Professional Documents
Culture Documents
007 Note
Uploaded by
Aniket Singh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesThe document discusses various topics related to communication including the evolution of communication methods from cave paintings to modern technologies like social media. It also discusses the elements and principles of communication, barriers to communication, types of verbal and non-verbal communication, importance of listening, business correspondence, importance of ethics, interviews and more. Key aspects of effective communication in the workplace like trust, engagement and productivity are also highlighted.
Original Description:
MMPC 7 Notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses various topics related to communication including the evolution of communication methods from cave paintings to modern technologies like social media. It also discusses the elements and principles of communication, barriers to communication, types of verbal and non-verbal communication, importance of listening, business correspondence, importance of ethics, interviews and more. Key aspects of effective communication in the workplace like trust, engagement and productivity are also highlighted.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pages007 Note
Uploaded by
Aniket SinghThe document discusses various topics related to communication including the evolution of communication methods from cave paintings to modern technologies like social media. It also discusses the elements and principles of communication, barriers to communication, types of verbal and non-verbal communication, importance of listening, business correspondence, importance of ethics, interviews and more. Key aspects of effective communication in the workplace like trust, engagement and productivity are also highlighted.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
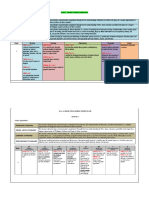
Evolution of Communication: Cave Painting > Through Symbols > Smoke Signals > Carrier
Pigeons > Postal System > Print > Radio > Telegraph > Television > Internet > E-Mail > Text
Message > Social Media.
Elements of Comm.: 1. Source 2. Message 3. Channels 4. Receiver 5. Environment 6. Context 7.
Interference
7C’s of Comm.: Clarity, Correctness, Conciseness, Courtesy, Concreteness, Consideration, Completeness
Barriers to Comm.: (i) Intrapersonal: Wrong assumptions, Varied perceptions, Differing
background, Wrong inferences, Blocked categories, Categorical thinking
(ii) Interpersonal: Limited vocabulary, Incompatibility of verbal and non-verbal messages,
Emotional outburst, Communication selectivity, Cultural variations, Poor listening skills, Noise
in the channel
(iii) Organisational: Too many transfer stations, Fear of superiors, Negative tendencies, Use of
inappropriate media, Information overload
Business Communication General Communication
Format It uses a specific format for It uses varied formats for
communication. communication.
Category It is usually formal in nature. It involves personal touch.
Extent/Reach It usually is practical & unbiased. It can be vast and can be fictitious and
biased, at times.
Demonstration/ It specifically follows the norms and It is informal and different methods
Presentation procedures of the organisation. can be used.
Aim/Intention It focuses on the aim of the organisation. It does not have a focus.
Kind/ nature/Pattern It is official in nature. It is personal in nature.
Feedback This requires feedback. Feedback may not be important.
Benefits of Effective Communication at Workplace: 1. It promotes trust 2. It promotes team
member loyalty 3. It enhances team member engagement 4. It improves teamwork 5. It
improves productivity 6. Communication fuels innovation 7. Resolves issues 8. It creates better
client relationships
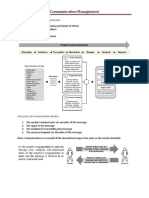
Process of Communication: 1. Source of Information (ideation) 2. Encoding 3. Channel of
Transmission 4. Decoding 5. Acting 6. Noise 7. Filters
Types of verbal communication: ● Oral communication ● Written communication
Types of Non-verbal Communication: ● Kinesics ● Sign language ● Proxemics ●
Chronemics ● Paralanguage ● Haptics ● Silence ● Meta-communication
Principles of Interpersonal Communication: ● Inescapable ● Irreversible ● Complicated ●
Highly contextual
Barriers to Interpersonal Communication: ● Language barrier ● Stress ● Position ● Attitude
● Distance
● Perceptions ● Culture ● Technology
Components of Listening: Hear > Comprehend > Retain > Recall
Features of Good Listening: 1. Reduces miscommunication 2. Increases confidence 3.
