inside the
ceiling: High house
Bahan dinding daripada – Muatan haba tentu tinggi
High specific heat capacity 1+1
batu-bata berongga//
kayu – Perubahan suhu rendah
Material of the wall from Low in temperature changes
hollow bricks// wood – Dinding lebih lambat panas
Wall heat up slower
Jenis bahan bumbung – Muatan haba tentu tinggi
daripada jubin konkrit High specific heat capacity
Material of the roof is – Perubahan suhu rendah
from concrete tile Low in temperature changes
– Penebat haba yang baik 1+1
Good heat insulator
– Mengurangkan haba
dipindahkan dari luar
rumah ke dalam rumah
Reduce heat transferred
from outside into the house
R dipilih kerana bilangan tingkap banyak, jarak dari
lantai ke siling tinggi, bahan dinding dari pada batu-
bata berongga dan jenis bahan bumbung daripada
1+1 10
jubin konkrit
R is chosen because many number of windows, floor to
ceiling distance is high, material of the wall is from bricks
and material of the roof is from concrete tile.
Jumlah 20
10 (a) Suatu ukuran bagi keupayaan konduktor untuk 1 1
menentang pengaliran arus elektrik
A measure of a conductor’s ability to oppose the flow of
electric current
(b) Mengurangkan kehilangan tenaga atau haba// 1
Meningkatkan kecekapan
Reduce energy or heat lost// Increase efficiency
Mengelakkan pemanasan lampau 1 2
Prevent overheating
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 7 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J8
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(c) – Panjang wayar pendek 1
Short length of wire
– Ketebalan wayar besar// Diameter wayar besar// Luas 1 2
keratan rentas wayar besar
Larger thickness of wire// Bigger diameter of wire// Bigger
cross-sectional area
(d) (i) M1 Penukaran unit/ Conversion of unit
90 1
t= = 1.5 jam/ hour
60
M2 Penggantian nilai/ Substitution of value
E = Pt
1 200
= ( 1 000 ) × 1.5 1
M3 Jawapan akhir/ Final answer
E = 1.8 kWj/ 1.8 kWh 1 3
(ii) Kos penggunaan tenaga elektrik
Cost of electrical energy consumed
= 1.8 × 0.218 × 14
= RM 5.49 1 2
(e)
Ciri-ciri Penerangan
Characteristics Explanation
Bilangan lilitan unsur – Dawai yang panjang 1+1
pemanas: Banyak Long wire
The number of turns of – Rintangan tinggi
heating element: Many High resistance
– Kerintangan tinggi
High resistivity
– Lebih banyak haba
More heat
Jenis bahan yang – Rintangan tinggi 1+1
digunakan untuk unsur High resistance
pemanas: Nikrom – Kerintangan tinggi
Type of material used as the High resistivity
heating element: Nichrome – Lebih banyak haba
More heat
Kadar pengoksidaan: Tidak mudah berkarat 1+1
Rendah Does not rust easily
The rate of oxidation: Low
Fius: 5 A Arus mengalir ialah 4.17 A. 1+1
Fuse The current flow is 4.17 A.
K dipilih kerana bilangan lilitan unsur pemanas banyak,
nikrom, kadar pengoksidaan rendah dan fius 5 A. 1+1 10
K is chosen because many numbers of turns of heating
element, nichrome, low rate of oxidation and fuse of 5A.
Jumlah 20
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 8 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J9
BAHAGIAN C
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
11 (a) Daya tunggal yang mewakili jumlah secara vektor dua 1 1
atau lebih daya yang bertindak ke atas sesuatu objek.
Single force represents the sum of two or more forces in vector
acted on an object.
(b) M1 Wx dalam Rajah 11.1 lebih kecil daripada dalam 1
Rajah 11.2
Wx in Diagram 11.1 is smaller than in Diagram 11.2
M2 Fx dalam Rajah 11.1 lebih kecil daripada dalam 1
Rajah 11.2
Fx in Diagram 11.1 is smaller than in Diagram 11.2
M3 Sudut, θ dalam Rajah 11.1 lebih kecil daripada 1
dalam Rajah 11.2
Angle, θ in Diagram 11.1 is smaller than in Diagram
11.2
M4 Semakin bertambah sudut, θ, semakin bertambah 1
Fx
The larger the angle, θ, the higher the Fx
M5 Semakin bertambah sudut, θ, semakin bertambah 1 5
pecutan
The larger the angle, θ, the higher the acceleration
(c) P
�
W R Atau
Or R W
�
P
Rajah mestilah dilukis berdasarkan:
Diagram should be drawn based on:
M1 Lukis dan label garis W yang betul 1
Draw and label correct line for W
M2 Lukis dan label garis R yang betul 1
Draw and label correct line for R
M3 Tandakan arah W dan R yang betul 1
Mark the correct direction of W and R
M4 Kedudukan α dan bentuk segi tiga yang betul 1 4
Correct position of α and shape of triangle
(d)
Ciri-ciri Penerangan
Characteristics Explanation
Kabel keluli// kuat – Menampung daya yang besar 1+1
Steel// Strong cable Withstand bigger force
– Tidak mudah putus
Not easily break
– Tidak berkarat
Not easily rusted
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 9 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J10
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
Ciri-ciri Penerangan
Characteristics Explanation
Menara keluli// kuat – Menampung daya yang 1+1
Steel// Strong tower besar
Withstand bigger force
– Tidak mudah patah
Not easily break
– Tidak mudah berkarat
Not easily rusted
1+1
Bilangan kabel yang – Menampung daya// berat
banyak yang lebih
Many numbers of cable Withstand more force// load
– Tingkatkan keseimbangan
Increase equilibrium
Ketegangan kabel yang – Tidak mudah putus 1+1
tinggi Not easily break
High tension of cable – Daya besar
Bigger force
Ketinggian tiang yang – Mengelakkan air
1+1
lebih tinggi melimpah ke jambatan
Height of pillar is high Avoid water spill on bridge
Diameter tiang yang – Kestabilan bertambah
lebih besar Increase stability 1+1
Bigger diameter of pillar
Banyak tiang – Menampung daya// berat
More pillars yang lebih besar 1+1
Support more force// weight
– Tingkatkan keseimbangan
Increase stability
1+1 10
– Menahan tindakan ombak
kuat// hakisan
Withstand strong wave//
errosion
[Maksimum: 10 markah]
[Maximum: 10 marks]
Jumlah 20
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 10 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J11
KERTAS MODEL PEPERIKSAAN SPM SET 1
KERTAS 1
1 C 2 B 3 B 4 A 5 A 6 C 7 A 8 D 9 C 10 D
11 B 12 C 13 B 14 B 15 A 16 C 17 B 18 A 19 A 20 C
21 B 22 A 23 C 24 C 25 C 26 D 27 D 28 B 29 D 30 B
31 D 32 D 33 D 34 B 35 B 36 C 37 D 38 A 39 D 40 D
KERTAS 2
BAHAGIAN A
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
1 (a) Kawasan di mana cas mengalami daya elektrik 1 1
A region where charge experiences electric force
(b) (i) Corak medan elektrik
Electric field pattern
1+1 2
(ii) Menghasilkan medan elektrik yang kuat 1 1
Produce strong electric field
Jumlah 4
2 (a) Kadar perubahan halaju 1 1
Rate of change of velocity
(b) (i) R 1 1
(ii) F = R – W 1 1
(c) R=F+W
= ma + mg
= (60)(2) + (60)(9.81) 1
= 708.6 N 1 2
Jumlah 5
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 11 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J12
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
3 (a) Pancaran termion 1 1
Thermionic emission
(b) Tenaga kinetik elektron telah bertukar kepada tenaga 1 1
cahaya apabila menghentam skrin.
The kinetic energy of the electrons converts to light energy as it
strikes the screen.
(c) 1 2
4.8 × 10–16 = mv
2
4.8 × 10 × 2
–16
v2 = 1
9.0 × 10–31
v = 3.27 ×107 m s–1 1 2
(d) (i) 1 1
(ii) Petua tangan kiri Fleming 1 1
Fleming’s left-hand rule
Jumlah 6
4 (a) Transformer injak turun 1 1
Step-down transformer
(b) (i) Arah dan magnitud arus ulang-alik berubah dan 1 1
menghasilkan perubahan dalam medan magnet
Direction and magnitude of alternating current changes and
produces change in the magnetic field
(ii) Apabila suis dihidupkan, medan magnet terbentuk 1
pada gegelung primer
When the switch is on, magnetic field will be formed at the
primary coil. 1 2
Pada gegelung sekunder, medan magnet berubah-ubah
menghasilkan d.g.e aruhan// arus aruhan
At the secondary coil, the magnetic field changes, producing
induced e.m.f// induced current.
