Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Degassing & Dehydration
Uploaded by
abdelwahab alneamah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views15 pagesThis document discusses degassing, dehydration, and desalting processes used in oil production. In degassing, gases are removed from the crude oil and either used or sold. In dehydration, water is removed to eliminate emulsions and inorganic salts which can cause corrosion. Crude oil naturally contains varying amounts of water and salts. Dehydration occurs in two stages, first removing salt via settling, chemicals, or a combination, then further processing at refineries. The goal is to reduce water and salts to levels that won't damage refining equipment.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses degassing, dehydration, and desalting processes used in oil production. In degassing, gases are removed from the crude oil and either used or sold. In dehydration, water is removed to eliminate emulsions and inorganic salts which can cause corrosion. Crude oil naturally contains varying amounts of water and salts. Dehydration occurs in two stages, first removing salt via settling, chemicals, or a combination, then further processing at refineries. The goal is to reduce water and salts to levels that won't damage refining equipment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views15 pagesDegassing & Dehydration
Uploaded by
abdelwahab alneamahThis document discusses degassing, dehydration, and desalting processes used in oil production. In degassing, gases are removed from the crude oil and either used or sold. In dehydration, water is removed to eliminate emulsions and inorganic salts which can cause corrosion. Crude oil naturally contains varying amounts of water and salts. Dehydration occurs in two stages, first removing salt via settling, chemicals, or a combination, then further processing at refineries. The goal is to reduce water and salts to levels that won't damage refining equipment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
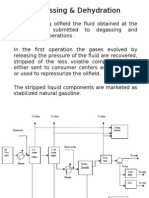
Degassing & Dehydration
In a producing oilfeld the uid obtained at the
wellhead is submitted to degassing and
dehydration operations .
In the frst operation the gases evolved by
releasing the pressure o the uid are recovered,
stripped o the less volatile components, and
either sent to consumer centers as natural gas
or used to repressurize the oilfeld.
The stripped liuid components are mar!eted as
stabilized natural gasoline.
Dehydration and desalting of
crude
The second operation aims to
completely eliminate the water that
appears in the uid orming stable
emulsions, and the removal o
water"soluble inorganic salts
associated with the water which, i
let in the oil, would give rise to
serious corrosion problems in the
course o refning operation.
#ll crude contain moisture and salts to
varying degrees.
$ater is li!ely to occur in emulsion orm
when the crude are naphthenic or sulurous.
(No harm may be expected to the
distillation column due to the presence of
moisture , as there is always steam in
distillation. However , crude has to be
dehydrated to remove the salts).
$ater being good solvent or these salts the
removal is very much e%ective in the orm o brine.
all o the e'isting salts, chlorides o calcium and
magnesium distinguish themselves in playing an
invincible role in overhead corrosion .
These salts in presence o steam at ()*"+** *
easily hydrolyze generating hydrochloric vapors.
These vapors cause corrosion to euipments
#ny crude that contains more than )
!gs -(*lbs o total salts e'pressed
in terms o sodium chloride per
thousand barrels may be regarded
as salty crude.
Dehydration o crude is practiced in
two stages, frst at the site and later
at the refnery.
#t the site -oil feld / salt is removed by
( settling or
+ by adding chemicals or
0 by ombination o these two.
rude possessing emulsiying characteristics are
not responsive to settling method1 these demand
demulsiying agent to increase the coalescence o
water drops.
-2oda ash, sodium hydro'ide, salt o atty acids
petroleum sulonates which assist coalescence o
water droplets.
#nother mechanical method is used
i.e. coalescence, means it is the
process by which two or more
droplets, bubbles or particles merge
during contact to orm a single
daughter droplet, bubble or particle.
# typical diagram o a coaleser is
given below/
# good amount o water should be available
in crude or such treatment 1 lac! o water
demands the resh additions to about +* 3 .
#ter adding the chemicals and water to the
desired e'tent the crude mi'ture is allowed to
stand 4)"5* o at () !gs6cm+ in huge tall
tan!s.