Increase productivity
4. Saves time and Cost
Types of Listening: ● Biased Listening ● Sympathetic Listening ● Empathetic Listening ●
Critical Listening
● International Listening ● Appreciative Listening ● Selective Listening ● Rapport Listening
Purpose of Business Correspondence: ● Maintaining proper relationship ● Organizational
goodwill ● Reduce employees’ turnover ● Increase productivity of employees ● Improve
customer satisfaction and retention
Types of Business Correspondence: ● Internal Correspondence ● External Correspondence ●
Sales Correspondence
● Personalized Correspondence ● Circulars ● Routine Correspondence
Ethical Standards: 1. Being Honest 2. Intending no harm 3. Fairness
Key Elements of Ethical Standards: 1. Objective 2. Morality 3. Consequences
Types of Interviews: 1. Screening or Telephonic Interview 2. Personal Interview 3. Behaviour-
based 4. Task-based or Test Interview 5. Stress Interview 6. Management-based Interview 7.
Focused Interview 8. Exit Interview
Process of Interview: ● Job description ● Advertising the job ● Screening ● Scheduling
interview ● Preliminary interview ● Personal interview ● Follow-up Hiring
Importance of ICT: ● ICT & E-commerce ● ICT & a new business ● Manufacturing
Innovations ● New Method of Manufacturing ● Customer feedback loop ● Reduction in
network latency ● ICT and advancements in health care systems ● Education's ubiquity and
universal accessibility ● ICT and Environmental Impact
Types of Presentation: 1. Informative Presentation 2. Persuasive Presentation 3. Motivational
Presentation
Five Filters Help to Polish and Chisel the Presentation: 1. Target Audience (Who) 2.
Purpose (Why) 3. Place (Where)
4. Time (When) 5. Content (What)
Objectives of Meetings: ● Sharing information ● Improving productivity ● Resolving
communication gaps ● Addressing the concerns of employees ● Forming policies ● Clearing
doubts ● Addressing staff grievances ● Obtaining feedback
Types of Meetings: Stand-up Meeting ● Weekly or Monthly Meeting ● Special Project
Meetings
Meetings can also be classified based on the focus area: ● Status-update meetings ●
Decision-making meetings
● Planning meetings ● Collaboration meetings ● Problem-solving meetings ● Brainstorming
meetings ● Team-building meetings ● Debrief meetings● Innovation meetings
Need for Written Communication: 1. Write to experience 2. Write to think 3. Write to create
4. Write to learn
Features of Written Communication: ● Extensive reading ● Constant writing ● Word
conscious/word seeker
● Purpose of writing ● Target audience ● Understanding of the subject
Significance of Virtual Meetings: 1. Interaction with colleagues at distance 2. Meetings with
clients and customers
3. Save cost and time
Platform for Virtual Meetings: 1. Option to record the Meetings 2. Chat options 3. Sync the
Meeting Information with calendar 4. Feature to Customise the Meeting room 5. Presence of
engagement feature 6. Option to modify records
Ways to make a Virtual Meeting Productive: 1. Define the objective of meeting 2. Decide
clearly who is driving the discussion 3. Maintaining virtual gathering decorum 4. Select the
options for choosing the appropriate questions
5. Establish connect with the audience on one-on-one basis 6. Keeping virtual participants on
task
Elements of Cross-Cultural Communication: Awareness, Preparation, Language, Humour,
Openness
Cross-Cultural Communication Barriers: Language, Nonverbal Communication,
Stereotypes, Cultural Bias, Anxiety
Overcoming Cross-Cultural Communication Barriers: Language, Written Communication,
Listening, Non-Verbal Communication
You might also like
- SOAPSTone AnalysisDocument2 pagesSOAPSTone AnalysisJanette StevensonNo ratings yet
- Merged Competencies G8Document43 pagesMerged Competencies G8MarivicEchavezBulaoNo ratings yet
- Chika Sensei's Japanese AcademyDocument13 pagesChika Sensei's Japanese AcademyHiro Hamada100% (1)