NP 240
=
NS 12
= 20 1
1
NPQ: NRS = 20:1 1 2
Pout = VIout
60 = (12)Iout
60 1 1
Iout = =5A
12
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 12 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J13
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
VSIS
Kecekapan/ Efficiency = × 100%
VPIP
12 × 5
80% = × 100% 1
240Iin
60
240Iin =
0.8 1 2
Iin = 0.3125 A
Jumlah 9
5 (a) Haba yang diperlukan untuk menaikkan suhu 1 kg bahan 1 1
sebanyak 1°C
Heat required to raise temperature of 1 kg substance by 1°C
(b) Muatan haba tentu kuali aluminium lebih besar daripada 1 1
kuali besi
The specific heat capacity of aluminium pan is larger than
iron pan
Masa diambil bagi kuali aluminium untuk mendidihkan 1 1
air lebih lama daripada kuali besi
The time taken for aluminium pan to boil water is longer than
iron pan
Perubahan suhu kuali aluminium adalah sama dengan 1 1
kuali besi
The change in temperature of aluminium pan is the same as
iron pan
Muatan haba tentu berkadar terus dengan masa diambil 1 1
untuk mendidih
The specific heat capacity is directly proportional to the time taken
to boil
Bahan penebat haba mempunyai muatan haba tentu 1 1
tinggi// lambat menjadi panas
Insulated heat material has high heat capacity// heats up slower
(e) (i) Pt = mcθ
= 0.5 × 4200 × (100 – 30) 1
5 × 60 1 2
= 490 W
(ii) Tiada haba hilang ke persekitaran 1 1
No heat lost to the surrounding
Jumlah 9
6 (a) Nukleus yang tidak stabil 1 1
Unstable nucleus
(b) 226
88
Ra → 222
86
Rn + 24He + Tenaga/ Energy 1 1
(c) (i) Jumlah jisim nuklid induk sebelum reputan dalam Rajah 1 1
6.1 lebih besar daripada Rajah 6.2
The mass of the parent nuclide before decays in Diagram 6.1 is
larger than in Diagram 6.2
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 13 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J14
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(ii) Jumlah jisim nuklid induk selepas reputan dalam Rajah 1 1
6.1 lebih besar daripada Rajah 6.2
The total mass of the parent nuclide after decay in Diagram
6.1 is larger than in Diagram 6.2
(iii) Perbezaan jisim sebelum dan selepas reputan dalam 1 1
Rajah 6.1 lebih besar daripada dalam Rajah 6.2
The difference in mass before and after decay in Diagram 6.1
is larger than in Diagram 6.2
(c) (i) Perbezaan jumlah jisim berkadar terus dengan tenaga 1 1
dibebaskan
The difference in total mass is directly proportional to the
energy released
(ii) Cacat jisim berkadar terus dengan tenaga dibebaskan 1 1
The mass defect is directly proportional to the energy released
(d) 16 → 8 → 4 → 2
3T = 3 × 5730 1
= 17 190 tahun/ years 1 2
Jumlah 9
7 (a) Fenomena pengeluaran elektron dari permukaan logam 1 1
apabila ianya disinari oleh alur cahaya
Phenomenon of electron emission from a metal surface when it
is illuminated by light
(b) (i) Frekuensi cahaya melebihi frekuensi ambang 1 1
The light frequency exceeds the threshold frequency
(ii) Tenaga cahaya berubah kepada tenaga elektrik 1 1
Light energy changes to electrical energy
(c) (i) Rendah 1
Low
Sebab: Lebih stabil 1 2
Reason: More stable
(ii) Jisim kecil 1
Small mass
Sebab: Kos rendah dan mudah untuk pemasangan 1 2
Reason: Low cost and easy for installation
Berputar pada tempatnya sentiasa bersudut tepat dengan 1
cahaya matahari
Rotating at fixed end and always perpendicular to sunlight
Sebab: Untuk meningkatan kecekapan penukaran tenaga 1 2
cahaya kepada tenaga elektrik
Reason: To increase efficiency in converting light energy to
electrical energy
Jumlah 9
8 (a) Pantulan cahaya 1 1
Reflection of light
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 14 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J15
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(b) (i)
Imej
Sinar 1 Image
Ray 1
C F Objek
Object
Sinar 2
Ray 2
Rajah dilukis berdasarkan:
Diagram is drawn based on:
M1 Lukis sinar 1 dan 2/ Draw rays 1 and 2 1
M2 Lukis imej/ Draw image 1 2
(ii) Maya, tegak dan besar/ Virtual, upright and magnified 1 1
[Mana-mana satu/ Any one]
(c) (i) Cermin cembung/ Convex mirror 1
Sebab: Medan penglihatan yang luas 1 2
Reason: Larger view of vision
(ii) Kedudukan cermin tinggi 1
High position of the mirror
Sebab: Liputan luas// Tiada halangan 1 2
Reason: Wide coverage// No obstacle
(d) Cermin S/ Mirror S 1 1
Jumlah 9
BAHAGIAN B
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
9 (a) (i) Jumlah momentum suatu sistem kekal tidak berubah jika 1 1
tiada daya luar yang bertindak ke atas sistem itu
The total momentum of a system remains unchanged in the
absence of an external force on the system
(ii) Kipas menyedut masuk udara lalu dimampatkan di dalam 1
kebuk pembakaran
A fan suck in air then compressed in the combustion chamber
Bahan api kerosin// parafin dipancut masuk ke dalam 1
kebuk pembakaran
Kerosene//Paraffin fuel is injected in the combustion chamber
Letupan berlaku dan menghasilkan gas ekzos berhalaju 1
tinggi ke belakang dengan momentum tinggi
Explosion occurs and a high speed hot gases are ejected
backwards with high momentum
Maka, terhasil satu momentum yang sama magnitud 1 4
tetapi bertentangan arah untuk menolak jet ke depan//
Momentum gas ke belakang = momentum jet ke depan
Then, produces momentum with the same magnitude but
opposite direction to propel the jet forward//
Momentum gas backward = momentum jet forward
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 15 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J16
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(b)
Ciri-ciri Sebab
Characteristics Reason
Diameter nozel kecil Gas keluar dengan halaju
Small diameter of nozzel tinggi 1+1
Gas moves out with high velocity
Kipas besar Menyedut lebih udara ke
Big propeller kebuk pembakaran
Suck more air into combustion 1+1
chamber
Kerosin atau parafin Becampur dengan udara
Kerosene or paraffin dalam kebuk pembakaran
dan meletup 1+1
Mix with air in the combustion
chamber and will explode
Kebuk pembakaran Lebih banyak pembakaran
besar untuk hasilkan momentum 1+1
Big combustion chamber besar
More fuel can be burnt to
produce bigger momentum
L dipilih kerana diameter nozel kecil, kipas besar,
kerosin dan kebuk pembakaran besar 1+1 10
L is chosen because of small diameter of nozzle, big
propeller, kerosene big combustion chamber
(c) (i) 1+1 2
Tujahan/ Thrust Seretan/ Drag
(ii) Momentum yang bertindak ke belakang
The momentum acting backward 1
Momentum = 100 × 200 1 2
= 20 000 kg m s–1
(iii) Momentum ke depan = Momentum ke belakang
= Momentum acting backward
= 20 000 kg m s–1 1 1
Jumlah 20
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 16 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J17
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
10 (a) Tekanan yang dikenakan ke atas cecair dalam suatu 1 1
bekas tertutup akan dipindahkan secara seragam ke
seluruh bahagian cecair itu.
Pressure applied to liquid in an enclosed container is
transmitted equally to all parts of the liquid.
(b) Apabila satu daya kecil dikenakan ke atas omboh A, satu 1
tekanan dihasilkan.
When a small force is applied to piston A, a pressure is produced
Tekanan ini dipindahkan melalui air secara seragam ke 1
omboh B
The pressure is transmitted equally through water to piston B
Satu daya output dihasilkan untuk mengangkat beban 1
An output force is produced to lift the load
Daya output besar kerana luas permukaan omboh B lebih 1 4
besar, F ∝ A
The output force is bigger due to larger surface area of piston
B, F ∝ A
(c)
Ciri-ciri Sebab
Characteristics Reason
Jenis cecair digunakan: Tidak mudah sejat// Tidak
Minyak hasilkan gelembung udara 1+1
Type of liquid used: Oil Does not evaporate easily//
Does not produce air bubbles
Nisbah luas omboh besar ke Hasilkan daya output
omboh kecil adalah besar besar
The ratio of surface area of Produce large output force
1+1
large piston to small piston is
large
Guna keluli sebagai paip Kuat// Tidak mudah
penghantar pecah// Tahan lama 1+1
Use steel as the transmission Strong// Does not break
pipe easily// Long lasting
Saiz takungan cecair besar Boleh angkat beban lebih
Big liquid reservoir tinggi 1+1
Able to lift load higher
R dipilih nisbah luas omboh besar kepada omboh kecil
besar, minyak, keluli dan saiz takungan minyak besar
R is chosen because big ratio of large piston to small piston, 1+1 10
oil, steel and big liquid reservoir
(d) (i) F
P=
A
10
= 1
0.004
= 2 500 Pa 1 2
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 17 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J18
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(ii) W = FY = PAY
= 2 500 × 0.2
= 500 N 1 1
(iii) Isi padu/ Volume X = Isi padu/ Volume Y
VX = VY
AX × hX = AY × hY
(0.004)(0.3) = (0.2)(hY)
1
hY = (0.004 × 0.3)
0.2
= 0.006 m 1 2
Jumlah 20
BAHAGIAN C
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
11 (a) Bilangan ayunan lengkap per saat 1 1
Number of complete oscillations per second
(b) Bandul D dan X sama panjang. Kedua-duanya 1
mempunyai frekuensi asli yang sama.
Pendulums D and X has the same length. Then, both have
same natural frequencies.
Apabila bandul X disesarkan, bandul-bandul lain turut 1
berayun kerana tenaga dipindahkan.
