Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fertility in Mares: The Non-Pregnant Mare
Uploaded by
Andres MartinezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fertility in Mares: The Non-Pregnant Mare
Uploaded by
Andres MartinezCopyright:
Available Formats
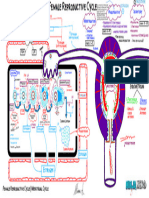
Fertility in Mares
The non-pregnant Mare
Ultrasound Examination of the Reproductive Cycle
Transitional Phase ER ANESTRU Anestrus
21 DAYS
WINT S
Multiple large follicles on both ovaries, edema in uterus can Ovaries small and inactive, uterus very soft, flattened without
vary due to differences in follicular activity and estrogen con- edema. 4-7 Days
centration.
Schematic Presenta-
SPRI
tion of the Annual
AUTUM
NG
Stages of the Mare’s First
Reproductive Cycle. Ovulation
Ovulation is indicated by the
blue dots
Diestrus Estrus
CY
CL L ES
A corpus haemorrhagicum and later corpus luteum can be vi- IN G C YC Dominant follicles at midstage of estrus. Depending on the
M AR US
sualized. Functionality of the CL can be determined by Doppler E, RE G U L A R ESTR stage of estrus and the individual pattern of the mare, various
ultrasound. The uterus is small, firm, round and homogenous. grades of edema can be visualized in the uterus.
21 DAYS
ER ANESTRU
WINT S
4-7 Days
N
SPRI
AUTUM
NG
First
Ovulation
Varying stages of Flatted, Moderate Obvious Extreme
edema of the uterus no edema edema edema edema
CY ES
CL CL
IN G CY
M AR US
E, RE G U L A R ESTR
The pregnant Mare
Ultrasound Examination Time Line
START
Day 11 Day 14-16 Day 25-35 Day 40-120
Yolk sac is first visible by First US examination: Second ultrasound exa- Endometrium cups act
ultrasound. Functional ensure presence of one mination: confirm di- autonomically and pro-
CL(s) on one or both or two embryonic vesi- agnosis of pregnancy. duce eCG. eCG has
ovaries are visible by cles. Examine the ova- Conceptus can be dis- predominately an LH
ultrasonography. Scan- ries for multiple luteal tinguished from a endo- function and supports
ning for cysts before structures. Multiple metrial cyst by presence the maintenance of the
pregnancy is important, conceptuses can still be of an embryo proper. primary CL and the de-
to avoid confusion. separated and crushed. Heart beat becomes vi- velopment of secondary
After crushing: examine sible from day 23. CL.
Until day 16 the mare again 2-3 days
later. Day 35 Day 55-80
Mobility phase: embryo
migrates through the Formation of endome- Fetal sex can be deter-
entire uterus.
Day 16-17 trium cups: fetal cells mined by rectal ultraso-
Fixation phase: embryo migrate to endometri- nography.
fixates itself at one of um and produce Equi-
the boundaries corpus ne Chorionic Gonadot-
uteri – uterus horn. rophin.
Common Abnormalities on Ultrasound
Endometrial Cysts Granulosa Cell
Endometritis and Tumor
Looks like a pregnancy.
Endometrial Cysts Can obstruct the uterine Due to inhibin production
lumen leading to failure of the affected ovary, the
Differences in the amount of maternal recognition contralateral ovary will be
of uterine fluid, echogeni- of pregnancy, or they can very small. GCT can produ-
city and edema. lead to early embryonic ce estrogens or testostero-
death. ne leading to behavioural
changes.
