Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del Norte
Uploaded by
Jam Hamil AblaoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del Norte
Uploaded by
Jam Hamil AblaoCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION IX , ZAMBOANGA PENINSULA
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF ZAMBOANGA DEL NORTE
________________________________________________________________________________________
LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET
(QUARTER 3 – WEEK 1 and 2)
Name: _______________________ Grade: 9 -______________ Score: _________________
Subject: TLE (AGRI-CROP PRODUCTION) Teacher: JAM HAMIL Q. ABLAO Date: __________________
Type of Activity:
Concept Notes Individual Formative Others
Laboratory Pair/Group Summative ___________
________________________________________________________________________________________
Lesson/Topic: Planting Crops
Learning Targets: Know methods of digging holes
• Apply recommended amount of fertilizer
.Reference: K to 12 Crop Production modules
What is Digging?
• Digging in gardening is equivalent to ploughing in agriculture. Soil digging is the most essential and primary
activity of land preparation for gardening.Good digging makes the soil porous, improves the drainage, and
removes obstacles from the plants roots. All hard objects such as boulders, stones, roots of trees, etc. weeds, as
far as possible should be remove after digging.
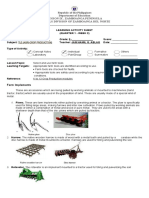
Digging Techniques
• Digging may be simple digging, double digging or deep trenching.
Simple Digging
• In simple digging soil is dug with a spade, turning inside out, without removing it from the bed. Remember that in
digging soil which is richest, and the best should remain at the top. Example 20-25 cm (8-10in.)
• Small stones in the soil may be retained during simple digging as they help in drainage and also keep the root
system cool. The roots of the plant are not obstructed by the stone as they can bypass them. In case of seedbeds
sieving of soil is advised as the root system of seedlings are delicate.
Double Digging and Trenching
• In double digging (one spit digging), the width of the
bed is usually divided into strips of 40-60 cm *1.5 to
2ft). The depth to which soil is dug depends on the
requirement of the plant.
• The soil is dug first up to one spit. The topsoil of 20-25
cm is removed outside the bed.
• The bed is then further dug up to another spit (20cm)
for two spit digging.
• All big stones, metal pieces, hard fibres, etc. are
remove.
• At the bottom of the second spit 5- 7 cm (2-3 in) layer
of small stones and gravel, grass, leaves, etc.is added
to improve drainage. It is manured and mixed thoroughly with the soil.
• The second trench is in drug one spit deep, and topsoil of this trench is transferred to the first trench.
• Second spit depth is dug and prepared as in the first trench.
• The topsoil of the first trench is transferred to the second trench. This way, double digging or trenching is then
complete.
• If the bed is divided into more than two strips, the process is repeated furtherwith the modification that topsoil of
the first strip is transferred to the last trip.
• In similar manner triple digging or deep trenching can also be done where top 2 layers of soil are removed and
transferred to adjacent strips.
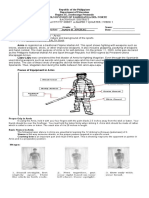
Tools in digging Hole
- When most people want to dig a hole, they reach for a spade. There’s nothing wrong with this approach, but
there are better hole- digging tools available –namely Garden Augers. Augers have several advantages over other
tools, including:
• Easy to use, even for people with limited physical abilities
• Loosens the soil, making it easier for roots to spread
• Requires a little physical effort to operate
Dig Properly Sized Holes
• The size of the hole you dig for your plant is critically important. A hole that is too small could suffocate the roots
or hinder plant growth. In the case of seeds, a hole that is too deep could prevent the seed from germinating at all.
Seeds
• A seed should be planted no deeper than twice its width. For example, if the seed is one quarter of an inch wide,
it should be planted no deeper than onehalf of an inch.
• In addition to shallow hole, seeds also need loose, airy soil. To loosen the soil effectively, use a hand- held
garden auger to dig several holes. This will help loosen the soil. Put the soil back into the hole once it’s been dug
– you won’t need a hole that deep for your seeds.
