Professional Documents
Culture Documents
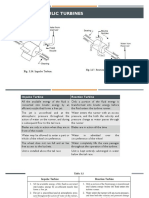
Hydraulic Turbine
Uploaded by
sami almjan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views19 pagesThere are two main classifications of hydraulic turbines: impulse and reaction turbines. Impulse turbines derive energy from the kinetic energy of fluid flowing through nozzles, while reaction turbines generate energy from changes in fluid pressure and velocity as it passes through rotor blades. Common impulse turbines are Pelton wheels, while common reaction turbines are Francis and Kaplan turbines. Francis turbines operate under medium heads and utilize both impulse and reaction effects to rotate the runner blades and generate power. Kaplan turbines are axial-flow reaction turbines suitable for large volumes of water at low head.
Original Description:
advantages and disadvantages for all types of hydraulic turbines
Original Title
Hydraulic Turbine Ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThere are two main classifications of hydraulic turbines: impulse and reaction turbines. Impulse turbines derive energy from the kinetic energy of fluid flowing through nozzles, while reaction turbines generate energy from changes in fluid pressure and velocity as it passes through rotor blades. Common impulse turbines are Pelton wheels, while common reaction turbines are Francis and Kaplan turbines. Francis turbines operate under medium heads and utilize both impulse and reaction effects to rotate the runner blades and generate power. Kaplan turbines are axial-flow reaction turbines suitable for large volumes of water at low head.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views19 pagesHydraulic Turbine
Uploaded by
sami almjanThere are two main classifications of hydraulic turbines: impulse and reaction turbines. Impulse turbines derive energy from the kinetic energy of fluid flowing through nozzles, while reaction turbines generate energy from changes in fluid pressure and velocity as it passes through rotor blades. Common impulse turbines are Pelton wheels, while common reaction turbines are Francis and Kaplan turbines. Francis turbines operate under medium heads and utilize both impulse and reaction effects to rotate the runner blades and generate power. Kaplan turbines are axial-flow reaction turbines suitable for large volumes of water at low head.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
Hydraulic Turbine
Hydroelectric power plant
Classification of Hydraulic Turbines: working principle
Impulse Turbine: The pressure of liquid does not change while flowing
through the rotor of the machine. Pressure change occur only in the
nozzles of the machine. Eg : Pelton Turbine.
The energy to rotate an impulse turbine is
derived from the kinetic energy of the fluid
flowing through the nozzles.
Classification of Hydraulic Turbines: working principle
Reaction Turbine: The pressure of liquid changes while it flows through
the rotor of the machine. The change in fluid velocity and reduction in
its pressure causes a reaction on the turbine blades.Eg: Francis and
Kaplan Turbines
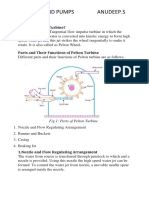
• Parts of pelton turbine
Nozzle with flow regulating arrangement
• Runner with split buckets
• Casing
• Braking nozzle
• The Basic Working Principle
When a high speed water jet injected through a nozzle
hits buckets of Pelton wheel; it induces an impulsive
force. This force makes the turbine rotate. The rotating
shaft runs a generator and produces electricity. Pelton
turbine transforms kinetic energy of water jet to
rotational energy
• Francis Turbine: Penstock: It is a large size pipe which conveys
water from the upstream to the dam/reservoir to the turbine runner.
Spiral Casing: It constitutes a closed passage whose cross-
sectional area gradually decreases along the flow direction; area is
maximum at inlet and nearly zero at exit. Guide Vanes: These
vanes direct the water on to the runner at an angle appropriate to
the design, the motion of them is given by means of hand wheel or
by a governor.
• Governing Mechanism: It changes the position of the guide
blades/vanes to affect a variation in water flow rate, when the
load conditions on the turbine change. Runner and Runner
Blades: The driving force on the runner is both due to impulse and
reaction effect Draft Tube: It is gradually expanding tube which
discharges water, passing through the runner to the tail race.
• WORKING Francis turbine operates under medium heads.
Water is brought down to the turbine through a penstock and directed to a
number of stationary blades fixed all around the circumference of the runner.
These stationary blades are called as guide vanes. Water under pressure, enters
the runner from the guide vanes towards the center in radial direction and
discharges out of the runner axially.