Esaote S.p.A. Via Melen 77, I-16152 Genova - www.esaote.com/veterinary - esaote.veterinary@esaote.com
Ultrasound pictures with special thanks to: W.K. Hendriks, DVM Dipl. ECAR. Scientific Sources: 1) England, Gary C.W. Fertility and Obstetrics in the Horse, third edition, England, Blackwell publishing (2005);
2) Hendriks, W. K. & Stout, T.; Esaote MyLibrary Equine Reproduction – Mare, Version 1.0, Esaote Europe BV, (2009). 3) Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Utrecht University, Syllabus Voortplanting en Obstetrie (2011) - Esaote Veterinary 160000155
You might also like
- Guidelines: Sustainability Assessment of Food and Agriculture SystemsDocument268 pagesGuidelines: Sustainability Assessment of Food and Agriculture SystemspetronilaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Gr.11Document23 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Gr.11Heba AliNo ratings yet
- Molecular Plant Breeding & Tissue Culture TechniquesDocument20 pagesMolecular Plant Breeding & Tissue Culture TechniquesNasir Hussain FarazNo ratings yet
- Spermatogenesis and OogenesisDocument23 pagesSpermatogenesis and OogenesisGerlJerl100% (1)
- DLP Earth and Life ScienceDocument3 pagesDLP Earth and Life ScienceLowel Andrew Batomalaque100% (3)
- Lecture 1 - Reproductive Physiology 2021Document10 pagesLecture 1 - Reproductive Physiology 2021Winnie PillyNo ratings yet
- Mitosis WorksheetDocument1 pageMitosis WorksheetFrician Bernadette Muyco100% (1)
- Chapter 2, Unit 1, Human Anatomy and Physiology 1, B Pharmacy 1st Sem, Carewell PharmaDocument21 pagesChapter 2, Unit 1, Human Anatomy and Physiology 1, B Pharmacy 1st Sem, Carewell Pharmaom441693No ratings yet
- FI Rstyear (1 Semester) : Uni T S Cat Egor y P EDocument3 pagesFI Rstyear (1 Semester) : Uni T S Cat Egor y P EVictor De Veyra IINo ratings yet
- The DR Abcde Approach Expl Ai Ned Through A Owchart.: Danger ResponseDocument1 pageThe DR Abcde Approach Expl Ai Ned Through A Owchart.: Danger ResponseAhmed Al-HashediNo ratings yet
- Unit 4, Pharmaceutics 1, B Pharmacy 1st Sem, Carewell PharmaDocument13 pagesUnit 4, Pharmaceutics 1, B Pharmacy 1st Sem, Carewell PharmaSuma PharmaNo ratings yet
- M A R T: I Ndi Vi Dualgoalpl AnDocument2 pagesM A R T: I Ndi Vi Dualgoalpl Anricsymon domingoNo ratings yet
- (Lea) Industrial Security ManagementDocument17 pages(Lea) Industrial Security ManagementLouie Mar MaquintoNo ratings yet
- Students NEARS200: Week-End Migration OF 1armistice DAY Observed AT Special Chapel ProgramDocument3 pagesStudents NEARS200: Week-End Migration OF 1armistice DAY Observed AT Special Chapel ProgramBobcat NewsNo ratings yet
- (Lea) Industrial Security ManagementDocument17 pages(Lea) Industrial Security Managementjoshua saladagaNo ratings yet
- StrataCamMini BrochureDocument2 pagesStrataCamMini BrochureLuis GutierrezNo ratings yet
- The EYE Lens MethodDocument1 pageThe EYE Lens Methodcakic.vanjaNo ratings yet
- TOS ComputationDocument2 pagesTOS ComputationJerome MagdaongNo ratings yet
- My CV-1Document1 pageMy CV-1Sri Premaya - KAILASANo ratings yet
- WCEF2023 Programme Overview 2xDocument1 pageWCEF2023 Programme Overview 2xvipin kumarNo ratings yet
- Portafolio Florez-GalvisDocument36 pagesPortafolio Florez-GalvisNicolás FlorezNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 07-Mar-2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan 07-Mar-2023Vriddhi AhujaNo ratings yet
- Bo NCM116 DSDocument3 pagesBo NCM116 DSJoycee BoNo ratings yet
- Samsung Corporate Name ListDocument1 pageSamsung Corporate Name Liststartupbin33No ratings yet
- Special Senses) 3. Photoreceptors - Rods and Cones - KeyDocument1 pageSpecial Senses) 3. Photoreceptors - Rods and Cones - Keyranag59100No ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology) 22. Female Reproductive Cycle - Menstrual Cycle - KeyDocument1 pageEndocrine Physiology) 22. Female Reproductive Cycle - Menstrual Cycle - Keyhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology - 25. Male Reproductive System - Erection - Ejaculation - KeyDocument1 pageEndocrine Physiology - 25. Male Reproductive System - Erection - Ejaculation - Keyranag59100No ratings yet