Small Plants
• When digging a hole for a small plant no more than three inches wide, use a bulb auger to dig a hole between
six and twelve inches deep. Insert the root ball into the hole then cover the base of the plant with excess soil.
Large Plants
• For a plant that is larger than three inches wide, dig a hole about twice the diameter of the pot and about one
and half to two times deeper than the depth of a plant. Use your quart pot auger to dig hole. After the hole is dug,
backfill the hole with some excess soil until the plant has enough height to stand on it’s own. Insert the plant and
backfill the hole. Again, do not cover the stem of the plant more than the plant already has been covered
Trees
• To plant a containerized tree, use a quart pot plant auger. Trees need holes that are three to four times wider
than the container. The hole should be no deeper than container. Set the root ball in the hole and backfill around
the tree.
RECOMMENDED AMOUNT OF FERTILIZER
- Means the recommended rate of fertilizer application expressed in kilograms N,P and K per hectare.
- P2O5 and 30 kg K2O per hectare
Types of fertilizer Application
1. Basal application – right before the last harrowing, one or two days before planting, drain all water from the
field and apply ½ of the recommended nitrogen(N) , all phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) depending on the
variety of used and the age of seedlings when transplanted. It will be best to use a combination of organic and
inorganic fertilizers in the basal application using 10bags of organic fertilizer per hectare together with the ½
recommended rate of inorganic fertilizer.
2. Top dress – timely application of top dress fertilizer is very important to supply the needed nutrients for healthy
and long panicle (rice). Apply or broadcast the remaining nitrogen 5-7 days before panicle initiation of 70-72
days before maturity. (Rice crop)
3. Foliar Application – different brands of foliar fertilizer have different composition but the method and timing of
application are the same. Start application 45 days after transplanting at 10-14 days interval
CORRECT AMOUNT OF FERTILIZER TO BE APPLIED
• In computing the right amount of fertilizers to be applied in a given area, make use of the result of soil analysis
and the recommended rate of application of fertilizers. It requires the ability to compute for the fertilizer need in a
given crop per unit area. One way of expressing fertilizer rate is by kilogram nitrogen (N) phosphoric acid (P2O5)
and kilogram soluble potassium (K2O) per hectare. Another way is by bags of the fertilizer material per hectare.
For farmers it is advisable to use the latter but for extension men, the former is used to facilitate communication.
The amount of fertilizer to be applied per hectare to supply a certain amount of plant nutrients depends on the
recommended rate and composition of the fertilizer material to be used.
ACTIVITY.
ENUMERATION
1-3. Give the three types of fertilizer application
4-10. Illustrate the table example for foliar application (instead of the given example rice/crops). Write the following
amounts of fertilizer to be used, time of application, interval and rate. Here are other plants to be examined. Write on a
separate sheet of paper.
- CORN
- VEGETABLES
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT FOR QUARTER 3 WEEK 1 AND 2
EVALUATION: Encircle the letter of the correct answer
1. Digging in gardening is equivalent to _________________ in agriculture?
a. Soil c. Ploughing
b. Roots d. Harrowing
2. ______________ is digging the soil with the use of spade turning inside out without removing it from the bed
a. Double digging c. Double digging
b. Simple digging d. Trenching
3. In planting seeds what kind of auger you are going to use to dig several holes?
a. Bulb auger
b. Hand – held auger
c. Quart part auger
d. Quart pot plant auger
4. In planting trees what kind of auger you are going to use to dig hole?
a. Quart pot plant auger
b. Quart pot auger
c. Bulb auger
d. Hand – held garden auger
5. In planting small plants what kind of auger you are going to use for digging hole?
a. Quart pot auger
b. Bulb auger
c. Hand – held auger
d. Quart pot plant auger
6. In foliar application how many days interval is needed before the second application?
a. 15-20 days
b. 10-14 days
c. 5-8 days
d. 10-15 days
7. When is the best time to apply top dress?
a. Before panicle initiation
b. After panicle initiation
c. Maturity
d. after transplanting
8. In basal application what is the best fertilizer combination?
a. Organic and inorganic fertilizer
b. Nitrogen and potassium
c. Foliar and top dress
d. Potassium and phosphorus
9. How you are going to express fertilizer rate?
a. Kilogram
b. Ton
c. Pound
d. Gallon
10.When is the best time to apply foliar fertilizer?