Demulsiying chemicals , i necessary are
added in very small amounts. 7etention time
is about 85 hours.
7esin, asphalts, organic acids, and
solids which are produced with the oil,
and aid in the ormation o a tough flm
around the droplet, thus isolating each
separate water droplet rom the other.
The flm which isolates the water
droplets rom the other must be
bro!en beore coalescence ta!e place
The fnal phase o the coalescence
process is the collision o these small
water droplets under the inuence
You might also like
- Crude Oil TreatmentDocument27 pagesCrude Oil TreatmentmahmoudNo ratings yet
- Removing Contaminants From Crude Oil - AthlonDocument5 pagesRemoving Contaminants From Crude Oil - AthlonIrene CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Oilfield Processing Volume Two Crude Oil Manning Part 1Document221 pagesOilfield Processing Volume Two Crude Oil Manning Part 1rohl55100% (2)
- Degassing and DesaltingDocument15 pagesDegassing and DesaltingMuhammad MohtashimNo ratings yet
- Desalter TheoryDocument10 pagesDesalter TheoryPraneethNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02A - DesaltingDocument30 pagesLecture 02A - DesaltingJorge Enciso AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Refining Processes1Document73 pagesPetroleum Refining Processes1Arun DasNo ratings yet
- De SaltersDocument15 pagesDe SaltersMuhammad Arslaan100% (2)
- API - Intro To Oil and Gas ProductionDocument10 pagesAPI - Intro To Oil and Gas Productionfoobar2016No ratings yet
- SWS Paper FinalA4Document17 pagesSWS Paper FinalA4faisalmuradNo ratings yet
- Emulsion Breaking PDFDocument22 pagesEmulsion Breaking PDFNovrie100% (1)
- The Effective Way of Separating WaterDocument38 pagesThe Effective Way of Separating WaterIrshad Muhammad100% (4)
- Oil-Water Separation TechnogiesDocument4 pagesOil-Water Separation TechnogiesBrian FreireNo ratings yet
- Surface FacilitiesDocument20 pagesSurface Facilitiesheriku_mulyaNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Refineries Waste Water - AssignmentDocument29 pagesPetroleum Refineries Waste Water - AssignmentIastra100% (2)
- Desalting Heavy Crude Oils - The Venezuelan ExperienceDocument10 pagesDesalting Heavy Crude Oils - The Venezuelan ExperienceDomingoAPerazaS100% (1)
- Design Calculations MalidduwaDocument72 pagesDesign Calculations MalidduwaUmesg100% (1)
- WEF AM13 Participants 34ezx6jlxk PDFDocument76 pagesWEF AM13 Participants 34ezx6jlxk PDFMeggie Gathee KimariNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil Desalting ProcessDocument24 pagesCrude Oil Desalting ProcessamirejazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Emulsion & Oil/Water Separation: I. Oil Export SpecificationDocument21 pagesChapter 10: Emulsion & Oil/Water Separation: I. Oil Export SpecificationThanh Tùng PhạmNo ratings yet
- Treatment Processes in Petroleum RefiningDocument6 pagesTreatment Processes in Petroleum RefiningtalhaNo ratings yet
- Desalting Crude OilDocument13 pagesDesalting Crude Oilpardise4000No ratings yet
- Crude Oil Desalting ProcessDocument18 pagesCrude Oil Desalting Processiancu_jianu_60% (1)
- DesaltDocument8 pagesDesalt7awyNo ratings yet
- Dewatering and Desalting Crude OilDocument2 pagesDewatering and Desalting Crude OilRichard ObinnaNo ratings yet
- Assignment of StatisticsDocument3 pagesAssignment of StatisticssadafilyasNo ratings yet
- Desalting of Crude OilDocument14 pagesDesalting of Crude OilHammad Hashmi100% (4)