- Swornstatementofassets, Li ABI LI TI EsandnetworthDocument2 pagesSwornstatementofassets, Li ABI LI TI EsandnetworthReden villarmaNo ratings yet
- Bou Azzer East Dyke Swarm (EL BAMIKI) - CopieDocument40 pagesBou Azzer East Dyke Swarm (EL BAMIKI) - Copiemouad ouhNo ratings yet
- Banner 2023Document1 pageBanner 2023ackonboham2No ratings yet
- Newspaper Noti Ce Board: Background OF THE Study ObjectivesDocument1 pageNewspaper Noti Ce Board: Background OF THE Study ObjectivesIsrael PopeNo ratings yet
- Modi FI Edlearnerenrollmentandsurveyform: THI Sformi SnotforsaleDocument3 pagesModi FI Edlearnerenrollmentandsurveyform: THI Sformi Snotforsalezyronkris arrazNo ratings yet
- African E-Waste Conference 11-13 Aug - PosterDocument1 pageAfrican E-Waste Conference 11-13 Aug - PosterMuchiri NahashonNo ratings yet
- Evecareersguide PDFDocument82 pagesEvecareersguide PDFMilos DukicNo ratings yet
- Partograph For MoodleDocument37 pagesPartograph For MoodleNoelle Grace Ulep BaromanNo ratings yet
- Educati On: References Avai Lable Upon RequestDocument1 pageEducati On: References Avai Lable Upon RequestSledmasterNo ratings yet
- Issue 23 Digital Transformation Digital VersionDocument64 pagesIssue 23 Digital Transformation Digital VersionAhmad FaizalNo ratings yet
- HR 190 310 Full Application FINAL AnthonyWilloughbyDocument2 pagesHR 190 310 Full Application FINAL AnthonyWilloughbyapi-25835246No ratings yet
- Cer Mi X SL: Ceratoni C MATDocument1 pageCer Mi X SL: Ceratoni C MATChetna BhanwalNo ratings yet
- Journal 072012 PDFDocument84 pagesJournal 072012 PDFDannilo Amorim CerqueiraNo ratings yet
- Math 121 - Calculus 1 (Differential Calculus)Document6 pagesMath 121 - Calculus 1 (Differential Calculus)Ajon RuizoNo ratings yet
- Blue Water: Transition ToDocument16 pagesBlue Water: Transition ToAnmol ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- BTR Day 1-2 @filesneetpgDocument197 pagesBTR Day 1-2 @filesneetpgSiddarth ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- P. E.1:Movementenhancement: EngageDocument8 pagesP. E.1:Movementenhancement: EngagePia Mariane EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Market Forecasting 1942418000Document94 pagesMarket Forecasting 1942418000Kunal SolankiNo ratings yet
- Guidance FOR Radio Installations CH A P T e R 2 SurveysDocument10 pagesGuidance FOR Radio Installations CH A P T e R 2 SurveysNguyễn Đức TựNo ratings yet
- The ASEAN Oct Nov 2021 Digital v1Document72 pagesThe ASEAN Oct Nov 2021 Digital v1Vingie AbrioNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 English Coursebook Curriculum Sample July 2021Document37 pagesGrade 7 English Coursebook Curriculum Sample July 2021Haajirah AzgerNo ratings yet
- Nomor Keput Us An Pendi R I An: 74/ BST/ P/ 65 Fakultas I LMU Sosi AL DAN Poli TI KDocument1 pageNomor Keput Us An Pendi R I An: 74/ BST/ P/ 65 Fakultas I LMU Sosi AL DAN Poli TI KBENGKEL PONSELNo ratings yet
- TheraCOm Infographics Group6 MARIANO AlessandraDocument1 pageTheraCOm Infographics Group6 MARIANO AlessandraAlessandra Dominique MarianoNo ratings yet
- Si NGL E Mar R I Ed Wi Dowed Separ at Ed: Downl Oadedby:Lymarkampati N-Mon, Jul27,20204: 04PmDocument1 pageSi NGL E Mar R I Ed Wi Dowed Separ at Ed: Downl Oadedby:Lymarkampati N-Mon, Jul27,20204: 04PmMark WawaNo ratings yet
- Attendance FormatDocument1 pageAttendance Formatjar.maintenance22No ratings yet
- Communicate With The World: English Class ScheduleDocument3 pagesCommunicate With The World: English Class ScheduleCeleste RosaladaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledapi-54508565No ratings yet
- Gawat Darurat05242019182632Document2 pagesGawat Darurat05242019182632Arie Yustava RezzaNo ratings yet
- Pal Et T E: Educati ONDocument1 pagePal Et T E: Educati ONCharlesNo ratings yet
- Paper TestDocument27 pagesPaper TestDương Nguyễn TùngNo ratings yet