a. Early in the morning
b. Late afternoon
c. Early in the morning or late in the afternoon
d. Midnight
Prepared by:
JAM HAMIL Q. ABLAO
SST – I / BNHS
Technology and Livelihood Education (T.L.E) 9 – AGRICROP PRODUCTION
Summative Assessment for Quarter 2 – Week 7 & 8
Name: ______________________________ Section: 9 -_______________ Score:________
MATCHING TYPE. Connect using lines from Column A to Column B and write the combination letter - number
answer on the space provided below. (ex. __A4___1.)
COLUMN A COLUMN B
1. is an imaginary line
connecting all points of
equal elevation across a
______1. SQUARE SYSTEM A. slope. In a hilly area, a lot of
depressions, ridges,
furrows, and place surface
are found.
2.the trees are planted at
the corners of an equilateral
triangle. Six such triangles
B. are joined together to form a
______2. RECTANGULAR SYSTEM hexagon.
3.is the same as the square
system except for the
addition of a tree in the
_____3. QUINCUNX OR DIAGONAL C. center of each square. In
SYSTEM this system, the number of
trees planted in the same
area is almost double.
4.the trees are planted in
the same way as in a
square system except that
_____4. HEXAGONAL SYSTEM D. the distance between rows
will be more than the
distance between plants in
the same row.
5.the trees are planted in
four corners of a square
keeping the same distance
between rows and from
_____5. CONTOUR SYSTEM E. plant to plant in the same
row.
You might also like
- Acp NC II Dig Holes g11 q3 w4-6Document14 pagesAcp NC II Dig Holes g11 q3 w4-6Romar N. SantosNo ratings yet
- Horticulture 10 Q4 Week1Document8 pagesHorticulture 10 Q4 Week1jf2ralbaNo ratings yet
- Primary Secondary Tillage Equipment PDFDocument13 pagesPrimary Secondary Tillage Equipment PDFГарпия Сова100% (1)
- Self Sufficient Gardener: John Seymour's Deep Bed MethodDocument6 pagesSelf Sufficient Gardener: John Seymour's Deep Bed MethodPennsylvania Association for Sustainable Agriculture100% (1)
- Agricultural Crop Production 11 - Q2 - W4Document6 pagesAgricultural Crop Production 11 - Q2 - W4Jennifer DuranNo ratings yet
- Module 11 Biointensive GardeningDocument22 pagesModule 11 Biointensive GardeningMelikteNo ratings yet
- Flowering Plants (2) Potting and Repotting of Flowers and Ornamental PlantsDocument2 pagesFlowering Plants (2) Potting and Repotting of Flowers and Ornamental PlantsArnab PaulNo ratings yet
- Ai8211-Crop & Husbandry Lab ManualDocument47 pagesAi8211-Crop & Husbandry Lab Manualpa ndiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual FoaDocument23 pagesLaboratory Manual FoaVijayNo ratings yet
- Primary, Secondary Tillage and Land ModificationsDocument34 pagesPrimary, Secondary Tillage and Land ModificationsMohit Awasthi100% (1)
- Learning Area Grade Level Quarter Date: Tle - Agri Crop 9 3Document4 pagesLearning Area Grade Level Quarter Date: Tle - Agri Crop 9 3Jade MillanteNo ratings yet
- Forest TutorialDocument6 pagesForest TutorialMuddassarNo ratings yet
- TillageDocument8 pagesTillageindiatrends 24100% (1)
- Secondry TillageDocument37 pagesSecondry TillageAqib UmarNo ratings yet
- Land PreparationDocument86 pagesLand PreparationLove RainNo ratings yet
- Tle 10 C.O 2NDDocument25 pagesTle 10 C.O 2NDJenny ParttimeNo ratings yet
- Drought Tolerant GardenDocument4 pagesDrought Tolerant GardenMkiliNo ratings yet
- SLHT - Agri Crop 9 - Week 1Document5 pagesSLHT - Agri Crop 9 - Week 1Ivy AventunaNo ratings yet
- LawnDocument10 pagesLawnIykykNo ratings yet
- TLE 10 May V. OnaDocument4 pagesTLE 10 May V. OnaJoy Alea-Abrenica WalesNo ratings yet