- Business CommunicationDocument56 pagesBusiness Communicationvicky181089No ratings yet
- Oral and Written CommunicationDocument5 pagesOral and Written Communicationshahid75% (4)
- Lecture 1 - Foundation of Business CommunicationDocument45 pagesLecture 1 - Foundation of Business CommunicationThùy DungNo ratings yet
- Technical CommunicationDocument38 pagesTechnical CommunicationS x D100% (1)
- Class Module in Content and Pedagogy For The Mother-TongueDocument103 pagesClass Module in Content and Pedagogy For The Mother-TongueKarlyn AntonaNo ratings yet
- 1st Year - Communicative English Lab Manual PDFDocument65 pages1st Year - Communicative English Lab Manual PDFPriscilla Sherene MBANo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument38 pagesCommunicationNikhil Bhamare100% (2)
- Persuasive and Analytical Writing For Business CommunicationDocument56 pagesPersuasive and Analytical Writing For Business CommunicationSaranjam Khan100% (1)
- Business CommunicationDocument30 pagesBusiness CommunicationGokul Raaz100% (2)
- Class Notes (Business Communication)Document43 pagesClass Notes (Business Communication)Ghufran AhmedNo ratings yet
- Kas 204 Module 5 PptsDocument61 pagesKas 204 Module 5 PptsAvishek RaiNo ratings yet
- Mastering Team Skills and Interpersonal CommunicationDocument49 pagesMastering Team Skills and Interpersonal CommunicationRaffi MouradianNo ratings yet
- Professional Communication SkillsDocument8 pagesProfessional Communication SkillsScene TrapNo ratings yet
- Communication in The WorkplaceDocument67 pagesCommunication in The WorkplaceGlaiza VillaverNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Strategy (E2) - Unit 2 - CH 8 Managing Organisational Relationships (Student PDFDocument47 pagesManagement Accounting Strategy (E2) - Unit 2 - CH 8 Managing Organisational Relationships (Student PDFMushaisano MudauNo ratings yet
- Note Book-Communication SkillsDocument72 pagesNote Book-Communication SkillsDevansh VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document17 pagesLecture 1HumzaNo ratings yet
- Gateways To CommunicationDocument32 pagesGateways To Communicationthakur_neha20_903303100% (1)
- Module 1 and 2Document42 pagesModule 1 and 2AryanNo ratings yet
- GD N Tech EthicsDocument30 pagesGD N Tech EthicsrichakkNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document24 pagesLecture 1Minah AliNo ratings yet
- Technical Writing and Presentation MODIFIED 2019Document260 pagesTechnical Writing and Presentation MODIFIED 2019RoseNo ratings yet
- Communication SkillsDocument12 pagesCommunication SkillsalokpandeygenxNo ratings yet
- Lead Workplace CommunicationDocument5 pagesLead Workplace CommunicationMintesnot AdeNo ratings yet
- M-05 Business Communication Skills - FinalDocument166 pagesM-05 Business Communication Skills - FinalJaveria AkramNo ratings yet
- M-05 Business Communication Skills - FinalDocument166 pagesM-05 Business Communication Skills - FinalJaveria AkramNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Effective Communication - Can You Hear Me?Document31 pagesChapter 6: Effective Communication - Can You Hear Me?Grace Esther 예특No ratings yet
- Business Communication NotesDocument33 pagesBusiness Communication NotesBharath KumarNo ratings yet
- U5E7 - Communication Challenges For Sustainability - EN - NotesDocument24 pagesU5E7 - Communication Challenges For Sustainability - EN - NotessilbersterneNo ratings yet
- Why Communication Is Critical To ProjectsDocument16 pagesWhy Communication Is Critical To ProjectsRonillo PormonNo ratings yet
- 1-Managerial Communication IntroDocument36 pages1-Managerial Communication Introsushil_bhattara6864No ratings yet
- Collaboration, Interpersonal Communication, and Business EtiquetteDocument30 pagesCollaboration, Interpersonal Communication, and Business EtiquetteAdjeiNo ratings yet