• Due to the difference of pressure between guide vanes and the runner (called
reaction pressure), the motion of runner occurs. As the water flows through the
runner its pressure and angular momentum reduces, This will produce a reaction
force on the runner blades. The pressure at inlet is more than that at outlet. The
moment of runner is affected by the change of both the potential and kinetic
energies of water. After doing the work the water is discharged to the tail race
through a closed tube called draft tube
• It is a axial flow reaction turbine
Kaplan turbine water flows parallel to the axis of
rotation of the shaft. It is a axial flow reaction turbine.
It is suitable when large quantity of water at low head
is available. Main parts are Guide vanes Hub with
vanes or runner of the turbine Draft tube
• For Kaplan turbine shaft of the turbine is vertical
Lower end of the shaft is made larger called HUB or
BOSS The vanes are fixed on the hub & hence it acts
as a runner. The vanes of the hub are adjustable for
Kaplan turbine
You might also like
- TurbinesDocument49 pagesTurbinesKeerthi VarmanNo ratings yet
- Module IV BmeDocument108 pagesModule IV BmeAnonymous VDnLHNG7QQNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Module 6Document31 pagesPresentation On Module 6Rushikesh MantriNo ratings yet
- Hydro Power PlantDocument52 pagesHydro Power PlantNicole PalomaresNo ratings yet
- ME-Laboratory Report: Submitted By: Felisilda, Amelia MDocument30 pagesME-Laboratory Report: Submitted By: Felisilda, Amelia MAllen EspeletaNo ratings yet
- Turbine Type 1Document35 pagesTurbine Type 1Fiza AhmadNo ratings yet
- Reaction TurbinesDocument3 pagesReaction Turbinesadvay.m.phadkeNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic TurbinesDocument28 pagesHydraulic TurbinesSaurabh Badola100% (1)
- Water Turbines: Our SubtopicDocument28 pagesWater Turbines: Our SubtopicVaish NaoNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 1Document19 pagesAssignment # 1Salman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hydro TurbinesDocument12 pagesHydro TurbinesBetty NegusseNo ratings yet
- Pelton TurbineDocument5 pagesPelton Turbinegauravarora93No ratings yet
- Hydraulic TurbinesDocument9 pagesHydraulic TurbinesVinayaka GpNo ratings yet
- TurbineDocument19 pagesTurbineTawsiful AlamNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Turbines WordDocument4 pagesHydraulic Turbines WordsubNo ratings yet
- Typer of TurbineDocument24 pagesTyper of TurbineRatul HasanNo ratings yet
- TurbinesDocument50 pagesTurbinesbalapriya2393% (14)
- HydraulicDocument21 pagesHydraulicMayankBhattNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document7 pagesUnit 5eyobNo ratings yet
- Pelton Turbine Is A Tangential Flow Impulse TurbineDocument14 pagesPelton Turbine Is A Tangential Flow Impulse TurbineAdhanom G.No ratings yet
- Pelton Turbine Is A Tangential Flow Impulse TurbineDocument14 pagesPelton Turbine Is A Tangential Flow Impulse TurbineMarfizalNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document38 pagesUnit 4Hitesh AroraNo ratings yet
- Study of Francis TurbineDocument4 pagesStudy of Francis TurbineSuryansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic TurbinesDocument45 pagesHydraulic TurbinesAshlin Augusty100% (1)
- Francis TurbineDocument45 pagesFrancis TurbineAshish AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic TurbinesDocument14 pagesHydraulic Turbineshussen belewNo ratings yet