When pendulum X is displaced, all pendulums start to oscillate
because energy is transferred.
Bandul X dan D berada dalam keadaan resonans. 1
Pendulums X and D are in resonance.
Bandul D berayun dengan amplitud maksimum. 1 4
Then, pendulum D oscillates at the maximum amplitude.
(c) (i) Frekuensi gelombang bunyi sama 1
Frequency of sound waves are the same
Panjang gelombang bunyi di kawasan udara sejuk lebih 1
pendek daripada di kawasan udara panas
The wavelength of sound waves in cold air region is shorter
than in hot air region
Arah perambatan gelombang bunyi dalam Rajah 11.2 1 3
menjauhi permukaan Bumi manakala arah perambatan
gelombang bunyi dalam Rajah 11.3 mendekati
permukaan Bumi
The direction of propagation of sound waves in Diagram 11.2
moves away from the Earth surface while the direction of
propagation of sound waves in Diagram 11.3 moves toward the
Earth surface
(ii) Semakin besar panjang gelombang bunyi, semakin tinggi 1 1
laju gelombang bunyi.
The greater the wavelength of sound wave, the higher the
speed of sound wave
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 18 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J19
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(iii) Apabila laju gelombang bunyi tinggi, arah perambatan 1 1
gelombang bunyi semakin mendekati permukaan Bumi
As the speed of sound waves is higher, the direction of
propagation of sound waves is toward the surface of the
Earth.
(d)
Ciri-ciri Sebab
Characteristics Reason
Pembesar suara di tempat Tiada halangan
tinggi To prevent blocking 1+1
Loudspeaker at high place
Jarak di antara dua Jarak di antara dua bunyi
pembesar suara besar kuat berturutan, x kecil
Distance between two Distance between two loud 1+1
loudspeakers is large sounds, x is small
Bahan dinding lembut Menyerap bunyi dan
Soft board material mengelak gema 1+1
Absorbs sounds to avoid echoe
Mikrofon di belakang Mengelak bising
pembesar suara To avoid noise// humming 1+1
Microphone is behind the sound
loud speakers
Bahan untuk lantai: Menyerap bunyi dan
Permaidani atau kayu mengelak gema 1+1 10
Material for the floor: Absorbs sounds to avoid echoe
Carpet or playwood
Jumlah 20
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 19 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J20
KERTAS MODEL PEPERIKSAAN SPM SET 2
KERTAS 1
1 D 2 A 3 C 4 B 5 B 6 D 7 A 8 A 9 D 10 D
11 A 12 A 13 C 14 C 15 B 16 C 17 C 18 D 19 A 20 D
21 A 22 C 23 B 24 C 25 C 26 D 27 C 28 D 29 D 30 B
31 C 32 B 33 B 34 D 35 B 36 A 37 D 38 C 39 C 40 C
KERTAS 2
BAHAGIAN A
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
1 (a) (i) Katod/ Cathode 1 1
(ii) Menerima gelombang cahaya elektromagnet dan 1 1
memancarkan elektron dari permukaan logam
Emission of electron from a metal surface when it is illuminated
by an electromagnetic wave
(b) Frekuensi gelombang cahaya lebih besar daripada 1 1
frekuensi ambang logam
Frequency of light wave is larger than threshold frequency of
the metal
(c) Frekuensi cahaya foton berkadar terus dengan tenaga 1 1
kinetik fotoelektron yang dipancarkan
The frequency of light of photon is directly proportional to the
kinetic energy of photoelectron emitted
Jumlah 4
2 (a) (i) Arah jauh dari magnet// Ke kanan
Direction away from magnet// To the right
S/S
1 1
U/N
(ii) Petua tangan kiri Fleming/ Fleming’s left-hand rule 1 1
(iii) 1
S/S 1 4
U/N
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 20 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J21
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(b) Gerakan rod kuprum semakin laju// jauh 1 1
The movement of the copper rod faster// further
Jumlah 9
3 (a) 3 1 1
(b) Pelakuran nukleus 1 1
Nuclear fusion
(c) (i) Jisim sebelum tindak balas/ Mass before reaction
= 2 × 2.01410 = 4.0282
Jisim selepas tindak balas/ Mass after reaction
= 3.01603 + 1.00867 = 4.0247
Cacat jisim/ Mass defect
m = 4.0282 – 4.0247 1
= 0.0035 u.j.a/ amu 1 2
(ii) Tenaga/ Energy
E = 0.0035 × 1.6 × 10–27 × (3 × 108)2 1
= 5.229 × 10–13 J 1 2
Jumlah 6
4 (a) Tolak atau tarik 1 1
Push or pull
(b) (i)
(ii)
F
1+1 2
FY
(c) FY = F sin 60°
= 32 sin 60° 1
= 27.71 N 1 2
(d) Daya paduan (ke bawah)/ Resultant force (downwards)
= 10 + 27.71 1
= 37.71 N 1 1
(e) (i) Ya, cara yang digunakannya berkesan. 1 1
Yes, the method used is efficient.
(ii) Jumlah daya paduan ke bawah besar 1 1
Total downward resultant force is bigger
Jumlah 9
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 21 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J22
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
5 (a) Berat ialah daya tarikan graviti 1 1
Weight is gravitational force
(b) (i) Berat budak lelaki kurang daripada berat bapanya. 1 1
The weight of the boy less than the weight of his father.
(ii) Isi padu air disesarkan oleh budak lelaki lebih kecil 1 1
daripada isi padu air disesarkan oleh bapanya.
The volume of water displaced by the boy is smaller than
the volume of water displaced by his father.
(iii) Daya apungan ke atas budak lelaki lebih kecil daripada 1 1
daya apungan ke atas bapanya.
The buoyant force acted on the boy is smaller than the
buoyant force acted on his father.
(c) (i) Daya apungan berkadar terus dengan isi padu air 1 1
disesarkan.
Buoyant force is directly proportional to the volume of water
displaced.
(ii) Daya apungan = berat air disesarkan 1 1
Buoyant force = weight of water displaced
(d) FB = ρVg
800 = 1 000 × V × 9.81 1
V = 0.08 m3 1 2
(e) Berat bongkah kayu = daya apungan 1 1
Weight of wooden block = buoyant force
Jumlah 9
6 (a) Dalam ketara ialah jarak di antara permukaan air 1 1
dengan imej
Apparent depth is the distance between the surface of water
with the image.
(b) (i) Dalam nyata bagi Rajah 6.1 lebih tinggi daripada 1 1
Rajah 6.2.
The real depth for Diagram 6.1 is higher than the real depth
for Diagram 6.2.
(ii) Dalam ketara bagi Rajah 6.1 lebih tinggi daripada 1 1
Rajah 6.2.
The apparent depth for Diagram 6.1 is higher than the
apparent depth for Diagram 6.2.
(iii) Dalam nyata berkadar terus dengan dalam ketara 1 1
The real depth is directly proportional to the the apparent depth
(iv) Pembiasan 1 1
Refraction
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 22 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J23
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(c) (i) 1+1 2
(ii) H
n=
h
0.4
1.33 = 1
h
0.4
h= = 0.30 m 1 2
1.33
Jumlah 9
7 (a) Rintangan tinggi apabila gelap 1 1
High resistance in the dark
(b) Pada waktu siang, rintangan PPC paling rendah iaitu
0.5 kΩ
At day time, the resistance of LDR is the lowest which is 0.5 kΩ
2 000
VBC = ×6 1
(2 000 + 500)
= 4.8 V 1 2
(c) (i) PPC di litar tapak 1
LDR is at the base voltage
Sebab: Lampu boleh menyala pada waktu malam// Rintangan 1 2
tinggi pada waktu malam// Voltan tapak tinggi waktu malam
Reason: Bulb can light up at night// High voltage// High
resistance at night
(ii) Perintang 1
Resistance
Sebab: Untuk menghadkan arus tapak 1 2
Reason: To limit base current
(iii) Suis geganti 1
Relay switch
Sebab: Memerlukan voltan tinggi 1 2
Reason: Need to use high voltage
Jumlah 9
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 23 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J24
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
8 (a) (i) Antinod 1 1
Antinode
(ii) Puncak bertemu puncak// Lembangan bertemu lembangan 1 1
Crest meets another crest// Trough meets another trough
(b) ax
𝜆=
D
5×8 1
=
50
1 2
= 0.8 cm
(c) (i) Interferens memusnah 1
Destructive interference
Sebab: Amplitud sifar// Tiada bunyi 1 2
Reason: Zero amplitude// No sound
(ii) Poros 1
Porous
Sebab: Menyerap bunyi// Bunyi tidak boleh dipantulkan 1 2
Reason: Can absorb sound// Sound cannot be reflected
(iii) R 1 1
Jumlah 9
BAHAGIAN B
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
9 (a) Haba ialah sejenis tenaga 1 1
Heat is a form of energy
(d) Air laut dan pasir menerima jumlah haba yang sama 1
daripada Matahari.
The sea water and the sand received same amount of heat from
the Sun.
Air laut mempunyai muatan haba tentu yang lebih tinggi 1
berbanding pasir.
The sea water has higher specific heat capacity than the sand.
Peningkatan suhu pada pasir adalah lebih tinggi 1
berbanding air laut.
The rise of temperature on the sand is higher than the sea
water.
Maka, pasir lebih cepat panas berbanding air laut. 1 4
Thus, the sand becomes hot faster than the sea water.