- Learning Area Grade Level Quarter Date: Tle - Agri Crop Nine ThreeDocument4 pagesLearning Area Grade Level Quarter Date: Tle - Agri Crop Nine ThreeÁthymosNo ratings yet
- Manure in MalawiDocument7 pagesManure in Malawiluis ruperto flores100% (2)
- Planting StakingDocument2 pagesPlanting StakingRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- Tools and Equipment: PloughDocument9 pagesTools and Equipment: PloughJm RectoNo ratings yet
- Land Preparation and Planting PracticesDocument17 pagesLand Preparation and Planting PracticesQuinnee Vallejos86% (7)
- Az 1022Document3 pagesAz 1022NVAzirNo ratings yet
- Soil Sampling ProcedureDocument5 pagesSoil Sampling ProcedureMaheshNo ratings yet
- Raised Bed Garden MethodsDocument36 pagesRaised Bed Garden MethodsMD BNo ratings yet
- TEACHER-Made-Learners-Home-Task Agricultural 2Document3 pagesTEACHER-Made-Learners-Home-Task Agricultural 2Marjune RedondoNo ratings yet
- FrontWalk GardenPlanDocument3 pagesFrontWalk GardenPlanSomill HwangNo ratings yet
- Plantation Establishment and ManagementDocument36 pagesPlantation Establishment and ManagementKecha Taye100% (4)
- Group 2 Coffee and CacaoDocument18 pagesGroup 2 Coffee and CacaoMark SisonaNo ratings yet
- G11 LAS in ACP Q2Wk2 Tools Materials and Equipment For Land Preparation and Land ClearingDocument5 pagesG11 LAS in ACP Q2Wk2 Tools Materials and Equipment For Land Preparation and Land ClearingEleanor CabungcagNo ratings yet
- Potting and RepottingDocument2 pagesPotting and Repottingrashichauhan2k193986No ratings yet
- Q1 Part 6Document22 pagesQ1 Part 6Tsukigami TempestNo ratings yet
- How To Make A Mini Forest With Miyawaki MethodDocument7 pagesHow To Make A Mini Forest With Miyawaki MethodLuís Palma RodriguesNo ratings yet
- 2 Plant CropsDocument46 pages2 Plant CropsRyan Paul CaalemNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Low Land Rice Cultivation: Submitted ToDocument25 pagesAssignment - Low Land Rice Cultivation: Submitted ToShubham ChauhanNo ratings yet
- CRSC2 Exer-2Document17 pagesCRSC2 Exer-2Michael Jeffrey P. PantasticoNo ratings yet
- FAITH GardeningDocument46 pagesFAITH GardeningCindy Torres Subaan100% (2)
- AGR3502 Rice Production: Food CropsDocument36 pagesAGR3502 Rice Production: Food CropsSleeping BeautyNo ratings yet
- En How To Establish Paulownia Plantation1Document5 pagesEn How To Establish Paulownia Plantation1mackaneNo ratings yet
- Cultivating Vegetables: - Create A Peace GardenDocument8 pagesCultivating Vegetables: - Create A Peace GardenathertsNo ratings yet
- Installing Landscape PlantsDocument40 pagesInstalling Landscape PlantsRarImABigBear023No ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Land PreparationDocument8 pagesMODULE 1 Land Preparationariolamarygrace08No ratings yet
- Specialized Gardening TechniquesDocument0 pagesSpecialized Gardening TechniquesAdrian PostavaruNo ratings yet
- Straw Bale GardensDocument4 pagesStraw Bale Gardenszpataki1No ratings yet
- PP Production Practices For Annual CropsDocument159 pagesPP Production Practices For Annual CropsRhene BarcelonNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Module1 - G7-8 - Agri-Crop-Production - Balungao NHSDocument6 pagesQ2 - Module1 - G7-8 - Agri-Crop-Production - Balungao NHSDirty Sam LicudoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Tle Seven Use of Farm Tools.Document53 pagesLesson 1 Tle Seven Use of Farm Tools.Jhonxen Pogi100% (1)
- What Are Organic ManuresDocument34 pagesWhat Are Organic ManuresPrit Ranjan Jha100% (4)
- 1 Hand-ToolsDocument2 pages1 Hand-Toolsdairyl.virreyNo ratings yet