- Speaking Templates For All 8 Parts of CELPIP. Structure & SamplesDocument11 pagesSpeaking Templates For All 8 Parts of CELPIP. Structure & SamplesPiyush Sharma100% (2)
- DESALTERSDocument48 pagesDESALTERSPRET1971100% (1)
- RCM FormatDocument3 pagesRCM FormatjsphdvdNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil DesaltingDocument14 pagesCrude Oil DesaltingDucViking100% (1)
- Oily Waste Water Cleanup by Gas FlotationDocument17 pagesOily Waste Water Cleanup by Gas Flotationsivainduri100% (2)
- Flow Assurance - AOEDocument19 pagesFlow Assurance - AOEAmeya SaneNo ratings yet
- Sour Water Where It Comes From and How To Handle ItDocument10 pagesSour Water Where It Comes From and How To Handle ItRamon IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil DesaltingDocument5 pagesCrude Oil DesaltingAhmed Mohamed Khalil0% (1)
- Suez University Faculty of Petroleum andDocument14 pagesSuez University Faculty of Petroleum andAsh BuzNo ratings yet
- 03 04 Petroleum Waste Water Desalter Case StudyDocument6 pages03 04 Petroleum Waste Water Desalter Case StudyivandavidmtNo ratings yet
- Desalting Paper Musleh1Document18 pagesDesalting Paper Musleh1Ahmed Mohamed KhalilNo ratings yet
- Lec.1 Desalting ProcessDocument30 pagesLec.1 Desalting ProcessAhmed RedaNo ratings yet
- The Disposal of Ield Waste Water: Wright DaviesDocument7 pagesThe Disposal of Ield Waste Water: Wright DaviesDanivian HigginsNo ratings yet
- PETROODocument6 pagesPETROOaya mahmoudNo ratings yet
- PPT-CH 5Document24 pagesPPT-CH 5chemical todiNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Oil Special ProblemsDocument34 pagesTreatment of Oil Special ProblemsUdeme JohnNo ratings yet
- Ass 2 STDocument15 pagesAss 2 STraunNo ratings yet
- 08 AWT Water Disposal SystemsDocument8 pages08 AWT Water Disposal Systemscarlos neiraNo ratings yet
- EmulsionsDocument14 pagesEmulsionsPaolo CavaioniNo ratings yet
- PetroleumDocument15 pagesPetroleumstephen mwendwaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04Document16 pagesLecture 04Touseef IsmailNo ratings yet
- ABSTRACTDocument7 pagesABSTRACTRawda SeragNo ratings yet
- Pretreatment of Crude Oil Before RefiningDocument5 pagesPretreatment of Crude Oil Before RefiningMD Redwan IslamNo ratings yet
- A Quick Look at DesaltingDocument12 pagesA Quick Look at DesaltingGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- CHE10406, Crude Oil DesaltingDocument1 pageCHE10406, Crude Oil DesaltingMechanicalNo ratings yet
- Ion ExchangeDocument2 pagesIon ExchangeStellaNo ratings yet
- Zero LiquidDocument6 pagesZero LiquidEr Govind Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Earth: Chemistry Half Yearly Exam StudyDocument96 pagesThe Chemical Earth: Chemistry Half Yearly Exam StudykhoocumberNo ratings yet
- ӀӀӀ.2. Tách các tạp chất cơ học, muối và nướcDocument8 pagesӀӀӀ.2. Tách các tạp chất cơ học, muối và nướcViệt Anhd TrầnNo ratings yet
- EmulsionsDocument14 pagesEmulsionsام عبدالرحمن الشيخ100% (3)
- Oil Water Separation - PTQ - Q22013 PDFDocument3 pagesOil Water Separation - PTQ - Q22013 PDFMohamed TallyNo ratings yet
- Wet Crude ProcessingDocument39 pagesWet Crude Processingabdelwahab alneamahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument19 pagesChemistry ProjectAadarsh MouryaNo ratings yet
- Penggunaan Sodium Polyacrylate Untuk Proses Demulsifikasi Minyak-AirDocument6 pagesPenggunaan Sodium Polyacrylate Untuk Proses Demulsifikasi Minyak-AirRahmi Nur Anisah Nasution 2003114489No ratings yet
- Measurement of Oil and GreaseDocument4 pagesMeasurement of Oil and GreaseMKPashaPashaNo ratings yet