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 24 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J25
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(c)
Ciri-ciri Penerangan
Characteristics Explanation
Mempunyai penutup Mengurangkan kehilangan
kaca haba 1+1
Has glass cover Reduce heat loss
Menyerap lebih banyak
Panel hitam
haba daripada Matahari 1+1
Black panel
Absorb more heat from the Sun
Banyak bilangan Luas permukaan yang lebih
gegelung paip besar untuk pemindahan 1+1
Many number of pipe haba.
coils Bigger surface area of heat
transfer
Muatan haba tentu
Memindahkan haba lebih
rendah 1+1
cepat
Low specific heat
Transfer heat faster to get hot
capacity
Pemanas air solar Q dipilih kerana mempunyai
penutup kaca, panel hitam, bilangan gegelung paip yang
banyak dan muatan haba tentu rendah. 1+1 10
Solar water heater Q is chosen because it has glass cover,
black panel, high number of pipe coils and low specific heat
capacity.
(d) (i) Qair/water = mc𝜃 = 2 × 4 200 × (50 – 30) 1
= 168 000 J 1 2
(ii) Qair/water = Q logam/metal
168 000 = mc𝜃 = 0.5 × c × (90 − 50) 1
20 × c = 168 000 1
c = 8 400 J kg−1 °C−1 1 3
Jumlah 20
10 (a) (i) Rintangan dalam, r ialah rintangan terhadap gerakan 1 1
cas disebabkan oleh elektrolit di dalam sel kering.
Internal resistance, r is the resistance against the moving
charge due to the electrolyte in the dry cell.
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 25 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J26
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(ii) Voltan 1
Voltage
0 Arus
Current
Daya gerak elektrik = pintasan y 1
Electromotive force = y-intercept
Rintangan dalam, r = kecerunan graf 1 3
Internal resistance, r = gradient of graph
(iii) Rintangan dalam bertambah 1 5
Internal resistance increases
(b) (i) R = 5 + 5 = 10 Ω
1 1 1 1
= +
R 10 15
10
R= = 3.33 Ω 1 2
3
(ii) Ɛ = IR + Ir
1.5 = 1(3.33 + 0.5)
I = 0.4 A 1
V = IR = 0.4 × 3.33 1
V = 1.332 V 1 3
(c)
Ciri-ciri Penerangan
Characteristics Explanation
Mengurangkan rintangan 1+1
Sel kering boleh dicas dalam// Tahan lama
Rechargeable dry cell Less internal resistance//
Long lasting
Menghasilkan d.g.e. lebih 1+1
Susunan bersiri
berkesan//
Series arrangement
Produce more effective e.m.f.
Wayar tebal Mengurangkan rintangan 1+1
Thick wire Less resistance
Bilah kipas plastik Lebih ringan 1+1
Plastic fan blade Lighter
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 26 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J27
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
Kipas mini V dipilih kerana menggunakan sel kering 1+1 10
boleh dicas, susunan bersiri, diameter wayar yang tebal
dan bilah kipas plastik.
Mini fan V is chosen because it uses rechargeable dry
cell, series arrangement, thick wire and plastic fan blade.
Jumlah 20
BAHAGIAN C
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
11 (a) Kadar perubahan momentum 1 1
Rate of change of momentum
(b) (i) Objek dalam Rajah 11.2 lebih keras daripada objek 1
dalam Rajah 11.1
Object in Diagram 11.2 is harder than object in Diagram 11.1
Masa tindak balas ke atas kaki kanan Ali dalam Rajah 1
11.2 lebih pendek daripada dalam Rajah 11.1.
Reaction time on Ali’s right foot in Diagram 11.2 is longer than
in Diagram 11.2.
Kesakitan yang dialami oleh Ali dalam Rajah 11.2 lebih 1 3
kuat daripada dalam Rajah 11.1.
Pain experience Ali in Diagram 11.2 is stronger than in
Diagram 11.1.
(ii) Semakin keras objek tersebut, semakin pendek masa 1 1
tindak balas.
The harder the object, the shorter the reaction time.
(iii) Semakin pendek masa tindak balas, semakin besar daya 1 1
impuls.
The shorter the reaction time, the larger the impulsive force.
(c) Tukul cerucuk dinaikkan kepada satu ketinggian di atas 1
cerucuk dan dibiarkan jatuh.
Pile hammer is risen to a certain height above the pile and it is
allowed to fall.
Tukul cerucuk yang lebih berat dan berhalaju tinggi 1
menghasilkan momentum yang besar.
Heavy weight and high velocity of the pile hammer produce a
large momentum.
Momentum yang tinggi ini dipindahkan ke cerucuk. 1
The high momentum of the pile hammer is transferred to the
pile.
Kemudian, menolak cerucuk ke tanah dengan satu daya 1 4
yang besar.
Then, drives the pile into the ground with a large force.
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 27 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J28
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(d) Aspek Penjelasan
Aspect Explanation
Raket kukuh// raket Tidak mudah patah// Ringan 1+1
karbon fiber Does not break easily// Lighter
Strong racquet// carbon
fiber racquet
Meningkatkan daya geseran// 1+1
Pemegang getah Lebih cengkaman
Rubber grip Increase frictional force// More
grip
Tali tegang Daya impuls tinggi 1+1
High tension string High impulsive force
Kedudukan raket tinggi
Tenaga keupayaan tinggi 1+1
High position of the
High potential energy
racquet
Ikut lajak Perubahan momentum tinggi 1+1 10
Follow through High change in momentum
Jumlah 20
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 28 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J29
KERTAS MODEL PEPERIKSAAN SPM SET 3
KERTAS 1
1 A 2 B 3 A 4 B 5 D 6 D 7 B 8 C 9 D 10 A
11 A 12 C 13 B 14 C 15 C 16 D 17 A 18 B 19 D 20 B
21 C 22 C 23 B 24 A 25 A 26 D 27 A 28 D 29 D 30 D
31 A 32 B 33 A 34 D 35 C 36 B 37 B 38 D 39 C 40 C
KERTAS 2
BAHAGIAN A
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
1 (a) (i) Arus ulang-alik 1 1
Alternating current
(ii) Arus terus 1 1
Direct current
(b) (i) Diod 1 1
Diode
(ii) Membenarkan arus mengalir dalam satu arah sahaja 1 1
Allow current to flow in one direction only
Jumlah 4
2 (a) (i) 1 1
Sinar cahaya
daripada objek
Ligh ray from
object
Prisma kaca
45°
Glass prism
45°
Pemerhati
Observer
(ii) Pantulan dalam penuh boleh berlaku 1 1
Total internal reflection can occur
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 29 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J30
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(iii) Sinar cahaya 1 1
daripada objek
Ligh ray from
object
Prisma kaca
Glass prism
Pemerhati
Observer
(b) 1
n=
sin c
1
sin c = = 0.658 1
1.52
c = 41.14° 1 2
Jumlah 5
3 (a) (i) Arus yang dihasilkan apabila terdapat perubahan 1 1
medan magnet
Current produced when there is a change in magnetic field
(ii) Terdapat pemotongan medan// fluks magnet 1 1
Cutting of magnetic field// flux
(b) (i) Utara/ North 1 1
(ii) 1 1
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 30 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J31
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(c)
Voltan output
Output voltage
Sudut putaran
Angle of rotation
1+1 2
Jumlah 6
4 (a) (i) Tiada pemindahan haba bersih antara dua objek dan 1 1
kedua-dua objek mempunyai suhu akhir yang sama
There is not net flow of heat between two objects and
both objects have the same final temperature
(ii) Haba mengalir daripada air mendidih ke termometer. 1
Heat flows from hot water to the thermometer.
Sehingga ia mencapai keseimbangan terma. 1
Until it achieves thermal equilibrium.
Suhu air sama dengan suhu yang ditunjukkan oleh 1
termometer.
Temperature of water equal as the temperature shown by the
thermometer.
Tiada haba bersih mengalir. 1 4
No net heat flows.
(b) (i) Haba dibebaskan oleh M = haba diserap oleh air
Heat released by M = heat absorbed by water
m1c1𝜃1 = m2c2𝜃2 1
(0.5) × (800) × (100 – T) = (0.2) × (4 200) × (T – 30) 1
40 000 – 400T = 840T – 25 200 1
1 240T = 65 200
T = 52.58 °C 1 4
(ii) Tiada haba hilang ke persekitaran 1 1
No heat lost to the surrounding
Jumlah 9
5 (a) Arus/ Current 1 1
(b) (i) Konduktor dalam Rajah 5.2 lebih panjang daripada 1 1
konduktor dalam Rajah 5.1.
The length of the conductor in Diagram 5.2 is longer than the
conductor in Diagram 5.1.
(ii) Bacaan ammeter dalam Rajah 5.2 lebih kecil daripada 1 1
bacaan ammeter dalam Rajah 5.1.
The reading of ammeter in Diagram 5.2 is smaller than the
reading of ammeter in Diagram 5.1.
(iii) Bacaan voltmeter dalam kedua-dua rajah adalah sama. 1 1
The reading of voltmeter for both diagrams are equivalent.
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 31 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J32
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(c) (i) Panjang konduktor berkadar terus dengan rintangan 1 1
konduktor.
The length of the conductor is directly proportional to the
resistance of the conductor.
(ii) Rintangan berkadar songsang dengan arus. 1 1
The resistance is inversely proportional to the current.