- Farm Tools LessonDocument35 pagesFarm Tools LessonLyra Bacus MatulinaNo ratings yet
- Keyhole PDFDocument3 pagesKeyhole PDFspiritualbeing100% (1)
- Technology and Livelihood Education 7: Michael R. AñoraDocument31 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education 7: Michael R. AñoraMICHAEL ANORANo ratings yet
- Acp NC Ii - Perform Direct Seeding - G11 - Q3 - W7-8Document18 pagesAcp NC Ii - Perform Direct Seeding - G11 - Q3 - W7-8Romar N. SantosNo ratings yet
- Nursery ManagementDocument69 pagesNursery ManagementRidip ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- LP-agri 9Document8 pagesLP-agri 9jamaica malleroNo ratings yet
- AgronomyDocument99 pagesAgronomyrgopinath5100% (1)
- Organic Agriculture Gr11 - Q2.module3 LRDocument18 pagesOrganic Agriculture Gr11 - Q2.module3 LRJam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Organic Agriculture Gr11 - Module7.finalDocument16 pagesOrganic Agriculture Gr11 - Module7.finalJam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Organic Agriculture Gr11 - Module3.finalDocument15 pagesOrganic Agriculture Gr11 - Module3.finalJam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Organic Agriculture Gr11 - Q2.module6 LRDocument20 pagesOrganic Agriculture Gr11 - Q2.module6 LRJam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Organic Agriculture Gr11 Module8.FinalDocument20 pagesOrganic Agriculture Gr11 Module8.FinalJam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- LAS PE 7 Q2 Week5Document3 pagesLAS PE 7 Q2 Week5Jam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- LAS MUSIC 7 Q2 Week2Document3 pagesLAS MUSIC 7 Q2 Week2Jam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Explain The Characteristics, Signs and Symptoms of Eating Disorders (H7N-Iid-F-26)Document3 pagesExplain The Characteristics, Signs and Symptoms of Eating Disorders (H7N-Iid-F-26)Jam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- LAS ARTS 7 Week3Document3 pagesLAS ARTS 7 Week3Jam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson/Topic: Learning Target(s) : Reference(s) : Grade 7 MUSIC and ARTS BookDocument3 pagesLesson/Topic: Learning Target(s) : Reference(s) : Grade 7 MUSIC and ARTS BookJam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Common Farm EquipmentDocument3 pagesCommon Farm EquipmentJam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- LAS ARTS 7 Week4Document3 pagesLAS ARTS 7 Week4Jam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Bacungan I District Learning Activity Sheet Mapeh 7 Quarter 2 Week 7Document3 pagesBacungan I District Learning Activity Sheet Mapeh 7 Quarter 2 Week 7Jam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Tle 9 Q3 W5&6Document5 pagesTle 9 Q3 W5&6Jam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteDocument4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteJam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteJam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteJam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteDocument4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteJam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteDocument6 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteJam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteJam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteJam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteJam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteJam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteJam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteJam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga Peninsula Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteJam Hamil AblaoNo ratings yet