- Wet Crude ProcessingDocument39 pagesWet Crude Processingabdelwahab alneamahNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Product On The Product's SDS SheetDocument2 pagesHazardous Product On The Product's SDS Sheetabdelwahab alneamahNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. IdentificationDocument8 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1. Identificationabdelwahab alneamahNo ratings yet
- MSDS - EN - PrimaCover Robust - Primaverde BVDocument4 pagesMSDS - EN - PrimaCover Robust - Primaverde BVabdelwahab alneamahNo ratings yet
- BOPs StackDocument20 pagesBOPs Stackabdelwahab alneamahNo ratings yet
- BDG TutorialDocument11 pagesBDG TutorialyassineNo ratings yet
- Paper Bridge CompetitionDocument5 pagesPaper Bridge Competitionzia.mudassir2No ratings yet
- Milestone - Applied StatisticsDocument2 pagesMilestone - Applied StatisticsSachin BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Problems and Constraints in Banana Cultivation: A Case Study in Bhagalpur District of Bihar, IndiaDocument9 pagesProblems and Constraints in Banana Cultivation: A Case Study in Bhagalpur District of Bihar, IndiaVasan MohanNo ratings yet
- FPS Scope matrix-NSC-KRCDocument27 pagesFPS Scope matrix-NSC-KRCBaladaru Krishna PrasadNo ratings yet
- The Return of "Patrimonial Capitalism": in The Twenty-First CenturyDocument16 pagesThe Return of "Patrimonial Capitalism": in The Twenty-First CenturyjlgallardoNo ratings yet
- France (Comparative Local System)Document9 pagesFrance (Comparative Local System)Ahmed TarekNo ratings yet
- The Technical University of KenyaDocument5 pagesThe Technical University of KenyaEng Stephen ArendeNo ratings yet
- PCSBP Slides V5Document109 pagesPCSBP Slides V5wemoap i.s.No ratings yet
- Zebrafish Poster Portrait Eupfi Sep 2106 Final SubmittedDocument1 pageZebrafish Poster Portrait Eupfi Sep 2106 Final Submittedapi-266268510No ratings yet
- Geography SyllabusDocument4 pagesGeography SyllabusmvrthedocNo ratings yet
- Tech Support: Unscramble The QuestionsDocument16 pagesTech Support: Unscramble The QuestionsCarlos .LopezNo ratings yet
- BME-02 Initial Testing and EvaluationDocument2 pagesBME-02 Initial Testing and EvaluationPAPPU RANJITH KUMARNo ratings yet
- PTW-06 Electrical Work PermitDocument3 pagesPTW-06 Electrical Work PermitjayNo ratings yet
- Pe V RepublicDocument2 pagesPe V RepublicKen ChaseMasterNo ratings yet
- Sid WindowsDocument6 pagesSid WindowsEleva Tu IntelectoNo ratings yet
- Pre Requisite Programs Main PresentationDocument19 pagesPre Requisite Programs Main PresentationASIF EJAZNo ratings yet
- Case Study Horosho enDocument4 pagesCase Study Horosho enMaster ManojNo ratings yet
- Packet Filtering FirewallDocument9 pagesPacket Filtering FirewallEnoch L SNo ratings yet
- Catalogue 6Document64 pagesCatalogue 6Adrian DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Biometric SystemDocument8 pagesBiometric SystemAayush SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- PVC Pipe Industry Analysis in PakistanDocument4 pagesPVC Pipe Industry Analysis in PakistanOlufemi MoyegunNo ratings yet
- The Factory Act 1948 ObjectivesDocument24 pagesThe Factory Act 1948 ObjectivescontactsoniNo ratings yet
- Arc 488Document7 pagesArc 488Apoorva SinghNo ratings yet
- Olano Alarcon Razuri 2009 Understanding The Relationship Between Planning Reliability and Schedule Performance PresentationDocument17 pagesOlano Alarcon Razuri 2009 Understanding The Relationship Between Planning Reliability and Schedule Performance PresentationRich GamarraNo ratings yet