- Pumps & TurbinesDocument27 pagesPumps & TurbinesAbhilash S SNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 01: ObjectDocument12 pagesExperiment No. 01: Objectpurushottam prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Applied Hyd TrbnsDocument92 pagesApplied Hyd TrbnsKadaikodi PaamaranNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Turbines (Part - I)Document31 pagesHydraulic Turbines (Part - I)Hammas Ahmed MirNo ratings yet
- Main Components of Francis Turbine: 1. Spiral CasingDocument3 pagesMain Components of Francis Turbine: 1. Spiral CasingaliriazNo ratings yet
- Francis Turbine: Working and Governing MechanismDocument22 pagesFrancis Turbine: Working and Governing MechanismJayesh vyas100% (1)
- Hydraulic Turbines and PumpsDocument15 pagesHydraulic Turbines and PumpsSachin Chaturvedi100% (1)
- Design of Water Turbine For HE PPDocument28 pagesDesign of Water Turbine For HE PPAjejejeNo ratings yet
- 8.reaction TurbineDocument22 pages8.reaction TurbineAS PrinceNo ratings yet
- BCM Hydralic TurbinesDocument4 pagesBCM Hydralic TurbinesThulasi RamNo ratings yet
- Type of TurbineDocument19 pagesType of Turbinechevrolet merahNo ratings yet
- In Francis Turbine Water Flow Is Radial Into The Turbine and Exits The Turbine AxiallyDocument2 pagesIn Francis Turbine Water Flow Is Radial Into The Turbine and Exits The Turbine AxiallyMohammad NafeesNo ratings yet
- Module-3 (HM)Document14 pagesModule-3 (HM)Nikhil SekharanNo ratings yet
- TurbineDocument14 pagesTurbineArjit GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Turbone InfoDocument5 pagesTurbone InfoDebajyoti NandyNo ratings yet
- 1 b1 Hydro Power Plant TurbinesDocument27 pages1 b1 Hydro Power Plant TurbinesWinston LibangaNo ratings yet
- SBP-Turbine (Compatibility Mode)Document37 pagesSBP-Turbine (Compatibility Mode)Nitin KhetadeNo ratings yet
- Turbines: M Usama Zia Bilal Hassan Syed M Raza NaqviDocument45 pagesTurbines: M Usama Zia Bilal Hassan Syed M Raza NaqviUsama ZiaNo ratings yet
- Reaction Turbine: BY Engineer Ghulam MurtazaDocument25 pagesReaction Turbine: BY Engineer Ghulam MurtazaDawood MasihNo ratings yet
- PumpDocument196 pagesPumprahul kumar75% (4)
- Unit 4Document55 pagesUnit 4Ashish KhariNo ratings yet
- Group Member Name Id Card NoDocument12 pagesGroup Member Name Id Card NolataNo ratings yet
- Pelton Wheel and Francis Turbine: Guided by Krunal PatelDocument21 pagesPelton Wheel and Francis Turbine: Guided by Krunal PatelAd Man GeTigNo ratings yet
- Turbines: (Pelton, Cross Flow, Kaplan and Francis)Document19 pagesTurbines: (Pelton, Cross Flow, Kaplan and Francis)Muhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Turbines and PumpsDocument24 pagesTurbines and PumpsANUDEEP SNo ratings yet
- Francis TurbineDocument16 pagesFrancis Turbinepoluri manicharanNo ratings yet
- Francis TurbineDocument11 pagesFrancis TurbineYaswanth saiNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - TurbinesDocument70 pagesModule 4 - TurbinesASHITA K BNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Water TurbineDocument20 pagesProject Report On Water TurbineNAVEEN ROY67% (3)
- Components of Francis TurbineDocument7 pagesComponents of Francis TurbineMustafa ZahidNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Machines and Fluid Power LabDocument24 pagesHydraulic Machines and Fluid Power LabDilshad CMNo ratings yet
- Group 2Document21 pagesGroup 2Talha SaeedNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Turbines and Its ClassificationDocument18 pagesHydraulic Turbines and Its ClassificationAdhanom G.No ratings yet
- How to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesFrom EverandHow to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Fuel-Air CycleDocument29 pagesFuel-Air Cycletej patelNo ratings yet
- Catalog AllDocument42 pagesCatalog AllPutra SeptiadyNo ratings yet