- Business Communication Foundations: How Do You Find Students in Communication ?Document26 pagesBusiness Communication Foundations: How Do You Find Students in Communication ?vijaykondi7No ratings yet
- Business Communication Assignment 1Document12 pagesBusiness Communication Assignment 1John GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Business Comm.Document5 pagesBusiness Comm.Erika Mae BarreraNo ratings yet
- Welcome: Communication SkillsDocument201 pagesWelcome: Communication SkillskgvenkateshNo ratings yet
- Ge Comm-Ppt2Document49 pagesGe Comm-Ppt2Jenny BayengNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication - Learner GuideDocument13 pagesOral Communication - Learner GuideNathanielNo ratings yet
- Mizan Atvet College: Participating in Workplace CommunicationsDocument18 pagesMizan Atvet College: Participating in Workplace CommunicationsYaread bitewNo ratings yet
- Communication and Decision-Making: Functions of Organizational CommunicationDocument6 pagesCommunication and Decision-Making: Functions of Organizational CommunicationErleneClariseChavezNo ratings yet
- Business CommunicationDocument7 pagesBusiness CommunicationAnkur SinhaNo ratings yet
- Business Communication: by Dr. Amna BatoolDocument17 pagesBusiness Communication: by Dr. Amna BatoolAhmad HassanNo ratings yet
- Business Comm NotesDocument15 pagesBusiness Comm NotesHimanshu ShuklaNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument12 pagesEnglishAbubakar KhanNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS COMMUNICATION - Unit 1 - Business Communication BasicsDocument26 pagesBUSINESS COMMUNICATION - Unit 1 - Business Communication BasicsKeshalini Perambalam0% (1)
- Xyz 1 13Document13 pagesXyz 1 13tarunNo ratings yet
- Communication For Business (2005) SummaryDocument12 pagesCommunication For Business (2005) SummaryJN100% (1)
- Communication Management: Goals of Interpersonal CommunicationDocument8 pagesCommunication Management: Goals of Interpersonal CommunicationSameer SharmaNo ratings yet
- Positive Communication - 1Document22 pagesPositive Communication - 1ashokNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument40 pagesUntitledyounakiraNo ratings yet
- Effective Communication Strategies For Professional SuccessDocument3 pagesEffective Communication Strategies For Professional SuccessRocket RookieNo ratings yet
- BizcommDocument41 pagesBizcommVaibhav KumarNo ratings yet
- Business Communication: by Mrs. Hira AyazDocument33 pagesBusiness Communication: by Mrs. Hira Ayazjavaid musaNo ratings yet
- Revision Pwcand WTDocument10 pagesRevision Pwcand WTme taNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills For International Projects: SubtitleDocument14 pagesCommunication Skills For International Projects: SubtitleDana TanasescuNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument5 pagesCommunicationmagicalsouvenirNo ratings yet
- Good Communication Skills by AnuDocument14 pagesGood Communication Skills by AnupkjindleNo ratings yet
- Suport de Curs An 3 Sem 6 Comunicare in AfaceriDocument39 pagesSuport de Curs An 3 Sem 6 Comunicare in AfaceriGaby CototiuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Business Communication, Management, and Success (Pp. 2-16)Document8 pagesChapter 1: Business Communication, Management, and Success (Pp. 2-16)Ankit GautamNo ratings yet
- How to Speak Workplace English with Confidence: Mastering Communication Skills for Professional SuccessFrom EverandHow to Speak Workplace English with Confidence: Mastering Communication Skills for Professional SuccessNo ratings yet
- Ques - Distinguish Between Operating Activities, Investing Activities and Financing Activities?Document12 pagesQues - Distinguish Between Operating Activities, Investing Activities and Financing Activities?Aniket SinghNo ratings yet
- Ques - How Politico-Legal Environment Impact Various Business?Document12 pagesQues - How Politico-Legal Environment Impact Various Business?Aniket SinghNo ratings yet