- Landscape - Earthforms & PlantsDocument81 pagesLandscape - Earthforms & PlantsTilak BodduNo ratings yet
- The Complete Guide To Growing Corn in Containers - Garden and HappyDocument17 pagesThe Complete Guide To Growing Corn in Containers - Garden and HappyDavid BumbaloughNo ratings yet
- Nysed Part D Lab Review Rel DivDocument14 pagesNysed Part D Lab Review Rel Divapi-235160519No ratings yet
- Dalbergia Sissoo, Sheesham - 0.5 KG SeedsDocument3 pagesDalbergia Sissoo, Sheesham - 0.5 KG SeedsBibhuti JhaNo ratings yet
- Bowes 2011 JofE ArticleDocument21 pagesBowes 2011 JofE Articlethedrune4realzNo ratings yet
- Brahms Living CollectionsDocument25 pagesBrahms Living CollectionsEdna Lais BertinNo ratings yet
- Concept of Seed Quality and Seed Quality TestingDocument19 pagesConcept of Seed Quality and Seed Quality TestingKumari Rajani100% (1)
- Durian Production Guide Updated 2017Document26 pagesDurian Production Guide Updated 2017Bong EscanillaNo ratings yet
- SR 59 (10) 58-59Document2 pagesSR 59 (10) 58-59Sai KesavNo ratings yet
- PLANT SHIELD LeafletDocument1 pagePLANT SHIELD LeafletSonia BadaNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Institutional Pharmacy and Life SciencesDocument11 pagesInternational Journal of Institutional Pharmacy and Life SciencesEbhii FeraniNo ratings yet
- MACARANAS Compilation of Plant - SAMPLEDocument2 pagesMACARANAS Compilation of Plant - SAMPLENiña Joy T. MacaranasNo ratings yet
- 1-Seed Selection and PropagationDocument18 pages1-Seed Selection and Propagationchandra DiveshNo ratings yet
- All Branches of BiologyDocument31 pagesAll Branches of BiologyYhan Brotamonte Boneo100% (1)
- High School Research. Sea Weed ExtractDocument18 pagesHigh School Research. Sea Weed ExtractMaricris OcampoNo ratings yet
- Glencoe Life Science2Document93 pagesGlencoe Life Science2Cosmina MariaNo ratings yet
- 4a-Ancient Indian Engineering BotanyDocument44 pages4a-Ancient Indian Engineering BotanyAshok NeneNo ratings yet
- CpSci 101 - Module 5 - Lesson 1 and 2Document7 pagesCpSci 101 - Module 5 - Lesson 1 and 2Regan Roldan RolaNo ratings yet
- Miami Beach 41st Street CorridorDocument41 pagesMiami Beach 41st Street Corridorthe next miami100% (1)
- Demonstrate Care and Management of Seedlings: Lesson 3Document17 pagesDemonstrate Care and Management of Seedlings: Lesson 3Marycon Nacito100% (1)
- Seed Technology & ProductionDocument106 pagesSeed Technology & ProductionRhene BarcelonNo ratings yet
- LP in Science VIDocument5 pagesLP in Science VIJudy C. BelardoNo ratings yet
- ASEAN National FlowersDocument5 pagesASEAN National FlowersNajida FadliyahNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants: 1. Root 2. Stem 3. Leaf 4. Flower 5. Fruit 6. SeedDocument52 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants: 1. Root 2. Stem 3. Leaf 4. Flower 5. Fruit 6. SeedPrasanth Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Plants and Society 7th Edition Levetin Test Bank 1Document33 pagesPlants and Society 7th Edition Levetin Test Bank 1davidthomasifeajqbnds100% (20)
- FernsDocument4 pagesFernsJam CA ☆No ratings yet
- Orchid Names The BasicsDocument9 pagesOrchid Names The BasicsA Zahili A ManafNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument7 pagesPlant Kingdomchannel of dhyanaNo ratings yet
- Short Stories The Lucky Seed AnswersDocument2 pagesShort Stories The Lucky Seed AnswersRobert GloverNo ratings yet
- Garden DesignDocument127 pagesGarden DesignDebbianW80% (5)