- Ultra Mega Power ProjectDocument5 pagesUltra Mega Power ProjectAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaics: Safety & Efficiency Codes, StanDocument22 pagesPhotovoltaics: Safety & Efficiency Codes, StanMohsinNo ratings yet
- TMP 21165-S220 Cagi 1001802177504Document1 pageTMP 21165-S220 Cagi 1001802177504John TheodorouNo ratings yet
- Facts On Libya: Oil and Gas (IEA 21 February 2011) OilDocument3 pagesFacts On Libya: Oil and Gas (IEA 21 February 2011) OilsakshisurimbaNo ratings yet
- True or False - Collection of Objective QuestionsDocument8 pagesTrue or False - Collection of Objective QuestionsJagdeep ArryNo ratings yet
- Building A Phase ConverterDocument11 pagesBuilding A Phase ConverterAlvaro Del Cid100% (1)
- Renewable Energy in Nepal Challenges and OpportunitiesDocument11 pagesRenewable Energy in Nepal Challenges and OpportunitiesBhandari PrakashNo ratings yet
- ME152P 2 - C3 - Final Plate - Diesel Power PlantDocument88 pagesME152P 2 - C3 - Final Plate - Diesel Power PlantkeaneNo ratings yet
- 21-26 MW TM2500 Mobile 50-60Hz Dual Fuel PDFDocument16 pages21-26 MW TM2500 Mobile 50-60Hz Dual Fuel PDFÄness BŝŁm Řm EverNo ratings yet
- Clipper Windpower Liberty BrochureDocument7 pagesClipper Windpower Liberty Brochuregabriel_danutNo ratings yet
- PAC History The Start of ProtectionDocument7 pagesPAC History The Start of Protectionluhusapa-1No ratings yet
- Chapter No. 1 Power System Relaying by StanleyDocument72 pagesChapter No. 1 Power System Relaying by StanleyMuhammad Qanit100% (4)
- B.S. en 2005Document1 pageB.S. en 2005Kalim HaralNo ratings yet
- Tracer AN (50 100A) Manual EN V3.3Document40 pagesTracer AN (50 100A) Manual EN V3.3viktorybg2020No ratings yet
- Nuclei: Chapter ThirteenDocument17 pagesNuclei: Chapter ThirteenBhoomika VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Annexure-1 Grid Transformer Recommendation - DelCEN 2500 HVDocument2 pagesAnnexure-1 Grid Transformer Recommendation - DelCEN 2500 HVSAEL SOLARNo ratings yet
- 11th Science MHT Cet Triumph Physics McqsDocument14 pages11th Science MHT Cet Triumph Physics McqsRamesh kumar83% (6)
- Lab Manual Grade 10 - 2020-2021Document10 pagesLab Manual Grade 10 - 2020-2021Analyah GordonNo ratings yet
- Offshore Wind Black Sea EN WEBDocument57 pagesOffshore Wind Black Sea EN WEBLyubomir SirkovNo ratings yet
- Alstom HRSG OM PDFDocument630 pagesAlstom HRSG OM PDFSrajanShettyNo ratings yet
- Fluid Machinery Turbine Lecture 1Document22 pagesFluid Machinery Turbine Lecture 1Jarred TañedoNo ratings yet
- Euromax: Three-Pass Hot Water BoilerDocument1 pageEuromax: Three-Pass Hot Water BoilerLEONARDO MOLERO CLEMENTENo ratings yet
- Rectifier Circuits Diodes and Rectifiers Electronics TextbookDocument8 pagesRectifier Circuits Diodes and Rectifiers Electronics TextbooknellaiNo ratings yet
- Chaos and Nonlinear Psychology Keys To Creativity in Mind and Life Shan Guisinger Full ChapterDocument67 pagesChaos and Nonlinear Psychology Keys To Creativity in Mind and Life Shan Guisinger Full Chaptersummer.yates611100% (5)
- Fujitsu ASYA24LCC Part NumbersDocument17 pagesFujitsu ASYA24LCC Part NumberstfilipposNo ratings yet
- TUKLAS (Physical Science Category)Document20 pagesTUKLAS (Physical Science Category)Ruth Carin - MalubayNo ratings yet
- Transportation Engineering: Sonali Goel, Renu Sharma, Akshay Kumar RathoreDocument14 pagesTransportation Engineering: Sonali Goel, Renu Sharma, Akshay Kumar RathoreIgoor Morro MelloNo ratings yet
- Unlocking Sustainable Energy - A Comprehensive Overview of Photovoltaic Solar PanelsDocument2 pagesUnlocking Sustainable Energy - A Comprehensive Overview of Photovoltaic Solar PanelsFernando Moreira da SilvaNo ratings yet