- Womens HealthDocument94 pagesWomens HealthLynseyNo ratings yet
- Elementary RqaDocument11 pagesElementary RqaEd FloresNo ratings yet
- AC Case StudyDocument7 pagesAC Case StudySanthoshNo ratings yet
- Mind MappingDocument1 pageMind Mapping21COMP009RUDRAPATELNo ratings yet
- Mce35 Exam Final2021 2022Document5 pagesMce35 Exam Final2021 2022Elizabeth De GalaNo ratings yet
- Potstars Survivor Record SheetDocument1 pagePotstars Survivor Record SheetNess AdramelechNo ratings yet
- Tasche Marketing PlanDocument18 pagesTasche Marketing PlanAngeline De LeonNo ratings yet
- Celestial Motif of The Celestial City of The Elohim: LaodiceaDocument1 pageCelestial Motif of The Celestial City of The Elohim: LaodiceaHans Cristobal Placencia OlateNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14 Cellular RespirationDocument18 pagesLesson 14 Cellular RespirationGinalyn QuimsonNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 4 On Central DogmaDocument3 pagesProblem Set 4 On Central DogmaPaulomon EdrozochuNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii-Week 7 Lesson 31: Modes Of: Reproduction of Flowering PlantsDocument76 pagesUnit Ii-Week 7 Lesson 31: Modes Of: Reproduction of Flowering PlantsLendel Mariz O. CepilloNo ratings yet
- Importances of Reproduction OrganismsDocument17 pagesImportances of Reproduction OrganismsPORCHE CAYENNE MACAN GTSNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Third Quarter Exam Final Answer OrigDocument4 pagesScience 10 Third Quarter Exam Final Answer Origbernadette delgadoNo ratings yet
- Alternative Splicing As A Source of Phenotypic DiversityDocument14 pagesAlternative Splicing As A Source of Phenotypic DiversitySergio VillicañaNo ratings yet
- GR 8 PT 1st GPDocument8 pagesGR 8 PT 1st GPFLORENCE G. QUERONo ratings yet
- UBT-13 Paper (20-03-24)Document48 pagesUBT-13 Paper (20-03-24)anshchau2007No ratings yet
- 8th Guide - Plant Reproduction AsexualDocument3 pages8th Guide - Plant Reproduction AsexualJuanJo ZapataNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Apoptosis and Necrosis in Cell DeathDocument13 pagesThe Effects of Apoptosis and Necrosis in Cell DeathSundayNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Cell Division:mitosisDocument3 pages1.6 Cell Division:mitosisAzahra SaptoroNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Final Exam Notes For Daly's Cell Bio Class at Purchase CollegeDocument3 pagesCell Biology Final Exam Notes For Daly's Cell Bio Class at Purchase CollegeTori RoggenNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch03 Plant Kingdom PDFDocument5 pages11 Biology Notes ch03 Plant Kingdom PDFakash guptaNo ratings yet
- Female Anatomy 07Document41 pagesFemale Anatomy 07Rudolph Antony ThomasNo ratings yet
- A Quantitative Study of Nocodazole's Effect On HeLa Cells'Document6 pagesA Quantitative Study of Nocodazole's Effect On HeLa Cells'Albert FengNo ratings yet
- Human Embryology, Research and EthicsDocument42 pagesHuman Embryology, Research and EthicsnorjannahhassanNo ratings yet
- 193223103225ass Rea Revision Worksheet1 8 Class Annual PDFDocument1 page193223103225ass Rea Revision Worksheet1 8 Class Annual PDFmekuzi goergeNo ratings yet
- Sex Determination in MammalsDocument33 pagesSex Determination in MammalsBinita SedhaiNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3. Module 2. Heredity: Inheritance and VariationDocument3 pagesQuarter 3. Module 2. Heredity: Inheritance and VariationEric LucenteNo ratings yet
- Human Embryology NotesDocument67 pagesHuman Embryology NotesRahul TyagiNo ratings yet
- FullDocument8 pagesFullrocambolescas perthNo ratings yet
- Reproductive PhysiologyDocument40 pagesReproductive PhysiologyBaiq Trisna Satriana100% (1)
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division - DPP-04Document3 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division - DPP-04Vishal SorteyNo ratings yet
- Biology E-Portfolio: Kin Calvin M. MartinezDocument5 pagesBiology E-Portfolio: Kin Calvin M. MartinezCalvin MorenoNo ratings yet