0% found this document useful (0 votes)
180 views5 pagesHVAC Design Calculations Overview
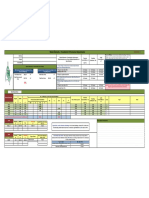
The document calculates the cooling load for a cold storage facility. It summarizes:
1) The transmission load through walls, roof and floor based on U-values and surface areas.
2) The product load from product exchange and respiration based on mass, specific heat, and temperature differences.
3) The internal heat loads from people, lighting, fans and other equipment run times and power ratings.
4) The infiltration load based on air changes, volumes, and temperature differences.
5) The total daily cooling load is calculated to be 73.55 kWh with a safety factor of 88.27 kWh, requiring a refrigeration capacity of 6.30 kW.
Uploaded by
IFMSCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
180 views5 pagesHVAC Design Calculations Overview
The document calculates the cooling load for a cold storage facility. It summarizes:
1) The transmission load through walls, roof and floor based on U-values and surface areas.
2) The product load from product exchange and respiration based on mass, specific heat, and temperature differences.
3) The internal heat loads from people, lighting, fans and other equipment run times and power ratings.
4) The infiltration load based on air changes, volumes, and temperature differences.
5) The total daily cooling load is calculated to be 73.55 kWh with a safety factor of 88.27 kWh, requiring a refrigeration capacity of 6.30 kW.
Uploaded by
IFMSCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
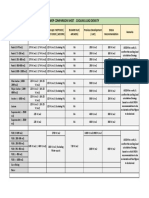
- Cooling Load Calculations: Details the calculations for transmission load, product load, internal heat load by people and lighting, illustrating how each contributes to the overall cooling requirements.
- Equipment and Infiltration Loads: Calculates the load from equipment including fans and motors, and considers infiltration effects on the cooling load.
- Material Properties and Day-to-Day Variables: Lists U values, areas, ambient conditions, and daily product variables affecting the cooling demand.
- Operational Parameters: Covers operational factors such as fan numbers and run hours, defrost cycles, and space volume changes.
- Environmental and Structural Specifications: Specifies area, equipment details, environmental conditions, and structural requirements for the site.