(d) (i) 3
2R = =1Ω
3
RP = RQ = 0.5 Ω
1
VP = IRP = 3 × 0.5
= 1.5 V 1 2
(ii) Bacaan voltmeter berkurang 1 1
The reading of voltmeter decreases
Jumlah 9
6 (a) (i) Tenaga solar/ Solar energy 1
Sebab: Tenaga boleh diperbaharui 1 2
Reason: Renewable energy
(ii) Gelombang mikro/ Microwave 1
Sebab: Frekuensi tinggi// Kuasa penembusan tinggi// 1 2
Tenaga tinggi
Reason: High frequency// High penetrating power// High energy
(b) Satelit R 1 1
Satellite R
(c) (i) Pecutan graviti di Bulan
Gravitational acceleration on the Moon
GM
g=
R2
(6.67 × 10 −11)(7.35 × 1022)
= 1
(1.75 × 106)2
= 1.60 N 1 2
(ii) Halaju lepas
The escape velocity
2GM
v=
R
2(6.67 × 10 −11)(7.35 × 1022) 1
=
1.75 × 106
= 2.37 × 103 N atau / or 2 367 N 1 2
Jumlah 9
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 32 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J33
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
7 (a) Berat kapal = daya apungan = berat air disesarkan 1 1
Weight of ship = buoyant force = weight of water displaced
(b) (i) FB = ρVg = W = mg
ρVg = mg
1.02 × 103 × V = 4.7 × 108 1
V = 460 784 m3 1 2
(ii) Isi padu bahagian kapal yang terendam di Laut Sulu 1
lebih besar.
The volume of the portion of the ship immersed in the Sulu sea
is larger.
Sebab: Kapal mesti menyesarkan air yang banyak untuk 1 2
mengekalkan daya apung yang sama.
Reason: The ship must displaced more water in order to
maintain the same buoyant force.
(c) (i) Suhu tinggi 1
High temperature
Sebab: Menambah daya apungan// Ketumpatan udara 1 2
dalam belon rendah.
Reason: Increase buoyant force// Density of air inside the
balloon is smaller.
(ii) Saiz belon besar 1
Big balloon
Sebab: Daya apungan tinggi// Menambah isi padu udara 1 2
disesarkan
Reason: High buoyant force// Increase the volume of air
displaced
Jumlah 9
8 (a) Penyebaran gelombang apabila melalui celah atau 1 1
halangan.
Spreading of waves when passes through a slit or obstacles.
(b) Bunyi berfrekuensi rendah 1 1
Low frequency sound
Pembesar suara
Loudspeaker λ
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 33 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J34
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(c) (i) Panjang gelombang dalam Rajah 8.2 lebih besar daripada 1
dalam Rajah 8.3.
The wavelength in Diagram 8.2 is larger than in Diagram 8.3.
(ii) Corak gelombang dalam Rajah 8.2 lebih membulat 1
daripada Rajah 8.3.
The wave pattern in Diagram 8.2 is more circular than in
Diagram 8.3.
(iii) Semakin besar panjang gelombang, semakin membulat 1
corak gelombang.
The larger the wavelengths, the more circular the patterns of
the waves.
(iv) Semakin besar panjang gelombang, semakin jelas kesan 1 4
pembelauan.
The larger the wavelengths, the diffraction of the waves is more
obvious.
(d) v = 𝑓𝜆
330 1
𝜆=
100
= 3.3 m 1 2
(e) Amplitud berkurang 1 1
Amplitude decreases
Jumlah 9
BAHAGIAN B
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
9 (a) Objek jatuh disebabkan oleh daya tarikan graviti sahaja 1 1
An object falls due to gravitational force only
(b) (i) Pecutan graviti = 9.81 m s–2 1 1
Gravitational acceleration = 9.81 m s–2
(ii) v = u + at
= 0 + (9.81 × 2) 1
= 19.62 m s−1 1 2
(iii) 1 2
s = ut + gt
2
1
= 0 + ( × 9.81 × 22 ) 1
2
= 19.62 m 1 2
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 34 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J35
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(b) Di dalam udara, bola besi sampai ke bawah lebih awal. 1
In air, the iron ball reached at the bottom earlier.
Terdapat rintangan udara yang bertindak ke atas bulu 1
ayam disebabkan luas permukaannya yang besar.
There is air resistance acts on the feather due to its large
surface area.
Di dalam vakum, kedua-dua bola besi dan bulu ayam 1
sampai ke bawah dalam masa yang sama.
In vacuum, both iron balls and feather reached the bottom at
the same time.
Kedua-dua objek ditarik oleh daya graviti yang sama 1 4
kerana tiada rintangan udara.
Both objects are pulled by the same gravitational force because
no air resistance.
(d)
Spesifikasi Penjelasan
Specification Explanation
Badan gentian
Ringan// Ketumpatan rendah 1+1
karbon
Lighter// Low density
Carbon fibre body
Supaya pengayuh berada pada
kedudukan aerodinamik// 1+1
Pemegang bengkok
Kurangkan rintangan udara
Drop handle
To ensure the cyclist at aerodynamic
position// Reduce air resistance
Luas permukaan kecil// Tekanan 1+1
Tayar tirus tinggi// Lebih cengkaman
Narrow tyre Small surface area// High pressure//
More grip
Tayar tanpa bunga Kurangkan geseran 1+1
Tyre without thread Reduce the friction
Basikal trek R dipilih kerana badan dibuat daripada 1+1 10
gentian karbon, pemegang bengkok, tayar tirus dan tanpa
bunga.
Track bicycle R is chosen because with carbon fibre body, drop
handle, narrow and without thread tyre.
Jumlah 20
10 (a) Kadar perubahan halaju/ Rate of change of velocity 1 1
(b) (i) WX = W sin 30°
= (1 500) × (9.81) sin 30° 1
= 7 357.5 N 1 2
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 35 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J36
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(ii) F = 7 357.5 – 2 500
= 4 857.5 N 1 1
(iii) F = ma
= 1 500a = 4 857.5
4 857.5 1
a=
1 500
= 3.23 m s−2 1 2
(c) Naik ke atas: Kereta bergerak menentang daya tarikan 1
graviti dan nyahpecut.
Moves upward: The car moves against gravitational force and
decelerate.
Perlu tekan minyak untuk menambah daya tujah ke 1
depan dan memastikan kereta tidak bergerak menurun.
Need to press the accelerator to increase the thrust and make
sure the car does not move downward.
Turun ke bawah: Kereta sedang memecut. 1
Move downward: The car is accelerating
Tekan brek untuk perlahankan kereta dengan menambah 1 4
daya geseran.
Press the brake to slow down the car by increasing the
frictional force.
(d) Aspek Alasan
Aspects Reason
Kaedah tolak Daya ke bawah, FY besar 1+1
Push method Large downward force, FY
Jumlah daya ke bawah
1+1
Jisim besar (W + FY) besar// stabil
Large mass Total downward force
(W + FY ) larger// stable
1+1
Bilah pemotong besar Potong lebih banyak rumput
Large cutter blade Cut more grass
Daya dikenakan ke bawah FY 1+1
Sudut antara
besar (FY = F sin 𝜃, 𝜃 besar,
pemegang besar
FY besar)
Large angle between
Large force acting downward, FY
the handle
(FY = F sin 𝜃, large 𝜃, large FY )
Mesin rumput M dipilih kerana menggunakan kaedah 1+1 10
tolak, berjisim besar, bilah pemotong besar dan sudut
antara pemegang besar.
Lawnmower M is chosen because using push method, large
mass, large blade and large angle between handle.
Jumlah 20
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 36 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J37
BAHAGIAN C
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
11 (a) (i) Tindak balas nuklear apabila satu nukleus yang 1 1
beratmembelah menjadi dua atau lebih nukleus yang
lebih ringan dengan membebaskan tenaga yang banyak.
Nuclear reaction when a heavy nucleus splits into two or more
lighter nuclei while releasing a large amount of energy.
(ii) Pembelahan nukleus ialah pemecahan nukleus berat. 1
Nuclear fission is the splitting of a heavy nucleus.
Pelakuran nukleus ialah gabungan beberapa nukleus 1
ringan.
Nuclear fusion is the combining of several light nucleus.
Terdapat kehilangan jisim bagi kedua proses. 1
There is lost in mass for both processes.
Tenaga dibebaskan bagi kedua-dua proses.
Energy is released for both processes.
E = mc2 1
iaitu/ in which
E = jumlah tenaga dibebaskan/ total energy released 1 5
m = cacat jisim/ mass defect
c = laju cahaya dalam vakum/ speed of light in vacuum
(b) Neutron menghentam nukleus uranium. 1
Neutron bombarded a uranium nucleus.
2 atau 3 neutron dihasilkan. 1
2 or 3 neutrons are produced.
Neutron yang dihasilkan akan menghentam nukleus 1
uranium yang lain.
The neutrons produced will bombard another uranium nucleus.
Bagi setiap tindak balas, lebih banyak neutron dihasilkan 1
menyebabkan tindak balas berantai.
For each reaction, more neutrons are produced causing a chain
reaction.
Sehingga jisim genting tercapai. 1
Until the critical mass is reached.