- Ques - What Is HRM? Describe Evaluation of HRM and Its Components?Document10 pagesQues - What Is HRM? Describe Evaluation of HRM and Its Components?Aniket SinghNo ratings yet
- Ques - What Is Organisation Culture?Document14 pagesQues - What Is Organisation Culture?Aniket SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To Strategic ManagementDocument17 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To Strategic ManagementRonald Reagan AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Eca433 At1 Year 7 Dance Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesEca433 At1 Year 7 Dance Lesson Planapi-355399236100% (2)
- FSF2D Course Handout 2015 2016Document7 pagesFSF2D Course Handout 2015 2016Elizabeth ProvostNo ratings yet
- Languages - Exercises 0Document2 pagesLanguages - Exercises 0PaulinaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Assessmnet Rubrics.Document4 pagesAssignment Assessmnet Rubrics.Waqas AkramNo ratings yet
- Trinity College Dublin Interview Questions With Admit - Ding Interview Reports - 2020Document3 pagesTrinity College Dublin Interview Questions With Admit - Ding Interview Reports - 2020Reynald SuzNo ratings yet
- AP Psychology - Myers Module 17-22 VocabularyDocument7 pagesAP Psychology - Myers Module 17-22 VocabularyJaakkiiee YungNo ratings yet
- Schools of Educational PhilosophyDocument1 pageSchools of Educational PhilosophyEdwin EstreraNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Tech Lesson Book Introduction To Web Design, Web DesignDocument4 pages7th Grade Tech Lesson Book Introduction To Web Design, Web Designapi-411651004No ratings yet
- 1.difinitions of PersonalitiesDocument9 pages1.difinitions of PersonalitiesSri DharNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 NotesDocument3 pagesUnit 1 Notesapi-300762638No ratings yet
- MSR PPT Format - 2022Document10 pagesMSR PPT Format - 2022Hima N TalatiNo ratings yet
- Assess MidtermDocument34 pagesAssess MidtermJohnaliza LabanNo ratings yet
- Preparing Students For The Future TechnologyDocument2 pagesPreparing Students For The Future TechnologyLeane Enero DarayNo ratings yet
- Students' Perceptions and Expectations in The Virtual Faculty Exchange Program The Case of Higher Learning Institutions in The Philippines and IndonesiaDocument4 pagesStudents' Perceptions and Expectations in The Virtual Faculty Exchange Program The Case of Higher Learning Institutions in The Philippines and IndonesiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Mini Lesson RationaleDocument3 pagesMini Lesson Rationaleapi-322136237No ratings yet
- HG Teaching GuideDocument2 pagesHG Teaching GuideKinberly AnnNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Theories: by Sara M. 1801395Document35 pagesHuman Resource Management Theories: by Sara M. 1801395Grace MañaleNo ratings yet
- Lets Build A House LessonDocument5 pagesLets Build A House Lessonapi-276590409No ratings yet
- Curricula in FinlandDocument37 pagesCurricula in FinlandMaria MarinelaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Management Styles: NO: 1. It's Not NecessaryDocument8 pagesUnit 1 Management Styles: NO: 1. It's Not NecessaryjulianaNo ratings yet
- Obtl in Teaching ProfessionDocument11 pagesObtl in Teaching ProfessionCherry BobierNo ratings yet
- NCP MentalDocument6 pagesNCP MentalMarius Clifford BilledoNo ratings yet
- A Literature Review of The Research On The Uncanny Valley: July 2020Document13 pagesA Literature Review of The Research On The Uncanny Valley: July 2020João Paulo CabralNo ratings yet
- W73037 GCE A English Language & Literature 9EL0 An Accessible VersionDocument4 pagesW73037 GCE A English Language & Literature 9EL0 An Accessible VersionRumana KhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Personal Development - Lesson 2Document12 pagesLesson Personal Development - Lesson 2Elio SanchezNo ratings yet