Neutron
Neutrons
Maks
Nukleus
uranium 4
Uranium
nucleus
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 37 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J38
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(c)
Aspek Penjelasan
Aspects Explanation
Tidak stabil// Nombor proton
Bahan api: Uranium 1+1
Fuel: Uranium
besar
Unstable// Large proton number
Pepejal Mudah dikendalikan
Easy to handle
1+1
Solid
Bahan api yang Dapat diguna lama// Tidak perlu
separuh hayat ditukar dengan kerap
panjang Use longer time// Do not need to 1+1
Long half life of fuel replace frequently
Bahan untuk rod: Menyerap neutron// Kawal tin-
Kadmium dak balas berantai 1+1
Material for the rod: Absorb the neutron// Control the
Cadmium chain reaction
Bahan untuk
moderator: Grafit Memperlahankan halaju neutrons
Material for To slow down the fast neutrons 1+1
moderator: Graphite
Elak kebocoran radiasi daripada Maks
Dinding konkrit
reaktor nuklear ke persekitaran 1+1 10
tebal
Prevent leakage of radiation from
Thick concrete wall
the reactor core to the surrounding
Jumlah 20
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 38 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J39
KERTAS MODEL PEPERIKSAAN SPM SET 4
KERTAS 1
1 C 2 C 3 B 4 D 5 D 6 D 7 C 8 D 9 C 10 B
11 A 12 C 13 C 14 A 15 A 16 C 17 D 18 B 19 D 20 C
21 B 22 D 23 C 24 B 25 D 26 A 27 B 28 C 29 B 30 A
31 C 32 D 33 A 34 B 35 D 36 C 37 A 38 C 39 B 40 C
KERTAS 2
BAHAGIAN A
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
1 (a) Sesaran 1 1
Halaju =
Masa
Displacement
Velocity =
Time
(b) a = kecerunan graf
gradient of graph
10
=
10 1
= 1 m s−2 1 2
(c) Halaju seragam 1 1
Uniform velocity
Jumlah 4
2 (a) Daya graviti antara kedua-dua jasad adalah berkadar terus 1 1
dengan hasil darab jisim kedua-dua jasad dan berkadar
songsang dengan kuasa dua jarak antara pusat dua jasad
tersebut.
The gravitational force between the two bodies is directly
proportional to the product of the mass of the two bodies and
inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the
centers of the two bodies.
(b) [(6.67 × 10−11)(60 × 80)]
F= 1
42
= 2.00 × 10−8 N 1 2
(c) Daya tarikan graviti akan berkurang 1 1
Gravitational force decreases
(d) Kerana daya graviti antara Abdullah dan Karam Singh 1 1
adalah terlalu kecil berbanding berat mereka.
Because the gravitational force between Abdullah and Karam
Singh is too small compared to their weight.
Jumlah 5
3 (a) Daya paduannya adalah sifar 1 1
Resultant force is zero
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 39 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J40
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(b) 1
T2 1 2
55°
70°
W
55°
T1
(c) (i) W = mg = 150 × 9.81
= 1 471.5 N 1 1
(ii) T1 = T2 = T
Hukum sinus/ Law of sines:
W T
=
sin 70° sin 55°
(1 471.5 × sin 55°) 1
T=
sin 70°
1 2
= 1 282.74 N
Jumlah 6
4 (a) Aerofoil 1 1
(b) Udara berhalaju tinggi di bahagian atas menghasilkan 1
tekanan rendah di bahagian atas.
Air flow with high velocity at the top section produce lower
pressure at the top section.
Terdapat perbezaan tekanan dan hasilkan daya angkat ke 1
atas.
Difference in pressure and produce lift or upward force
Prinsip Bernoulli 1 3
Bernoulli’s principle
(c) (i) W = mg = 3.6 × 105 × 9.81 1
= 3 531 600 N/ 3.53 × 106 N 1 2
(ii) Daya angkat = Berat = 3 531 600 N 1 1
Lift force = Weight = 3 531 600 N
(iii) F
P=
A
3 531 600
= 1
460
= 7 677.39 Pa 1 2
Jumlah 9
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 40 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J41
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
5 (a) (i) Litar sesiri 1 1
Series circuit
(ii) V = IR
3 = 1.5 × (R + R)
3
2R =
1.5 1
R=1 Ω 1 2
(b) (i) 240 V atau lebih tinggi 1
240 V or higher
Sebab: Nilai voltan yang sama dengan alat// Alat bekerja 1 2
secara normal
Reason: Voltage with same value as appliances// Appliances
working normally
(ii) Litar selari 1
Parallel circuit
Sebab: Jika salah satu alat tidak berfungsi, alat lain masih 1 2
boleh berfungsi
Reason: If one appliance not function, others still function.
(iii) Luas keratan rentas dawai besar 1
Large cross-sectional area of wire
Sebab: Rintangan kecil 1 2
Reason: Low resistance
Jumlah 9
6 (a) Bilangan ayunan lengkap dalam masa 1 saat 1 1
Number of complete oscillation in 1 second
(b) (i) Kedalaman air di kawasan X lebih tinggi daripada 1 1
kedalaman air di kawasan Y.
The depth of water in region X is higher than the depth of
water in region Y.
(ii) Panjang gelombang di kawasan X lebih panjang daripada 1 1
panjang gelombang di kawasan Y.
The wavelength in region X is longer than the wavelength in
region Y.
(iii) Kedalaman air berkadar terus dengan panjang 1 1
gelombang.
The depth of water is directly proportional to the wavelength.
(iv) Pembiasan 1 1
Refraction
(c) Di kawasan teluk, tenaga disebarkan ke kawasan 1
yang luas// tenaga berkurang.
At the bay, the energy is spread out to larger area// energy
decreases.
Amplitud sifar// Amplitud rendah// Air lebih tenang. 1 2
Zero amplitude// Low amplitude// Water is calm.
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 41 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J42
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(d) v1 v2
=
𝜆1 𝜆2
6 v2
=
8 5
30
v2 = 1
8
= 3.75 cm s−1 1 2
Jumlah 9
7 (a) Proses nukleus yang tidak stabil memancarkan zarah alfa 1 1
atau beta dan tenaga supaya ia menjadi stabil.
A proses which an unstable nucleus becomes more stable by
emitting alpha particles or beta particles and energy in order to
be more stable.
(b) (i) Aktiviti awal bagi kedua-dua rajah adalah sama. 1 1
Initial activity for both diagrams are equivalent.
(ii) Sela masa bagi Rajah 7.2 lebih lama daripada sela masa 1 1
bagi Rajah 7.1.
The time interval for Diagram 7.2 is longer than the time
interval for Diagram 7.1.
(iii) Kadar reputan radioaktif bagi Rajah 7.2 lebih rendah 1 1
daripada kadar reputan radioaktif bagi Rajah 7.1.
The rate of radioactive decay for Diagram 7.2 is lower than the
rate of radioactive decay for Diagram 7.1.
(c) (i) Kadar reputan radioaktif berkadar songsang dengan 1 1
sela masa untuknya menjadi separuh.
The rate of radioactive decay is inversely proportional to the
time interval for it to be halved.
(ii) Separuh hayat berkadar songsang dengan kadar reputan 1 1
radioaktif.
The half-life is inversely proportional to the rate of radioactive
decay.
(d) T 1 = 8 minit/ minutes 1 1
2
(e) 2 000 → 1 000 → 500 → 250 → 125 1
125 aktiviti/ activities 1 2
Jumlah 9
8 (a) Daya impuls 1 1
Impulsive force
(b) Momentum pelantak cerucuk berkurang 1 1
Momentum of the pile driver decreases
(c) (i) Pelantak cerucuk tinggi 1
High pile driver
Sebab: Hasilkan halaju tinggi apabila menghentam cerucuk 1 2
Reason: Produce high velocity when strike the pile.
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 42 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J43
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(ii) Tapak cerucuk yang tajam 1
Sharp base of the pile
Sebab: Tekanan tinggi dihasilkan supaya mudah tolak 1 2
cerucuk ke dalam tanah
Reason: Produce high pressure and easy to push the pile into
the ground
(iii) Sistem R 1 1
System R
(d) v2 = u2 + 2gs = 0 + (2 × 9.81 × 20) 1
v2 = 392.4
v = 19.81 m s−1 1 2
Jumlah 9
BAHAGIAN B
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
9 (a) (i) Haba yang diperlukan untuk menukarkan 1 kg bahan 1 1
dari cecair ke gas tanpa perubahan suhu.
Heat required to change 1 kg of substance from liquid to gas
at constant temperature.
(ii) Air mempunyai haba pendam tentu pengewapan yang 1
tinggi.
Water has high specific latent heat of vapourisation.
Periuk kukus mesti ditutup supaya stim tidak keluar dan 1
terkondensasi ke atas ikan.
The steamer is closed by a lid to prevent the steam from
coming out and it will condense on the fish.
Stim yang terkondensasi membebaskan haba pendam 1
tentu pengewapan.
The condensed steam will release specific latent heat of
vapourisation. 1 4
Ikan serap haba ini dan masak dengan cepat.
The fish absorbs the heat and can be cooked faster.
(b) (i) Pt = ml
Pt (0.1 × 1 000)(3.6 − 1.0)(60) 1
l= =
m 0.05
= 312 000 J kg−1 1 2
(ii) mc𝜃 = Pt 1
Pt (0.1 × 1 000)(4.8 − 1.0)(60)
c= = 1
m𝜃 0.05 × (218 − 78)
= 1 028.57 J kg−1 °C−1 1 3
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 43 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J44
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
(c)
Spesifikasi Sebab
Specification Reason
Bahan di antara dinding Penebat haba// Elak konduksi
dalam dan luar: Span haba 1+1
Material between inner Insulator// Prevent conduction
and outer wall: Sponge of heat
Injap pengembang Haba pendam diserap
besar semasa cecair menyejat//
Large expansion valve Mudah menyejat 1+1
Latent heat absorbed as the
liquid evaporates// Easy
evaporates
Banyak sirip penyejuk Membebaskan haba pendam
Many cooling fins ke persekitaran 1+1
Giving out latent heat of
vaporization to the surrounding
Ruang sejuk beku besar Menyimpan lebih banyak 1+1
Large freezer makanan
compartment Can keep a lot of food
Peti sejuk R dipilih kerana menggunakan span, banyak
sirip penyejuk, injap pengembang besar, ruang sejuk
beku besar. 1+1 10
Refrigerator R is chosen because uses sponge, many cooling
fins, large expansion valve, large freezer compartment.
Jumlah 20
10 (a) (i) Proses menukarkan arus ulang-alik kepada arus terus. 1 1
Process of converting alternating current to direct current.
(ii) Transformer berfungsi berdasarkan prinsip aruhan 1
elektromagnet.
Transformer works based on the priciple of electromagnetic
induction.
Apabila voltan arus ulang-alik, VP dikenakan ke atas 1
gegelung primer, arus ulang-alik mengalir melalui gegelung.
When alternating current voltage, VP is applied to the primary
coil of transformer, an alternating current flows throught the coil
Arus ulang-alik menghasilkan medan magnet yang 1
berubah-ubah dari segi magnitud dan arah.
The alternating current produces a magnetic field that changes
in magnitude and direction.
Maka terdapat perubahan medan// fluks magnet dalam 1
gegelung primer dan teras besi lembut.
Thus there is change in magnetic field// flux in the primary coil
and the soft iron core.
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 44 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J45
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
Teras besi lembut sebagai penghubung ke gegelung 1
sekunder.
The soft iron core as a link to the secondary coil.
Perubahan medan/ fluks magnet juga berlaku di gegelung 1
sekunder yang hasilkan daya gerak elektrik (d.g.e.)
aruhan, VS .
Change in the magnetic field/ flux also occurs in the secondary
coil which induces an electromotive force (e.m.f.) VS . Maks
Arus aruhan juga mengalir melalui gegelung sekunder. 1 4
Induced current also flows through the secondary coil.
(b)
Aspek Sebab
Aspect Reason
Transformer injak Untuk mengurangkan beza 1+1
turun keupayaan output
Step down transformer To reduce the output voltage
Nisbah gegelung
Untuk menghasilkan voltan 1+1
NP : NS = 20:1
output 12 V
Ratio of the coils
To produce output voltage of 12 V
NP : NS = 20:1
Untuk menghasilkan rektifikasi 1+1
Susunan 4 diod
penuh gelombang
4 diodes arrangement
To produce full wave rectification
Untuk meratakan voltan arus 1+1
Guna kapasitor
terus.
Use capacitor
To smooth the direct current voltage
Litar M dipilih kerana transformer injak turun, nisbah 1+1 10
NP: NS = 20:1, susunan 4 diod dan menggunakan kapasitor.
Circuit M is chosen because step down transformer, ratio
NP: NS = 20:1, arrangement of 4 diodes and use capacitor.
(c) (i) Voltan output/ Output voltage
= 12 V 1
(ii) Kecekapan transformer/ The efficiency of transformer
Kuasa input/ Input power = 240 × 0.5 = 120 W 1
Kuasa output/ Output power = 24 + 24 = 48 W 1
48
Kecekapan/ Efficiency = × 100 % 1
120
= 40 % 1 5
Jumlah 20
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 45 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J46
BAHAGIAN C
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
11 (a) Titik di mana semua cahaya selari menumpu 1 1
selepas dibiaskan.
A point where all parallel lights converged after refraction.
(b) Jarak objek dalam Rajah 11.1 lebih jauh daripada jarak 1
objek dalam Rajah 11.2.
The object distance in Diagram 11.1 is further than the object
distance in Diagram 11.2.
Jarak imej dalam Rajah 11.1 lebih dekat daripada jarak 1
imej dalam Rajah 11.2.
The image distance in Diagram 11.1 is nearer than the image
distance in Diagram 11.2.
Saiz imej dalam Rajah 11.1 lebih kecil daripada saiz imej 1
bagi Rajah 11.2.
The size of image in Diagram 11.1 is smaller than the size of
the image in Diagram 11.2.
Jarak objek berkadar songsang dengan jarak imej. 1
The object distance is inversely proportional to the image
distance.
Jarak objek berkadar songsang dengan saiz imej. 1 5
The object distance is inversely proportional to the size of image.
(c) Sinar cahaya adalah selari. 1
Light rays are parallel.
Kanta cembung menumpukan semua sinar cahaya. 1
Convex lens converges all light rays.
Pada titik fokus, F, keamatan cahaya tinggi dan suhu 1
bertambah.
At the focal point, F, the light intensity is high and the
temperature increases.
Haba diserap oleh kertas dan terbakar. 1 4
Heat is absorbed by the paper and burns.
(d)
Aspek Huraian
Aspects Explanation
Diameter kanta objek Lebih banyak cahaya
besar masuk 1+1
Large diameter of objective More light can enter
lenses
Panjang fokus kanta Pembesaran besar
objektif, fO : Panjang High magnification 1+1
The focal length of objective
lens, fO : Long
Panjang fokus kanta mata, Pembesaran besar
fe : Pendek High magnification 1+1
The focal length of eyepiece
lens, fe: Short
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 46 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
J47
Sub Markah
Soalan Jawapan
markah penuh
Kedudukan objek: Jauh/ Sinar cahaya adalah
Infiniti selari dan fokus di fO
The position of the object: Light rays are parallel and 1+1
Distant/ Infinity focused at fO
Kedudukan imej pertama: Imej nyata
Di titik fokus kanta Imej pada pelarasan
objektif normal 1+1 10
Position of the first image: Real image
At focal point of objective Image at normal adjustment
lens
Jumlah 20
4531 © Penerbit Mahir Sdn. Bhd. (183897-P)
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 47 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
Catatan
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 48 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
Catatan
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 49 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
Catatan
KM FIZIK SBP Jawapan (5th)22/3/22.indd 50 22/03/2022 12:40 PM
You might also like
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7No ratings yet
- January 2009 MS - Unit 2 Edexcel Physics A-Level PDFDocument11 pagesJanuary 2009 MS - Unit 2 Edexcel Physics A-Level PDFLotti LottiNo ratings yet
- NEET UG 2022 Question Paper Solutions by Aakash Code S5 PDFDocument74 pagesNEET UG 2022 Question Paper Solutions by Aakash Code S5 PDFANGELINE MaduNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2016Document17 pagesMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2016Mohamed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Yenepoya Pu CollegeDocument20 pagesYenepoya Pu Collegeshaxm098No ratings yet
- WPH04 01 Rms 20160817 PDFDocument14 pagesWPH04 01 Rms 20160817 PDFFuwad Abdul MuyeedNo ratings yet
- 9PH0 01 Rms 20190815Document18 pages9PH0 01 Rms 20190815senseiNo ratings yet
- Spotlight Phase-2: DAY-3 - TEST - JEE (Advanced)Document6 pagesSpotlight Phase-2: DAY-3 - TEST - JEE (Advanced)parv goyalNo ratings yet
- Gce As Marking Scheme: SUMMER 2016 Physics As - Unit 2 2420U20/01Document12 pagesGce As Marking Scheme: SUMMER 2016 Physics As - Unit 2 2420U20/01aNo ratings yet
- downloadChemistryA Levelpast PapersOCR AAS Paper 1November20202020MS20 20paper20Document16 pagesdownloadChemistryA Levelpast PapersOCR AAS Paper 1November20202020MS20 20paper20c yuNo ratings yet
- Ap22 Apc Physics 1 q3Document15 pagesAp22 Apc Physics 1 q3zlu99339No ratings yet
- MHT Cet Question Paper SetDocument17 pagesMHT Cet Question Paper SetjokesNo ratings yet
- Cblephpl 02Document9 pagesCblephpl 02HariNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Periodic Table Elements and Physical ChemistryDocument25 pagesMark Scheme Periodic Table Elements and Physical ChemistryEsam ELNOAMANYNo ratings yet
- Physics Answer N9 08Document15 pagesPhysics Answer N9 08Mohd Khairul Anuar100% (3)
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2015: GCE Chemistry (6CH05/01)Document24 pagesMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2015: GCE Chemistry (6CH05/01)Arpan SahaNo ratings yet
- 4MB0 02R MSC 20190307Document21 pages4MB0 02R MSC 20190307Humphery YangNo ratings yet
- October 2016 MS 2Document6 pagesOctober 2016 MS 2adannaajaegboNo ratings yet
- Cblephpl 03Document9 pagesCblephpl 03Akshpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Utkarsh Advanced 2024 Adv Test 5 19.6.2023Document15 pagesUtkarsh Advanced 2024 Adv Test 5 19.6.2023SamNo ratings yet
- 4CH1 1C Rms 20210604Document23 pages4CH1 1C Rms 20210604Kevin MattNo ratings yet
- 0580 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The March 2016 SeriesDocument5 pages0580 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The March 2016 SeriesheldiNo ratings yet
- 4CH1 1C MSC 20210517Document23 pages4CH1 1C MSC 20210517Abu Ostad Nishan100% (1)
- Scheme of Evaluation: Question No Answers/points To Be Covered MarksDocument2 pagesScheme of Evaluation: Question No Answers/points To Be Covered MarksParamita SahaNo ratings yet
- June 2013 MS - Unit P3 (H) Edexcel Physics GCSEDocument14 pagesJune 2013 MS - Unit P3 (H) Edexcel Physics GCSEmrudulaNo ratings yet
- Ap22 Apc Physics 1 q3Document15 pagesAp22 Apc Physics 1 q3王硕No ratings yet
- MHT Cet Physics Chemistry Question Paper Solution PDFDocument23 pagesMHT Cet Physics Chemistry Question Paper Solution PDFpranav kandalkarNo ratings yet
- 2022 JEE Main 18 SolutionsDocument20 pages2022 JEE Main 18 SolutionsHimanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Ebook Calculus For Business Economics and The Social and Life Scienc Brief Edition 11Th Edition Hoffmann Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument56 pagesEbook Calculus For Business Economics and The Social and Life Scienc Brief Edition 11Th Edition Hoffmann Test Bank Full Chapter PDFarianluufjs100% (14)
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Mathematics 0580/13 May/June 2020Document6 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Mathematics 0580/13 May/June 2020kdebipershadNo ratings yet
- 55-1-1 Physics Marking Scheme 2020Document18 pages55-1-1 Physics Marking Scheme 2020jyotibhalaNo ratings yet
- Terangganu-Answer Physics P2-Trial SPM 2007Document15 pagesTerangganu-Answer Physics P2-Trial SPM 2007kamalharmoza100% (1)
- Ms Preboard II Science XDocument7 pagesMs Preboard II Science Xchhayamaskare.3No ratings yet
- E2L Stage9 01 MS 3RP AFP tcm143-639948Document4 pagesE2L Stage9 01 MS 3RP AFP tcm143-639948chikwendumichelleNo ratings yet
- APhO 2016 T3 Marking SchemeDocument7 pagesAPhO 2016 T3 Marking SchemeВук РадовићNo ratings yet
- Test-3-Egtronics Devices PDFDocument11 pagesTest-3-Egtronics Devices PDFSumit KumarNo ratings yet
- KT 269 HK GonwdDocument4 pagesKT 269 HK GonwdClarissa SamanthaNo ratings yet
- JEE - Main Sample Papers - With Solutions by FIITJEE PDFDocument81 pagesJEE - Main Sample Papers - With Solutions by FIITJEE PDFSaliq Neyaz100% (1)
- NEET (UG) - 2022: Answers & SolutionsDocument70 pagesNEET (UG) - 2022: Answers & SolutionsPiyush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Introducton of Circuit AssignmentDocument8 pagesIntroducton of Circuit AssignmentYasa Islam JunayetNo ratings yet
- 2021 AMC10B Solutions FallDocument18 pages2021 AMC10B Solutions FallHan ZhengNo ratings yet
- 2021 Sarawak - SMK Physics K1 - K2 JawapanDocument8 pages2021 Sarawak - SMK Physics K1 - K2 JawapanJasrul JamalNo ratings yet
- 12th PhysicsDocument6 pages12th PhysicsAkash Kumar ParidaNo ratings yet
- Gate PI 2012Document17 pagesGate PI 2012Rahul PandeyNo ratings yet
- Solutions:: ECE - 606 Spring 2013 1Document7 pagesSolutions:: ECE - 606 Spring 2013 1Rashmi netamNo ratings yet
- STD Xii Physics Ms Set IDocument9 pagesSTD Xii Physics Ms Set IDevi prasath SelvakumarNo ratings yet
- 4024 w19 Ms 11Document7 pages4024 w19 Ms 11Inshal KhtkNo ratings yet
- English As A Second Language Stage 9 Sample Paper 1 Mark Scheme - tcm143-595850Document4 pagesEnglish As A Second Language Stage 9 Sample Paper 1 Mark Scheme - tcm143-595850Amenyawu JonathanNo ratings yet
- Questions & Solutions: GUJCET 2020 (PCE)Document12 pagesQuestions & Solutions: GUJCET 2020 (PCE)simranasifhuseinNo ratings yet
- 4024 s20 Ms 11 PDFDocument7 pages4024 s20 Ms 11 PDFAvinash DilipNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Mathematics (Syllabus D) 4024/11 May/June 2020Document7 pagesCambridge O Level: Mathematics (Syllabus D) 4024/11 May/June 2020tahir hayatNo ratings yet
- MT132 (M132) : Linear Algebra Tutor Marked Assignment: Plagiarism WarningDocument13 pagesMT132 (M132) : Linear Algebra Tutor Marked Assignment: Plagiarism WarninghaniNo ratings yet
- 2019 JC1 H2 Math Term 2 Revision Test (Marking Scheme) Q2 UpdatedDocument5 pages2019 JC1 H2 Math Term 2 Revision Test (Marking Scheme) Q2 UpdatedTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Beng (Hons) Mechanical Engineering Two Final Examination 6 Finite Element and Difference Solutions Module No: Ame6006Document9 pagesBeng (Hons) Mechanical Engineering Two Final Examination 6 Finite Element and Difference Solutions Module No: Ame6006Sameera AlweeraNo ratings yet
- 2020eir211s02 Memo Semester Test 2 MemoDocument8 pages2020eir211s02 Memo Semester Test 2 MemoMarco VisserNo ratings yet
- Jee Advance 1 Paper 1Document12 pagesJee Advance 1 Paper 1iLearn MathNo ratings yet
- Advanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionFrom EverandAdvanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Supports For Uninsulated PipesDocument12 pagesSupports For Uninsulated Pipesdepinfor lusofabrilNo ratings yet
- Astm 143Document3 pagesAstm 143JH_ProjectNo ratings yet
- Markov Chain Chapter 6Document42 pagesMarkov Chain Chapter 6durga0350% (2)
- Union Metal SemiconductorDocument4 pagesUnion Metal SemiconductorskinhugoNo ratings yet
- ShaperDocument5 pagesShaperRAFIULALAM75% (4)
- 3 WadhwaDocument10 pages3 WadhwaNaveen SharmaNo ratings yet
- 3815333Document80 pages3815333Sumbal KeranNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Viscosity of Different Liquids Using A Falling Ball ViscometerDocument9 pagesDetermination of The Viscosity of Different Liquids Using A Falling Ball ViscometerJarell BalajadiaNo ratings yet
- RT Acceptance Criteria For Pressure VesselDocument1 pageRT Acceptance Criteria For Pressure VesselkapsarcNo ratings yet
- Reverse Engineering ExamplesDocument13 pagesReverse Engineering ExamplesAfafNo ratings yet
- Answer Key For Apprenons Le Francais 2 PDFDocument4 pagesAnswer Key For Apprenons Le Francais 2 PDFMeera ChughNo ratings yet
- Lifting Hook ArrangementsDocument54 pagesLifting Hook ArrangementsMalavNo ratings yet
- ESP Cables: Exploration & ProductionDocument2 pagesESP Cables: Exploration & ProductionHimawan Sigit NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Annex 16Document33 pagesAnnex 16Windiarto AbisetyoNo ratings yet
- B&E Matrix - TemplateDocument11 pagesB&E Matrix - TemplateIvan JuniorNo ratings yet
- ThermosampleDocument5 pagesThermosampledeniel andalNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Physics Volume 2 Guide English Medium 215874 PDFDocument26 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Physics Volume 2 Guide English Medium 215874 PDFvasanthagokilam rajendranNo ratings yet
- Conversion Chart For HardnessDocument5 pagesConversion Chart For HardnessIshmael WoolooNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Part 2Document42 pagesService Manual Part 2fil24No ratings yet
- Photography NCFE Level 1 Certificate Project 1 - College LifeDocument6 pagesPhotography NCFE Level 1 Certificate Project 1 - College LifeNgel EvnsNo ratings yet
- Geo Thermal Update of Ecuador 2005-2010: Karwan SaeedDocument26 pagesGeo Thermal Update of Ecuador 2005-2010: Karwan SaeedKarwan DilmanyNo ratings yet
- 5990 5266en PDFDocument10 pages5990 5266en PDFJames MossNo ratings yet
- CFD OpenfoamDocument4 pagesCFD OpenfoamKush VermaNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument156 pagesPDFOki NurpatriaNo ratings yet
- Arndt Schultz Law and HomoeopathyDocument7 pagesArndt Schultz Law and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD Hom100% (4)
- Guido Busca (Auth.) - Heterogeneous Catalytic Materials. Solid State Chemistry, Surface Chemistry and Catalytic Behaviour CAP 2Document14 pagesGuido Busca (Auth.) - Heterogeneous Catalytic Materials. Solid State Chemistry, Surface Chemistry and Catalytic Behaviour CAP 2Romel RauraNo ratings yet
- Dust CollectorDocument24 pagesDust Collectorafroz ahmedNo ratings yet
- ASDA A2 ManualDocument583 pagesASDA A2 ManualClaudio Lourenço da Silva100% (1)
- Power System ReliabilityDocument11 pagesPower System ReliabilityDia Putranto Harmay100% (1)